All about moniliosis cherry

Cherry moniliosis is one of the ten most common crop diseases. Knowing everything about cherry moniliosis will be useful for both beginners and experienced gardeners - the disease is considered difficult, difficult to eliminate.

What it is?
Cherry moniliosis, or gray rot, or monilial burn, or fruit rot is a fungal disease. The causative agent is a parasitic fungus, ascomycete Monilia. The bacterium loves mid-latitudes, cold and humid climates. Often affects stone and pome fruits: cherries, plums, pears, apple trees. The disease looks characteristic: the branches dry, turn brown, the fruits become obviously inedible.
The disease can affect any species and varieties, although varieties of felt cherries are more resistant to it on average, but there is no 100% guarantee.


Symptoms of defeat
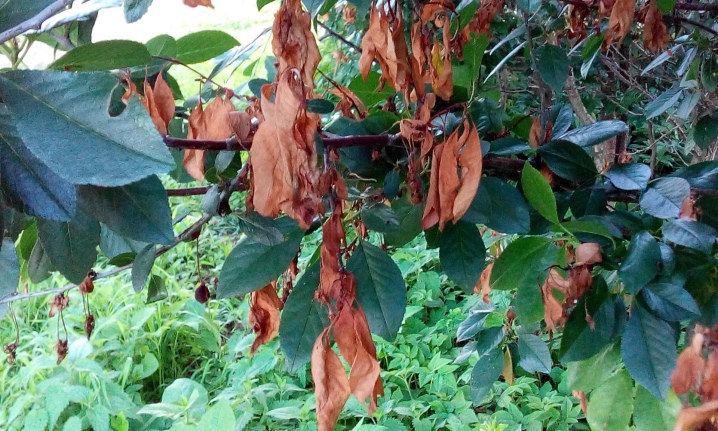
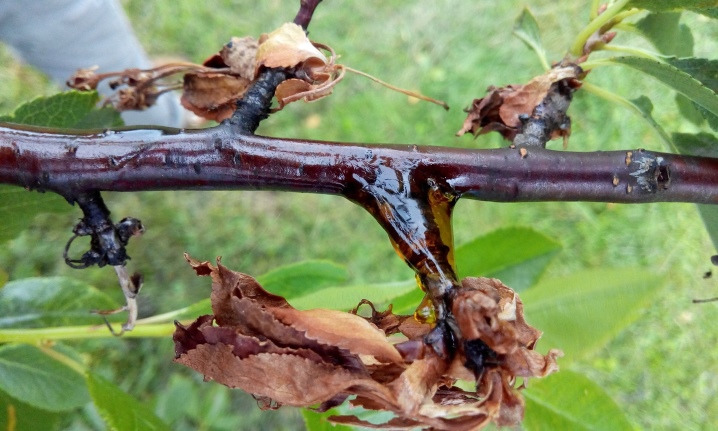
To understand that the cherry is sick in the early stages, you need to regularly examine the petioles and the lower surface of the leaves. Small white formations appear on them, similar to chains. Cracks can be seen on the bark, they are almost invisible, but there is an outflow of gum.
In the future, the spores are carried by wind or insects. On the fruits, brown weeping spots appear, with white tubercles, which are gradually able to "eat" the entire fruit. White pads are sources of spores. Affected fruits do not fall, they hibernate on the plant. Affected leaves dry out to a coppery color.
The parts of the plant most susceptible to fungus are young shoots and flowers. These organs dry out, the bark cracks, becomes covered with gum. Such a severe lesion is called a monilial burn. Affected plants are unable to produce crops.

Why does it appear?
The specific causes of the occurrence are difficult to determine. The pathogen can get to the area with the wind, from the neighboring area, with flying insects that will bring it on their paws. Ascomycete Monilia is a whole genus of micro-fungi, which includes different species. Some species infect forest berry crops, they are difficult to find in ordinary areas, they have a strong smell attractive to insects. Others have almost no smell, spores fall on cherries along with rain or wind. The most dangerous way for summer residents is new infected plants. Therefore, you should always carefully inspect and handle new seedlings before placing on the site.
Interesting: the group of ascomycetes also includes many useful fungi, for example, yeast.
How to treat?
If the disease has already been detected, they begin long, repeated treatment. One treatment is not enough, the disease is tenacious, viscous, the spores of the fungus are small, they can persist in any crack.
The fight against the disease involves complex measures and a combination of various methods, otherwise an epidemic and the complete death of cherry plantings are possible on the site.
- All affected branches are cut and burned. You need to cut off not along the border of the disease, but along healthy tissue, for example, below the lesion by 6-8 cm. Instruments are sterilized after each cut. It is rarely possible to save a heavily damaged plant; it is better to uproot it, or cut it off heavily.
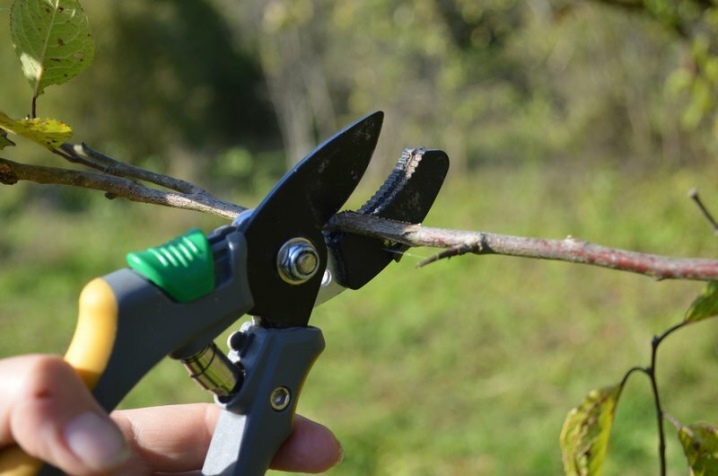

- Treatments with fungicides are carried out. The best remedy is chosen based on individual needs, the drugs are different. Not only cherries are processed, but also cherries, apples, pears, and other crops for which the disease is common.
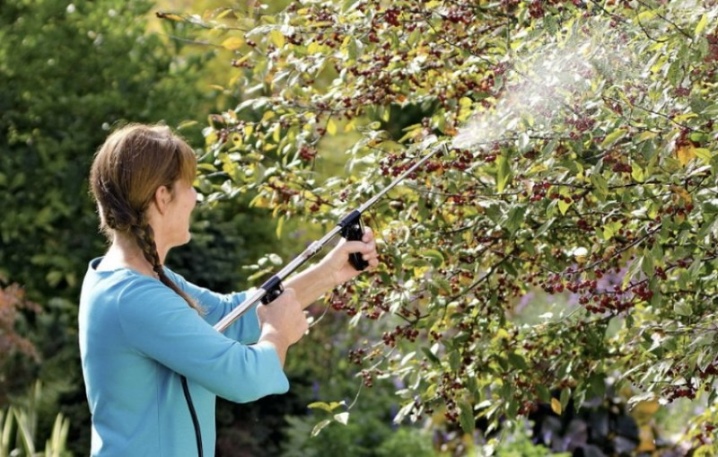

- Immediately after pruning, it can be treated with Bordeaux mixture or copper sulfate. These are universal antiseptics. The procedure is repeated before hibernation.In the spring, before flowering, you can spray with a 1% solution of "Fundazola". This universal scheme is suitable for the prevention of a not very advanced disease.
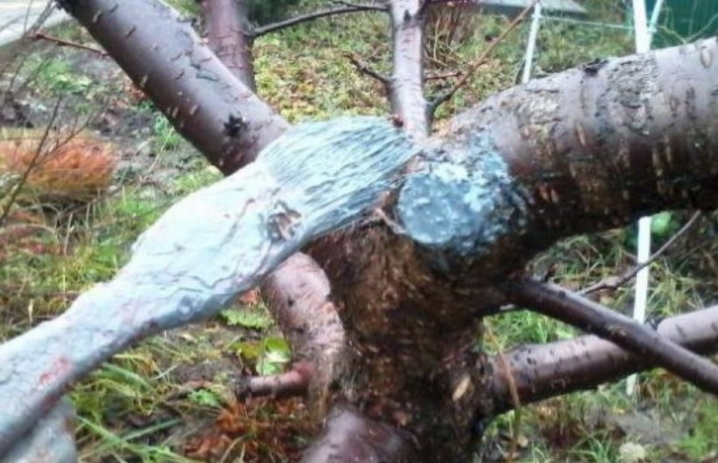

- Any damage to the plant is a gateway for infections. All cracks before wintering plants are carefully inspected, covered with garden varnish.

- The trunk circles are also carefully processed. It is advisable, in general, to remove the top layer of the soil and replace it with a disinfected one. You can also spill the soil with fungicides.

After flowering and in the summer, when the fruits have already set, it is difficult to process fungicides, therefore, preference is given to biological preparations. Folk remedies will help not so much to cure as to prevent the disease, you should not rely on them, but you can use them in combination with other measures.
Even after it was possible to get rid of the visible signs of the disease, the plantings are regularly examined and sprayed. You need to fight the disease on a regular basis.
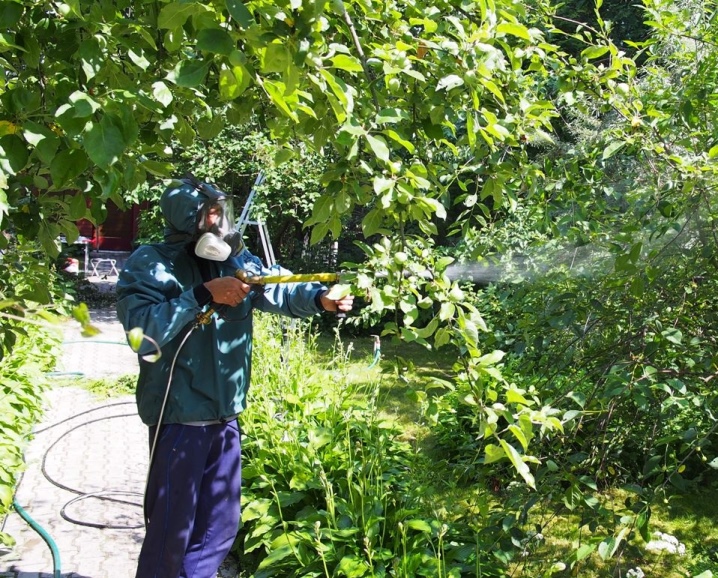

Chemicals
Before using any drug, carefully read the instructions. You can not thoughtlessly combine drugs, or use them in a different concentration.
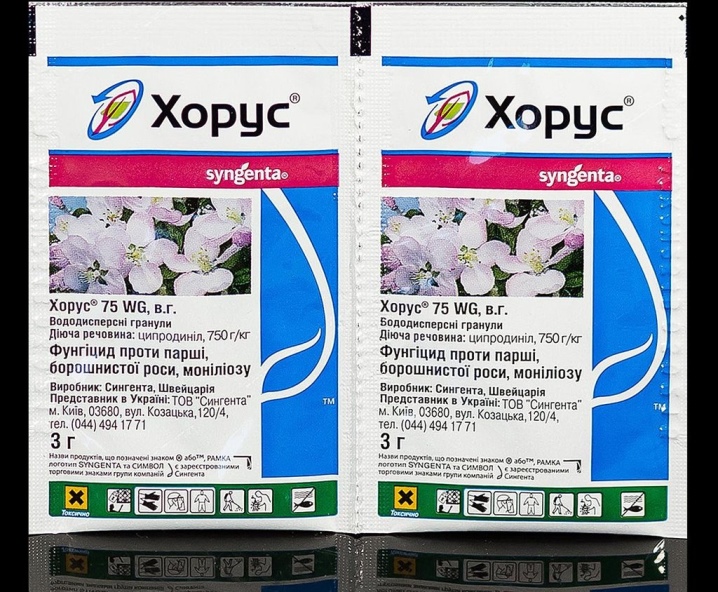
Horus is the most popular drug. Effective, comfortable. As part of the universal pesticide cyprodinil, which is widely used in agriculture. They are treated with wheat planting, apples against scab, all stone fruits against moniliosis, coccomycosis, clasterosporiosis.
It is a systemic drug that protects the plant by penetrating its tissues. It acts on mushrooms at the molecular level.
Two treatments are allowed per season. Sprayed for the first time before flowering, then the treatment is repeated after 10 days. 100 sq. m, 10 liters of the finished solution will be required, it is prepared by diluting 2-3 g of the drug in this volume of water.
Preparation and Precautions - As with all pesticides. The drug is first diluted in a small amount of water, stirred, then brought to the required volume. This is necessary so that the solution is uniform. The drug tends to settle, so when spraying a large area, you need to periodically shake or stir the solution. They work in special clothing, gloves, glasses and a protective mask are also needed.
Other effective chemicals: Topsin, Azocene, Delan, Rovral.
Bordeaux liquid is often in the arsenal of gardeners, it is it, after "Horus", that is most actively used to combat moniliosis. It is a mixture of copper sulfate and quicklime. Disinfects, dries, strengthens plant tissues. The treatment is carried out before the buds dissolve, in the green cone stage, repeated after flowering, then spraying is carried out 1 time in 7 days. The last treatment is no later than 15 days before harvest.
Preparation: Dissolve 100 g of copper sulfate in warm water, add water to 5 liters, quench 150 g of lime in a separate bowl and add up to 5 liters. Cool both solutions, and then copper sulfate is poured into lime. The finished mixture has a beautiful blue tint. This is a 1% blend recipe. To prepare 3%, 400 g of lime and 300 g of copper sulfate are taken for the same volume of water. To check, a nail is dipped into the liquid, if after a few minutes it becomes covered with a copper coating, the liquid is too acidic, lime must be added.
Use immediately after preparation. Wet weather and high temperatures make the chemical reactions of the mixture more intense, burns to the leaves are possible, therefore, it is necessary to process it in dry, moderate weather. Before the kidneys dissolve, you can use a 3% solution, then only 1%.
Other copper-based preparations: Abiga-Peak, Hom.

Biological preparations
Biological drugs have a completely different mechanism of action - like antibiotics. They do not kill the pathogen mechanically, but interact with it, causing its death. Contact ones act upon direct contact with the fungus, and systemic ones are substances that are capable of penetrating plant tissues and already in this indirect way achieve the goal.
If there are a lot of hard-to-reach places in the plantings, you need to choose a drug with a systemic effect.
"Fitoflavin" is an example of a drug that has both contact and systemic effects. It is necessary to spray in the budding phase, flowering and twice in the ripening stage of the fruit. It works for 15-20 days, then the treatment is repeated.
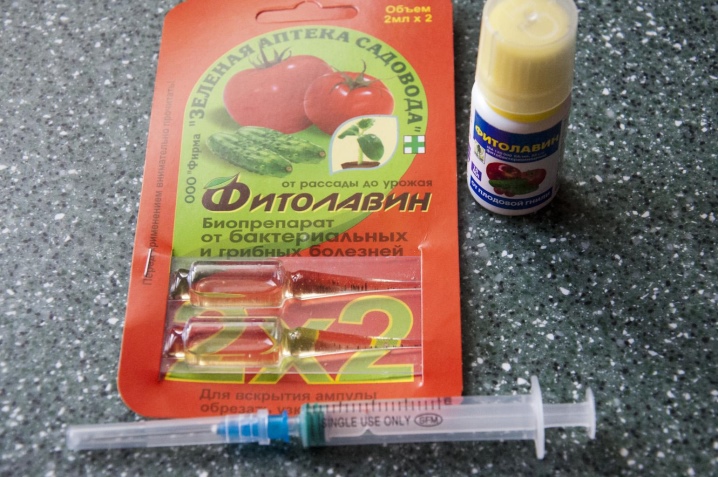
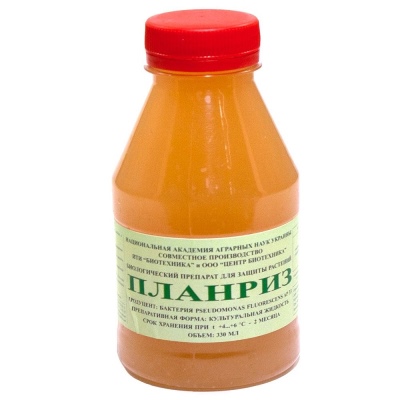
Treatments with drugs like Planriz or Gamair will be useful.
"Planriz" is a universal remedy for a wide variety of diseases, including scab, late blight, root rot. It is a concentrate of rhizosphere bacteria. They improve the microclimate in the garden. Treatments with "Planriz" do not directly affect moniliosis, but reduce the risk factors for the development of the disease, protect cherries from other diseases, microdamages.
It is used for spraying and, most importantly, for soil cultivation. When planting young seedlings, they are brought into the planting pits, the soil is shed. Treatments of the outer parts of plants can be carried out every 10-20 days, as needed.
Minus - cannot be stored for a long time, the drug is valid for 2-3 months. if stored in the refrigerator.

Gamair is Bacillus subtilis bacteria (the same as in Fitosporin) + a complex of metabolites. The manufacturer claims that the drug is more effective than Fitosporin. Available in tablet or powder form. Convenient because it can be used for any crops, to prevent a very wide range of diseases. Protects plantings for 20-30 days after treatment. You can apply in two ways: spraying the aboveground part, shedding the soil.
Important: a fixative is added to the working solution - a substance that will better keep the agent on parts of the plant. In the quality of "Velcro" can be used "Epin", "Zircon" or ordinary soap.
It should be borne in mind right away that biological products are less effective. While Horus demonstrates efficiency of 82-92%, Fitoflavin - 66-79%.
But they have advantages: environmental friendliness, safety for animals, fish, and other plants, do not cause addiction to pests, are not phytotoxic, convenient to use, they can be used as needed, processed during the period of active ripening of the crop. They are better combined with other drugs, chemical or biological. Gamair can be mixed with many insecticides, stimulants and fungicides right in the working solution.

Agrotechnical methods
A number of agronomic techniques reduce the likelihood of moniliosis damage to cherries.
- Site with good air movement. The less stagnant moisture, the less likely it is to be affected by the fungus. The wind that carries the spores is less dangerous than the humidity.
- Well maintained distance between seedlings. Do not thicken the planting.
- Timely removal of overgrowth that weaken the plant.
- Correct pruning, not too early and not too late. Both weaken the plants.
- Balanced feeding, high-quality watering, nutritious soil. Weakened plants are most affected.
Any measure that strengthens the natural immunity of the plant will be helpful.
Strong healthy cherries that do not lack trace elements are much less likely to be affected by any viral, bacterial and fungal diseases.
Periodically, fruit can be sprayed with stimulants.

Resistant varieties
The most resistant varieties to moniliosis are Dessertnaya Morozovaya, Nord Star, Igritskaya, Kharitonovskaya, Assol, Morozovka, Radonezh... The Bulatnikovskaya variety is distinguished by its excellent resistance to fungal diseases.
Good varieties "Ashinskaya" and "Dobraya" (this is a cherry-bird cherry hybrid), but they are not the most delicious. Other varieties of the above are stronger. Although the Dobraya variety is excellent in preparation, it has an excellent yield and perfectly tolerates severe winters.
For the Moscow region, it is worth considering "Dawn of Tataria" and "Early Yagunova" - they have not only good health, but also high winter hardiness.
Cherry variety "Vladimirskaya" often described as resistant, but in practice it is heavily affected by moniliosis without treatment. Gardeners still grow this variety - the fruits are very tasty.

Well stable "Shokoladnitsa" and "Turgenevka", but they can show themselves weak - depending on the care and the site.
If there is no time to care for varietal cherries, it is better to plant felt cherries, sandy (dwarf) or Besseya cherries. These species will be especially good for those who live in Siberia, Altai, the Far East. They are unpretentious, tolerate irrigation interruptions well, and are not damaged by frost.
Varieties should be selected zoned, bred for cultivation in the region by local fruit stations. They always have stronger health.

Preventive measures
Preventive examinations are very useful. Between the stages of the development of the disease, no more than 2 seasons pass, therefore, the disease can be detected even at the stage of cracks in the bark, it will not have time to reach the leaves and branches.
Other ways of preliminary protection.
- Timely treatment of any damage to the bark.
- Pruning - just on time and right. All large sections are sealed with garden varnish.
- The crop, even if it looks healthy, should not remain on the plant for the winter. Be sure to remove and burn all diseased fruits.
- Cleaning of fallen leaves is required. Mulching only with fresh sawdust, needles, agrofibre.
Before flowering, cherries are treated with Bordeaux liquid, "Horus" or copper-containing preparations. If the plants are healthy and grown in the right conditions, this protection may last for the rest of the season. The processing is repeated after harvest and in the fall.











The comment was sent successfully.