How to transplant grapes?
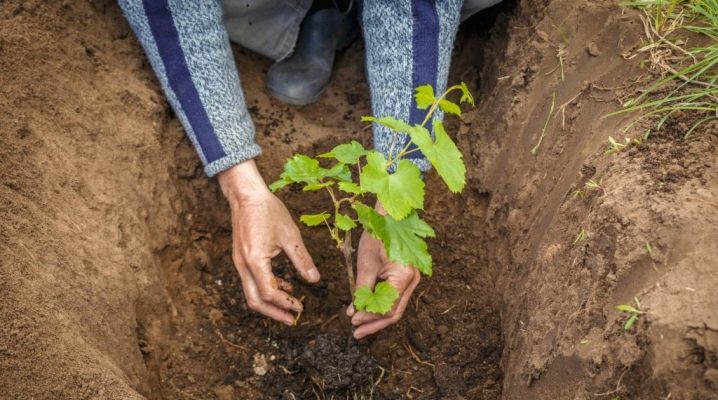

The layout of the garden is not always immutable and constant. There are situations when the planting has to be moved from place to place. The reasons for this are different: redevelopment, not very successful planting, construction, and so on. Grapes are quite flexible shrubs in terms of replanting, they tolerate this kind of change well and adapt well. It is possible to replant not only young, but also mature plants without loss of yield. But in order to achieve this, you need to know all the nuances and rules of transplantation.

The need for a procedure
The question "Can grapes be transplanted?" before gardeners is not worth it, he has long had one clear answer - yes, you can. However, doing this simply on a whim is not worth it, there must be reasons for this. Most often, gardeners are faced with the following options:
-
initially poorly chosen place, for example, little light, strong drafts, negative soil composition;
-
the varietal characteristics of the shrub were not taken into account, when powerful varieties were planted too close to each other, planting by varieties was not carried out;
-
plants in the neighborhood begin to interfere with the shrub and stop its full development;
-
redevelopment, when it is necessary to transfer the bush to another zone, since this place is intended for other purposes.

There are many reasons, but before starting the procedure, it is necessary to carefully and thoughtfully study the issue and find out how appropriate it is.... Transplant is a direct intervention in the development and growth of culture. This can lead to negative consequences. The following scenarios should be feared:
-
complete death of a shrub due to the loss of part of the root system - the risk is not great, but it is always there;
-
a change in fruiting in the negative direction - for several years the yield may be reduced or completely absent;
-
changes in the dessert qualities of the fruit;
-
an increase in the risk of various diseases, black cancer, phylloxera are especially dangerous.



If you are sure that the risks are justified and you cannot do without a transplant, consider the following measures. First of all, refuse to transplant the grape bush to the place where the bush or tree was removed. If you neglect this recommendation, the bush in the new place will grow weak, constantly hurt. For the procedure to be successful, it is necessary to take into account many nuances and fully follow the rules. This applies to the age of the plant, since mature individuals take root worse, it is also important to take into account the condition of the bush. The grapes must be dormant.

In addition, it is most important to properly dig up and transfer the bush, prepare a new site in advance, and carefully look after the plant after the operation.
Timing
No one will name perfect and universal dates when it is better to transplant grapes to another place. Each gardener must assess the climate conditions himself, make allowances for the region of residence. Traditionally, such procedures are shown in the spring and fall, like the usual planting. As for autumn, here the optimal period is considered when the foliage is dropped, and this will happen in September or October - depending on climatic features. Such work can be continued until the first frost appears.

If you live in the south, and the soil does not freeze during the winter, you can carry out the procedure during this period, for example, in January or February. In this case, you need to navigate during the thaws.Planting in a new place in spring occurs in the month when the soil thaws. The main thing is to be in time before the eyes begin to open up. The spring period is good because there is a sufficient amount of moisture in the soil, so the root system is well saturated.

If conditions are favorable for a transplant, do not postpone the procedure. The earlier you spend it, the higher the likelihood of a favorable development of the bush.... In summer, this procedure is traditionally not carried out, except at the end of August, in regions where foliage falls early. However, with a closed root system, the procedure can be carried out in the summer.

Dates are not the only nuance that needs to be taken into account, they must always be compared with the age of the plant and the type of root system - open or closed.
Features of the autumn procedure
The greatest advantage of this period is that there is time to take root, take root, and quickly grow into growth in the spring. Thus, the bush will not take a break in fruiting, unless the amount of harvest will decrease. But there are also disadvantages - the plant may not take root and freeze in frost, especially if you neglect care measures. It is important to mulch the soil around the bush well and cover it well.
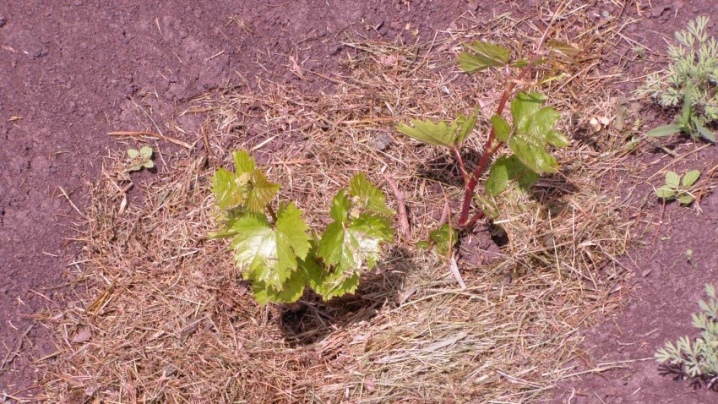

If you live in a region where frost is combined with a small amount of snow, you need to dig it in the fall, and plant seedlings with a closed root system only in the spring. The seedling should overwinter in a cool place - a cellar, basement.
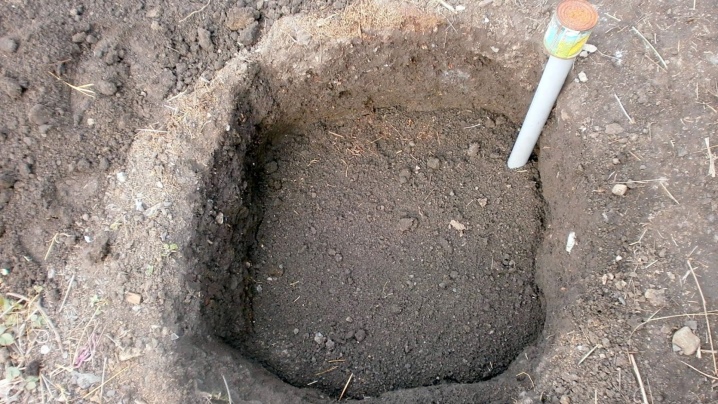

If the root system is open, then you need to immediately transplant the plant - in the fall.
Spring-summer procedure
The main disadvantage of spring transplanting a bush is that it will take root for a long time, it will grow later than necessary... Therefore, there is no need to wait for the ripening of the vine in the current season. The yield may be lost for 2-3 years. It is forbidden to plant a bush in the ground that is not warmed up enough. This will lead to the destruction of the roots and irrevocable death of the plant. The advantage of a spring planting is that a hole for a new bush is prepared in advance - either in the fall or in the previous summer season.
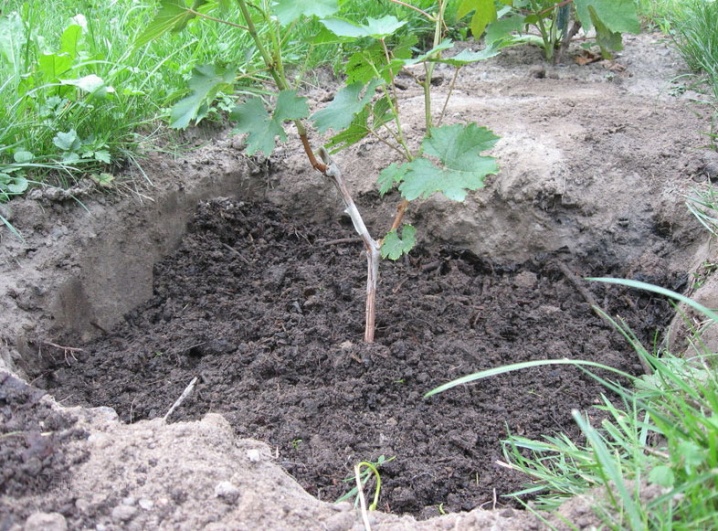

In winter, everything that is brought into the hole is rammed, the fillers fall evenly, the soil is qualitatively improved. As mentioned above, in the summer it is better to refuse this procedure altogether. A plant that is dug out during the growing season will be difficult to take root, it will have too much strength to restore the root system. This will cause the ground portion to suffer and the plant will either get sick or die. But seedlings at a young age with a closed root system can be transplanted in the summer.
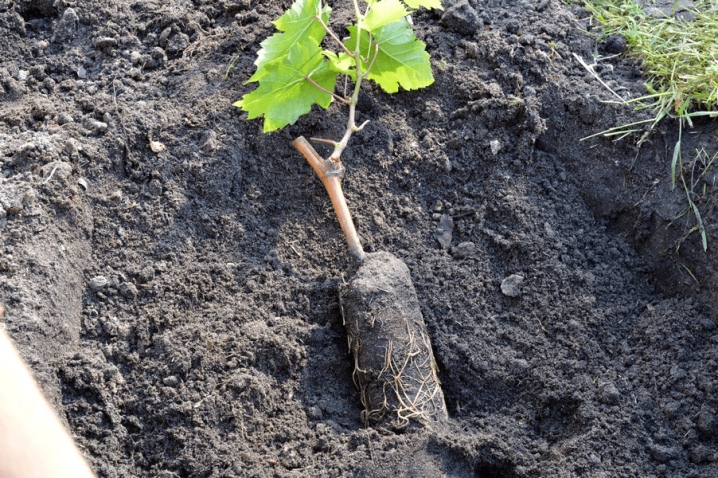

This should be done as carefully as possible, any damage to the roots will be disastrous.
Site selection and preparation
We must not forget that grapes are plants that actively respond to heat. Therefore, the new place should be well lit, protected from drafts and strong winds. Consider the moment that stagnant water for this shrub can be destructive. Accordingly, avoid transplanting to areas where groundwater is closer than 1 m from the surface.... If you place the grapes against the wall on the south side, it will receive much more heat.
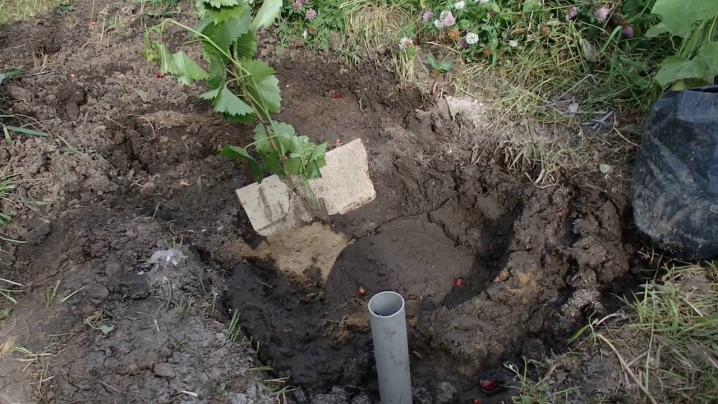

But you do not need to plant grapes next to the trees, they can shade the shrub and bring him other troubles. As for the composition of the soil, this plant is not too demanding; swampy zones and salt marshes are categorically unsuitable. When feeding the soil in a new place with compost, use compositions in which the presence of vines, grape foliage is excluded. Waste of this type is incinerated; feeding with this type of ash is quite acceptable. After a new landing site has been chosen, you need to prepare the hole. This is always done in advance, the minimum period is a month, and preferably six months.


If you transplant the plant earlier, when the soil subsides, root development will be disturbed.
There is no universal scheme for transplantation, so it is important to focus on the characteristics of your region. Gardeners should choose the scheme that suits their particular site. The place can be prepared in different ways, the depth of the hole is chosen taking into account:
-
climatic features;
-
the type of soil in the area;
-
the need and possibility of shelter for the frost period;
-
the presence or absence of snow cover.
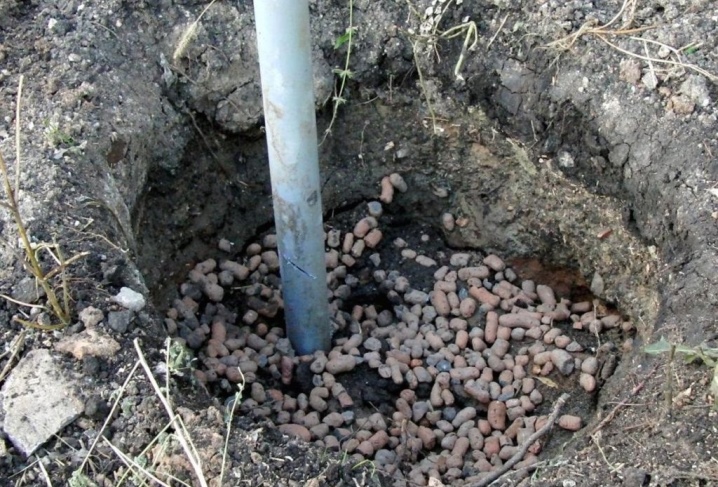

There are two main methods of transplanting: in pits and under a hydrodrill, but the second method is suitable only for young plants with short roots. If you are growing grapes on an industrial scale, the depth is selected in this way:
-
in the central European part of the country - about half a meter;
-
in Central Asian regions with fertile soil - from 55 to 60 cm;
-
on sandy soils - from 60 to 65 cm.
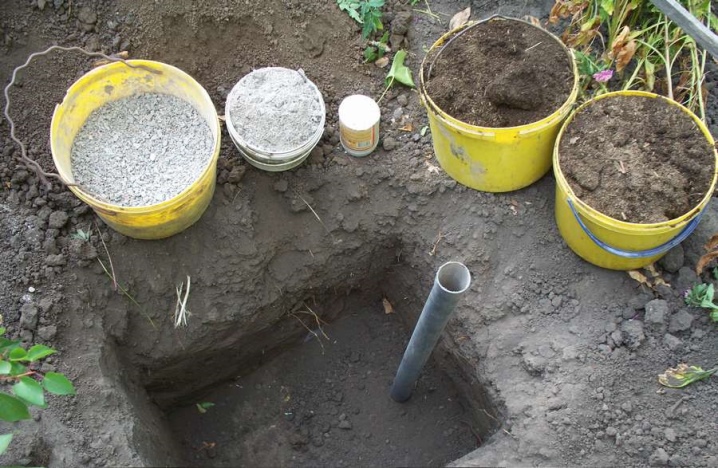

Those who are engaged in amateur gardening should focus on other numerical values and features:
-
in southern regions with good heating of the soil and its rapid drying - from 40 to 50 cm;
-
in the European part, Moscow region - from 30 to 40, but on elevated ridges;
-
in the northern regions, in the Urals, in Siberia - a trench planting method, otherwise it will not work well to cover for the winter, holes are dug deeper;
-
on a poor composition of soil, stony, sandy - meter-long pits with the obligatory application of organic and mineral fertilizers;
-
it is not necessary to fertilize on chernozem soils, the depth of the hole varies from 40 to 45 cm;
-
not light soils - from 50 to 60 cm;
-
on loams from 70 to 80 cm with the obligatory arrangement of a drainage layer of fine bricks, gravel, expanded clay.

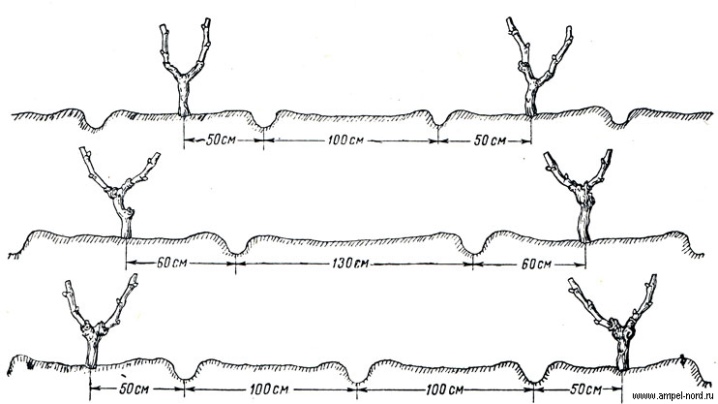
In addition, the age of the plant is taken into account when the hole is formed, as well as the size of the root system. If a lot of bushes are being transferred, it is important to correctly determine the distance between them. The strength of growth is taken as a basis:
-
between low-growing varieties, a two-meter indent or a little more is enough;
-
it is better to leave a distance of about 3 m between vigorous varieties.
The last stage in preparing the landing site is feeding. As mentioned above, it is not always necessary. But if the soil requires fertilization, then the soil is introduced into the hole by first connecting it with top dressing:
-
organic matter in the amount of 7 kg, humus, compost are suitable;
-
mineral compositions combining 250 g of wood ash, 85 g of ammonium sulfate and 180 g of superphosphate.



The ways
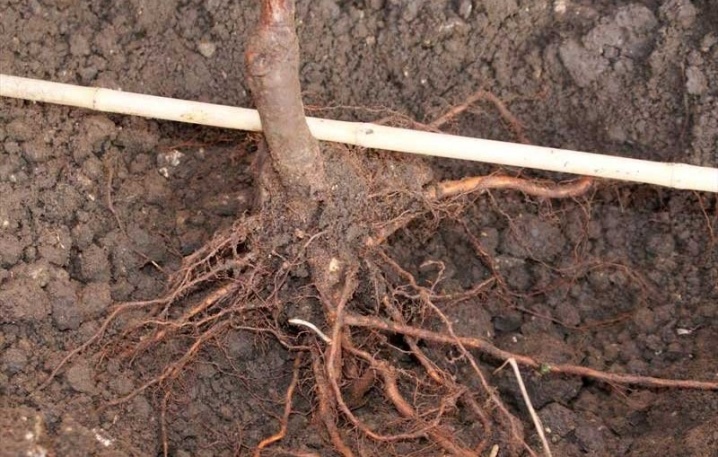
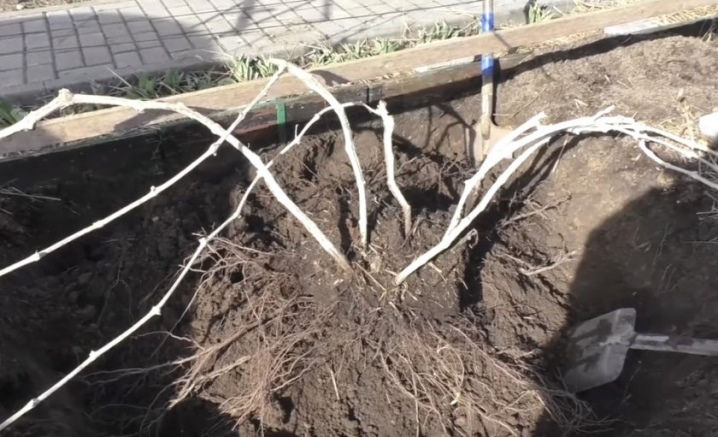
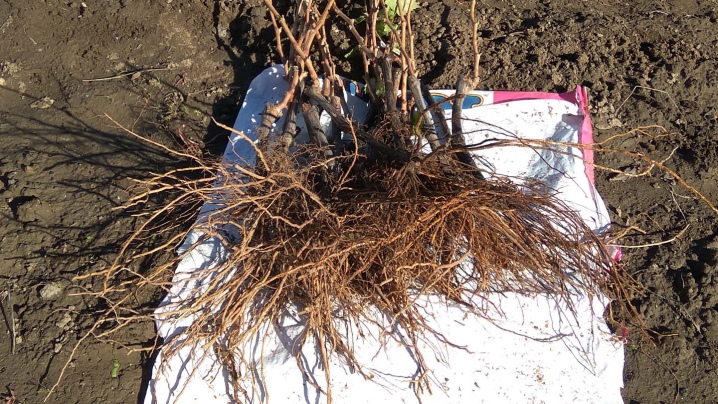
By itself, transplanting a plant from one place to another has the same algorithm as planting a young seedling. But there is one stage that distinguishes these procedures - a bush with or without leaves must first be dug correctly and carefully.
There are different digging methods used to transplant grapes and are suitable for beginners and professionals alike.

Transshipment
Over the years, the grapes become more susceptible to this kind of operations, the root system is developed, it is problematic to remove it. They cross the bush according to the following algorithm:
-
digging a bush, moving from the trunk by half a meter, while it is important to prevent damage to the roots of the nearby flora;
-
the root system is exposed as carefully as possible, if the roots go deep into the soil, they will have to be cut;
-
it is important to preserve the foundation, heel and all branches from it;
-
the bush is captured in volume and transferred to a pre-prepared area;
-
it is most convenient to arrange the bush during transshipment on a metal sheet, on a tarpaulin or immediately put it in a wheelbarrow, and then directly on these devices move the bush to a new place;
-
the root system is tied, wrap or peel the roots;
-
before carrying out transshipment, it is important to thoroughly moisten the soil, but only if you plan to replant with a lump of soil, bare roots do not need watering.

With a partial lump of soil
The algorithm of actions is as follows:
-
first, a hole is prepared, the size of which is selected according to the size of the earthen coma;
-
then the soil is moistened by introducing 2 buckets of water;
-
the dug out bush is lowered into the hole, and the tissue with which the root system is wrapped is removed at this stage;
-
the distance between the walls of the pit and the lump of soil must be filled with soil, while it must be moistened;
-
after the hole has completely fallen asleep, a circle is formed around the trunk, it is moistened again, as abundantly as possible;
-
it is best to add a root stimulant solution to the water.


With peeled roots
You can transplant a vine with peeled roots as follows:
-
the hole is prepared so that its size is at least 15 centimeters or slightly more than the length of the roots;
-
the hole must be well moistened and a fertile soil mixture with organic and mineral additives should be introduced;
-
after digging, the roots are cut, the maximum length is 30 cm;
-
a talker is bred from two parts of clay and one part of manure so that the consistency is similar to sour cream;
-
roots are dipped into it after pruning;
-
in the middle of the hole, a hill is created from the ground, a dug bush is placed on it;
-
the roots are carefully straightened;
-
to the middle, the hole is covered with soil, then it is moistened;
-
soil is introduced to ground level;
-
the circle near the trunk is rammed, moistened.

The shrub can be dug out with a hydraulic drill, for this the soil is first carefully worked out with a drill. It must turn into a slurry, then it is scooped out, while the roots remain intact. If this device is not on the farm, you can dig in a bush and thoroughly moisten it until the soil is completely saturated. Either before or after the transplant procedure, part of the bush above the ground must be shortened.

It is necessary to leave two or three shoots of the one-year-old, cut them into a couple of buds, closer to the base of the sleeve.
After the procedure, the grapes need careful and special care, especially during the first year. First of all, do not expect a full harvest from the bush. In the first season after transplanting, it is necessary to cut off all inflorescences, since it is important to direct all the forces of the plant to the development and regeneration of the roots. In addition, there are a number of other nuances that need to be considered regardless of the transplant method:
-
watering is carried out with a pipe or by the ground method, but in the first case, you need to monitor whether water penetrates to the roots;
-
the average number of waterings is from 3 to 5 per season, it depends on weather conditions, soil moisture;
-
watering must be completed in the middle of summer if the variety is early, or at the end if the variety is late;
-
every 2-3 weeks you need to loosen the soil in the near-trunk circle;
-
it is not necessary to additionally feed the plant if there is no sign of a lack of elements;
-
the transplanted bush needs to be covered for the winter, taking into account the climatic features of the region: mulch the ground, cover it with soil, cover it with any non-woven material;
-
several times it is necessary to spray the plants with Bordeaux liquid, otherwise the care for the transplanted bush is no different.





The nuances of transplanting bushes, taking into account age
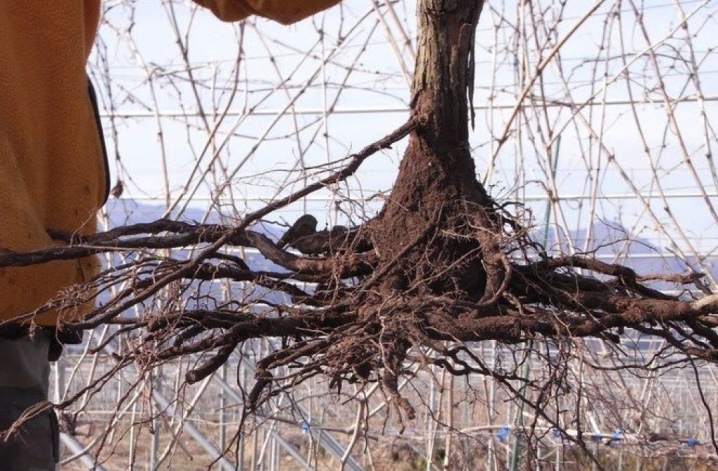
Plant transplant rules differ depending on the age of the plant. In the first 3 years, grape bushes are seedlings. A young seedling is distinguished by the fact that its root system is actively developing. An adult bush has thick, dense roots, its properties for recovery, development are reduced. From this we can conclude that the old bush takes root worse than a one-year-old or three-year-old, for example. However, even perennial grapes that are 7 or 10 years old can be transplanted and harvested.


The features of transplanting mature grapes are as follows.
-
It is almost impossible to dig up grapes four or five years old without damaging the roots.... The system goes deep into the soil a meter or more, but the bulk is at the level of 60 cm. Therefore, it is necessary to dig at least half a meter from the trunk, the pruning is done short by 5 or 6 eyes.
-
The root system of six-year-olds or seven-year-olds grows up to one and a half meters horizontally, but the most important part is within 60 cm.
-
The old bush, which is 20 years old, has a powerful root system that spreads up to two meters. The active part of the roots remains within 70 cm horizontally and 10 to 120 cm vertically.
-
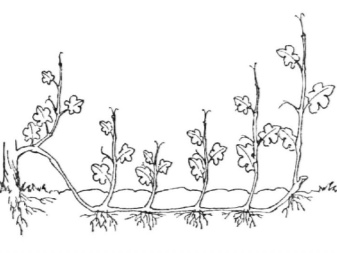
When digging, you can very much damage the roots, a large bush has little chances to take root. Therefore, it is recommended not to uproot the perennial, but to transfer it by layering, especially if the new place is not too far away.
-
A mature vine or young shoot is buried in soil and gradually takes root. This can take quite a long time - several months or even a year. The root system is formed during this period, but it is necessary to separate the layers from the mother bush in a couple of years, not earlier. Then the bush is removed.
-
An adult plant is transplanted with an earthen clod or open roots. The procedure with a lump is less traumatic and sometimes requires a special technique.
-
It is also important to take into account climatic features, and not just the age of the plant. If the climate is cold and humid, the root depth is much closer than on southern soils. On sandstones and rocky areas, the roots are the deepest.
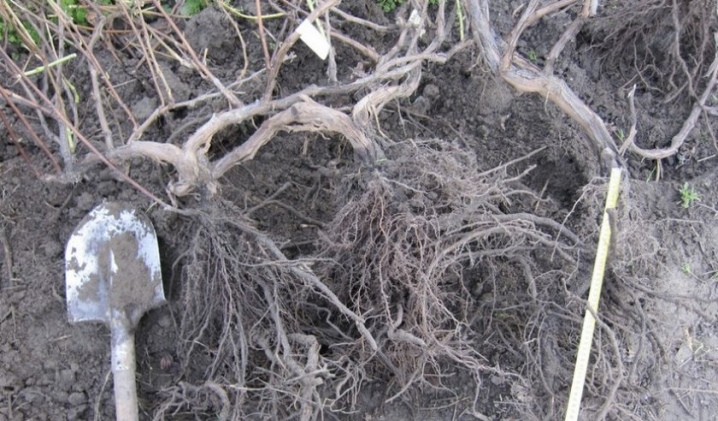

So, the older the bush, the more difficult it is to preserve the roots, with young plants it is easier, but here, too, there are some peculiarities.
-
Annual... It is important that the vine is ripe and the roots take root, so new shoots and bunches are cut off. Two vines are left, which must be allowed to ripen before the period when it will be necessary to cover the plant. In the next season, the buds of the ripe vine will give new shoots, of which you can leave one bunch of fruits.
-
Biennial... Rooting is already strong enough, the digging takes place 60 cm vertically and 30 cm horizontally. The vine is transferred along with the earthen clod. After transplanting in the spring, the vine is cut into three buds.
-
Three year old... There are already several ripe vines of this plant, so rooting can be carried out using layering. But you can transplant it with a whole bush. The digging is done in a circular manner, having moved away from the trunk by half a meter, and the digging is done 80 cm deep. The vine is cut into four eyes, while ripe cut branches are excellent for cuttings.



Ornamental grapes do not tolerate transplanting well, but age nuances do not matter.













The comment was sent successfully.