Varieties of potash fertilizers and their use
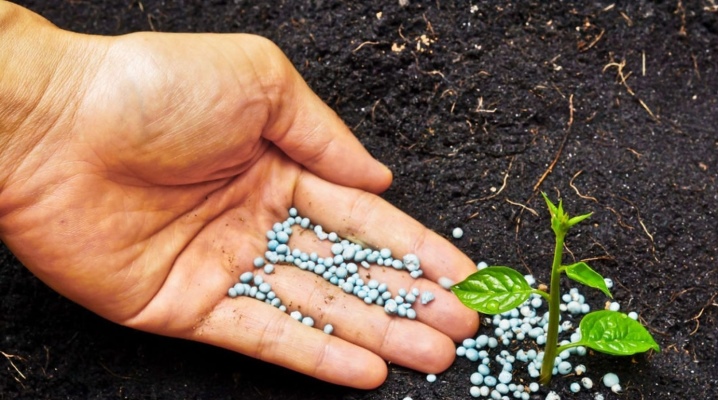

Every gardener knows that plants need nutrients for normal development and good growth, and the main one is potassium. Its shortage in the soil can be compensated for by applying potash fertilizers. They are available in various types, each of which has its own characteristics.

What it is?
Potassium fertilizer is a mineral that acts as a source of potassium nutrition for plants. It contributes to the active development of leaves, improving the palatability of fruits and the resistance of crops to various diseases. Potassium is also of great importance in the storage of the crop, thanks to which the fruits are stored much longer.

Today, mineral fertilizers based on potassium are considered the most demanded in agricultural activities; they are usually applied to soils that are characterized by a low content of this element. Most often, potash fertilizers are used for calcareous, podzolic, peat and sandy lands, which significantly increases productivity.
Potassium is most needed in crops such as grapes, cucumbers, tomatoes, potatoes and beets. To increase the efficiency of this element, it is recommended to simultaneously add nitrogen with phosphorus to the soil, since the mineral substance "does not work" without them. This fertilizer has other features - it can be applied only after the main soil cultivation.
In climatic zones with high levels of humidity and on light soils, potash fertilizers can be used before seedbed cultivation, usually in the spring.

Properties
The composition of potash fertilizers includes natural sources of potassium salts: chenite, sylvinite, alunite, polygolith, kainite, langbeinite, sylvin and carnallite. They play a huge role in the cultivation of crops and flowers, as they help to increase the resistance of plants to adverse environmental influences and drought. Besides, these fertilizers have the following properties:
- increase frost resistance;
- contribute to an increase in starch and sugar content in fruits;
- improve the taste and marketability of fruits;
- activate the processes of enzyme formation and photosynthesis.
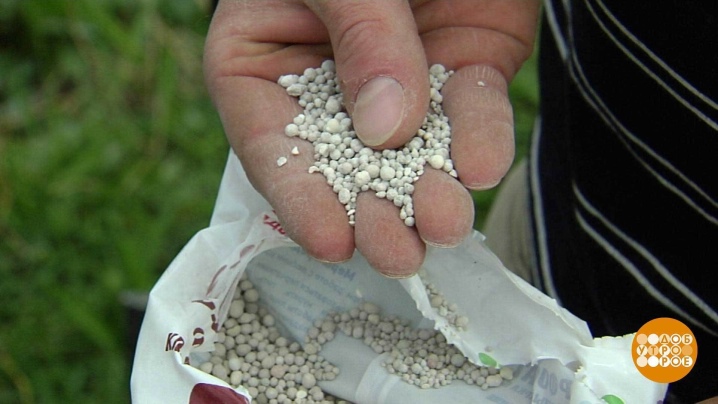

Potash fertilizers also have a major impact on the growth and development of crops by strengthening their immune system. They are considered a reliable barrier against harmful insects and are perfectly combined with other mineral elements.
The main advantage of these fertilizers is that they are easy to digest. The disadvantage is that they cannot be stored for a long time, and at high humidity, the composition quickly turns to stone. In addition, when introducing minerals, it is important to observe the dosage, since their excessive use can not only lead to a chemical burn of vegetables, but also harm a person - the plants will accumulate more nitrates, which will subsequently negatively affect the state of health.
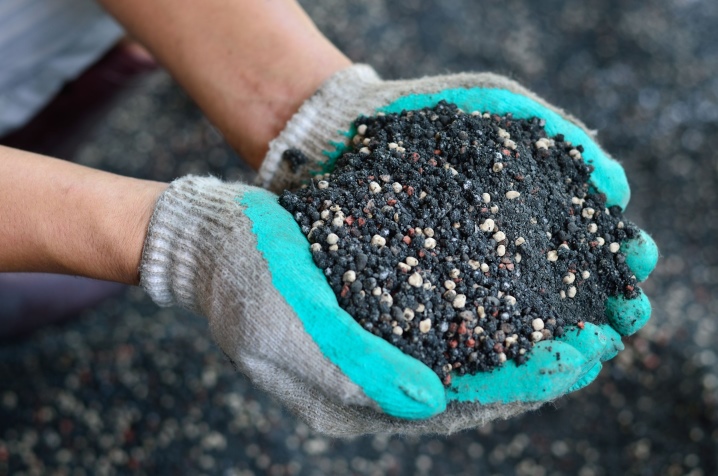

Views
Potash fertilizers are among the most used minerals in agriculture; they can have not only different names, but also their composition. Depending on the potassium content, fertilizers are:
- concentrated (include a high percentage of potassium carbonate, potassium chloride, sulfate and potassium magnesium);
- raw (natural minerals without chlorine);
- combined (additional salts of phosphorus and nitrogen are included in their composition).
According to the effect of potassium fertilizer, it can be physiologically neutral (does not acidify the soil), acidic and alkaline. According to the form of release, liquid and dry fertilizers are distinguished.
In addition to fertilizers produced in production, you can find potassium-containing substances at home - this is wood ash.
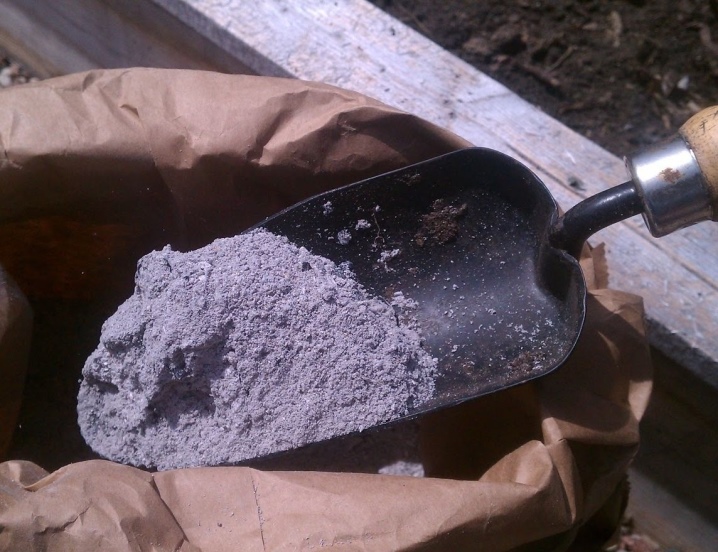

Sulfuric acid
Potassium sulfate (potassium sulfate) is a small gray crystals that dissolve well in water. This microelement contains 50% potassium, the rest is calcium, sulfur and magnesium. Unlike other types of minerals, potassium sulfate does not cake and does not absorb moisture during storage.
This substance fertilizes vegetables well, it is recommended to feed them radish, radish and cabbage. Due to the fact that potassium sulfate does not contain chlorine, it can be used at any time of the year to fertilize all types of soil.
Sulfuric acid fertilizers cannot be combined with lime additives.
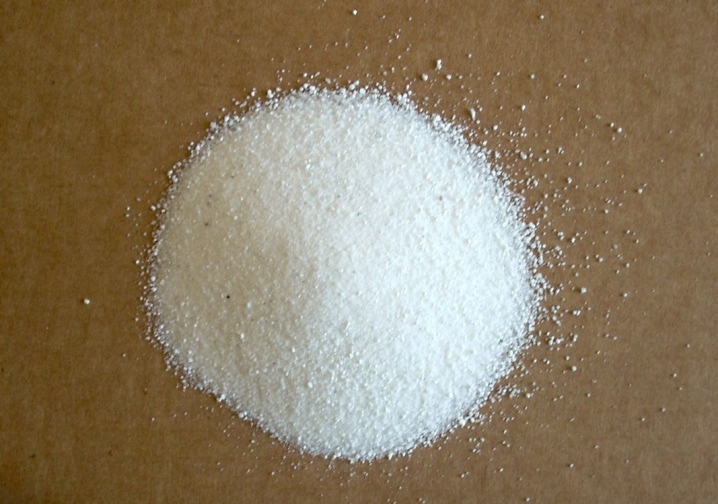

Wood ash
It is a common mineral fertilizer containing minerals such as copper, iron, magnesium, potassium and calcium. Wood ash is widely used in summer cottages, gardeners use it to feed root crops, cabbage and potatoes. It is good to fertilize flowers and currants with ash.
Besides, with the help of ash, strong acidity in the soil can be neutralized. Often wood ash is used as an additive to other minerals when planting seedlings in the ground; it can be poured both dry and diluted with water.
Cannot be mixed with nitrogen fertilizers, poultry manure, manure and superphosphate.
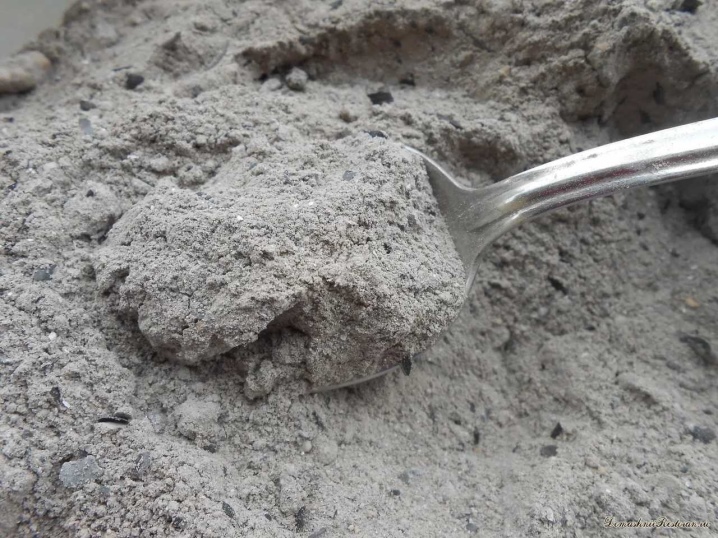

Potassium nitrate
This substance contains nitrogen (13%) and potassium (38%), which makes it a universal growth stimulator for all plants. Like all fertilizers containing potassium, saltpeter must be stored in a dry place, otherwise it quickly hardens and becomes unusable. Potassium nitrate is best applied in spring (when planting crops) and summer (for root feeding).
Its effectiveness directly depends on the level of soil acid: acidic soil absorbs nitrogen poorly, and alkaline soil does not absorb potassium.
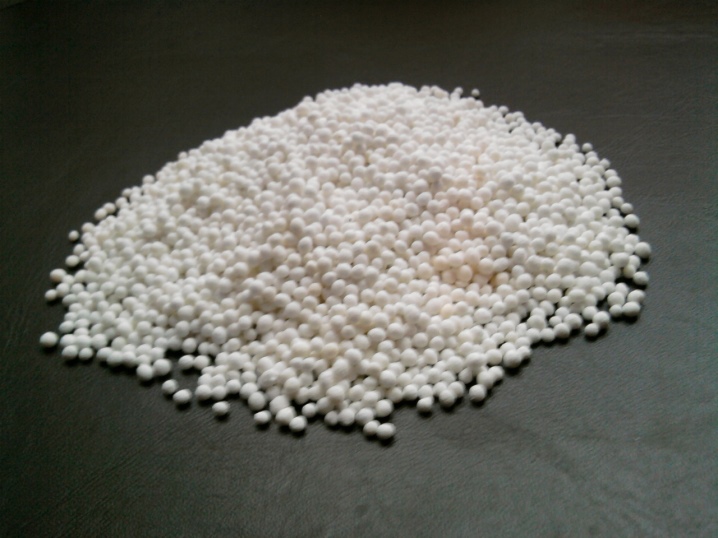

Kalimagnesia
This mineral fertilizer consists of magnesium and potassium (no chlorine). Ideal for feeding tomatoes, potatoes and other vegetables. It is especially effective on sandy soils. When dissolved in water, it forms a precipitate. The main advantages of potassium magnesium include good dispersibility and low hygroscopicity.

Potassium salt
It is a mixture of potassium chloride (40%). In addition, it contains cainite and ground sylvinite. It is usually used in the spring and summer to fertilize sugar beets, fruit and berry crops and root crops. To increase the effectiveness of potassium salt, it must be mixed with other fertilizers, but this must be done immediately before applying the mixture to the soil.
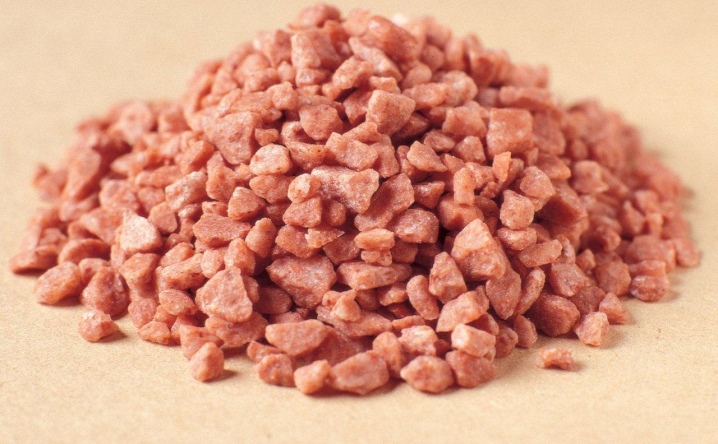

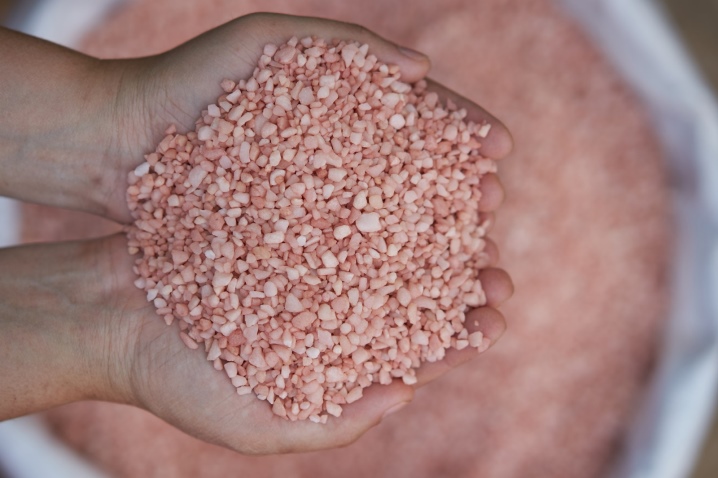
Potassium chloride
It is a pink crystal containing 60% potassium. Potassium chloride belongs to the main potassium-containing fertilizer, which can be used on all types of soils. Good for nourishing berry bushes, fruit trees and vegetables such as beans, tomatoes, potatoes and cucumbers. In order for chlorine to be washed out of the soil faster, fertilizer must be applied in the fall, otherwise it will increase the acidity of the soil.
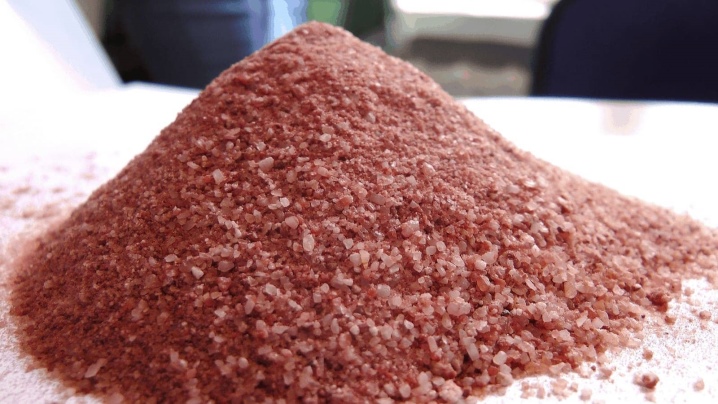

Potash
This is potassium carbonate in the form of colorless crystals that dissolve well in water. Potash is especially active in acidic soils. It can be used as an additional food for various vegetables, flowers and fruit trees.

How do you get it?
Potash fertilizers are widely used in agricultural activities for plant nutrition, since they dissolve well in water and provide crops with the necessary nutrition for growth and development.Today, the production of potash fertilizers is carried out by many factories in the country. The largest supplier of fertilizers is considered to be PJSC Uralkali; it manufactures products in Russia and exports them to many countries of the world.

The technology for obtaining potash fertilizers is different, since it depends on the characteristics of the composition of the mineral mixture.
- Potassium chloride. Raw materials are extracted from mineral formations, the flotation method is used. First, sylvinite is ground, then it is treated with a mother liquor, as a result of which the lye is separated from the sediment and separates crystals of potassium chloride.
- Kalimagnesia. It is obtained by processing chenite, resulting in the formation of fat. It can be produced in the form of a brick-gray powder or granules.
- Potassium sulfate. It is produced using a special technology by combining chenite and langbenite.
- Potassium salt. It is obtained by mixing potassium chloride with sylvinite. Sometimes potassium chloride is mixed with kainite, but in this case, a fertilizer with a lower potassium content is obtained.
- Wood ash. Residents of villages and summer residents usually get it from stoves after burning hardwood.


Signs of potassium deficiency
There is a lot of potassium in the cell sap of plants, where it is presented in an ionic form. As for the seeds, tubers and the root system of crops, their potassium content is insignificant. The lack of this element causes metabolic disorders in plant cells, which negatively affects their growth and development. The following external signs may indicate an insufficient amount of potassium.
- The leaves begin to quickly change their color. First they turn yellow, then turn brown, much less often turn blue. Then the edges of the foliage dry up and the cells of the leaf plate begin to die off.
- Many spots and wrinkled folds appear on the leaves. Leaf veins can also sag, after which the stem becomes thin and loses its density. As a result, culture slows down growth and development. This is due to the slowing down of simple and complex carbohydrate synthesis, which leads to a stop in protein production.
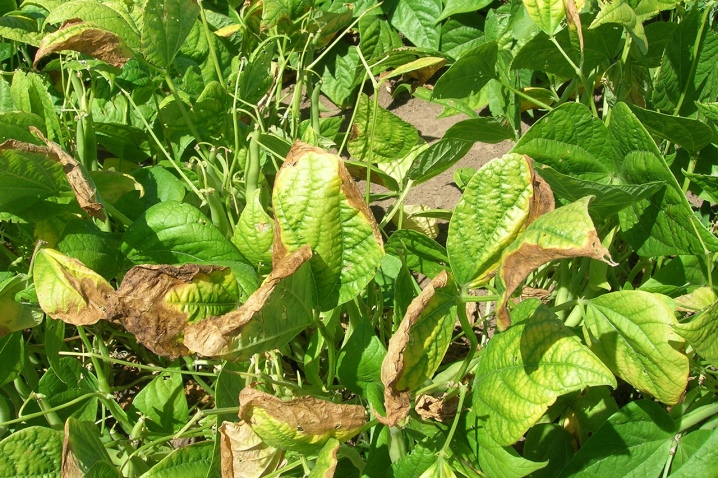

This usually occurs in the middle of the growing season and during plant growth. Many inexperienced gardeners confuse these external signs with other types of disease or insect damage. As a result, due to untimely potassium feeding, crops die.

Terms and rates of application
In agriculture, mineral fertilizers containing potassium are in great demand, but to obtain high yields, you need to know when and how to apply them correctly to the soil. In winter, potash fertilizers are used to feed plants grown in greenhouses, in spring - when sowing crops, and in autumn - before preparing (plowing) the soil.
Mineral fertilizers with potassium are also useful for flowers; they can be fed to plants growing in open soil and in closed flower beds. The need for these fertilizers is determined by the external state of the crops - if symptoms of potassium deficiency become noticeable, then fertilizing should be performed immediately.
This will help to avoid various diseases in the future and accelerate the growth and development of crops.

Potassium-containing fertilizers are applied in several ways.
- As the main top dressing when digging or plowing the land in the fall. Thanks to this method, potassium in the maximum amount enters the deep layers of the soil, providing plants with the opportunity to gradually receive useful trace elements.
- In the form of pre-sowing top dressing. In this case, small amounts of granules are poured into the holes where the plants will be planted. Additionally, you can add sulfates and other salts, which, when watering, will dissolve and nourish the root system.
- As an additional top dressing. For this, liquid fertilizers are usually used. Preparations containing potassium are placed in the soil in summer on the eve of flowering of ornamental crops, ripening of fruits or after harvesting.You can also apply additional fertilization if the plants are deficient in the mineral. The mixture is sprayed on the leaves or applied directly under the root.


It is worth remembering that potash fertilizers, which include chlorine, can be used exclusively in the fall, since this element has the ability to increase the acidity of the soil. If fertilized in the fall, then before planting plants, there is a margin of time, and chlorine has time to be neutralized in the soil.
As for the dosage of minerals, it depends on their type and the characteristics of growing crops. The composition of the soil also plays a huge role. If there is a lack of potassium in it, then the mineral must be introduced gradually, in small portions, so that the plants can evenly absorb potassium without the risk of its excess.
When feeding, it is recommended to alternate dry and liquid fertilizers. If the summer is rainy and the soil is wet, then powdered mixtures will be absorbed best, and in dry weather, liquid preparations will be more effective.

Potash fertilization rates are as follows:
- potassium chloride - from 20 to 40 g per 1 m2;
- potassium sulfate - from 10 to 15 g per 1 m2;
- potassium nitrate - up to 20 g per 1 m2.
How to apply?
When introduced into the soil, minerals containing potassium quickly react with its components, while the chlorine that remains is gradually washed out and does not cause harm. It is better to use such fertilizers in the fields in the fall (when plowing), when their composition mixes well with the moist layers of the earth.
In the garden, potash fertilizers are used as follows.
- For cucumbers. Sulfuric acid fertilizers containing at least 50% of the active substance are best suited for feeding this crop. White crystalline powder dissolves easily in water and does not contain chlorine. Before you start feeding cucumbers, you need to know the composition of the land and familiarize yourself with the requirements for growing a particular crop variety. Cucumbers are very demanding on the presence of potassium and, if there is a lack of it, they immediately begin to change color. Agronomists recommend fertilizing this crop before the appearance of fruits, for this you need to add 2-3 tbsp of water to 10 liters of water. l. granules, stir until completely dissolved and add to the root.

- For tomatoes. The best fertilizer for this crop is potassium sulfate or potassium chloride. Moreover, the first type is in great demand among gardeners, since it does not contain chlorine in its composition. Potassium chloride has also worked well, but it needs to be applied only in the fall after harvesting the fruits. In order for tomatoes to receive the right amount of useful microelements, it is necessary to comply with the rate of use of fertilizers, which is usually indicated by the manufacturer on the packaging. Typically, 1 m2 planted with tomatoes requires 50 grams of potassium sulfate.

- For potatoes. To get a high yield, potatoes need to be fed with potassium chloride or potassium salts in a timely manner. To do this, it is recommended to add 1.5 to 2 kg of potassium chloride powder or 3.5 kg of 40% potassium salt per hundred square meters. You cannot mix fertilizers with superphosphate and urea.

- For onions and cabbage. Potassium is of great importance for these crops, with a lack of it, the roots will develop poorly, and the fruits will stop forming. To prevent this, it is necessary to water the wells with an aqueous solution 5 days before planting seedlings in the ground (20 g of potassium chloride is taken for 10 liters of water). This also applies to onions, they are fed with liquid fertilizer in the spring, before the formation of the bulb.


Potash fertilizers are also very popular in personal plots, they are bought for the garden and lawn, where ornamental plants are grown. It is recommended to feed flowers with potassium sulfate, which can be combined with fertilizers containing nitrogen and phosphorus, while the dose of potassium should not exceed 20 grams per 1 m2.When flowers, trees and shrubs begin to bloom, it is best to use potassium nitrate, it is applied directly under the root of the plants.

An overview of potash fertilizers is presented in the video.













The comment was sent successfully.