How to choose a heater: compare the properties of EPS and mineral wool

Despite the variety of heaters in the modern construction market, mineral wool and extruded polystyrene foam (EPS) occupy a leading position. What is the difference between materials? Which one is best for a particular application?


Types and features of materials
Differences in the structure and technical properties of these heaters are due to the use of different materials and production technologies. Mineral wool is a fibrous insulation, the raw material for which is rocks, technical minerals or burnt slag (waste from the metallurgical industry).
Mineral wool fibers can be horizontally or vertically oriented, or arranged in a chaotic manner. Heaters of the latter type have the best indicators of thermal efficiency and sound insulation. A low coefficient of thermal conductivity is provided due to the fact that a large number of air bubbles accumulate between the fibers of the material - an effective heat insulator.
Minvata implies the use of a respirator when working. The cutting and installation of the material is accompanied by the release of a large amount of dust, which irritates the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract.


Depending on the base, mineral wool materials are divided into several types.
- Slagged. It is rarely used for insulating buildings, since it has low values of thermal efficiency and moisture resistance. Flammable and environmentally unsafe.
- Glass wool. The material is based on glass fibers, as well as dolomite, sand and binders. The production results in long and thin glass filaments formed into sheets. They are distinguished by their resilience and elasticity, high rates of thermal efficiency. The disadvantage is the presence of cutting surfaces. The fiber penetrates the skin, causing irritation, so work with glass wool should be done in special clothing.
- Basalt (stone) wool. The material is obtained by melting rocks such as dolomite, basalt. By heating rocks to a temperature of 1300-1500 ° C, semi-liquid raw materials are obtained. From it, fibers are pulled, which are formed into layers. Then the material is pressed and subjected to short-term high-temperature treatment.



The resulting material has low thermal permeability, good sound insulation performance. It belongs to vapor-permeable materials, allows the walls to "breathe" and thereby contributes to maintaining a favorable indoor climate. Unlike other mineral wool insulation, stone wool is characterized by moisture resistance. This, in turn, provides improved frost resistance.
The melting temperature of stone wool is about 1000 ° C, so it is a fire-resistant material. Containing natural ingredients, the material is environmentally friendly. Even when the temperature rises, the insulation does not emit dangerous toxins.
Finally, it is more convenient to use. Unlike glass wool, the material does not prick.


Expanded polystyrene is a gas-filled material consisting of many air bubbles. This insulation has 2 forms of release - foam and extruded polystyrene foam. The latter is a more advanced version, consists of closed cells isolated from each other.
EPS is made by swelling and subsequent welding of cells by means of hot (up to 100 ° C) water or steam. After that, the raw material is passed through the extruder. The result is a more durable material. EPPS, in comparison with foam, has better indicators of fire resistance and moisture resistance, releases less styrene during operation.


Comparison by characteristics
To compare materials, it is logical to analyze their performance according to the main characteristics that are important for heaters.
- Water vapor permeability. EPPS has a vapor permeability of 0.03 mg / (m * h * Pa). The indicators of mineral wool exceed this value by 10 times, that is, it passes moisture vapor 10 times better. This is a big plus for wooden houses, but not for buildings in which polymer materials are used. If mineral wool is trapped between two layers of synthetic coatings, then the resulting condensation will not find a way out and will remain inside the insulation. This will lead to wetting of the material and loss of thermal insulation properties. In principle, when extruded polystyrene foam is used in similar conditions, the situation will look similar. The only exception is that condensation can escape through seams and irregularities.
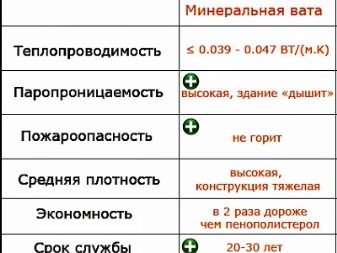
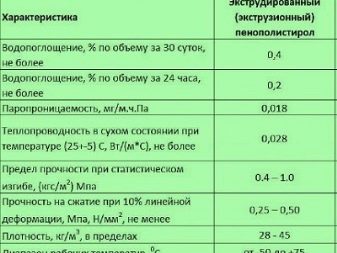
- Moisture resistance. Mineral wool is capable of absorbing 0.2-20% moisture from its mass. At the same time, when it gets wet, it loses its thermal insulation properties, since liquids conduct heat. In this regard, the use of mineral wool requires high-quality waterproofing. The varieties of stone wool that have a hydrophobic treatment are considered more moisture-resistant. EPS is capable of absorbing an average of 0.4% moisture, which is facilitated by a closed cell system. This allows in some cases to neglect the waterproofing, to use the material for insulating the basement, basements and to apply contact materials for finishing (primer, plaster) directly to the surface.



- Strength. The strength of any insulation depends on its density. The lower the indicators of the latter, the more additional protection the material needs. All heaters with a density of less than 250 kg / sq. m, in need of protection from external influences. EPPS is afraid of the influence of aggressive chemicals, exposure to UV rays, for mineral wool the main "enemy" is moisture, and for loose materials - wind.
- Fire resistance. Stone wool is considered non-combustible, and glass wool is a low-combustible material. When exposed to temperatures above 500 ° C, glass wool will not flare up. EPPS burns even at a temperature of 100-120 ° C, and it is very active. Moreover, toxic compounds are released during combustion. Depending on the brand of mineral wool (that is, the content of organic binders in it, subject to combustion), it has a class of NG (non-combustible material), G1 or G2 (weak and moderately combustible materials). EPS, regardless of the brand of products, always has a class G (that is, combustible). The flammability class, by the way, also varies depending on the type of material and ranges from G1 (slightly flammable) to G4 (highly flammable).
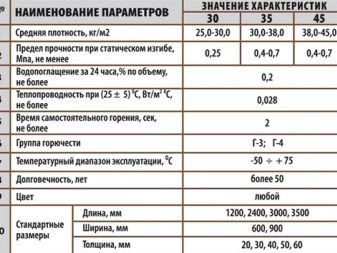

- Heat resistance. Stone wool and expanded polystyrene have identical thermal conductivity values. The thermal conductivity coefficient of stone wool is 0.042-0.036 W / (mK), EPS - 0.040-0.030 W / (mK). Glass wool is slightly inferior to these materials in terms of its thermal efficiency. According to experts, EPPS has the best thermal efficiency, since 90% of its composition is air voids formed by closed cells. In a mineral wool insulation that does not have such cells, warm air moves towards the cold one, as a result of which the room cools down faster. Only tile mineral wool can compare with expanded polystyrene material in terms of its thermal insulation properties.



- Load on supporting structures. Materials of equal thermal insulation characteristics have different weights and, accordingly, have different loads on the surfaces to be trimmed. So, for 1 sq. m when finishing with a 10-cm layer of extruded polystyrene foam accounts for 15 kg. The mineral wool used (density and thickness correspond in terms of their thermal efficiency to a similar indicator of EPS) will weigh about 20 kg / sq. m. At the same time, for heavier wool, more glue is required, which also increases the weight of the structure.


- Ease of installation. Both materials in work are quite simple and convenient, but there are some nuances in the installation process. So, expanded polystyrene is easily cut and glued, however, there is a high probability of preserving the seams and joints between the plates - future "cold bridges". In this regard, mineral wool insulation is much easier to lay without seams. However, work should only be carried out in a respirator, and if glass wool is used, special clothing is required.
- Environmental friendliness. EPPS releases styrene, which has a negative impact on human health. Stone wool is considered completely safe.
- Durability. EPSS can be operated for only 6-8 years. However, in the presence of protective hydro- and vapor-permeable layers on the layers of the material, the period of operation of the insulation reaches 25-30 years. Naturally, the cost of the material also increases.


The service life of mineral wool is 20-25 years, and if we are talking about dense sheets, then 30-40. It is not susceptible to mold, not of interest to rodents.
But the EPS is becoming the home for the latter.


Dignity
The advantage of both materials is the identical high thermal efficiency. And mineral wool materials are, in addition, an excellent sound insulating material. Both cotton wool and polystyrene foam insulation are versatile in use - they are suitable both for newly built buildings and for buildings undergoing restoration. Both insulation can be used in almost all areas of the building, insulate the room from the inside and outside.
The advantage of stone wool is its incombustibility. This makes it the optimal insulation for high-rise buildings, floors, garages and premises with increased safety requirements. In addition, mineral wool is used to improve the fire resistance of other insulation materials.


disadvantages
Perhaps the main disadvantage of EPS is its low resistance to open fire. Despite the presence of flame retardants in the composition, it quickly flares up and maintains combustion. If the entire building is insulated with extruded polystyrene foam, then in the event of a fire, its users risk being trapped in a fire. In addition, toxins are released during combustion. Inhaling them, even for a short time, leads to a significant deterioration in a person's condition.
Another disadvantage of EPS is considered to be its instability to the effects of aggressive agents, for example, contained in nitro lacquers. Even exposure to the vapors of many of them leads to the destruction of the material. On the other hand, glass wool and loose stone wool of low density shrink over time, which also leads to a decrease in their thermal insulation properties.
It is believed that the disadvantage of stone wool is its higher cost. This is indeed the case. But if you take into account the total cost of insulation with EPS and mineral wool, then the costs will be almost the same.
Of course, everything also depends on the manufacturer and the density of the material.


Choice for specific tasks
Concluding the comparative review of mineral wool and EPS, it will be fair to say that there are no “good” and “bad” insulation materials. The advantages and disadvantages of materials are due to the correctness of their application. In other words, the use of each type of insulation must correspond to its purpose.
EPPS is suitable for solving the following tasks:
- insulation of foundations, including surfaces (horizontal and vertical) in contact with damp, frozen ground;
- thermal insulation of facades and internal surfaces of buildings from various materials;
- insulation of floors in the basement, in the room under the screed;
- heat-insulating protection of non-ventilated roofs.


Mineral wool is an insulation material used for the following objects:
- wooden houses - insulation of the facade and internal surfaces;
- mansards, exploited attics, pitched roofs;
- brick, concrete and reinforced concrete buildings;
- objects and areas subject to high-temperature heating (bath walls, surfaces near fireplaces);
- gas and pipelines, heating systems and other objects of complex shapes;
- frame-panel buildings.


When using several layers of insulation at the same time, EPSP should not be placed outside the building, it is more logical to lay looser mineral wool over it. In this case, it will be possible to implement the principle of increasing vapor permeability from the inside of the room to the outside. For suspended facades, mineral wool is much more suitable, which functions perfectly, being ventilated with a similar system of organizing the facade, reliably protects the walls.
For three-layer facades, in addition to bulk insulation (expanded clay, perlite), EPS is used. It will also be the best option when applying thin-layer plaster to the facade.
The mixture can be applied directly to the insulation.



You can find out how to quickly insulate the walls in an apartment with your own hands by watching the video below.













The comment was sent successfully.