How can you plant an apple tree?

In order to get a new variety of apple trees on the site, it is not at all necessary to buy a whole seedling, it is enough to pin only a couple of new branches to an existing tree or bush. This method is called grafting and depends on the season, region and, most importantly, on the experience of the gardener and his accuracy.
The scion itself is not a very complicated procedure, so it is enough to thoughtfully read a couple of instructions and prepare everything you need so that a new plant blooms under the windows of the house.


The need for a procedure
Even novice gardeners for the most part have heard of such a concept as grafting. In essence, it is the fusion of two or more plants with different properties, varieties and even crops. Decades ago, gardeners noticed that wild apple varieties are better adapted to environmental conditions. They are more tenacious, tolerate cold more easily, but at the same time their fertility and taste of the harvest are significantly lower than that of selective apple trees. Grafting a cultivar to a wild trunk in order to increase resistance by crossing and at the same time preserve taste and fertility is the main task of such grafting, but far from the only one.
Apple trees are grafted in order to:
- propagate a rare favorite variety at a high speed;
- replace the boring apple tree variety;
- to increase the size and improve the taste of ripe fruits;
- to increase productivity and bring the term of fruiting closer;
- grow several different varieties on the same tree;
- form a low, lush crown for easy harvesting;
- ennoble the wild apple tree growing on the site;
- to enhance frost resistance of cultivated varieties;
- save a damaged or diseased tree.
Unlike an ordinary seedling, which begins to bear fruit in at least five years, a grafted cutting usually yields a harvest in the third year. Apple trees are planted not only by enterprising summer residents, but also by large fruit tree nurseries.


Timing
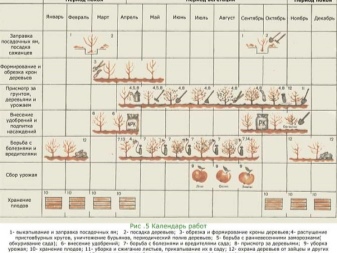
There is no one correct time for grafting plants, in theory, this can be done regardless of the season. However, each season has its own nuances, and some period is better for this, and some worse. If you pin the stalk too early or, conversely, late, it simply will not take root on the trunk.
- Spring... The most classic time for vaccination is spring. The procedure can be started only with the beginning of sap flow, while the tree growing on the site is still dormant after winter, but the vegetative processes have already started. Determining a specific day is quite simple: examine the buds and branches. If the buds begin to swell slightly, the branches turn red a little, and green tissue remains in the bark cuts, then you can safely graft this apple tree. It is worth focusing on the period from late March to early April.
- Summer... In the summer, grafting of new cuttings is rarely carried out. It is believed that this can severely damage the main tree. However, if this was not done in the spring, then you can find a suitable time at the end of July, when the fruits begin to pour. At this time, the apical bud should have already formed, and the bark is still easy to move away from the green tissues, as in the spring.
- Autumn... Vaccination in the fall can be done only in the south of our country, where there is no threat of early frosts. You can plant apple trees even until mid-October, but it is better to do this no later than September.
- Winter... Of course, you cannot plant trees growing in the garden in winter. But a young seedling, on which the gardener wanted to be vaccinated, can be dug up and brought into a warm room. This must be done at least a week before the procedure, and it must be carried out no later than mid-December. It will be possible to plant a grafted plant in open ground only by the end of March, so you will have to store it at home at a temperature not lower than -4 ° C.

What trees can you graft on?
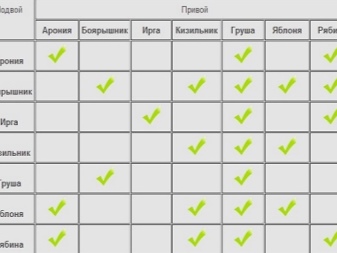
Unexpectedly, apple cuttings can be grafted not only on an apple tree of another variety, for example, selective Bellefleur to a common wild ranetka. They are often attached to other types of fruit trees. And Michurin managed to achieve a harvest even from an apple tree grafted onto a birch. But, of course, closely related crops remain the best options.
- On a pear. A fairly common method of grafting, which gives a consistently average yield and has been successfully tested by many gardeners. Most often it is done when there is not a single apple tree on the site, and it is impossible to grow it from a seedling for any reason.
- On a mountain ash. The apple tree is grafted to the mountain ash a little less successfully, but if the cutting has taken root, then the frost resistance of this variety and its unpretentiousness grow at times, and the taste of the fruit does not decrease. The only rule is to choose varieties with a late ripening period so that it coincides with the fruiting of the mountain ash itself.
- Hawthorn... A good option is a regular hawthorn bush. Since it is much lower than the apple tree, then the mature crown of the grown cuttings will not differ in special height, which will simplify harvesting. And besides, the hawthorn root system allows planting plants in swampy areas and in places with high groundwater levels, where an ordinary apple tree simply will not grow.
- To irgu. Another option for a low rootstock is irgi bushes. The stalk should be pinned almost at the very roots, and the grown apple branches should be provided with some kind of props, but in general such a grafting is possible.
- On the plum. Despite the fact that the apple is a pome fruit, and the plum is a stone fruit, both plants belong to the Rosaceae family, which allows grafting one on top of the other. However, since the branches of the apple tree are thicker and taller, it is more appropriate to plant the plum on the apple tree, and not vice versa. Large yields from such a procedure should not be expected.
- For the cherries. Another plant from the Rosaceae family is cherry. And, as in the case of a plum, it does not make much sense to plant an apple tree on it, but on the contrary, it is possible.
Vaccinations of apple trees on quince and viburnum are considered unsuccessful. Most often, a stalk grafted on them simply dies. And, of course, trees such as aspen or birch are not at all suitable for grafting, despite the fact that Michurin once succeeded in such an experiment.

Preparation
Before you start grafting different varieties of apple trees, you need to do some preparatory work. First, it is worth understanding the basic terms so as not to confuse them while reading the step-by-step instructions:
- scion - this is a twig of an apple tree, a stalk that is implanted to the trunk of another plant;
- rootstock - this is a tree or bush growing on the site, to which the scion is attached.
The next thing a novice gardener should pay attention to is the necessary tools and materials that an experienced breeder always has at hand. Of the tools you will need:
- small sharp hacksaw for large branches;
- secateurs for thin twigs;
- a sharp knife for cutting the bark;
- polyethylene or thick fabric;
- insulating tape;
- drying oil or special paint for covering the cutting at the end of the work.


The list of required materials includes only one single item:
- garden pitch, also called garden resin or simply putty. You can buy it in specialty stores for the home and garden, or you can make it yourself from tree resin, manure and animal fluff.This sticky mass perfectly heals the cut parts of plants and additionally strengthens the joint.
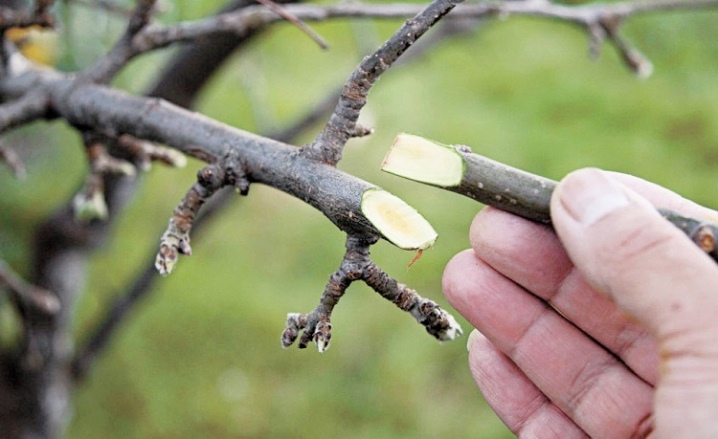
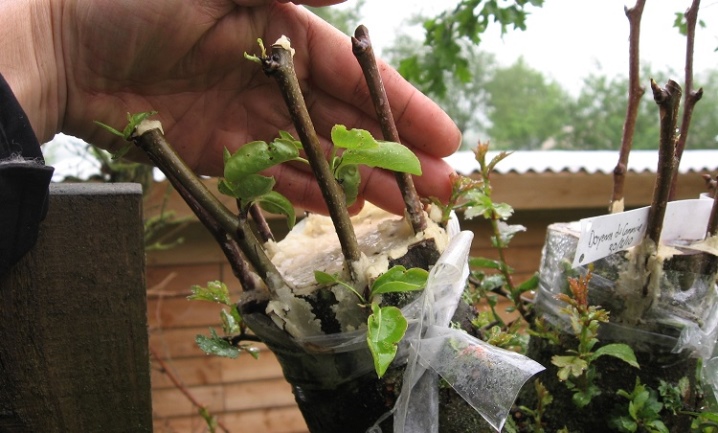
When everything you need is in store, you can harvest cuttings... For spring grafting, it is best to cut them at the beginning of winter, and for summer-autumn grafting - at the end of winter or even early spring. A suitable cutting should have the following characteristics:
- be healthy and without visible damage;
- do not have blossoming buds;
- have a length of 20 to 40 cm, a diameter of 5 to 7 mm;
- internodes must be long enough;
- the age of the plant from which the cutting is cut should be no more than 8-10 years;
- in cases where grafting is required to change the crown, it is worth choosing plants not older than 3 years.
Cut cuttings are tied in small bunches and wrapped tightly with a damp cloth. This is how they are stored until the beginning of the procedure. To increase the yield of the stock, you need to take cuttings from that adult apple tree, which gave a particularly plentiful harvest in the last 2-3 seasons.
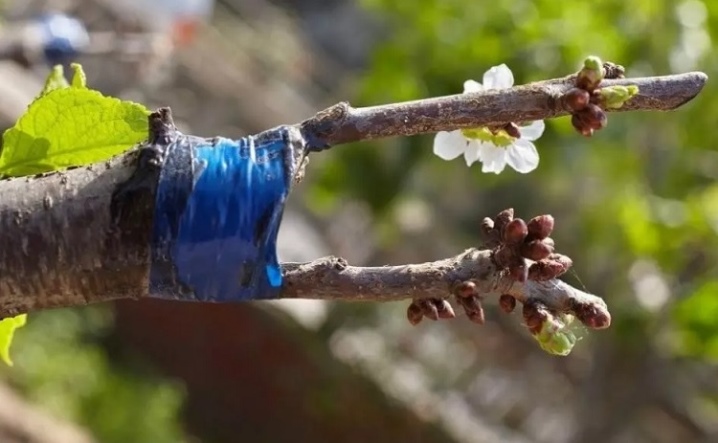

The ways
There are many different vaccination technologies, each of which has been tried by many generations of gardeners.... Some of them are quite simple and suitable for beginners, others are more difficult, but they allow the cutting to take root on the trunk faster. But all these methods require pre-treatment of hands and tools with disinfectants, as well as care and accuracy.
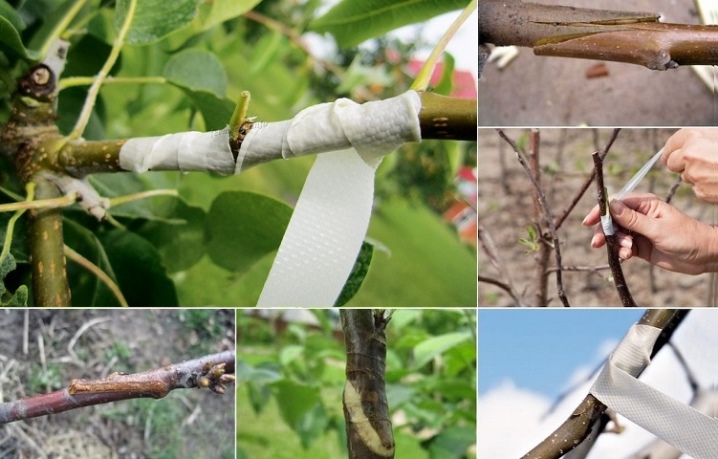

Copulation
The easiest way, which means in translation the usual "attachment". Suitable when both the rootstock and the scion have the same thickness. The step-by-step procedure is as follows:
- cuts are made on the stock and scion selected in thickness at the same angle;
- the trimmed stalk is applied to the stock at the cut and pressed tightly;
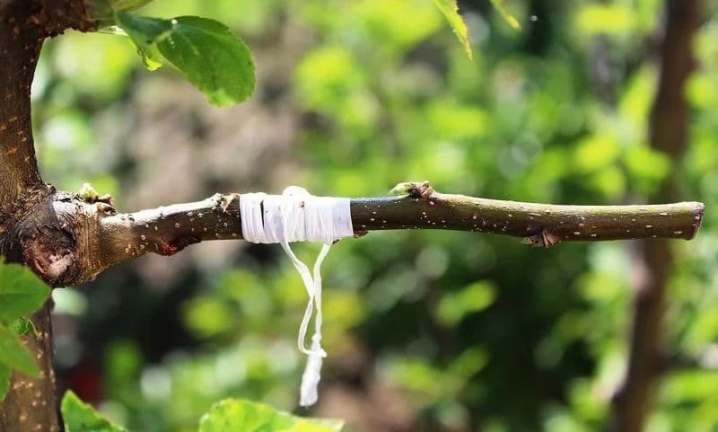
- putty is applied to the joint, after which the joint is fixed with electrical tape.
It is recommended to remove the harness after copulation and all other types of inoculation only after the cuttings have grown completely, not earlier than after a couple of months. And it's better not to remove the tape at all until the end of summer.

By the kidney
The kidney is often called the "eye", which is similar to the words "eye", "eye", therefore the whole procedure was called "budding". Small cuttings with a bud are suitable for her, which will be attached to the trunk as follows.
- Greens and twigs are removed from the stem of the stock, washed with plain water and wiped dry with a clean cloth.
- The stalk with the kidney is also peeled and wiped dry. Oblique cuts are made at the top and bottom of the kidney at a distance of 3-5 cm.
- At the grafting site, a T-shaped incision is made, where the stalk is placed. It is pushed into the bark so that only the upper part of the scion is visible, starting from the bud.
- No resin with manure is applied to the inoculation site, and the duct tape is wound so that the kidney remains open.

Into the cleft
Another simple way is to graft the apple tree into the cleft:
- the stock is cut and split into two parts with a grafting knife;
- cuttings are pointed at the bottom;
- pointed cuttings are inserted into a crack in the rootstock;
- the junction is filled with putty and wrapped with electrical tape.

For the bark
The method of grafting an apple tree for the bark is also simple. In this case, the stalk is cut obliquely, and at the rootstock, the bark is slightly pushed away from the trunk with a knife in place of the pruning, after which, like a wedge, the stalk is driven into the resulting crack.

Secateurs
For those who are not confident in their carpentry skills and fear that they will damage the cutting during pruning, the market for garden tools offers a special grafting pruner. With its help, the scion is cut, and after the back cut the scion is cut. The resulting slices look like two pieces of a puzzle and are ideal for the further method of conventional copulation.

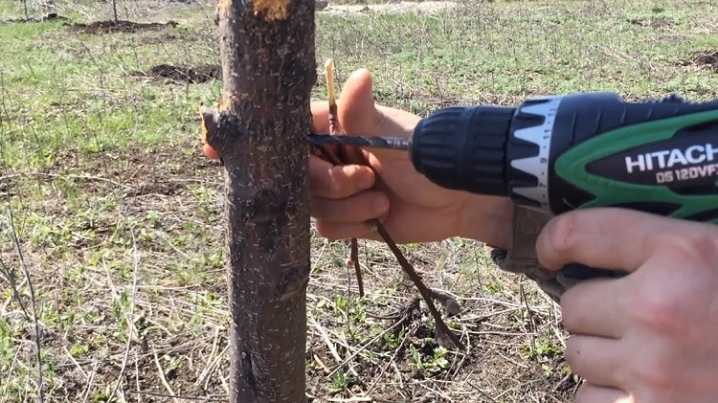
Drilling
A rather non-standard, but well-proven method is drilling. Using a screwdriver or a conventional drill, a 5-7 cm depression of a certain diameter is drilled into the stock.The tip of the scion is planed to a similar diameter, after which it is inserted into the resulting recess, covered with putty and fixed with electrical tape.

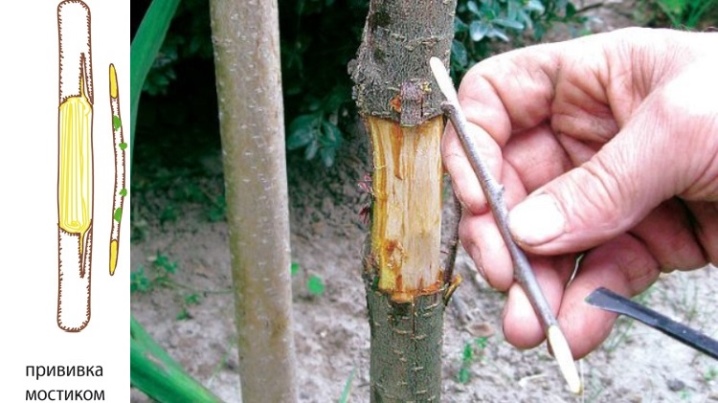
By the bridge
The difference between this vaccine and other species is that it is not intended for breeding new varieties. With its help, you can restore an apple tree that is sick or damaged by frost and heat. The procedure is not easy, only an experienced gardener can handle it.
Cuttings are selected 10-15 cm longer than the damaged area on the trunk. Their thickness should not exceed 5 mm for light defects and 10 mm for especially serious diseases. The step-by-step procedure is as follows.
- The damaged area is cleaned and wiped with a soft, damp cloth.
- The bark is slightly trimmed with a hacksaw or a sharp knife so as not to damage the green part.
- The buds are removed from the cuttings, the edges are cut obliquely. Depending on the width of the damaged area, you will need from 4 to 10 pieces.
- On the healthy bark of the trunk, T-shaped cuts are made above and below the stripped segment, into which the trimmed edges of the scion are inserted, slightly bending them in an arc-like manner, in the form of a small bridge.
- The vaccination site is covered with putty and fixed with electrical tape.

To the root
In cases where there are no trees on the site, but fresh hemp and roots remain, you can graft a stalk on them. This is done on a fresh cut using the "bark" method.
See the next video for how to do this.
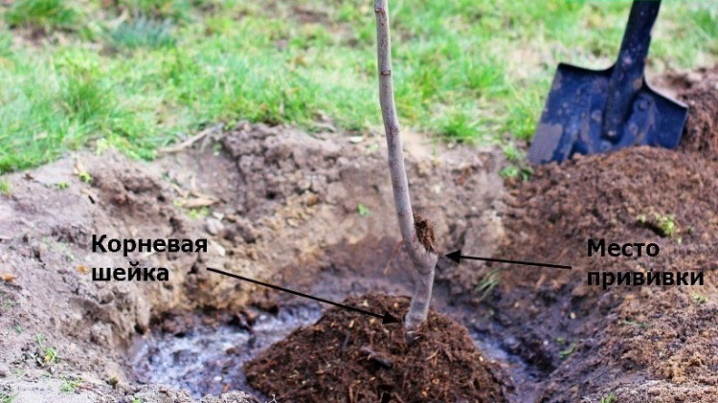
In the root collar
The root collar is a section of a plant in which all its roots converge, after which they pass into the trunk. It is located close enough to the ground. The grafting requires a small oblique cut of the trunk to a depth of 1-1.5 cm in this place and the usual attachment of the cut along the oblique cutting into this cut.

Into the crown
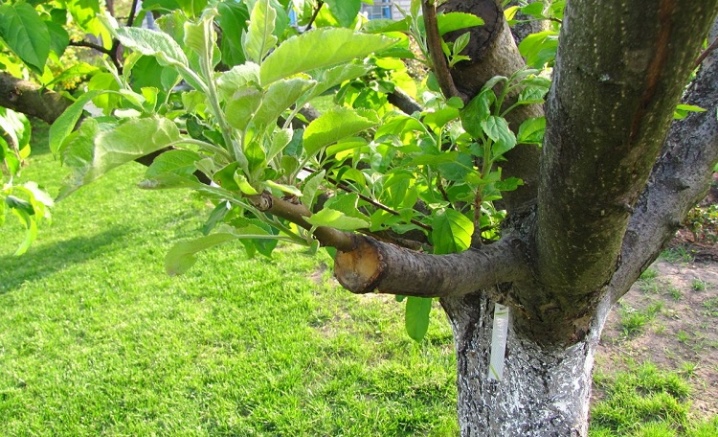
3-4 different varieties of the same species can be grafted into the crown of any garden tree. In this case, the cuttings are grafted at a height of a meter from the ground onto the thickest and healthiest branches that have grown from the trunk at an angle of no more than 50 and no less than 30 degrees.
The branches are cut and trimmed, after which the cuttings are attached to them using the selected grafting method. The splitting method is best in this case. After putty and electrical tape, the junction is additionally wrapped in polyethylene or a thick cloth for 2-3 weeks, and a paper bag is put on top to protect the cut from direct sunlight.

Side cut
This technology is similar to grafting into the root collar, but it is not done so low. A shallow cut is created on the side of the tree trunk, into which the scion cleaned from both sides is inserted.
The joint is treated with resin and wrapped with electrical tape.

According to the system of V. Zhelezov
An experienced gardener Valery Zhelezov, years ago, developed his own proven method of grafting an apple tree onto young 1-2-year-old seedlings at the very surface of the earth. The main conditions are:
- the same length and diameter of the seedling and scion;
- sleeping, buds that have not begun to bloom.
Such a scion is done at the very beginning of spring, when the snow has not yet completely melted. A 1-2 year old stalk is dug out of the snow and immediately, without preparation, is grafted into the split. The grafted seedling is covered with a cut plastic bottle and left to warm.
To prevent the bottle from being blown away by the wind, you can slightly squeeze it on the sides with two bricks.


The nuances of vaccination, taking into account the region
The only difference between apple grafting in different regions of our country is the timing of the procedure. So, in the Russian south, work can begin in the earliest spring, and in the fall, vaccinate almost until mid-October. The middle lane is not so supportive of gardeners and gives them a period from the end of April to the first days of autumn. At the same time, southern frosts can be even more dangerous for young cuttings than October frosts in the middle lane.
Apple trees in the Urals or Siberia should be planted only in summer, and only when the soil condition is suitable: the soil can be easily dug up by hand. Most often this is mid-July - early August.
Autumn and spring vaccinations are impossible in the Russian north.








The comment was sent successfully.