What are cherries and how to grow them?

Cherries are one of the most nutritious and delicious berries loved by both adults and children. There is nothing surprising in the fact that you can meet her in any garden or summer cottage. In our review, we will tell you more about the features of cherries, popular varieties, planting, care and reproduction rules.

Description
Cherry belongs to a subgenus of the genus Plums of the Pink family, occurs in tree and shrub forms. In the first case, its height reaches 10 m, and in the second - up to 2.5-3 m. The root system is pivotal, powerful, well developed. The bark of adult plants is gray, slightly shiny; in young plants, it has a reddish tint.
The arrangement is alternate, the leaves are elliptical, slightly pointed at the top. The color is dark green, the lower part is lighter. Length - 6-8 cm.
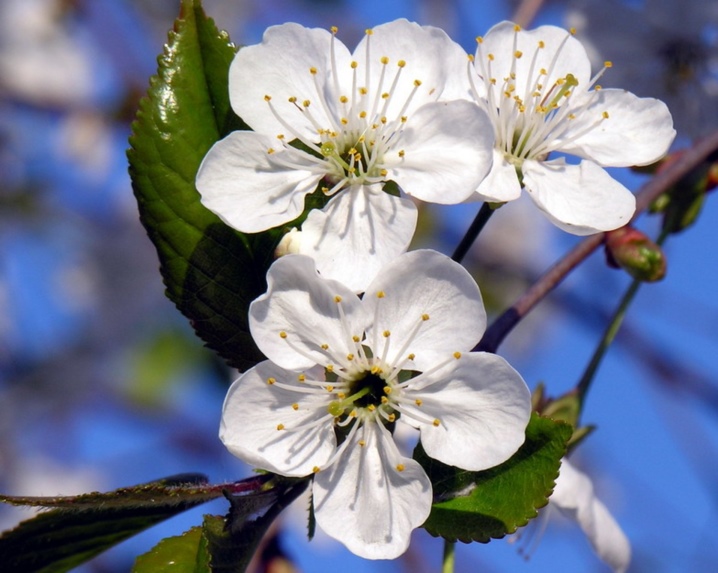
Blossoming is white. Flowers are collected in umbrellas of 2-3 pieces. The structure of the flower is complex: the perianth consists of 5 sepals and 5 petals, the number of stamens varies from 15 to 20, the pistil is one.

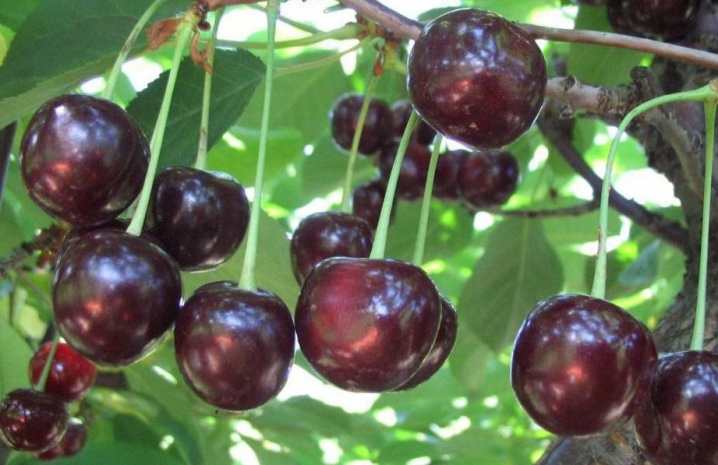
The fruits of the cherry tree are called berries. However, from a botanical point of view, this is not the case. Cherry fruits are drupes up to 1 cm in diameter, dicotyledonous class. The color is red, the pulp is juicy, sour-sweet.
To date, cherries are found exclusively in a cultivated form; they practically do not grow in the wild. Some botanists are inclined to consider common cherry a natural hybrid obtained naturally from steppe cherry and sweet cherry.
Life expectancy is 20-30 years, of which 10-18 years are active fruiting.

Popular species and varieties
Cherry life forms optimal for the middle zone of our country should have important characteristics:
- high winter hardiness;
- increased productivity;
- resistance to fungal infections.

Based on this, the following domestic varieties are most common for the Moscow region and the central strip of Russia:
- Lyubskaya - high-yielding self-fertile cherry, grows up to 2.5 m, which greatly facilitates the collection of fruits. The bark is brownish-gray, the crown is spreading. The pulp and skin of the berries is dark red. The taste is sweet with a pronounced sourness.
- Apukhtinskaya - late self-fertile cherry, looks like a bush. It grows up to 3 m. The berries are large, heart-shaped. The color is dark red, the taste is sweet, a slight bitterness is noticeable
- Youth - a frost-resistant high-yielding variety of a shrub type, grows up to 2.5 m. It is a hybrid of the varieties Vladimirskaya and Lyubskaya. The variety is resistant to most fungal infections. Drupes are dark red in color, the flesh is juicy, the taste is very delicate, sweetish with a pronounced sourness.
- In memory of Vavilov - a tall, cold-resistant, self-fertile variety. The fruits are sweetish-sour, the pulp is juicy, bright red.
- A toy - a hybrid variety obtained by crossing common cherries and sweet cherries. The berries are fleshy, deep red. The taste is refreshing.
- Turgenevka - one of the most common varieties of cherries. It grows up to 3 m, the crown has the shape of an inverted pyramid. Berries - burgundy, sweet and sour, have a heart-shaped shape. The only drawback of this variety is that it is self-fertile, therefore it is important to ensure the presence of pollinating varieties on the site.


Landing
Experienced gardeners prefer to plant cherries outdoors in springtime. If the seedlings are bought in the fall, you can just dig them in for the winter, straw or spruce branches will be a good shelter for them.
When buying planting material, pay attention to its appearance: the best choice would be a biennial plant with a stem 60 m long, 2-3 cm in diameter and strong formed skeletal branches.

Planting is performed at a time when the substrate warms up enough, but sap flow does not begin yet and the buds do not open. The site should be well-lit, optimal is clay and loamy soil, always well-drained with neutral acidity. Cherries are not recommended for planting in lowlands, where high humidity prevails and winds often blow. If the soil is acidic, it is necessary to calcify it; for this, dolomite flour or lime is scattered on the site at the rate of 400g / m2 and dug up.

It is advisable to fertilize the site with organic matter; for this, manure is applied - 1.5-2 buckets of organic matter are needed per 1 m2. The application of fertilizers containing phosphorus and potassium has a good effect.
Please note that manure and lime should be applied at different times.
If you plan to plant several cherries, the distance between them should be 2.5-3 m. For cross-pollinated varieties, the possibility of full pollination should be considered. In this case, you will have to plant at least four different types of cherries, they are placed on the garden plot according to the scheme 2.5x3 m for tall trees and 2.5x2 m for shrubs.

The landing hole is formed at the rate of 80-90 cm in diameter and 50-60 cm deep. When forming a pit, the upper fertile layer of the substrate must be mixed with wood ash, organic matter and mineral components. At the same time, it is undesirable to introduce nitrogen fertilizers into the sowing hole. this can burn the roots.
A peg is driven into the center of the hole and a seedling is placed on the north side of it. The roots are straightened and covered with the prepared soil mixture so that the root collar is located at the level of the soil or 3-4 cm higher. If the root collar is deepened, it will cause rotting of the cherry seedling.

The earth must be tamped and earthen sides formed. Pour a bucket of water into the hole. When all the moisture is absorbed, the earth in the near-trunk circle must be mulched with peat or humus. At the final stage, the seedling is tied to a support peg.
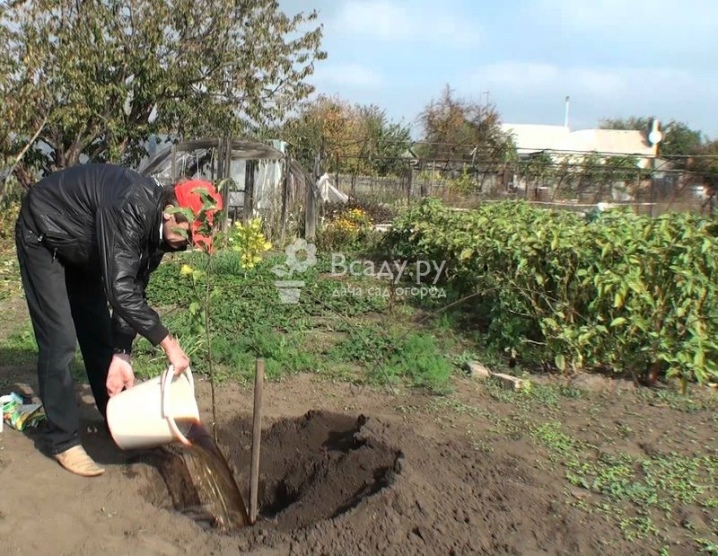

Care
Cherry care is practically no different from the agricultural technology of any other fruit and berry crop. Like all other garden plants, it needs watering, loosening the earth, removing weeds, applying top dressing, pruning and preparing for winter.

Watering
It is necessary to water the ground with such a volume of water that the soil in the near-trunk zone is completely wet to a depth of 45-50 cm. In this case, the soil should not sour, so watering should not be frequent. Young newly planted trees need to be watered every 10-14 days, if the summer is hot and dry, then weekly.
An adult plant is irrigated for the first time immediately after flowering, during the same period, top dressing is applied. The second watering is required for the cherries at the stage of berry pouring - at this moment, up to 5-6 buckets of water are poured under each tree. If the weather is rainy, then the amount of moisture can be reduced.
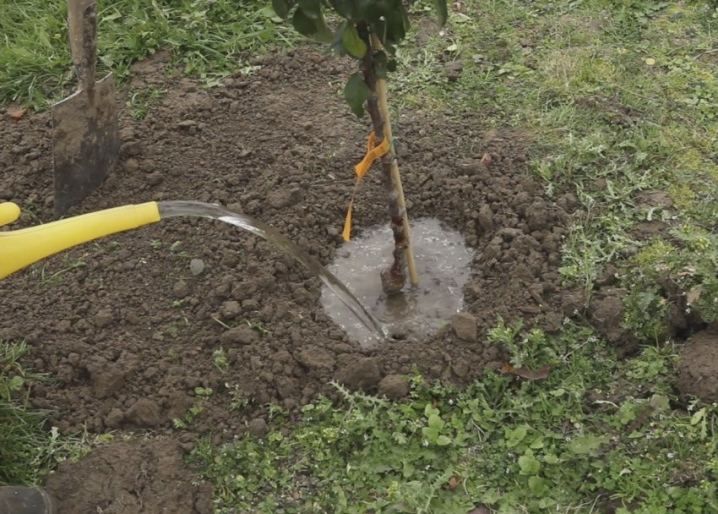

In October, when the leaves completely fall off, the plant needs moisture-charging pre-winter watering. Its purpose is to moisten the substrate to a depth of 80-85 cm. Such irrigation allows saturating the soil with moisture that plants need to acquire frost resistance. In addition, wet soil freezes much more slowly than dry soil.
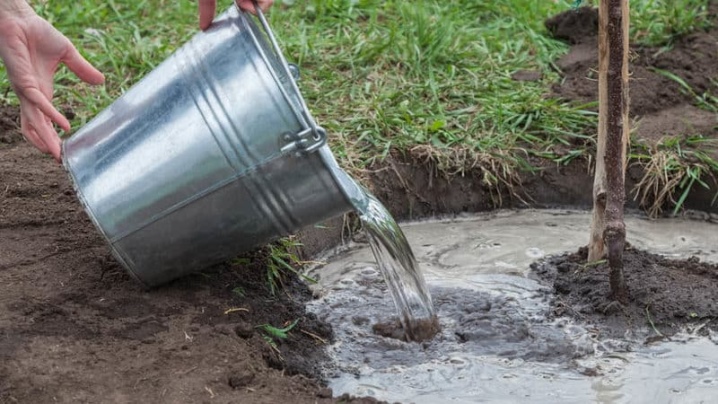

Top dressing
Once every two years, cherries are fed with organic fertilizers, they are introduced into the ground during autumn or spring digging. Besides, the plant will need mineral compositions: from phosphoric ones, superphosphate and potassium sulfate are usually added at the rate of 20-30 g / m2. Of the nitrogen compounds, the greatest effect is given by ammonium nitrate or urea. This treatment is carried out in early spring, and then immediately after the end of flowering.
Important: top dressing should not be applied to the near-trunk zone, but throughout the entire growing area of cherry trees. Before applying these fertilizers, the soil is thoroughly watered.
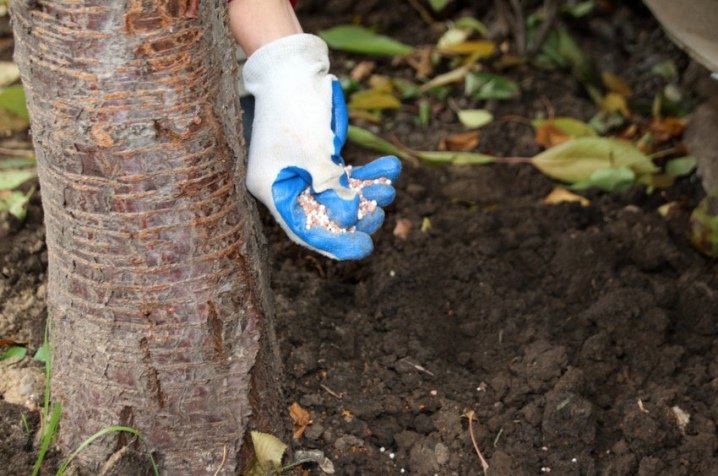

Foliar dressing gives a good effect. To do this, 50 g of urea is dissolved in a bucket of water and sprayed two to three times at intervals of a week. Processing is carried out necessarily in the evening or on cloudy days.
Pruning
The very first pruning of cherries is carried out in the spring before the start of sap flow. If the buds are already swollen, it is better to postpone it, otherwise the shortened injured branches may dry out. Autumn pruning is performed at the final stages of the growing season. Sick, dead and injured branches should be removed regardless of the season.
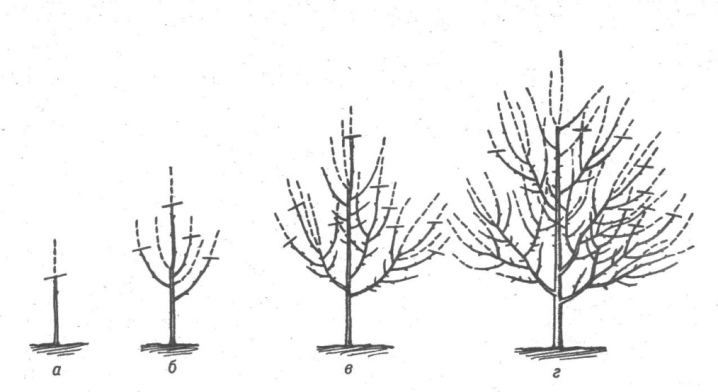
With young cherries planted this season, everything is simple. On tree-like branches, 5-6 of the strongest branches are left, on shrubs - up to 10. All the rest are cut completely into the ring, without leaving even hemp. Places of cuts are covered with garden pitch.
Tip: It is advisable to leave the healthiest branches growing from the trunk. They should be at least 15 cm apart and pointed in different directions.
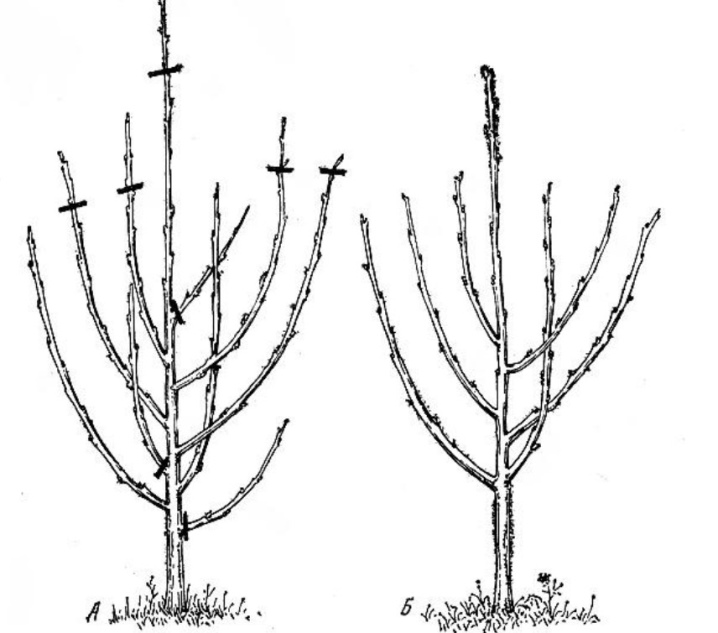
Starting from the second year, the formation of the crown is carried out as follows:
- first, all shoots and branches are cut out, thickening the crown, growing inside it;
- shoots that appear on the trunk are cut off;
- for tree cherries, branches that grow rapidly upward are also subject to shortening, otherwise it will subsequently be difficult to harvest;
- in bush plants, shoots are shortened to 45-55 cm;
- for sanitary purposes, all diseased and damaged shoots are cut out;
- a total of 8-12 skeletal branches should remain.
Pruning in autumn is not recommended, as a wound before frost makes the plant especially vulnerable and sensitive and can significantly damage the future harvest. In addition, it is undesirable to leave plants for the winter with broken shoots, then the cherry will be forced to feed them until the beginning of spring to the detriment of healthy branches. At negative temperatures, cherry bark and wood become brittle, and if the tree is injured, gum flow may begin. But if, nevertheless, there is a need for autumn pruning, the most important thing is to choose the moment between the end of the growing season and the beginning of the first frosts.
If you do not have time before the onset of cold weather, it is better to postpone processing until spring.

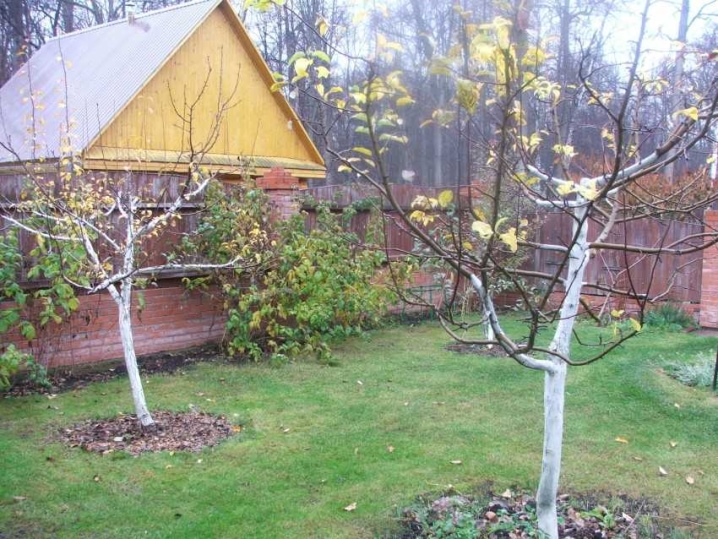
An adult cherry can withstand even the most severe frosts without shelter. Nevertheless, it is advisable to create frost protection for it. To do this, a snowdrift of freshly fallen snow is thrown into the near-trunk zone, and it is sprinkled on top with sawdust, straw or pine needles. The stem part and skeletal branches should be whitewashed with lime with the addition of copper sulphate.

Reproduction
Cherries can be propagated by seed or vegetative method, the latter involves the use of root shoots and cuttings. Seed propagation is rarely used in practice, mainly by breeders to develop new varieties of crops.
In amateur gardening, vegetative techniques are preferred.

Growing from seeds
After the fruit ripens, it is necessary to pull out the bone, clean it from the pulp, plant it in open ground and close it with agrofibre. The seedlings that appear in the spring are thinned out according to the 25x25 scheme. They take care of them in the same way as for young cherries: they moisten them in a timely manner, apply top dressing, remove weeds and loosen them. Next spring, when the buds begin to swell on young trees, they can be used to plant a cultivated scion.

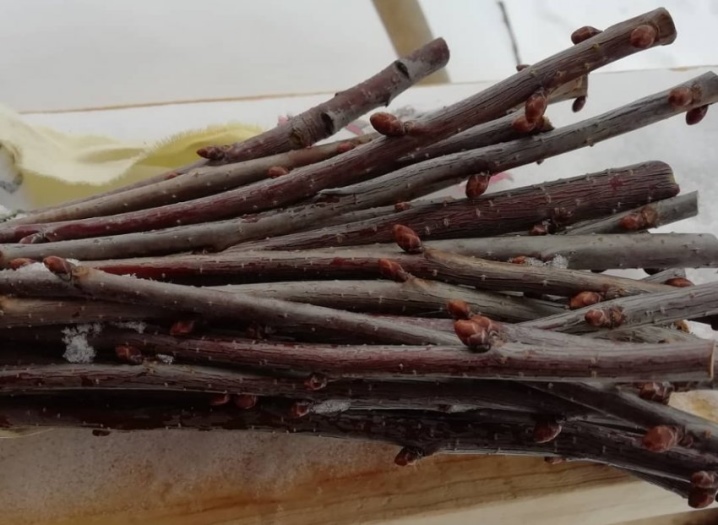
Green cuttings
Today it is one of the most common cherry propagation methods. Cuttings are a readily available material that every gardener has in abundance.Cuttings are made in the second half of June, at the time when cherry shoots start to grow actively.
For planting, you will need a container 30x50 cm in size and 10-15 cm deep, drainage holes should be provided in it. The box is filled with a soil mixture of coarse sand and peat, taken in equal proportions. The substrate is disinfected with a solution of potassium permanganate, then poured abundantly with water.
After that, you can start preparing the cuttings. To do this, in a 3-5-year-old plant, it is necessary to cut out healthy, not drooping, upward-growing shoots. It is advisable to choose those that grow from the southwest or south sides. The top with underdeveloped leaves is cut off from the blanks and several cuttings 10-12 cm long are cut so that each contains 5-8 leaves. The upper cut should go directly above the kidney, the lower cut 10 mm below the node. The cuttings prepared in this way are stuck into the ground at a distance of 5-8 cm and deepened by 2-4 cm, the ground around them is compacted and a greenhouse is equipped.
The cuttings are placed in a bright, but at the same time protected from direct ultraviolet rays, place. The leaves will tell you that the cuttings have taken root: they restore turgor, acquire a rich color. From this moment, you can begin to lift the film for hardening the cuttings and airing. For the winter, the resulting planting material is buried in the garden, and in the spring it is sent to a permanent place.

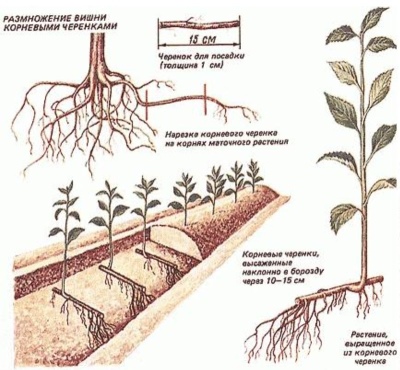
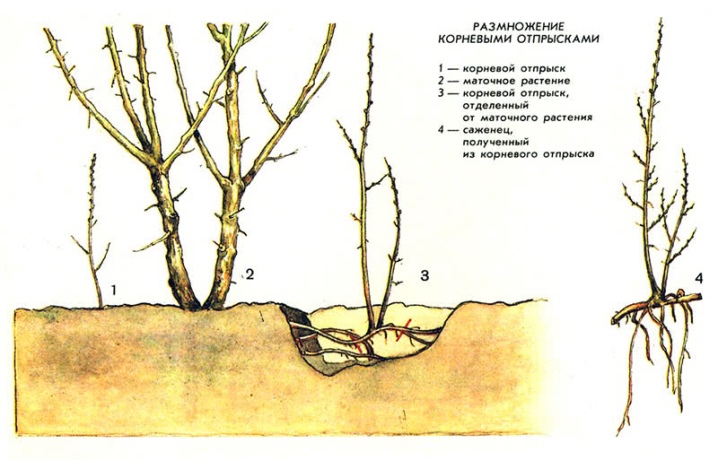
Root shoots
This method is in demand for propagation of own-rooted cherry species, usually root suckers of high-yielding varieties at the age of 2 years are used. They must have a branched ground part and a developed root system. It is best to take offspring that grow at some distance from the parent plant, otherwise their detachment can damage the roots of the culture.
For reproduction in the autumn, the root is cut, which connects the layers with the parent cherry. The cuttings are not planted, but left in the ground - in the spring they dug it out and planted on a permanent site.
Diseases and pests
Cherries are resistant to many diseases and pests. However, she too face infections.
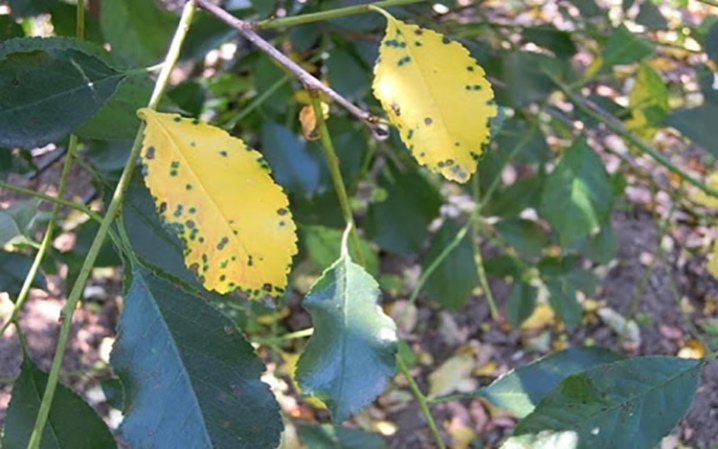
- Brown spotting. It is manifested by the appearance of yellowish-red and brown spots on the leaf blades. They can be accompanied by an abundance of black dots in which fungal spores live. Soon, the injured tissue dries up and falls off.
- Clasterosporium disease. A common disease of cherries and sweet cherries. The first symptom is light brown spots with red edging, which soon turn into holes, as a result of which the leaves dry and fall off. Damaged fruits become covered with purple, as if depressed spots, they quickly increase in size and take on the appearance of warts. The bark cracks and runs out of gum, which leads to the rapid wilting of the tree.
- Coccomycosis. It manifests itself as small red dots on the underside of the leaf plate, soon the leaves become covered with a pink bloom, and then dry out.
- Scab. It manifests itself in the form of olive-brown spots on the leaf blades. Cracks appear in the fruits and they rot.
- Moniliosis. It leads to drying out of branches and shoots, they become as if burnt in appearance. Chaotically located growths appear on the bark, the fruits rot, and gum flow begins in the bark.
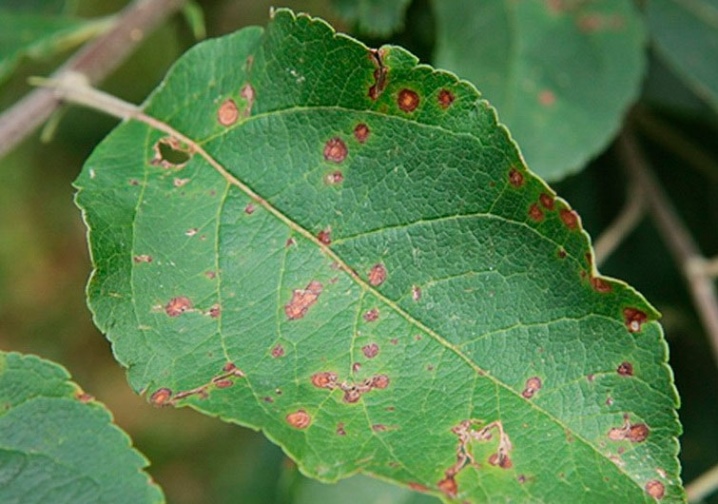

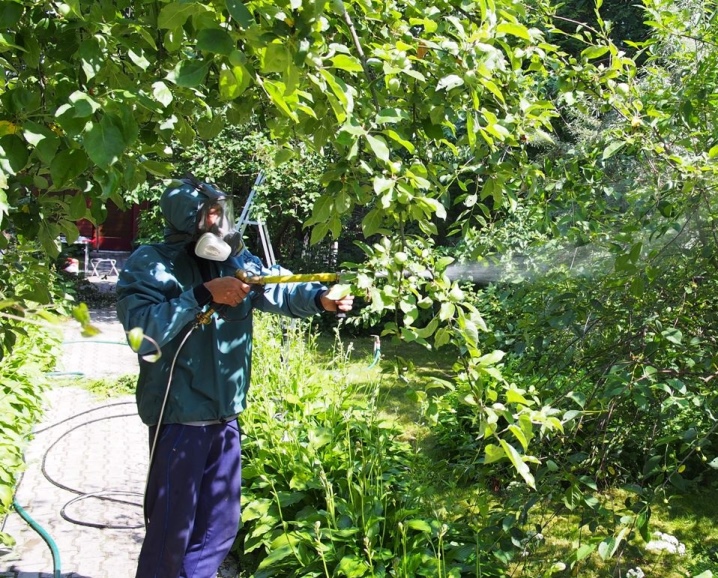
All of these fungal infections can be cured. To do this, it is necessary to remove all affected areas, and then spray and spill the soil with Bordeaux liquid. The treatment is carried out 3 times: at the early stage of bud break, immediately after the end of flowering and then 2 weeks after the second treatment.
Infections and disturbances in cherry cultivation often cause the appearance of gum. This manifests itself in the form of a release of a resinous thick substance from cracks in the bark, which quickly solidifies in air.Trees burnt in the sun or frozen in winter are most susceptible to this disease. If you do not stop the process in a timely manner, the branches will dry out, and this will lead to the wilting of the entire tree.
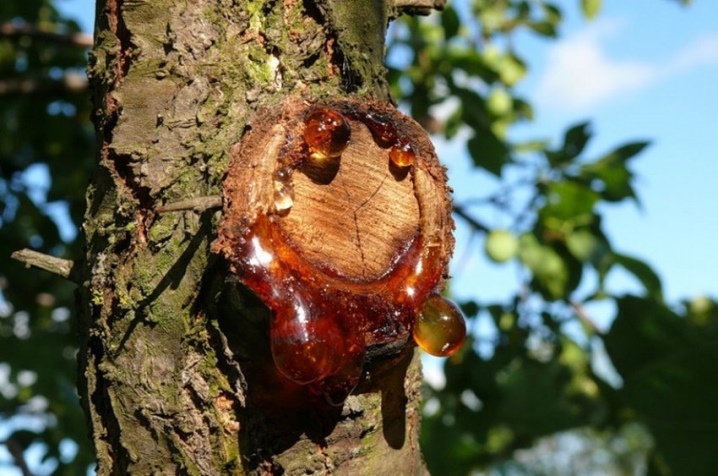

To cure the plant, you should clean the wound with a sharp knife and treat it with gruel from fresh sorrel. If there is no grass, you can take a solution of oxalic acid at the rate of 100 mg of the drug per 1 liter of water. After drying, the wound is covered with garden pitch.
Another common disease is the witch's broom. This fungus is a parasite on many fruit crops, its appearance leads to the appearance of sterile refined shoots. The leaves become pale and slightly pinkish, gradually shriveled. A grayish bloom appears on the lower part of the leaf plate; it contains spores of the fungus. To save the tree, you need to remove all the affected fragments and process it with a solution of ferrous sulfate.

Dangerous bacterial infections include root cancer. It manifests itself by the appearance of small growths on the roots. As they develop, they increase in diameter and harden. This leads to a weakening of the root system, such plants receive less nutrients and die.
Mosaic disease is a viral disease that leads to the appearance of stripes and arrows on the leaf blades. Such leaves curl and fall off, photosynthesis is suspended, and the cherry dies.
There is no cure for these diseases, the plants must be destroyed.

Insect pests are also dangerous for cherries. The greatest harm can be caused by cherry and bird cherry weevils, plum moth, public and pale-footed sawflies, subcrustal leafworm, as well as cherry aphid and hawthorn. Spraying with the preparations "Citkor", "Ambush", "Rovikurt", "Anometrin" helps to fight these parasites.

Interesting Facts
And in conclusion, we will introduce you to the most interesting facts about cherries.
- Modern Iran is considered the homeland of this plant, although some historical evidence indicates that it also grew in the Caucasus.
- The cherry tree is exceptionally frost-resistant. In its natural habitat, it can be found even in the Himalayas.
- The first mention of cherry in Russian history dates back to the middle of the XIV century. It is known that when Yuri Dolgoruky laid Moscow, the common cherry was the only fruit crop in that area.
- Cherries have medicinal properties. It relieves epilepsy and normalizes the nervous system.
- But the seeds and pits of cherries should not be eaten in large quantities, this can lead to serious poisoning.
- The world famous Japanese sakura is also one of the varieties of cherry. True, its fruits are completely inedible.














The comment was sent successfully.