Planting grapes in open ground in spring
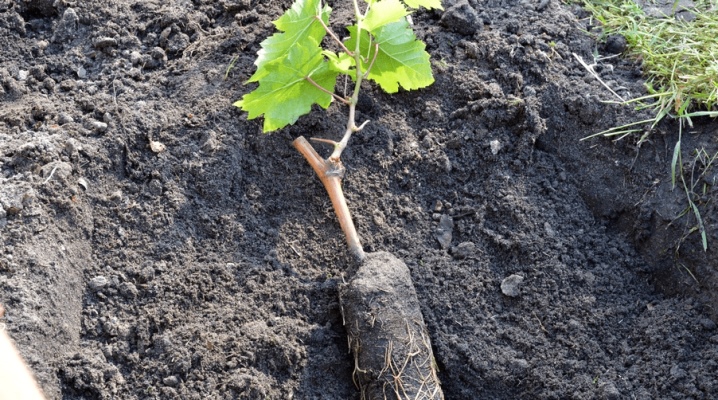

The spring planting of grapes in open ground will not cause much trouble for the gardener, if the time and place are correctly determined, and also do not forget about the preparatory procedures. The presence of four main landing options allows you to organize your site in the most successful way.
Advantages and disadvantages
Planting grapes outdoors in spring has both advantages and disadvantages.
Consider the positives.
- A significant plus is the time that the seedling receives to take root in a new place and get stronger before the cold weather arrives. By winter, its root system will develop so much that it will be able not only to provide food for the bush, but also to harvest in the next season. By the way, grapes planted in autumn are capable of bearing fruit with a delay of at least a year.
- It is possible to prepare a place for the vineyard in advance, after which the soil has time to rest and be nourished with useful substances.
- Also, by transferring the culture to its permanent habitat precisely in the spring months, in most cases it is possible to avoid a sharp cold snap, and therefore the seedling does not die from the cold after planting.
Comfortable weather conditions accelerate the adaptation process, the culture increases its resistance to low temperatures.
Nevertheless, the procedure still has a number of disadvantages.
- For example, spring warming is usually accompanied by the activation of pests and the development of fungal and infectious diseases. Without preventive treatments of the land, a bush that has not yet matured can become infected, not take root, or even die.
- There is a small possibility of the return of night frosts, as well as insufficient soil moisture after the snow melts. In a situation of a lack of moisture, accompanied by an increase in temperatures, the grapes will have to be watered from the very beginning of the season.
- Another relative disadvantage is that very few grape varieties are sold in the spring - you have to buy seedlings in the fall and organize appropriate storage for them, or you risk acquiring sick or frozen specimens.
Conditions and place
The timing of the spring planting of seedlings in open ground may differ slightly, depending on the specifics of the seedlings and the climatic characteristics of the region. So, from the second half of April to the middle of the next month, it is customary to deal with lignified annuals, and from the end of spring and almost until the end of June - green vegetating. In any case, it is important to wait until the ground is completely thawed and the average daily temperature is established, equal to plus 12-15 degrees.
In the southern regions of Russia, for example, in the Crimea or the Kuban, the planting period starts from the second April decade. An important condition is that the air is already warming up to +15 degrees, and well-lit areas of the earth - generally up to +20 degrees. Despite the warm weather, the seedlings are still covered with special material in case of frost at night. It is customary to plant grapes in the Moscow region and in the middle lane in May, starting from the second decade. By this time, the soil should already be well moistened, and the air should warm up to plus 15-17 degrees. On the territory of Belarus, this period begins after May 9.
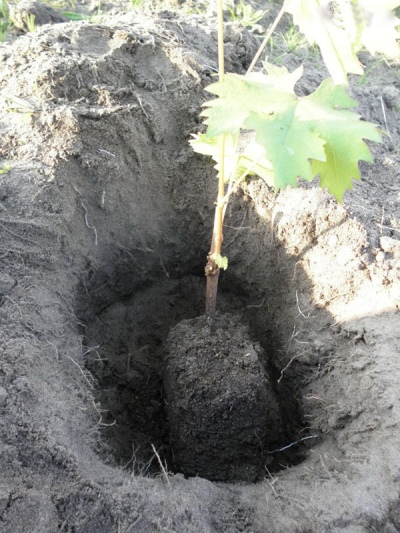

It is typical for the Urals and Siberia to plant crops in open ground from late May to mid-June. It should be mentioned that many gardeners living in these regions prefer to design a green screen for the vineyard. A structure with a height of 80 to 100 centimeters is assembled from boards and mounted on the north side of the beds. Its main purpose is to protect landings from cold winds.

Generally, if you plan to plant only a few grape bushes, then it is best to place them along the southern side of the fence or near the southern wall of the house. The formation of several rows will require organizing them on a gentle southern slope of the site, maintaining an orientation from north to south. The area should be well lit, but at the same time protected from drafts. In principle, to cope with the winds, you can place a hedge of trees with a taproot system next to it. The size of the bed should allow maintaining a gap of 3 to 6 meters between seedlings and large trees.
Otherwise, the neighbors will pull all the nutrients out of the soil, and the plants will have no room for growth.
If a vineyard turns out to be planted in the southern or western sides of large buildings, then the heat accumulated by the buildings during the day will be given to the plants at night. In no case should you plant seedlings in lowlands, the temperature drops of which the bushes will not survive, as well as in areas with a close location of groundwater.

Preparation
The more thoroughly the preparation of planting pits and material is carried out, the more likely it is for the successful adaptation of grapes in a new place.
Places
A place for the spring planting of grapes should be prepared even in the preceding autumn. So, sowing winter rye will be a good solution - this crop will improve the condition of the soil, and in spring, being left in the aisles, it will protect the seedlings from the wind, and the sand layer from scattering. When the vines are strong, the cut rye can be used as mulch.
The culture suits any soil, except for dense clay, but it reacts very poorly to pH levels below 5 units. Too acidic soil must undergo liming.

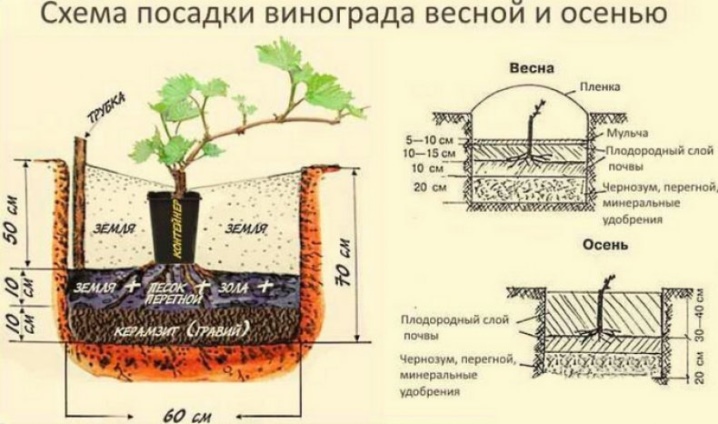
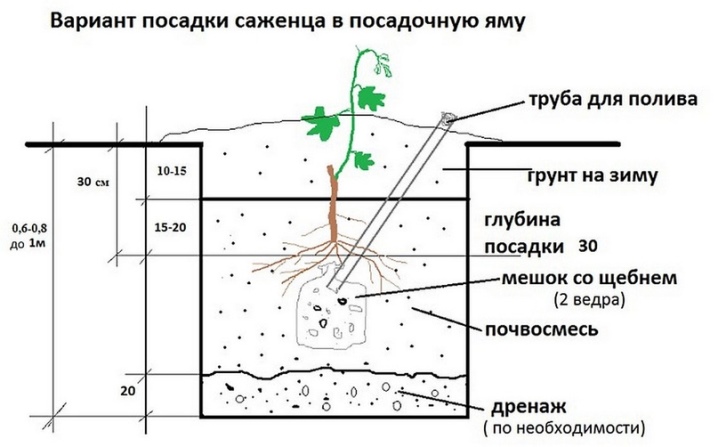
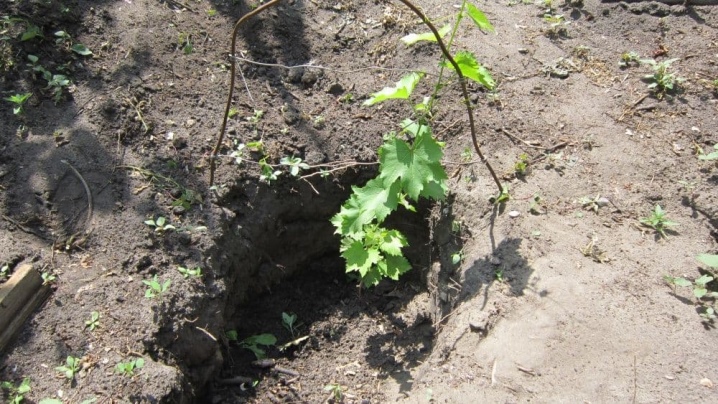
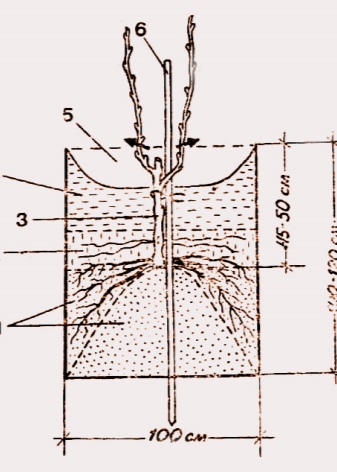
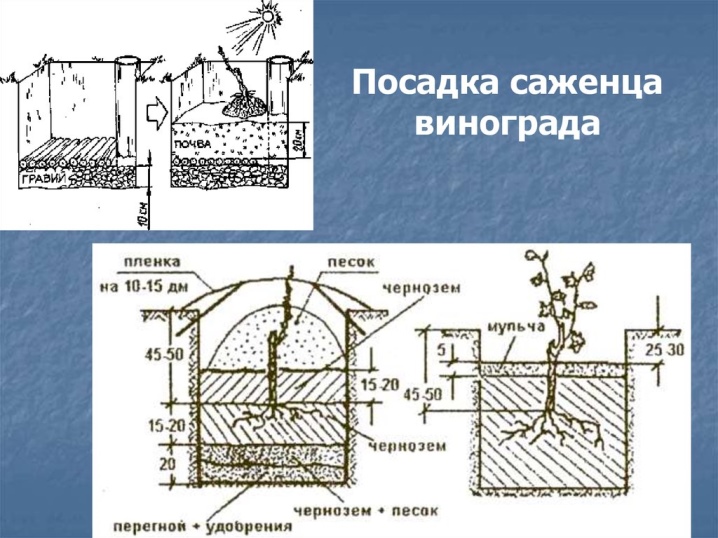
If, before planting, it was decided to feed the soil with organic matter, then it is allowed to use only fermented and rotted substances, for example, mullein, chicken droppings, humus or compost. Stimulating the root system will allow the addition of 100-300 grams of superphosphate, laid on the bottom of the hole. In addition, it is worth adding a couple of kilograms of wood ash to the recess. The depth of the pit, as well as its width, averages 80 centimeters. It is important that the roots of grape seedlings find themselves at a depth, as they can withstand temperatures no more than minus 6-7 degrees.

Saplings
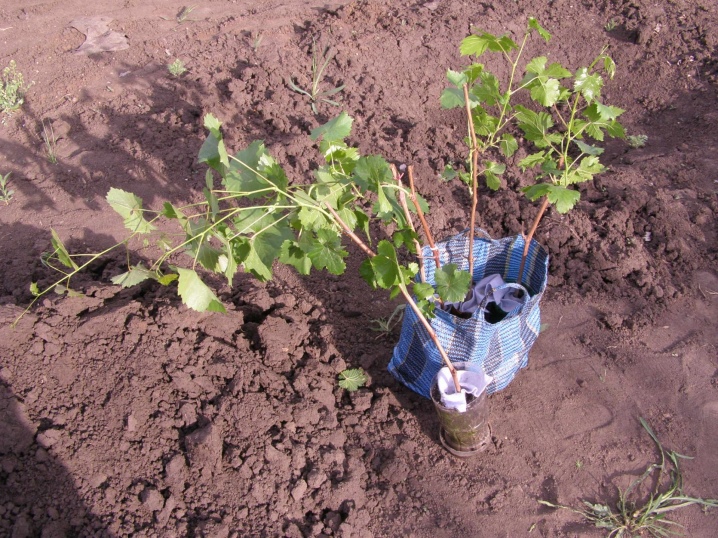
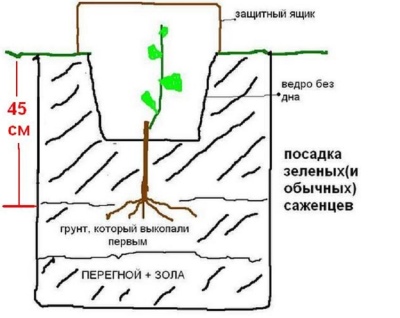
Seedlings transferred outdoors should be healthy and well developed. In gardening, it is customary to use two varieties: vegetative or lignified. The first, in fact, is a cuttings with several green leaves that are sent outdoors in early spring.
Green vegetative seedlings need hardening before planting. Otherwise, once in the open field, they will immediately burn out in the sun. Hardening begins with keeping the seedlings under a canopy or under wide tree crowns for almost a week, and then continues in the form of staying in the open sun for about 8-10 days.
It will not be superfluous to withstand the workpieces in a growth stimulator - purchased or homemade, made from a tablespoon of honey and a liter of water.
Lignified seedlings mean a one-year-old bush dug in the fall. Before planting, the plant will need to cut off the one-year shoot, leaving 3-4 eyes. The roots on all the upper nodes are removed, and on the lower ones they are only refreshed. However, for seedlings grown from shortened cuttings, only a refreshing pruning of the upper root processes is required.In order to prevent the development of fungal diseases, it makes sense to immerse the growth without a root in a mixture of 5 grams of "Dnoka" and 1 liter of water. It also makes sense to keep the cut seedling in a bucket of water for about an hour.

It is worth mentioning that in spring, grapes can also be planted with seeds for seedlings.
Material stratified over 2-4 months, disinfected and germinated on a damp napkin in the southern regions is sent to open ground in mid-March. If at first the grains are planned to be placed in a closed ground - in a pot on a windowsill or a greenhouse, then the sowing time varies from early March to the first May decade.


Landing technology
To successfully germinate a vine, a budding grower must figure out which planting technique is right for his particular conditions.
Classic
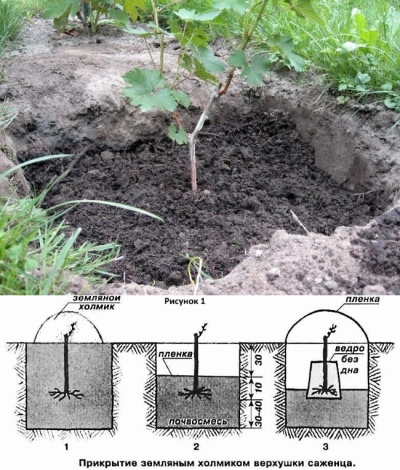
The step-by-step instructions for planting grapes according to the classic scheme looks quite simple. The seedling is freed from the container and, together with an earthen clod, is placed at the bottom of the hole. From the north side of the recess, a peg is immediately dug in, which will later be required for tying. The seedling is sprinkled with earth on top of the lump, which is immediately compacted and irrigated with warm water. After that, the pit is filled to the height corresponding to the first leaf.
On the trellis
This method requires the preliminary installation of trellises, the number of which corresponds to the number of seedlings. These supports are most conveniently constructed from metal tubes with a diameter of about 10 centimeters, on which the vine will be fixed with a wire wrapped in plastic protection. The diameter of the metal rod is usually chosen equal to 5 centimeters. The culture should be planted in the same way as with the classic planting. Its layout, as a rule, looks like 3 by 3 meters.
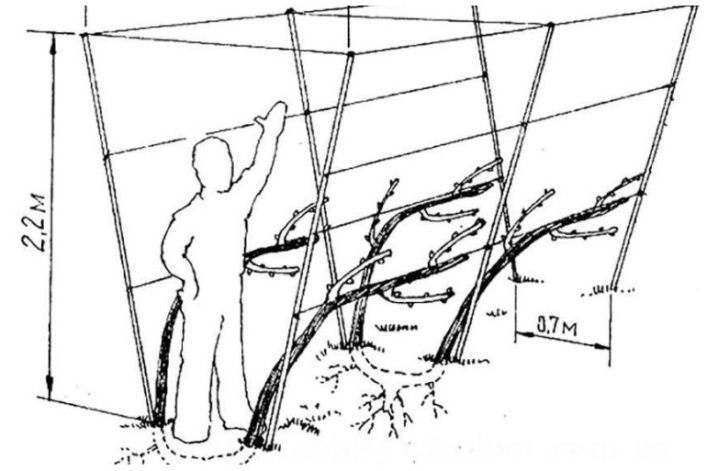
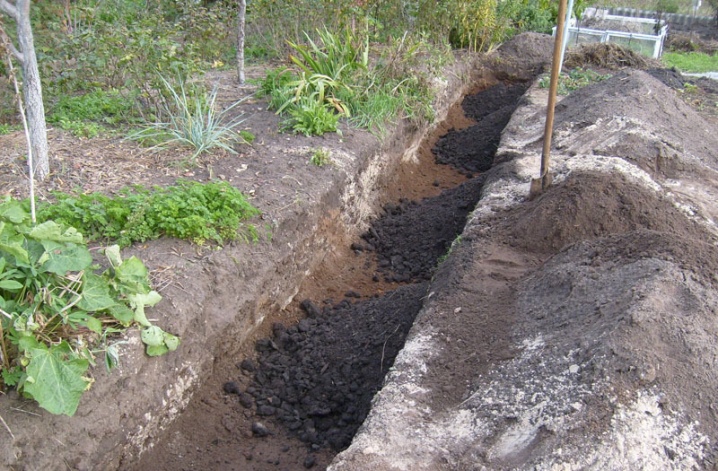
In the beds
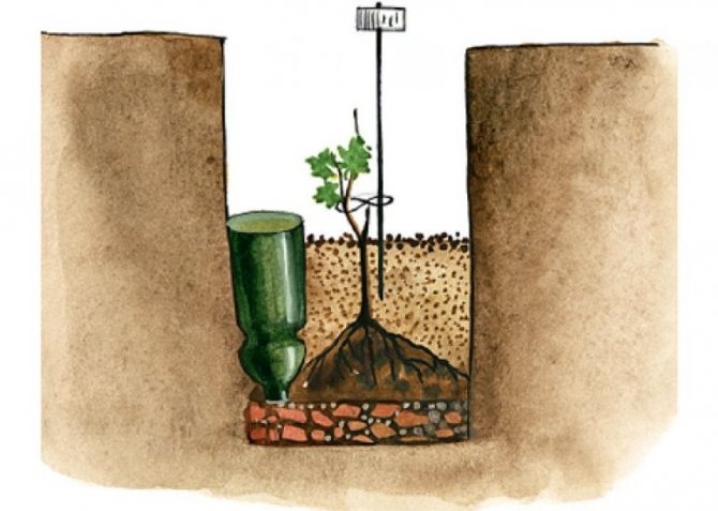
The organization of beds is especially popular in the northern regions of Russia, since such a system does not allow flooding and provides the grapes with the maximum amount of heat. It all starts with the formation of a trench going south. Its depth reaches 35-40 centimeters, length - 10 meters, and width - 1 meter. At the next stage, soil is ejected above 32-35 centimeters from the surface. After mulching and placing the insulation, the seedlings themselves are planted. Watering such a bed is carried out using a special tube.
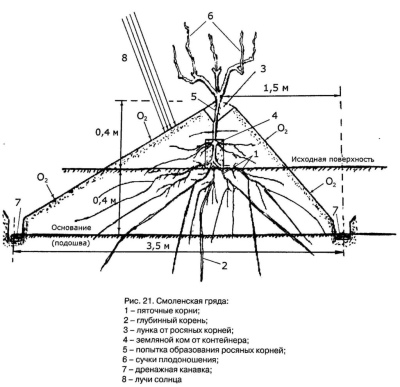
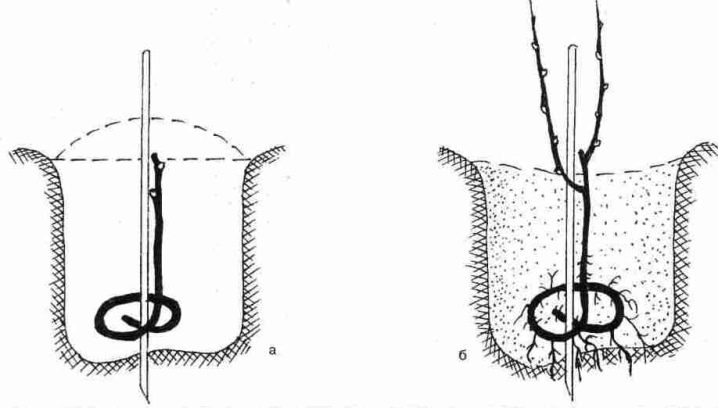
Moldavian
The specificity of the Moldovan planting requires twisting a long piece of healthy, ripe vine, for example, taken from a two-year-old grape. The workpiece, tied with a dense rope, is placed in a regular hole so that only 2-3 buds remain above the surface. In the future, everything happens similarly to the classical scheme.














The comment was sent successfully.