Features of chelated fertilizers and methods of their application

It is only possible to obtain healthy crops, viable planting of plants and a bountiful harvest through a competent and balanced supply of plant crops with the nutrients they need. In regions of high intensity of agriculture, a significant part of microelements is naturally extracted from the soil and its depletion, the content of well-assimilable compounds and forms in the soil decreases. The modern chemical industry offers gardeners an effective form of fertilizer called chelates. Such mineral complexes actively nourish plants with necessary microelements, are safe for soil, crops and humans.



What it is?
Chelated fertilizers, in fact, are a balanced combination of mineral-organic substances of a complex structure. It is based on a special chelating agentgrabbing substances like a claw. Hence, translated from Latin, the name of such complexes came from. The compound retains the ions of trace elements, bypassing the production of salts, in a soluble state. When the fertilizer begins to interact with the plant culture, the organic matter decomposes, and the element itself begins to be actively absorbed by the cells of the root system or penetrate into the seeds.
Nutrients are close in natural composition to vitamins and chlorophyll. Plants assimilate them very easily. Chelates have a long shelf life, do not deteriorate during transportation, and there are no artificial impurities in them.


On the basis of chelate compounds, practically all the latest preparations are created for the treatment of crops, increasing their vital activity. Chelating agents are complex acids, they have different strengths for binding ions and ratios of acidity of the medium. The effectiveness of micronutrients in this form of fertilization is much higher than conventional organic stimulants. Many professional plant growing companies, gardeners and summer residents actively use chelated fertilizers for soil or hydroponic systems due to their advantages:
- significant savings in consumption due to the increased concentration of trace elements and a high degree of assimilation;
- a high degree of absorption of nutrients, which gives an increase in yield and an increase in taste;
- safety of use, absence of accumulation of nitrates, careful impact on crops, environmental friendliness.



Types of chelated fertilizers
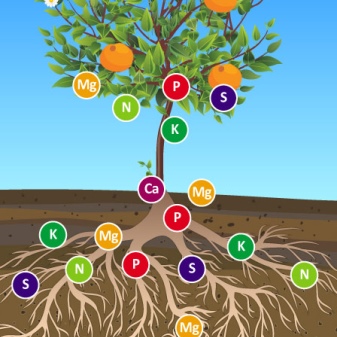
The most important trace elements responsible for metabolic processes, cell growth, and enzyme production for plants are iron, copper, zinc, calcium, manganese, cobalt, boron. They serve as key pillars in the continuous growth process, maintaining resistance to negative factors, productivity and crop yield.
The lack of each of the elements in any degree leads to a significant decrease in the quality indicators of development. Lack of iron will provoke the growth of weak and small leaves with yellowness and drying of the branches. A low content of zinc and copper will lead to a slowdown in growth, curvature of shoots, and a change in the natural color of fruits. A low level of manganese and molybdenum will affect the appearance of the leaves and their early wilting.
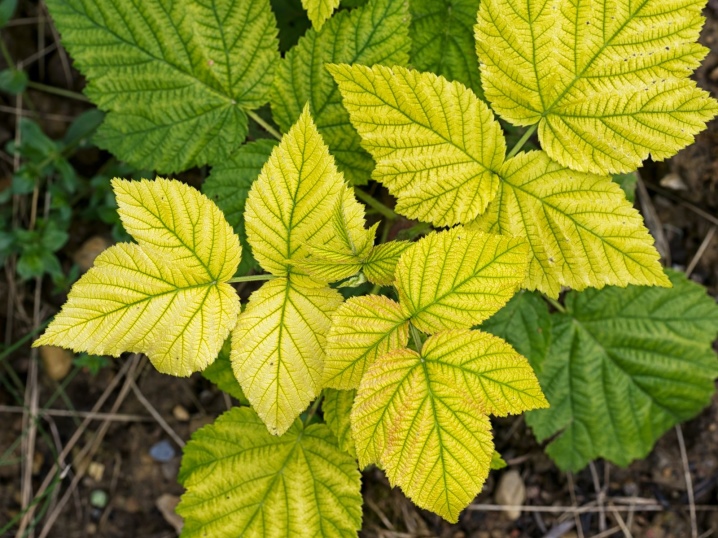

Various types of chelated fertilizers, which include the necessary elements for the life of plants, will help prevent these possible problems.
They can contain both one microelement and several at once in a complex combination. Microfertilizers based on salts of basic metals are presented as liquid concentrated aqueous solutions or powders... The types of chelates vary by the degree of ion binding, soil typefor which they are intended, and the specific species of plants.


The line of chelated fertilizers is represented by options with iron, calcium, zinc and a number of other important elements.
- Iron chelate belongs to the most important group of micronutrients required for foliar and root feeding of horticultural crops. It allows plants to actively develop, provides them in the right amount for this, and promotes recovery. The formula of this type of chelate consists of atoms of neutral organic matter and ferrous iron, thanks to which the fertilizer is highly effective. The chelated shell, which protects the microgranules of the active substance, creates, in symbiosis with iron, an ideal process of absorption into the structure of plants and vegetable crops.

- Water-soluble fertilizer chelated calcium is a sought-after source of this trace metal.... In the now widespread hydroponic growing systems, this chelate is in great demand due to the good solubility of trace elements of salts. Calcium necessary for plants is actively absorbed by the vegetative system, increases resistance to various diseases, enhances quality development, eliminates deficiencies in the nutritional properties of soil and substrates.
Calcium chelate dissolves in the nutrient solution along with other types of fertilizers. When adding it, it is necessary to take into account the dosage rates and the level of water hardness.


- Zinc chelated fertilizers are characterized as an effective form of water-soluble trace minerals and provide a good degree of nutrient bioavailability. A decrease in zinc levels is fraught with stunted growth for the plant, reduced yield and reduced life cycle. Soluble zinc chelate is indispensable for almost all types of horticultural crops and is applicable in high-tech growing systems to eliminate these phenomena as much as possible.
The active agent of zinc is delivered to the plant, increases the nutrient medium, the quality and ripening time of fruits and berries.

When are they needed?
Agrotechnical features of plant growth sometimes lead to an uneven content of trace elements, and then fertilizing with organometallic chelated fertilizers is necessary. The rate of their assimilation is 35% higher in comparison with traditional salts of elements due to the fact that chelates do not enter into cross-unstable compounds. The modern type of fertilizers exceeds the efficiency of phosphates and sulfates due to their high solubility and penetration into plant cells at different growth phases.
For various types of fertilizing in open ground or in greenhouses for vegetable crops, chelated micronutrient fertilizers are applicable to adjust the nutrition of plants. Chelates are able to protect them from fungal diseases, increase germination and immunity several times.
They are indispensable for synthesizing a full-fledged vitamin and trace element composition of the crop, when a spectrum of chemical useful elements is introduced into the plant environment.

How to apply?
Chelated preparations are selected depending on the needs of the crop and soil. These fertilizers are applied in different forms:
- root dressing;
- drip irrigation;
- foliar feeding;
- soaking seeds in solution.
The most common chelates are in liquid form, less common are dry fertilizers that need to be diluted according to instructions.

For more information on the features of using chelated fertilizers, see the next video.













The comment was sent successfully.