What and how to feed the beets?

When growing beets, many novice gardeners often neglect top dressing, believing that this unpretentious crop does not need them. However, it is the timely and competent application of fertilizers that is one of the factors that have a positive effect on the size, shape, taste and quantity of root crops. What are the features of beet dressing? What fertilizers and at what stages of development does it need? How can you feed her during the summer months? You will find the answers to these questions in our article.

Features of feeding
Beets are a popular crop that loves to grow in fertile soils and are painfully deficient in nutrients. Lack of micro- and macroelements is the main reason due to which beets form small fruits of an ugly shape with mediocre taste. At the same time, an overabundance of nutrients in the soil, noted with excessively frequent feeding, has an equally negative effect on the culture. So, with an overabundance of micro- and macroelements in beets, green mass is actively formed, and root crops, on the contrary, lag behind in development and growth. Along with this, the commercial qualities of root crops also deteriorate: they acquire an ugly shape, a bitter or watery taste.
Experienced gardeners also remind that the high nitrogen content in beets makes them unsuitable for food. It is known that this culture, along with radish, early white cabbage, is capable of accumulating a large amount of nitrates - harmful substances that pose a threat to the human body.


Thus, when growing beets, the gardener must observe not only the feeding schedules, but also the recommended fertilization rates.
It is important to take into account that at each stage of development of this culture, different types of fertilizing are needed, containing nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium. To the greatest extent, this culture needs nutrients, micro- and macroelements in the first few weeks after germination. During this period, she needs nitrogen-containing top dressing, stimulating the active growth of green mass and the development of the root system. Further, the strengthened young beets are fed with phosphorus and potassium preparations, which help to strengthen the immunity of the crop, increase its yield, and improve the taste of root crops.

Overview of necessary fertilizers
For feeding beets, one-component and complex organic and mineral fertilizers are used. They are applied in accordance with the feeding schedule, observing the recommended dosages and consumption rates.
- Manure - a valuable organic fertilizer containing a large amount of nitrogen in an easily digestible form. In small quantities, it contains phosphorus and potassium - substances necessary for beets at the beginning of the growing season and at the stage of root crops formation.
For plant feeding, only rotted manure (horse or mullein) is used, but in no case fresh, as this can lead to the development of fungal diseases.
For feeding beets, a liquid solution of rotted manure is used (prepared in a ratio of 1 part of manure and 8-10 parts of water). The aisles are spilled with a solution, spending about a liter per 1 running meter of planting.


- Chicken droppings - another very effective organic fertilizer, rich in nitrogen and its compounds.Like manure, chicken droppings are used for dry planting in autumn, as well as for feeding young plants in the form of a solution. To prepare the latter, 1 part of the manure is poured with 12 parts of water. It is important to note that solutions based on manure and manure are poured only in the aisles, but in no case under the base of the plants, as this can cause a burn of the root system.

- Ash - natural micronutrient fertilizer containing a large amount of valuable minerals. For plant nutrition, only wood ash is used, obtained as a result of burning branches, logs, twigs. It is strictly not allowed to take ash obtained from burning household waste and diseased plants for feeding. You can start feeding the beets with ash immediately after it rises (the recommended frequency of ash feeding is 1 time in 1-2 weeks). Top dressing is carried out before each watering by adding dry ash under the plants (the recommended consumption rate is 1 glass of ash per 1 square meter of planting).


- Urea - a powerful mineral fertilizer, almost half consisting of nitrogen. Top dressing with urea promotes the active build-up of green mass of beets, stimulates the setting of root crops. For root dressing, use a solution prepared from 1 tsp. urea and 10 liters of water. To enhance the effect, it is allowed to add 1 tsp to the resulting solution. superphosphate. The recommended consumption rate is 1 liter of solution per 1 square meter of planting.
It should be noted that experienced gardeners do not recommend feeding sugar beets with urea (but only table and fodder beets), since they often slow down in growth after applying this fertilizer.

- Yeast (dry and pressed) - an environmentally friendly and safe product that is often used by gardeners to fertilize their crops. Beet yeast feeding improves the taste of root crops, increases its yield and resistance to pathogens and insect pests. For feeding, use a nutrient solution prepared in the following way:
- 100 g of yeast and 0.5 cups of sugar are diluted in 5 liters of warm, settled water;
- insist the solution for 18-24 hours;
- before use, dilute the solution with settled water in a ratio of 1:10, respectively.

The resulting solution is used to feed beet sprouts, spending about 1 liter per 1 square meter of plantings.
It is important to note that it is recommended to feed the beets with yeast feed no more than 3 times during the entire growing season.


- Top dressing of beets with iodine - a simple and affordable way to increase the yield of the crop, improve the taste of root crops. In addition, iodine, being a powerful antiseptic, has an effective prophylactic effect against various beet pests and pathogens. A weak iodine solution (20 drops of the drug per bucket of water) is used to process row spacing in beet plantings. The same solution is allowed to process plantings in order to prevent the development of various diseases.

- Table salt (not iodized, but ordinary) - one of the simplest improvised means used by gardeners for feeding beets. The introduction of a saline solution can significantly improve the taste of root crops, make them sweeter and juicier. For dressing, use a solution prepared from 1 tbsp. tablespoons of salt and a bucket of settled water. The recommended consumption is 10 liters of solution per 1 square meter of planting.

- Herbal infusion ("green fertilizer") - a simple, but very effective and environmentally friendly fertilizer that you can make with your own hands from weeds. The most preferred for use are green manure plants: sweet clover, alfalfa, mustard, mallow, lupine. In addition to them, gardeners use nettle, burdock, whitewash, wormwood, quinoa, wood lice for the preparation of "green fertilizer".To prepare the infusion, the collected weeds are crushed with a sharp knife or pruner, placed in a large container, filled with water and left for several days. After the appearance of an unpleasant odor, indicating the fermentation of the contents of the container, the infusion is drained and used for feeding the beets. Before use, the infusion is diluted with water in a 1: 1 ratio. Top dressing with "green fertilizer" allows not only to strengthen the immunity of the crop and increase its yield, but also to improve the structure and fertility of the soil.


- "Bordeaux" - ready-made complex fertilizer, with a balanced composition, the basis of which is nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
This fertilizer is highly recommended to use when growing beets on poor, infertile soils, where they do not grow well, forming small fruits with mediocre taste.
This drug is used during the arrangement of the beds, and also used to feed the crop during the period of its active development and growth. For the entire season, feeding is carried out twice: the first time - in the phase of formation of 2-3 true leaves, the second - after 2-3 weeks. The recommended consumption rate of dry matter is 20-30 g per 1 square meter of planting. The fertilizer is evenly distributed between the rows after watering and then carefully embedded in the soil using a small garden rake. It is allowed to use this fertilizer when growing beets in seedlings, observing the consumption rates provided for in the instructions.


- Superphosphate (single or double) - a very popular mineral fertilizer among gardeners, containing a large amount of phosphorus. Top dressing of beets with superphosphate increases yields, enhances the culture's resistance to pathogens of fungal diseases, and improves the taste of root crops. This fertilizer is used at the stage of preparing the beds for planting beets, when sowing seeds and during the cultivation period. The consumption rate of the funds depends on the stage at which it is applied.


- Potassium sulphate - a highly effective mineral fertilizer that increases productivity and improves the taste of root crops. They use it in the second half of summer, when the growth and development of the green mass of plants is completed and the active formation of rosettes begins.


- Boric acid - an inexpensive pharmaceutical preparation with antiseptic and insecticidal effects. Feeding beets with a boric acid solution, according to experienced gardeners, can improve the taste of root crops, prevent cracking and increase the crop's resistance to pathogens and insect pests. For root dressing, a solution prepared from 10 g of the drug and 10 liters of warm water is used, for foliar dressing (spraying) - a solution prepared from 4 g of the drug and 10 liters of water.
During preparation, it is important to ensure that the crystals of the preparation completely dissolve in the water, otherwise the preparation may burn the plants.

What can you feed by months?
To get a good harvest of beets, it must be systematically fed, observing a certain schedule for the introduction of certain fertilizers. To the greatest extent, this culture needs additional feeding in the summer, at the height of the growing season. To avoid confusion with the frequency and frequency of fertilization, gardeners are guided by the calendar of fertilizing beets by months.
In June
At the beginning of summer, beets begin to build up their green mass, forming a thick juicy root (root crop). At this stage, she needs fertilizers containing a large amount of nitrogen. For fertilizing the culture in June, use a solution of rotted manure (1 part mullein and 10 parts water). To enhance the effect, 20 g of potassium chloride is added for every 10 liters of solution. The aisles are spilled with a solution, spending 1 liter per 1 square meter of plantings.


In the absence of a mullein, feeding can be carried out using a solution of chicken manure (the preparation method is presented above). Instead of chicken, pigeon droppings are allowed.
It is important to take into account that it is categorically impossible to use fresh manure or bird droppings.

In July
In the middle of summer, beets need additional feeding that stimulates the growth and development of root crops. At this stage, nitrogen fertilizers are excluded and the culture is fed with phosphorus and potassium-containing fertilizers. Superphosphate, which activates the development of root crops, but does not enhance the growth of green mass, is optimal for dressing at this stage. Fertilizer is applied to the soil at the rate of 50 g per 1 square meter of planting.

In August
At the end of summer, feeding is carried out with great care, since at this time the formed roots begin to accumulate substances that enter the soil. The last feeding is carried out 3-4 weeks before harvesting (the timing is determined based on the characteristics of the cultivated beet variety). At this stage, you can feed the culture with superphosphate according to the July scheme or use the following recipe:
- 3 tbsp. spoons of superphosphate;
- 1 tbsp. a spoonful of potassium sulfate;
- 10 liters of water.
The aisles are spilled with a solution, spending 1 liter per 1 square meter of plantings. Additionally, you can treat the culture with an ash or yeast solution.



Application scheme
To make the roots large and sweet, gardeners feed the crop according to a certain scheme. It should be adhered to at all stages of beet growing: from the moment of sowing seeds to the stage of root crop formation.
The stage of preparing the beds for sowing beet seeds requires special attention. So, during autumn digging, rotted manure should be introduced into the soil with a layer of 2 to 5 centimeters. Additionally, to deoxidize the soil, it is recommended to sprinkle dolomite flour, spending 2-3 glasses per 1 square meter. In the absence of these components during the arrangement of the beds for beets, you can use the complex fertilizer "Bordeaux" or superphosphate.


Before sowing seeds, it is recommended to embed a mixture of superphosphate, ammonium nitrate and potassium sulfate into the soil (10 g of each substance per 1 running meter).
These components are embedded in the soil only if no fertilizers were applied earlier at the stage of preparing the beds.
When growing beets through seedlings (seedling method), the first feeding is carried out 10-14 days after picking into separate pots or transplanting seedlings to a permanent place. At this stage, ready-made complex fertilizers ("Bordeaux") or organic fertilizers (solution of rotted manure or droppings) are used. It is not recommended to immediately feed the seedlings after planting in a new place (both indoors and outdoors), as this can harm their root system.


After thinning the seedlings in the open field, the beets are fed with a mixture prepared from urea, potassium sulfate and superphosphate (30 g of each component per bucket of water). Primary feeding is carried out by spending 1 liter of solution per 1 sq. meter landings.
The next feeding is carried out 3 weeks after the first. At this stage, use the same three-component solution or ready-made fertilizer (Bordeaux).
The third feeding is also carried out after 3 weeks using a two-component solution prepared from superphosphate and potassium sulfate (40 g of each component per bucket of water). The beets no longer need nitrogen fertilizers at this stage.


It is allowed to feed beets of late varieties for the fourth time - 3-4 weeks before harvesting root crops. At this stage, you can use the same two-component solution as for the third dressing.
In addition, with the main dressing, gardeners fertilize the beets with ash, spray them with a solution of salt, boric acid or iodine. Good results are obtained by regular application of "green fertilizer", which can be used for both root and foliar dressing. Such dressings allow not only to increase the yield of the crop, but also to enhance its resistance to pathogens of various diseases.

Useful Tips
In the process of growing beets, you should carefully monitor its condition, growth and development rates. In most cases, by the appearance of a culture, it is possible to timely determine its needs for a particular micro- or macroelement.
So, if the beet tops acquires a red tint (with the exception of varieties that are typical), this may indicate a deficiency of sodium, potassium or phosphorus. Often, reddening of the leaves indicates an increased acidity of the soil. In this case, you can spray the plants with a salt solution or feed them with phosphorus-potassium fertilizer. Ash is used to deoxidize the soil.

If the leaves of beets turn yellow and dry out, this may indicate a lack of nitrogen. Most often, this problem makes itself felt at the beginning of the growing season of the crop if the feeding schedule is not followed. To eliminate the problem, root feeding with nitrogen-containing fertilizers is performed.
Yellowing of the leaves can also result from sunburn. To avoid this problem, you should follow the correct technique and watering regime. Plants should be watered in the morning or evening hours, when the sun is least active. The same condition applies to spraying crops when carrying out foliar dressing.


When growing beets, it should be borne in mind that this crop is not moisture-loving. Excessive watering is one of the reasons for the development of fungal diseases, a decrease in yield and a deterioration in the taste of fruits.
To the greatest extent, beets need abundant and regular watering during the period of emergence and at the stage of active formation of root crops.
In the latter case, it is watered about 2 times a week, spending up to 20 liters per 1 square meter of planting. It is recommended to stop watering 2-3 weeks before harvesting.
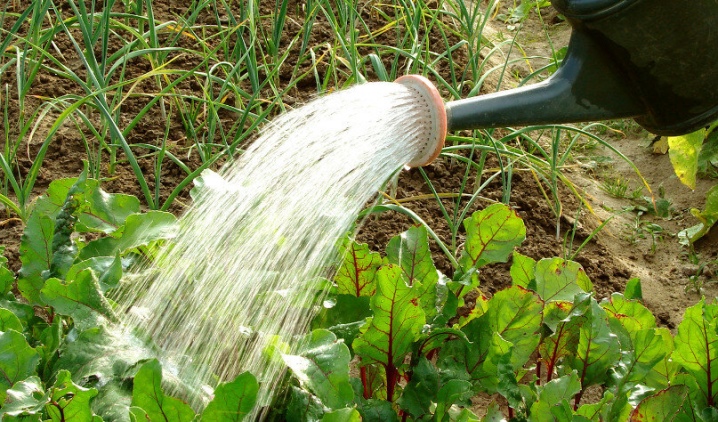

Experienced gardeners recommend feeding beets after watering. This technique not only avoids scalding the root system of the crop, but also promotes better absorption of nutrients contained in the feeding.
To prevent the defeat of beets by fungal diseases, it is recommended to process it several times a season for prophylaxis with fungicidal preparations (Fundazol, Fitosporin). About 1-1.5 months before harvesting, preventive treatments should be stopped.


About what and how to feed the beets, see below.













The comment was sent successfully.