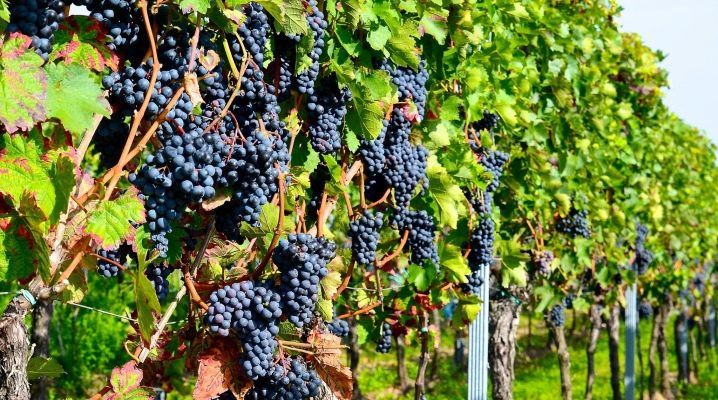
All about the vine

How to germinate?
Recently, in the garden plots, you can increasingly find the vine. However, not all gardeners manage to achieve the ripening of the plant. It is worth considering in more detail the peculiarities of the culture and the methods of growing it on the site.

What it is?
The vine is a harsh-resistant plant that can withstand drought in hot countries and the first frost in cold regions.
In addition, the bush quickly takes root even on infertile soils, in sandstones and on rocky rocks.


One of the reasons for the high adaptability of a plant is its structure. The vine includes:
- trunk;
- root system;
- crown.
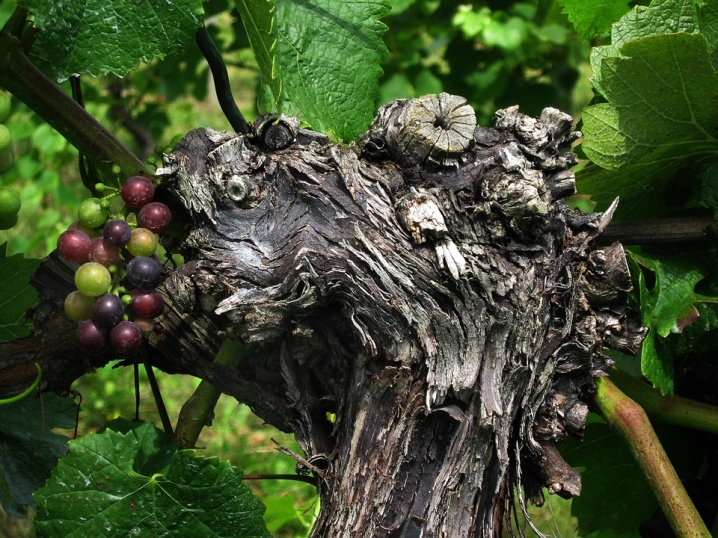
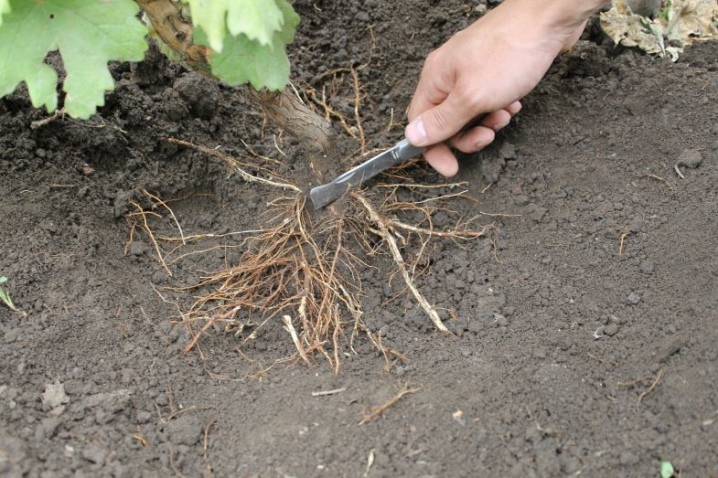
The vine has very strong roots that can go deep into the ground - for the sake of extracting nutrients - for 6 or more meters. Interestingly, nutrients are deposited in the system so that the vine gradually receives the necessary portion of natural fertilizers.

By location, the roots of the grapes are divided into:
- superficial;
- lateral;
- basic.
The former grow near the surface and absorb rain moisture.
The lateral and main roots are designed to assimilate nutrients and water that they extract from the depths of the soil.
On the crown of the vine there are sleeves and shoots, where inflorescences, bunches of grapes, tendrils and leaves develop during the period of active growth.

Stages of development
To grow grapes efficiently, it is important to understand what stages of maturation the plant goes through.
- The beginning of the movement of juices. The vegetation of the vine starts at the moment when the juices begin to move along the trunk. This period begins in the spring, when the air temperature rises to 10 degrees Celsius and above. It is important at this moment, when the growing season begins, to cut the dried grapes.
- Height... When the juice reaches the desired points, the variety will begin to grow. The air temperature during this period should not fall below 15 degrees. Successful growth of the grapes will require a grower to ensure that the plant does not die and the young stems do not intertwine. When the vine reaches a height of 30 cm, it must be tied up.
- Bloom... On average, the stage lasts from 2 to 3 weeks. Fertilizer must be applied to the soil 15–20 days before. When the vine begins to bloom, it is important to ensure timely removal of weak buds so that the plant does not waste strength on their support.
- Ripening of berries. In the process of fruit growth, care must be taken to remove berries infected with parasites or diseases. Additionally, gardeners are advised to remove stepchildren, pre-chasing shoots. All this will help to improve the quality of the crop and increase its quantity.
The last period is leaf fall. At this stage, the growing season ends, the plant goes to sleep.
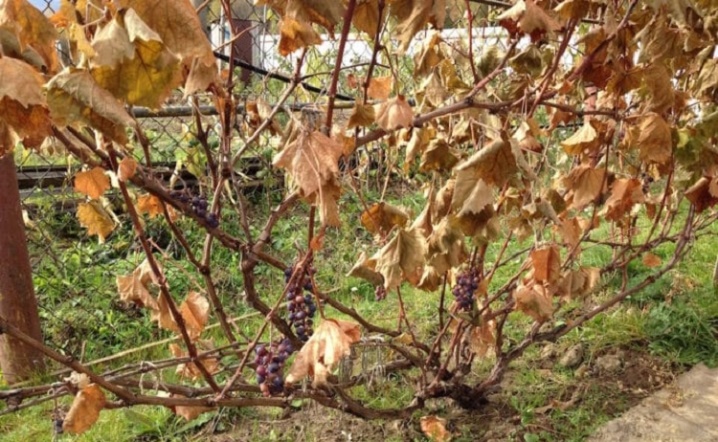

What to do for ripening?
To get a good harvest from the vine, it is necessary to start the first work on the ripening of the crop in spring.
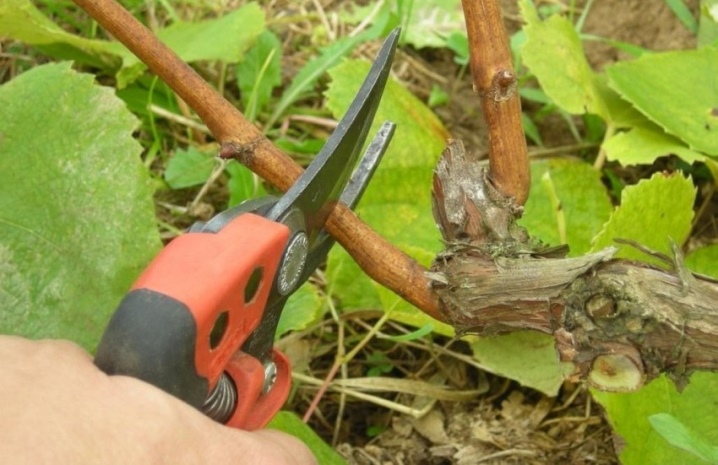
- Regularly removing the greenery will reduce the risks of plant deterioration during wintering. Pruning weak shoots will reduce the costs of the plant for the development of unnecessary shoots and will allow you to focus on the formation of large and juicy berries.
- Productivity needs to be planned and rationed, so that the plant has the strength to survive the winter.
- Throughout all periods (growth, flowering and fruiting) grapes need fertilize by introducing compounds under the root and leaf.
Taking these recommendations into account will speed up the ripening process of the berries and strengthen the plant so that it can survive the winter.

Overdoing it with ripening is also not worth it, since the grapes are sensitive to stress. One bush can withstand a certain amount of berries, and any overload will lead to a deterioration in the condition of the plant.
With an abundance of fruit, the grapes most likely will not survive the winter. A starving vine, on the other hand, will produce a small and tasteless crop.
Particular attention should be paid to the grapes that grow in the northern regions. On the shoot, it is worth leaving only 1-2 bunches so as not to overload the plant and keep it stock of useful components for the winter. In the most severe conditions, gardeners additionally shorten the vine by a third of the brush, and part of the crop is harvested in the fall, even if it is not ripe.
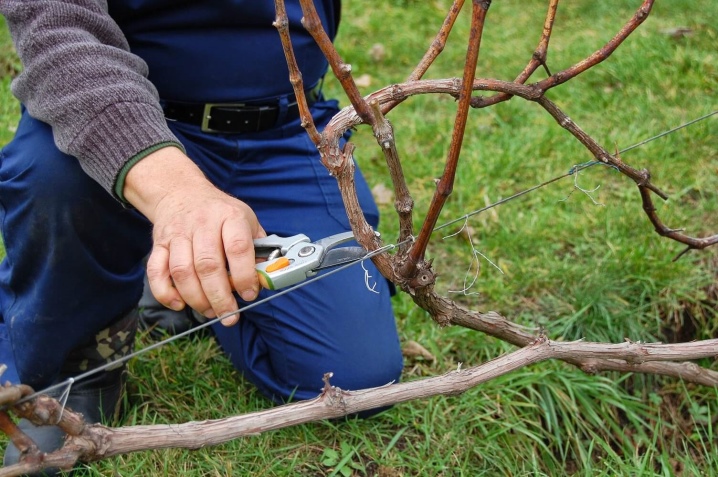

Often, in vigorous grape varieties, the tops are broken, thus stopping the growth of stepchildren and accelerating the formation of the vine. At the end of August, excess foliage is removed, exposing the cuttings on which the fruits swell.
This approach ensures efficient ventilation of the plant.
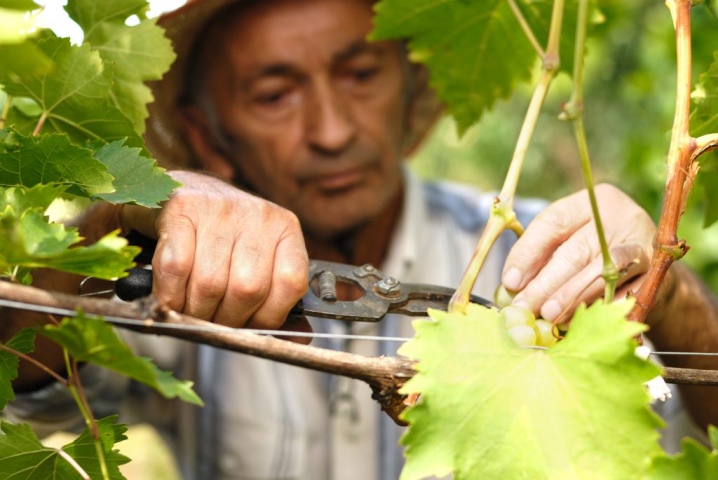

It is important to remember that only a healthy vine can prepare for winter. Therefore, it is important to monitor the condition of the bush and take preventive measures:
- protect against fungi;
- treating diseases;
- reduce watering when there is a risk of rotting.
Dangerous enemies of grapes are gray rot, spotting and powdery mildew, which the plant is exposed to in early summer. The infected bush bears poor fruit or does not produce berries at all, dying by winter.
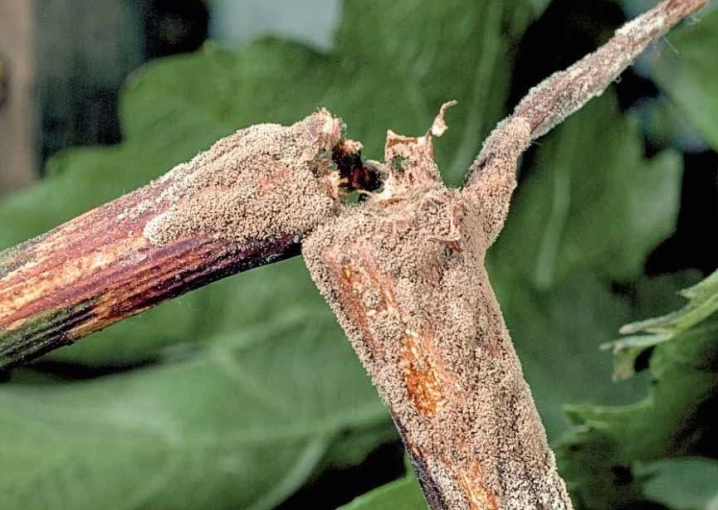

Finally, the rainy and little sunny summer prevents the grapes from ripening. Such conditions lead to the formation of fungus on the stems of the vine, which negatively affects the growing season. Artificial stimulation by means of "green" operations will help to solve the problem: removal of stepchildren, followed by thinning of the foliage. During the wet period, the soil is additionally loosened so that the roots receive a sufficient amount of oxygen. With this approach, the likelihood of normal ripening of the berries is high.

How to germinate?
When planting a vine, it should be borne in mind that it can grow on saline soils. However, at the same time, the plant does not like lowlands, where fog gathers in the evening, the temperature drops.
In order for the plant to take root quickly, it is recommended to provide the grapes with:
- excellent illumination;
- good air circulation between berries;
- regular pruning and watering.

Here are some other special requirements.
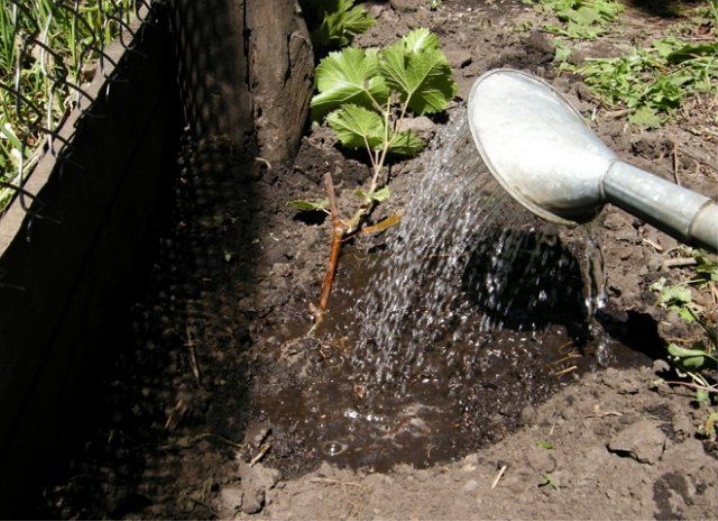
- Timely watering... The best option would be to water the soil once a week in the case of growing grapes on the sand and once every 2 weeks when planting a crop in black soil.
- Fertilization. Grapes love humus, peat, and chicken droppings. Fertilizers provide the plant with plenty of nutrients.
- Weeding... Regular cleaning of weeds, followed by treatment of grapes from pests, will prevent the death of plants.
- Pruning... It is better to cut them off immediately when old or sluggish leaves are found, so that the grapes do not waste energy trying to restore the shoots.
Also, gardeners recommend tying up the vine, since it does not have its own rigid skeleton. It is better to fix the plant near the supports, ledges.













The comment was sent successfully.