What is Surinamese cherry and how to grow it?

Novice and experienced gardeners will benefit greatly if they know what Pitanga (Surinamese cherry) is and how to grow it. In addition to the general description and planting at home, it is advisable to study also the care of eugenia single-flowered, preparation for winter. A separate important topic will be its reproduction, as well as protection from insects and pathological processes.


Spreading
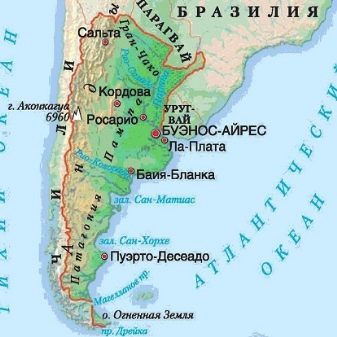
It is believed that the Surinamese cherry comes from the tropical regions of the American continent. In nature, it populates:
- north of Argentina;
- a large part of Brazil (on the river banks and on the forest edges);
- Paraguayan and Uruguayan territories.
The agrarians who appreciated the advantages of this plant have established its cultivation in other tropical corners of the planet. However, for the first time, botanists have given a systematic description of the Surinamese cherry in only one of the Italian gardens. It is curious that for a long time Eugenia one-flowered was considered brought from Indian Goa. But in fact, she got there thanks to the Portuguese, who exported her seeds from Brazil. It is also grown by Argentine, Venezuelan and Colombian farmers.
As an ornamental culture, Surinamese cherry is grown:
- in the Hawaiian Islands;
- on the islands of Samoa;
- in Sri Lanka;
- on Indian territory.
Much less often it is cultivated in the south of China and the Philippines. Such a plant is also interesting for some farmers in tropical Africa. Quite a long time ago, they began to grow it on the Mediterranean African coast. In the continental United States, Surinamese cherry is grown in California and Florida, but there it is used primarily as a garden hedge. Already in the 18th century, it was planted in Bermuda, and according to some sources - since 1922 in Israel.

Description
The tropics and generally southern areas abound in a variety of plants. And each of them is somewhat unique. Surinamese cherry, which in a number of sources is named as eugenia single-flowered or simply pitanga, stands out even against this general background. There are, as is often the case, and other names:
- Barbados cherry;
- Brazilian cherry;
- nagapira;
- red Brazilian cherry;
- cayenne.
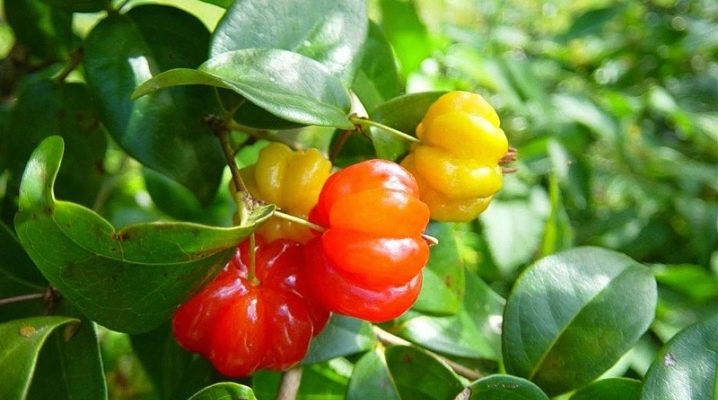
And this is not a complete list. Along with the bright scarlet variety, there is also a very rare dark crimson variety, sometimes its fruit generally reaches almost black in color. Biologically, it is an evergreen shrub with intensive branching.
Sometimes, however, the pitanga is a medium-sized tree. In such cases, the maximum heights are 4 and 10 m, respectively. However, some shrub forms are limited to a height of 2 m.
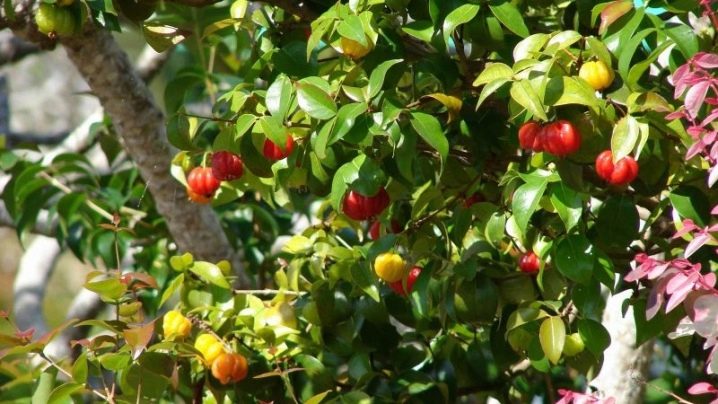

Foliage is placed in the opposite pattern. It has a simple ovoid shape. The length of the leaflets is 2.5-6 cm. The width varies from 1.5 to 3 cm. All leaves have 7, 8 or 9 lateral veins. A rounded or moderately heart-shaped form of leaf bases is noted. The records themselves shine a little. They are typically dark green in color. However, on a cold, dry day, the foliage of eugenia actively turns red. Surinamese cherry is characterized by a creamy white color of flowers. They exude a sweet smell and have a cross-section of 15-30 mm. There are both single and collected in groups of 2-4 flowers. Each of them has 4 petals. There are also 50 to 60 protruding white stamens.
The flowering period begins when the shoots of the previous growing season are growing.Also at this time, the main share of shoots grows in the current season. Most often, you can see the blossoming Surinamese cherry in September. However, the fruit can appear twice or thrice in a year. Ribbed berries have an almost full-fledged ball shape, their cross-section ranges from 20 to 40 mm. Inside contains orange or red pulp. It contains 2 or 3 small seeds that have a light brown tone. These seeds are inedible and taste expressively bitter. Ripe berries of the Surinamese cherry turn green, then orange. Gradually, they get a bright scarlet and even more saturated color.
The peel of the fruits of this plant is not too thin. She is tender. The color of the pulp differs little from the peel, sometimes only a little lighter. However, the difference is different - in a particularly strong aroma and juiciness. The pulp of this plant is characterized by sweetness, although there are also sweet and sour specimens. In some cases, Surinamese cherry annoys people with a resinous sensation. It is unattractive even for those who are used to exotic dishes. The pulp accounts for about 60-65% of the fruit weight. It will ripen in about 35-40 days. An overripe crop will quickly fall off and deteriorate.


Landing
An exotic guest is very unpretentious and endures unfavorable conditions. Short frost periods and even rather long drying out do not negatively affect it. Despite the undemandingness of the land, you will still have to prepare the site very carefully. The entire territory is cleared of plant debris before planting. Additionally, digging and the introduction of organic or mineral fertilizers are required, taking into account the nuances.
Disembarkation can be done in spring or mid-autumn before it gets too cold. The choice of sunny, with weak shade, areas is encouraged. Surinamese cherries require a normal or mild acidic soil reaction. Damp areas will require the use of drainage material.
It is possible to deepen the seedlings, but not below the root collar.


Care
Watering and feeding
This point must be given special attention when growing Surinamese cherries at home. Normally, the first fruiting occurs in the second season of development. Watering this plant should be done in moderation. It should be activated in hot weather. Additionally, it is worth resorting to mulching so that moisture is retained more productively. Surinamese cherries feel better with light drying of the earth than with overflow. The moment when irrigation is necessary is determined simply - at a depth of 2 cm, the earth must be dry. It is important to remember that you will have to use distilled or thoroughly boiled water.
Even a slight harshness can negatively affect the state of the culture. In addition to classic watering, full immersion is allowed - which allows you to thoroughly wet the earthen lump. The latter method is especially good when growing bonsai. In winter, between waterings, the lump of earth should have time to dry out thoroughly. Therefore, the frequency of watering is further reduced. If the room is hot and the air is dry, leaf spraying is recommended. For spraying, use again boiled or distilled water.
The time of active growth of the Surinamese cherry begins in March. It then covers the period up to the end of August. During all this time, the plant is fed every 14 days with a complex fertilizer for ornamental deciduous crops. In this case, the dosage should be half as much as prescribed by the manufacturers.
In the resting phase, you need to feed only bushes in the form of bonsai, and exclusively with specialized fertilizers.


Crown formation
Surinamese cherries respond well to trimming and shaping. It is optimal to resort to this procedure in the spring months. But if you need to pinch the shoots urgently, it is allowed to do this all year round.Instead of pruning, adjusting the growth of the shoots with wire wrapped over the soft tissue helps to give the desired direction of growth. The edges of the wire are fixed in the soil; it must be completely removed after a maximum of 90 days of continuous use.
Preparing for winter
This procedure should be carried out gradually, smoothly. Temperatures are reduced without unnecessary jumps, but steadily. At the same time, the frequency of irrigation is reduced. As soon as daylight hours decrease, it is necessary to compensate for this. It is desirable to solve a similar problem using phytolamps.

Reproduction
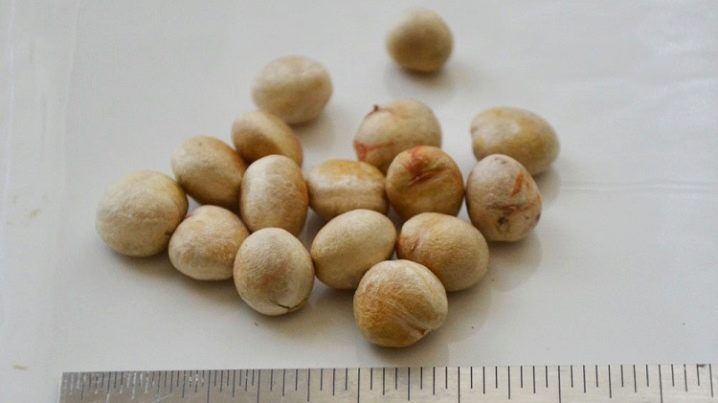
Pitanga is fairly easy to propagate with bones. They are distinguished by increased germination. If fresh seeds are buried in productive soil and care for such plantings, they will certainly germinate. This will take approximately 45-60 days. The seedling of late spring and early summer will be ready for planting in a stable place in mid-autumn, when the weather is still relatively warm. For reproduction of eugenia, partially lignified cuttings are also used. Ideally, they are approximately 100 mm long. In order for the green parts to take root better, they are treated with a growth activator. The optimal substrate is a combination of quality flower soil with vermiculite or perlite. It is very important when rooting to maintain a stable humidity of the environment.
When the plant hardens, it is kept in greenhouse conditions for about 60 days. Then it is smoothly transferred to the usual content. Seating is allowed only after the perfect completion of adaptation. Elongated eugenias are bred using air layers. In this case, rooting is carried out in the same way as indoor vines. The acquisition of seeds is very difficult. Without careful control of temperature and environmental properties, germination will be difficult. Sowing is carried out to a depth of 5-10 mm. Normal cultivation is possible at 22-24 degrees.
The development of the Surinamese cherry is fast, but flowering in difficult cases can even begin at 6-7 years.

Diseases and pests
If over-watered, Surinamese cherries can be affected by root rot. It is impossible to solve the problem without transplanting into new soil. Affected roots are cut and sprinkled with powdered charcoal on the cut points. Among insects, the threat is whitefly, aphids, slugs, scale insects and mites. To suppress them, specialized drugs are used.
Also, difficulties can be expressed in:
- leaf spot (if the ground is excessively wet);
- shedding foliage from excess moisture;
- similar dropping, but as a result of the heat.











The comment was sent successfully.