Nuances of grape propagation by layering

There are many effective ways to propagate grape bushes - by seeds, cuttings, grafts. In this article, we will talk in more detail about the simplest method - dropping in the vine and getting layering. This is a simple process, if you know the basic rules and subtleties of the procedure, then even a novice gardener can cope with it.

Advantages and disadvantages
One of the simplest and most ubiquitous methods of propagating vines is to use cuttings. This method has been proven for centuries and is suitable even for beginners. The technique gives a good result when breeding difficult-to-root varieties.
Layers are rooted stems obtained by dropping and subsequent separation from the parent bushes. In the process of rooting, the young plant is directly connected with the mother bush, due to which it is provided with adequate nutrition.
This stimulates the active emergence and growth of roots.
The technique of propagation of grapes by layering has its own undoubted advantages:
-
simplicity of execution - does not require special skill, the presence of special skills and tools;
-
minimum expenditure of time, effort and money;
-
preservation of all varietal characteristics of the parent plant;
-
a high level of survival rate, even for difficult-to-root varieties that are not suitable for any other breeding methods;
-
the possibility of harvesting the next year;
-
the rapid expansion of the vineyard area.
This technique is often used by nurseries that profit from the sale of seedlings.
However, the method also has its drawbacks:
-
it is suitable exclusively for those land plots where there were no diseases affecting the roots;
-
the development of cuttings requires the expenditure of the vital forces of the parent plant, therefore the mother bush is greatly depleted.
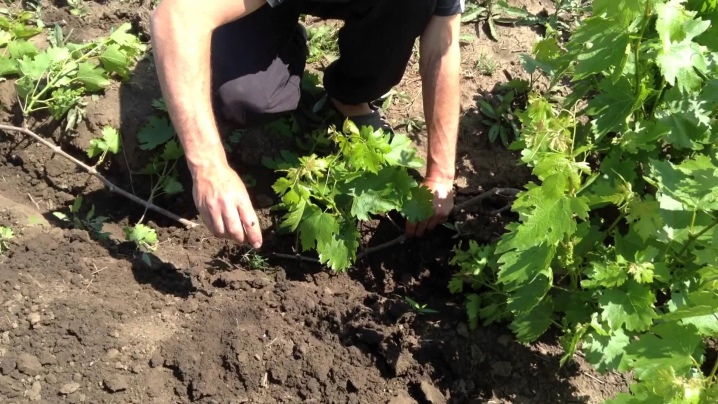

Basic conditions
In order for the layering method of propagation to be effective, and roots appear on the buried fragments of the vine, it is important to observe a number of conditions.

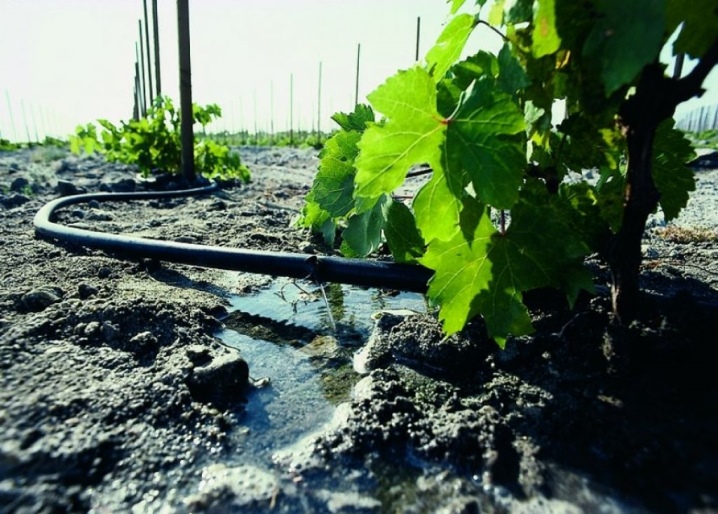
Humidity
The main factor of root formation is constantly moistened soil. Several techniques are used to retain moisture in the ground:
-
regular abundant watering;
-
mulching the breeding zone with peat, straw or cut grass;
-
creating a darkening of the soil using plastic / metal sheets, slate, cardboard or boards.

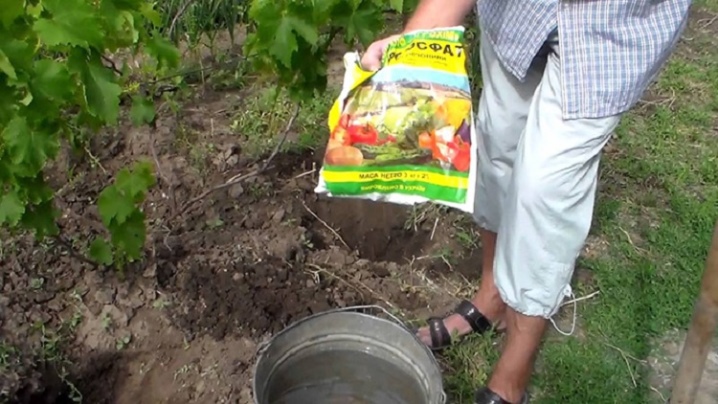
Top dressing
The supply of nutrients directly affects the rate of root formation. Therefore, the layers must be fed. For this purpose, organic and mineral fertilizers are applied to the soil.

Dipping depth
Active growth of the root mass is possible only in the dark. Grapevine cuttings must be buried to a depth of about 15-20 cm.
This will minimize the risk of sunlight penetration, and in addition, maintain sufficient humidity parameters.
If the vine is not dug deep enough, the penetrating light will slow down the rooting process. In this case, it is necessary to additionally cover the ground with dense material.
How to propagate in different layers?
The layering method combines several options.
Green
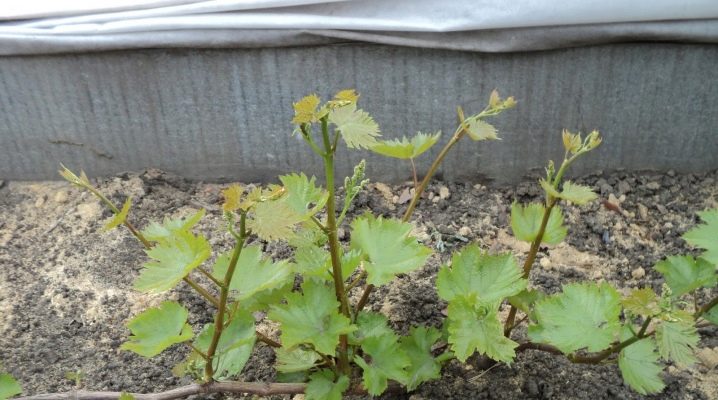
The main advantage of propagation with green layers is good rooting of the vine and increased survival rate.To carry out reproduction, it is necessary to choose the most powerful, healthy bush with exceptionally good yields. It is desirable that it be located in a spacious area.
Preparation for propagation of the grape bush begins during spring pruning. At this stage, two or three green shoots are kept near the base, which will subsequently be laid in the soil.
Strong, healthy shoots that grow as close to the ground as possible are the best choice.

The next stage of work is carried out in the summer, when the shoots reach a length of 2-2.5 m, but at the same time retain their flexibility. To do this, perform a few simple steps.
-
Near the bush, you need to dig a ditch about 50 cm deep and wide. Its walls should be steep.
-
Drainage is laid out at the bottom - it can be expanded clay, crushed stone or broken brick.
-
The pit is filled by a third with organic matter mixed with garden soil. Thoroughly spill the substrate.
-
Layers are carefully laid in the resulting ditch. They need to remove antennae, leaves, and stepchildren in advance.
-
After that, the track is partially covered with garden soil, thoroughly rammed and irrigated at the rate of 15 liters for each running meter.
-
After all the moisture has been absorbed, the ditch is completely covered with soil.
-
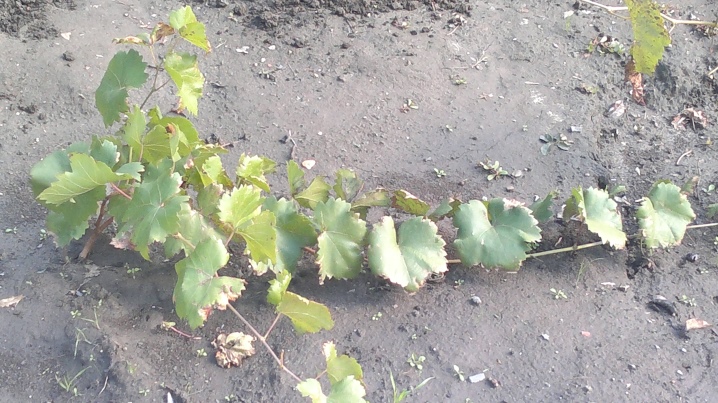
The upper part of the shoot, placed in the ground, is brought up and attached to the pegs with a soft twine. At the top, you need to keep about 3-4 leaves, while the growth point should be above the ground level.
-
After 3-4 days, the sprinkled layers are irrigated, after which the irrigation procedure is repeated regularly throughout the summer period. It must be accompanied by loosening, mulching and removing all weeds.
-
From mid-August, the tops of the layers must be broken off to stop the growth of the aerial part of the future seedling. In this way, nutrients will be redirected to root growth.
-
At the end of September - the first decade of October, the layers are carefully dug up. They need to be separated from the parent plant, placed in a container filled with soil, and then placed in a cool, damp place.
-
In April-May, a young plant can be planted on a permanent site.


Perennial
This technique involves the use as a planting material for rooting a perennial arm of a grape bush together with young vines.
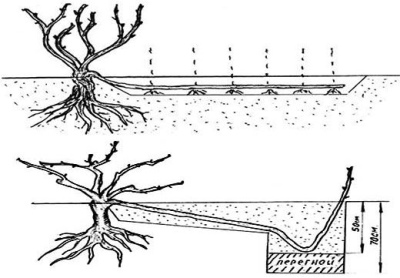
In this case, a trench is made near the bush to a depth of 40-60 cm, manure or compost mixed with garden soil is placed in it.
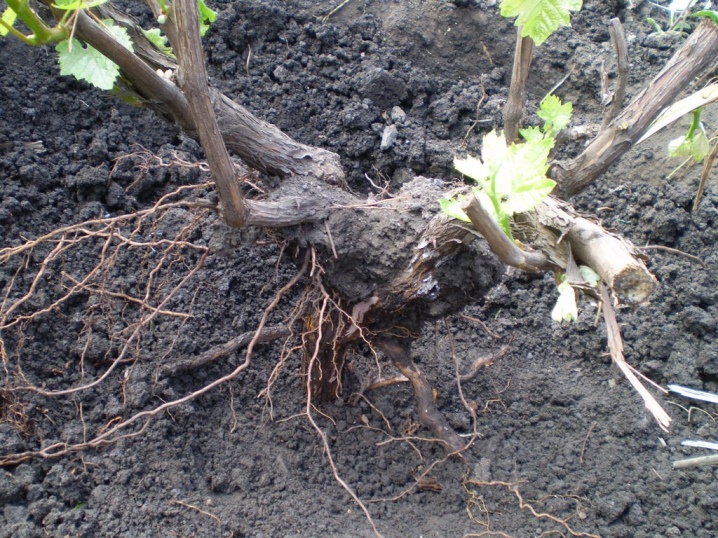
To obtain a young seedling, one shoot is deepened so that only the top with 3-5 eyes remains above the soil surface.

Hilling the head of the bush
This method is optimal for producing compact-shaped planting bushes. This is an efficient way. However, the cultivation of cuttings in this case is accompanied by a strong depletion of the parent plant.
In the spring, when the shoots grow up to 130 cm, they must be shortened by 1-2 eyes. After that, the parent bush is spud with drained loose earth. In the fall, the resulting hill is carefully dug up, the rooted shoots with a developed root system are carefully separated and planted.

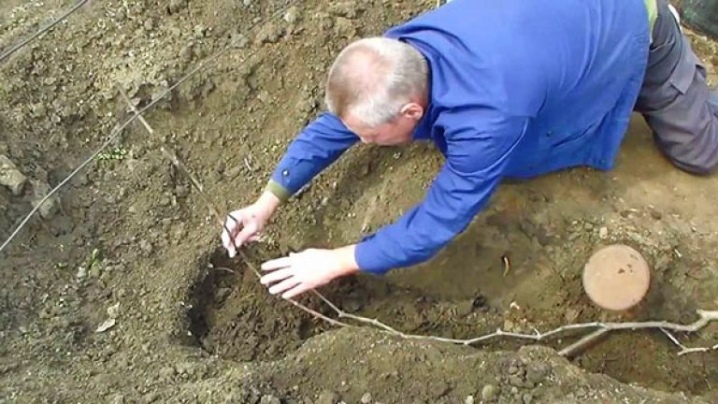
Short way
This technique is optimal for propagating varieties of grapes with shortened shoots. It is advisable to carry out this procedure in the summer, in which case the first harvest of berries can be harvested in the fall.
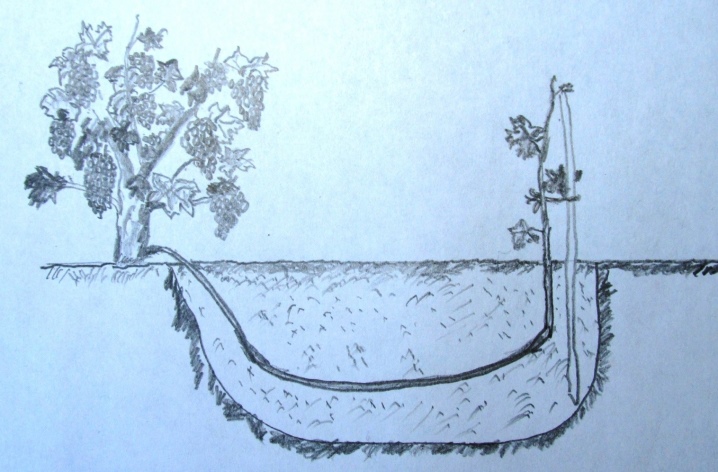
Before starting work, next to the parent bush, you should dig a small hole 5-10 cm deep and carefully moisten it.
After that, a part of the shoot is lowered into it so that the top of about 10-20 cm remains above the soil surface. Then the hole is covered with nutritious soil mixture and tamped well, a peg is placed near the top, and the vine is tied up.

Air
This method of propagation of grapes is based on the growth of new roots on old woody shoots.
-
For reproduction, the most powerful shoot is selected, all the leaves are removed from it, at a distance of 15-25 cm from the top, an annular incision of the bark with a width of 3-5 mm is formed.
-
The area of the incision is covered with moistened moss, and wrapped with a film of any dark color.
-
After some time, young roots will grow in this place.
-
In autumn, the seedlings are pruned, moved to containers and hibernated in a cool place.
-
With the arrival of persistently positive temperatures, new plants are dug up and moved to open ground.
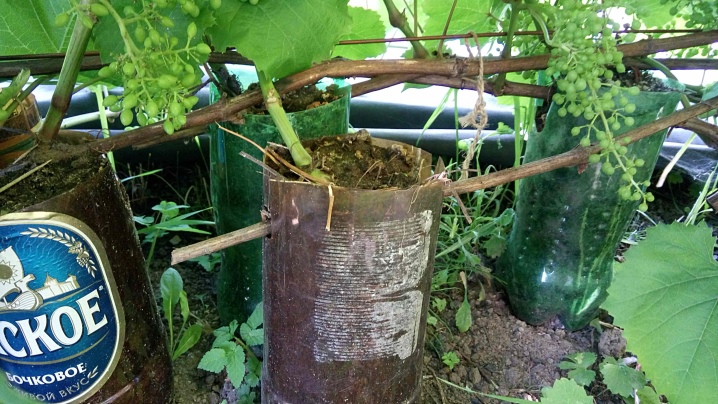

Lignified
This method of propagation by layering demonstrates good adaptation parameters of young shoots - this is due to double feeding. Nevertheless, the method is quite lengthy, since the final separation of young layers from the parent bushes is carried out only 3 years after the start of the operation.
-
A hole is dug 50-60 cm in depth near the parent bush, drainage is poured into it, and a layer of organic fertilizers mixed with the substrate is laid out.
-
The lowest shoot is carefully bent to the soil, lowered into the hole so that only the top with three to four eyes remains above the soil surface.
-
Already in the first year after this, new branches should appear; under favorable conditions, they can even give a small harvest.


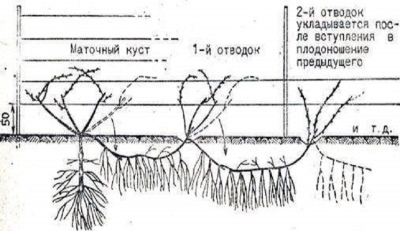
Chinese method
This method allows you to get from 15 to 25 seedlings in the shortest possible time. Usually used for poorly rooted grape varieties.
-
With the beginning of spring, the strongest strong shoots are chosen from the parent bush, placed as close to the ground as possible.
-
Then, trenches with a depth of about 30 cm are formed, covered with compost mixed with potassium fertilizer and superphosphate.
-
A shoot is placed in this hole and fixed with a hairpin in 2-3 places.
-
After that, the trench is carefully sprinkled with garden soil and thoroughly irrigated.
-
As new shoots from young buds grow, the soil must be filled up.

Kataviak
This technique involves reproduction not by layering, but by large bushes.
It is in demand for the reconstruction of mature vineyards, as well as, if necessary, move them to a new site.
To date, it has not become widespread due to the complexity and resource intensity of the work.
-
After you pick up a bush for transplanting, a ditch is dug between the place where it is currently growing and the place where you plan to transplant it. Its depth and width must be at least 50 cm.
-
A layer of organic matter mixed with the garden substrate is laid out on the bottom.
-
Then they pick up a couple of powerful shoots, remove the eyes and leaves from them.
-
The first shoot is carefully bent in the form of a loop, led under a bush, and then taken out near the parent plant. The second is taken immediately to a new site.
-
The tops of both shoots are cut off, no more than 3 fruiting buds should remain above the surface.
-
At the end of the work, the future bush is sprinkled with a substrate and moistened
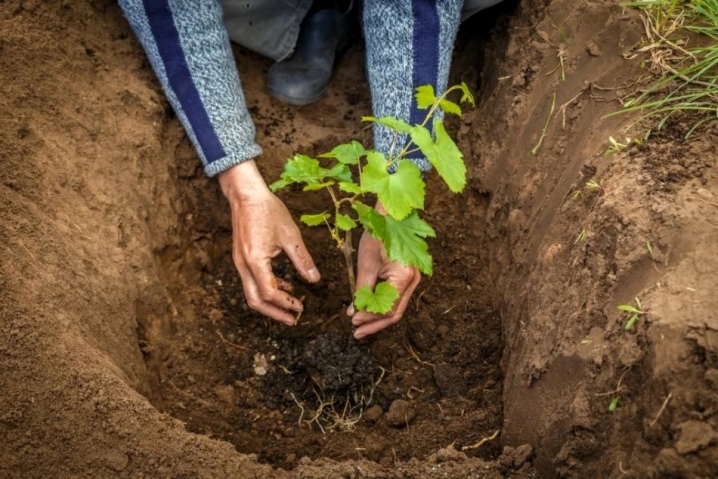

The nuances of reproduction, taking into account the period
Reproduction by layering has its own subtleties, taking into account the time of year. So, if the procedure is carried out on summer days, then you can start work only after the grape vine grows to 230-250 cm. In the middle lane, this coincides with the end of July - the first half of August. For reproduction, the strongest are selected, growing close to the soil.
All the leaves are cut off from them and placed in a ditch, after which they are sprinkled with a substrate so that only the top with a couple of three eyes remains on the surface.

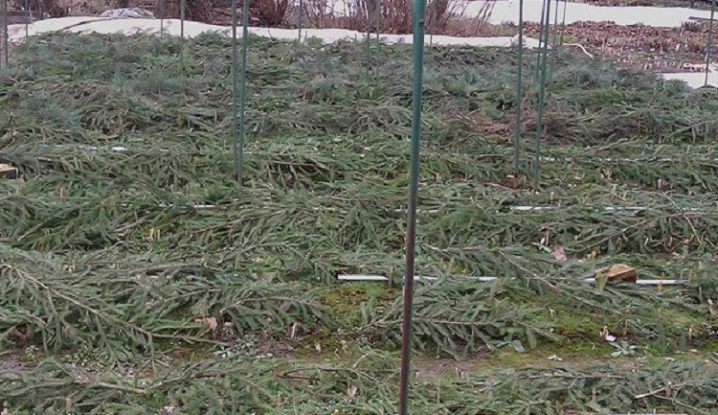
The same technique is used for the autumn formation of layers. The only difference is that during this period the plant does not need fertilizing, especially nitrogen - they will cause a rapid growth of the green mass and the shoots will not have time to get stronger before the onset of frost. In addition, the trench with a layering must be additionally insulated; it is best to use a layer of spruce branches with a thickness of at least 30 cm for this.

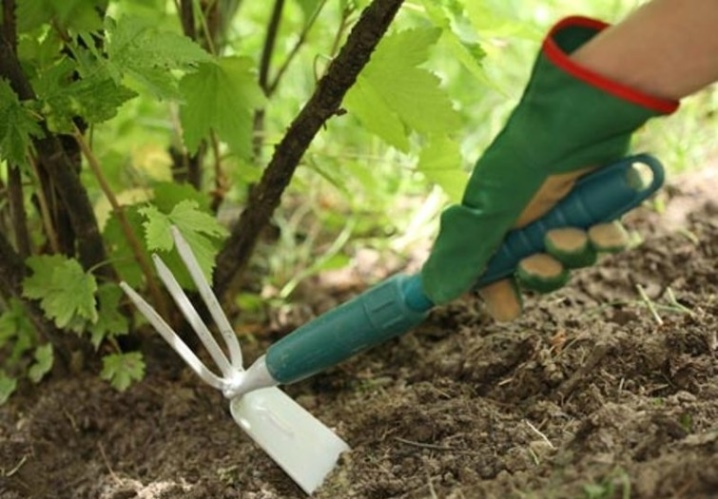
Follow-up care
Caring for grape cuttings is not very difficult.It is based on timely watering, regular loosening of the soil and getting rid of weeds. It will be correct to water at intervals of 10 days. All weeds are uprooted as soon as they form. The earth near the bushes is loosened and dug up.









The comment was sent successfully.