Viola: description, types and cultivation
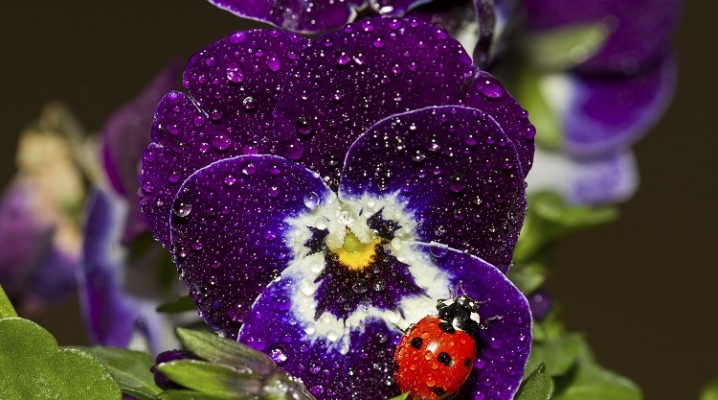

Garden viols are spectacular representatives of the world of decorative flora, striking the imagination with a wealth of colors and shapes. An impressive color palette, amazing varietal and species diversity, as well as unpretentiousness to growing conditions - all these and many other features have determined the popularity of viols in gardening, street gardening and landscape design. In the article, we will consider the varieties of these plants, we will analyze how to properly grow garden violets and care for them.


Peculiarities
To begin with, it should be noted that the term "viola" means a whole genus of annuals and perennials that are part of the violet family. According to specialized sources, this family includes from 500 to 700 species of representatives of the flora world, a significant part of which is widespread in ornamental gardening.
Despite this, among amateur flower growers, the term "viola" usually means only one of the species - tricolor violet (Viola tricolor), better known as "Pansies". Theoretically, the collective name "viola" is applicable to this species, since it is also part of the violet family.


However, it should be borne in mind that this species is not the only representative of both the specified family and the genus of violets (Viola) itself. Thus, from a scientific point of view, the use of the term "viola" only in relation to plants of the type violet tricolor cannot be considered correct.
Representatives of the genus violet (Viola) are ubiquitous in geographic zones with a temperate climate. A significant part of the species is concentrated in North America, New Zealand, Japan, Australia. Many species of these plants are found in the South American Andes.
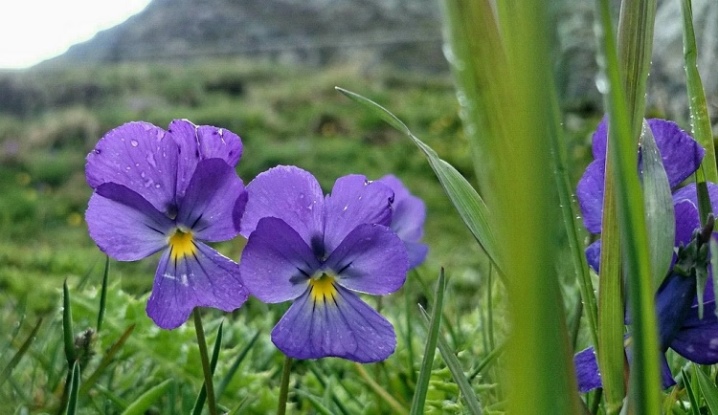

The overwhelming majority of representatives of the violet genus are herbaceous annuals and perennials with simple, dissected or feathery leaves and single flowers, from which fruit-boxes are later formed.
Most viols are grown by gardeners for decorative purposes, some varieties are cultivated for fragrant flowers.


Varieties
The huge species diversity of violets includes annuals and perennials, some of which are found in the wild. In gardening and urban landscaping, mainly cultivated species and varieties of viols, bred by breeders, are used. Below are the most famous varieties and varieties of violets, many of which have rightfully won the love of flower growers and landscape designers.


Marsh violet
Herbaceous perennial that grows mainly in areas with high humidity. Its natural habitat is lowlands, river floodplains, wet meadows, forests and swamps. Plants of this species have a low (up to 15 centimeters) stem, root rosette of leaves, single small flowers (up to two centimeters in diameter).
The color of the petals ranges from milky white to bluish-lilac shades.

Fragrant violet
A variety of herbaceous perennials with a height of about 15 centimeters. Plants of this species form a dense rosette of dark green leaves and single small flowers with a pleasant and strong aroma. The color of the flowers is deep purple or white.
Plants are actively used in urban landscaping, decoration of gardens, parks and squares.

Dog violet
A variety of perennial plants with short branching roots, thin low stems (5 to 15 centimeters high), ovoid leaves, single pale blue flowers of irregular shape. This species grows mainly in forest zones.

Horned violet
Or viola cornut - a type of perennials capable of forming dense and lush pillow-like curtains. Plants have low (up to 20 centimeters in height) stems, simple oval leaves and small fragrant flowers. The color palette of flowers includes milky white, pale blue and dark blue shades.

Viola tricolor or tricolor
Another popular name for "Pansies" is a variety of the violet genus, which includes annuals, biennials and perennials with a height of 10 to 30 centimeters. In floriculture, the most widespread is the hybrid form called the Viola Vittrock. A characteristic feature of the plants of this variety is beautiful and large flowers of a bright tricolor color.

"Freezel Sizle"
An improved hybrid series of Wittrock violas, distinguished by their extraordinary decorative effect. Plants have a compact rosette of leaves; during the flowering period, they form large double flowers with strongly corrugated edges. The color palette is very diverse and includes both light pastel shades and deep purple, lilac, lemon-yellow tones.
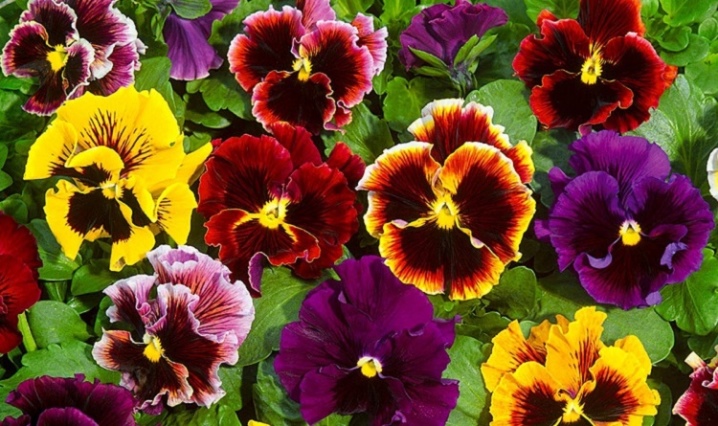

"Little Red Riding Hood"
An early flowering variety of Viola Wittrock, notable for its very spectacular appearance. Plants form neat, proportional bushes about 20 centimeters high. The flowers are large, reaching 8 centimeters in diameter. The color of the petals is deep crimson, with a contrasting dark brown spot in the center.

"Black crystal"
The original Viola Vittrock variety with large (about 7-8 centimeters in diameter) flowers of a dark anthracite color. Plant height is on average 15 to 20 centimeters.

Cool Wave
Luxurious series of Vittrock ampel viols, designed for growing in hanging pots, containers, balcony boxes. It is allowed to grow plants in the open field as a ground cover. The characteristic features of the violets of this series are early, fast and intense growth, lush and long flowering.
The series contains violets of lilac-blue, lemon-yellow, milky-white, yellow-blue colors.
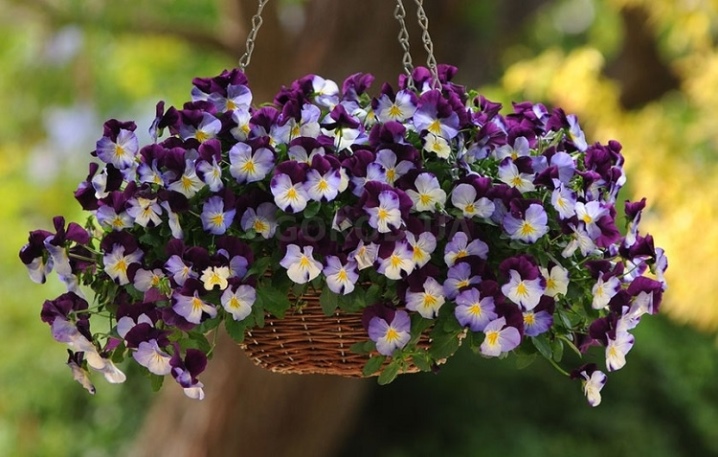

"Blue carbuncle"
A spectacular series of Vittrock violas with large (up to 8 centimeters in diameter) flowers of sky-blue and lavender shades. Plants form low compact rosettes of leaves. Viols of this series look good both outdoors, where they are grown as curbs and ground cover plants, and in portable containers.

"Bambini"
A very attractive variety of Viol Vittrok, distinguished by its extraordinary decorative effect. The flowers are large, purple-lilac or deep burgundy with a lemon-yellow center. The petals are round, velvety.

"Germanicus"
An unpretentious and very effective variety of Viol Vittrok, characterized by increased resistance to low temperatures. This series is represented by a mixture of colors, which includes white-violet, orange-yellow, brown-yellow colors.
The variety is recommended for the creation of flower beds, borders and ridges.

"Butterfly wings"
An original variety, notable for its abundant and spectacular flowering. The upper petals of the flowers are painted in a deep crimson color, the lower petals are lemon yellow. There is a rounded black mark at the base of the lower petals, contrasting favorably with the red-yellow range. As stated in the description, the variety is winter hardy, resistant to low temperatures.

How to plant?
Planting viols is a fairly simple, but painstaking and responsible procedure.If you plan to grow the plants outdoors, you need to choose the right place for them. Despite their unpretentiousness, viola painfully tolerate a lack of lighting and drafts. The best place for them is a well-lit and wind-protected area with fertile loamy soil.
On sandy soils, poorly retaining moisture, and in shaded places, viols are also able to take root, but in these cases their flowers will be small and rare. The deficiency of nutrients in the soil also negatively affects the size and number of flowers.
It is highly undesirable to plant seedlings in lowlands and places with a high level of groundwater. In this case, increased soil moisture can cause the development of fungal root diseases and even plant death. It is allowed to sow seeds directly into open ground, however, the seedling method is considered the best and more popular. The timing of planting viola seedlings is determined based on the weather conditions and the climate of the area. In most cases, flowers are planted in April or May.


Plants will take root well in a soil mixture consisting of fertile soil with the addition of crushed charcoal and humus. To prepare such a soil when growing viols in containers, the following proportions of the components are used:
- 5 pieces of garden land;
- 1 part coal;
- 1 part humus.
It is allowed to add one part of peat and sand to the soil mixture. These components improve the moisture and air permeability of the soil, which has a positive effect on the growth rate and development of plants. Before planting, in the selected area, the holes are equipped, maintaining a distance of 10-15 centimeters between them. Then, in each hole, a bush of seedlings is placed, and the roots are covered with earth. Further, the soil from the sides is carefully compacted, and the plants are watered with warm, settled water.
Plants grown as perennials are transplanted to a new location every 3 years. During transplantation, large overgrown bushes are separated, and the cuttings are planted in the traditional way.


How to care?
Growing viols is a fun and easy activity that does not require a lot of effort and time. These unassuming plants do not have too high requirements for care, to which they respond with abundant and long flowering.
The basic rules for the care of viols provide for the provision of conditions such as:
- sufficient light during the day;
- compliance with the irrigation regime;
- timely fertilization;
- regular weed removal (when grown outdoors);
- Constantly checking plants for signs of disease or pest activity.


So that the plant can fully develop and delight with gigantic and bright flowers, he needs enough sunlight... The easiest way to achieve this is by growing flowers in mobile containers and flowerpots. When growing viols in the open field, it is important to determine the most illuminated place for them in advance. Given that these plants have a fibrous and superficial root system, it is important to ensure that the ground does not dry out on hot days.
Water the viols as needed, trying to direct the stream of water closer to the roots. It is not recommended to irrigate so that the water can get on the leaves or flowers.
The optimal time for watering is sunrise or sunset. Watering in the midst of a sunny day is strongly discouraged as it can burn your plants. It is best to water the viola with warm, settled water. Cold water is not used for irrigation.


During the period when the plant is preparing for flowering, it needs feeding. They are also needed during flowering, when viols spend a lot of energy on the formation of new buds. Plants are fed with ordinary superphosphate about once every 3-4 weeks. Complex mineral fertilizers for flower crops are also suitable as top dressing. It is not recommended to feed viola with organic fertilizers.
Viols growing in open ground must be promptly cleaned of germinating weeds. Drowning out garden violets, weeds not only prevent them from fully developing, but also create favorable conditions for the development of diseases and pests. In addition, weed-covered flower beds look very unpresentable. Some growers recommend to loosen the ground in flower beds with viola.
This procedure should be carried out very carefully so as not to damage the roots of plants that are located close to the surface of the earth.


In very hot and sunny weather, garden violets can be slightly shaded. Flowers growing in containers can be temporarily removed from the scorching sun, and when its activity subsides, the pots and flowerpots can be returned to their usual place.
When growing viols both in the open field and on the balcony, the plants should be inspected regularly. This simple procedure allows you to control the condition of plants, timely identify traces of diseases or pest activity. Dry leaves and flowers must be removed regularly. They not only make plants unkempt, but also create favorable conditions for the existence of parasites and pathogens.

Reproduction
These flowering plants are propagated in several main ways. In particular, gardeners use breeding methods such as:
- seminal;
- cuttings;
- branching.
Perennial viols are propagated by dividing the bush. This procedure is performed during transplantation using a knife with a clean and sharp blade. Places of cuts after division are treated with charcoal powder.



Seeds
A very simple and quite effective method for growing garden viols involves the use of seeds. In this flower culture, the seeds are distinguished by high germination, which lasts for 2-3 years or more.
Before sowing, it is necessary to prepare a planting container (plastic container or wooden box), plastic wrap, a spray bottle with settled water. The seeds are sown pinch at a time, distributing them in the grooves. After sowing, it is allowed to lightly sprinkle the seeds with a mixture of finely ground earth and sand. At the end of the procedure, the ground is moistened with water from a spray bottle, and the tray is covered with polyethylene.


The first shoots usually sprout 7-8 days. The germination rate of seeds depends on the variety and variety of viola. Before the emergence of shoots, the film is periodically removed from the tray to ventilate the container. As soon as the seeds germinate, the film is finally removed, and the container with the seedlings is moved to a cool place, where the air temperature is about + 10 ° C. To prevent the seedlings from stretching, they need to provide abundant, but diffused lighting.
Young plants should be protected from direct sunlight. Too dense crops need to be thinned out. During thinning, weaker specimens are removed, giving stronger seedlings the opportunity to fully develop.
After 2-3 true leaves are formed at the seedlings, they are dived in boxes or pots. Some growers, after 2-3 weeks, pick again, although usually there is no particular need for a repeated procedure. In April-May, the grown seedlings are determined for a permanent place.
It should be noted that garden viols are usually grown as annuals. In this case, sowing seeds for seedlings is carried out in February-March. The seeds of perennial viols are planted in the ground before winter.


Cuttings
Valuable varieties of perennial viols are often bred using green cuttings. Only healthy and well-developed shoots with 2-3 internodes are suitable for plant propagation.The cuttings are rooted in moist soil, deepening their lower cut by about half a centimeter. To speed up the rooting process, it is better to protect the cuttings with a cap made of light-colored fabric. While the planting material is taking root, the fabric should be regularly moistened.
This method of breeding viols is usually resorted to between May and July. If the grower observes all the recommendations for performing this procedure, green cuttings take root after 3-4 weeks. If the cuttings were planted in the garden in May - early June, then the established plants will bloom by the end of summer.
If the procedure is carried out later than July, young viols will bloom only the next year.


Layers
Perennial viols can be propagated using cuttings. For this, the longest and healthiest shoots are used, which are pinned to the ground and slightly instilled. It is recommended to carry out this procedure in September. In this case, the layers will be able to take root before the onset of frost. In the spring of next year, when foliage begins to appear on the plants, the established layers are separated from the mother bushes and transplanted to a permanent place.
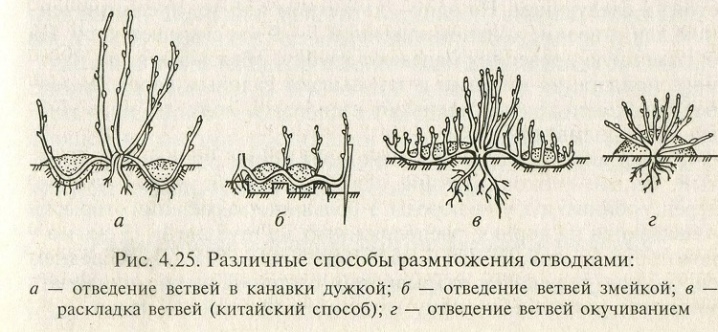
Diseases and pests
Garden viols are considered to be quite hardy plants, resistant to diseases and pests. However, non-observance of the rules of caring for them almost always leads to a decrease in immunity and the development of unpleasant consequences.
One of the most common diseases of these flowering plants is powdery mildew. Typically, this problem occurs when the abuse of fertilizers containing nitrogen. The characteristic symptoms of this disease are the formation of a white-gray plaque on the leaves, flowers and buds of plants. Treatment involves treating infected viols a solution of soda ash with the addition of the drug "Fundazol".


Blackleg - another insidious disease that affects viola in violation of the rules of care. Its development is facilitated by such factors as:
- thickening of landings;
- unsuitable temperature regime;
- high air humidity;
- abuse of watering.
The main symptom of the disease is darkening and thinning of the base of the stems. A diseased plant begins to creep along the ground, and then withers. For treatment, drugs "Fundazol", "Previkur", "Fitosporin" are used.
Both plants and soil should be treated with these preparations.

Gray rot - a dangerous disease that develops most often in violation of the irrigation regime, high air humidity, and an excess of nitrogen in the soil. A characteristic feature of this disease is the appearance of gray fluffy clusters on the leaves. Treatment in this case is carried out with the use of drugs "Fundazol" or "Captan".
The appearance of cobweb traces on the leaves may indicate a spider mite injury. This pest feeds on plant juices, as a result of which they begin to turn yellow, dry, and lag behind in development. For the fight use drugs "Fufanon", "Actellik", "Fitoverm".

Strawberry nematode Is a very dangerous parasite that poses a serious threat to plants. The fact that garden viols became victims of this pest is evidenced by the weakening of their condition and a significant lag in development. The leaves of plants become tough, wrinkled. Treatment involves removing the affected parts of the plant and processing it. universal pesticide "Ditox".
Another extremely dangerous pest - root-knot nematodethat affects the root system of plants. Affected viols begin to lag sharply behind in development, wither, and lose their attractiveness. A characteristic sign of damage is the formation of nodes, swellings, and other suspicious formations on the roots of plants.
It is recommended to destroy the infected plants. In some cases, long-term complex treatment with the use of systemic nematicides ("Marshal", "Alanicarb") is possible.

Use in landscape design
Unpretentiousness, resistance to low temperatures, long and abundant flowering have led to the popularity of garden viols in landscape design. These delightful flowers look spectacular in both single and group plantings. They get along well with other decorative cultures, allowing landscape designers and gardeners to implement original and bold solutions.

Garden viols are used to create flower beds as main, auxiliary or framing plants. With their help, you can equip magnificent carpet plantings - monochromatic or variegated.


The small height of mature plants allows them to be used to create decorative borders. Compositions in which garden viols are combined with diastia, nemesia, ornamental cabbage are very effective and colorful.

To decorate home gardens, garden viols are usually used, grown in flowerpots, hanging pots, and portable containers. The verandas and terraces, decorated with pots with ampel-shaped plants, look quite elegant.

When planning to create in your garden a flower bed of viols and other decorative annuals (perennials), one should take into account their color, height, timing and duration of flowering.
It is desirable that these parameters in plants correspond to each other as much as possible. Thanks to this, the blooming flower bed will look the most organic.


For information on how to grow good viola seedlings, see the next video.
































































































The comment was sent successfully.