All about the formation of tomatoes

Growing tomatoes is a rather complicated and painstaking process. It begins with planting seedlings grown in advance into the ground. One of the important conditions for agricultural technology was the correct formation of the stems of the bush. To get a good harvest of tomatoes, you need to follow some agronomic rules.

Why is the procedure needed?
Tomatoes, like other vegetables and fruit crops, need the correct growth of the bush. The future harvest depends on how the plant bush is formed. At the genetic level, tomatoes have an established ability to intensively develop vegetative organs. It would seem that this is a good quality, because future fruits develop on additional shoots. But a large number of shoots does not always lead to good yields. The plant very often lacks resources and micronutrients to provide all the fruits. That is why the bushes need to be formed correctly.
The first step in the formation of culture can be called picking seedlings. In this case, the formed root breaks off itself, thereby shortening a little. Then new root shoots begin to form, which allow the plant to better absorb the necessary trace elements from the ground and the right amount of moisture. The formation process itself is built from certain events, which will be discussed below.
All shaping activities have one goal - to get a high-quality and high yield.

If you do not fulfill them, then:
- the culture will begin to thicken, which will lead to disease;
- leaves and stems will begin to shade each other;
- more abundant watering and increased use of fertilizers will be needed;
- it will be more difficult for the roots to provide vitamins to the lower part of the bush;
- the culture will bloom profusely, but the fruits will be weak, small, few in number;
- on tall varieties of tomatoes, mainly the lower fruits will ripen.
The correct formation of tomato bushes will allow:
- get a better harvest;
- improve fruit quality: tomato size, flavor and sugar percentage;
- direct microelements and nutrients to the formation of ovaries and their ripening instead of foliage;
- increase resistance to viral, fungal and other types of diseases;
- lighten the bush;
- making treatment against diseases and pests much easier;
- remove unnecessary shoots that do not yield crops;
- accelerate the ripening of fruits;
- reduce the frequency of watering and save on fertilizing;
- save landing area.

Basic principles
The correct formation of tomato bushes means performing the following steps:
- pinching;
- topping;
- trimming leaves;
- ovary normalization;
- tying up plants.
Let's consider the procedures separately.

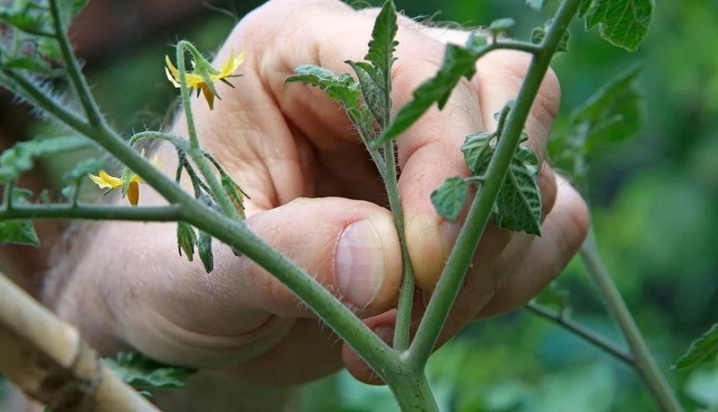
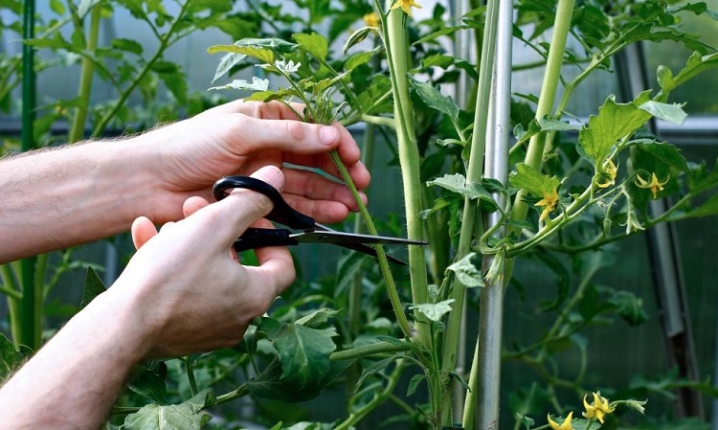
Stepping
Grasshopping is the artificial removal of lateral shoots or shoots (stepchildren). Breeders do not recommend carrying it out earlier than 14 days after planting seedlings in the ground. During this time, the young plant will take root, it will be easier for him to undergo this operation. You can remove unnecessary processes by cutting off with scissors or breaking off with your hands. The main thing is that the lateral shoot is not overgrown: its size should not exceed seven centimeters. Only then will the stressful procedure go smoother.
The first step is to determine the number of fruiting shoots that are planned to be formed. It is recommended to remove stepchildren at intervals of 7-10 days.Or there is another option - to choose varieties that give a small number of stepchildren. If it is decided to form a tomato bush from several trunks, it is recommended to leave the stepson, which has formed under the first flower ovary. If two or three trunks are supposed, then the stepchildren are left with the skipping of several internodes. In some cases, the growth point is redirected.
This is required for some tall tomato varieties in order to obtain a higher yield. For replacement, a formed strong shoot is left under the lower flower ovary. The main stem is pinched after another 1-2 ovaries have been formed. With the abandoned stepson, the same operations are carried out as with the main main stem. This is a garter, the removal of unnecessary side shoots. In some cases, growth is restricted.

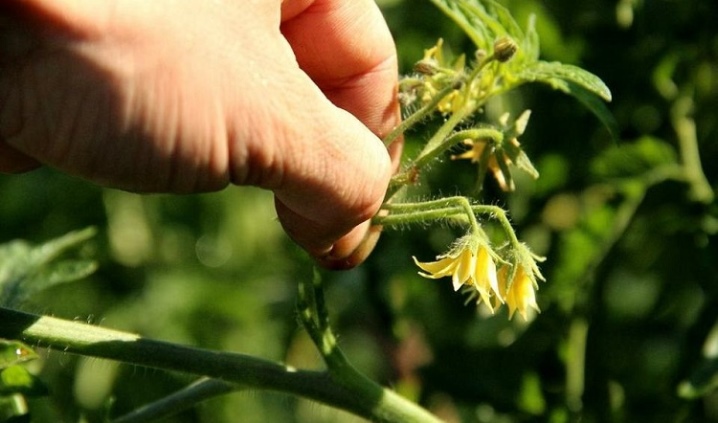
Topping
Pinching is an action during which the growth of the main stem is limited. This is done artificially. They use this technique for tall varieties of tomatoes that are grown in greenhouses or in those regions where the summer is quite short. Pinching helps the fruit to form faster and ripen in a short summer period. This principle of formation is also used to increase the size of the fruits themselves.
The pinching process is recommended in the early morning. It is used in the event that a bush is formed from one stem. Often, unnecessary, newly formed shoots are also pinched if the fruits do not have time to ripen before the onset of cold weather.

Removing or pruning excess leaves
Usually, the lower leaves are removed when the fruit cluster is already formed and the pouring process has begun. At this time, the leaves that are located under the formed brush are removed. This is necessary in order for the bush to be better ventilated. The fruit ripening process will be accelerated. Before the formation of the fruit ovary, the leaves were needed to feed tomatoes, and also served as a source of various substances. But as the ovaries form, the abundance of leaves begins to interfere with the development of the fruit. After removing the leaf plates, the tomato bush becomes drought tolerant.
There are two ways to remove sheet plates: by pinching or trimming. The operation must be carried out carefully so that the top layer of the stem is not damaged. It is recommended to remove no more than 3-4 sheet plates at the same time. Before the procedure, the soil should not be too damp.
It is recommended to start watering tomato bushes one day after the procedure. Fulfillment of this condition will preserve the quality of the fruit, and their skin will not crack.

Normalization of ovaries
It is also necessary to normalize the volume of fruit ovaries. These are optional steps, but in some cases they should not be ignored. The ovaries can become deformed or too small due to inappropriate care or bad weather. To prevent low-quality tomatoes from wasting micronutrients, it is recommended to remove them to further form normal tomatoes.
Fruits that are too small may also be located at the tips of the mushrooms, and tomatoes that are close to the main stem develop normally. Small fruits can also be removed so that leftover tomatoes develop properly.

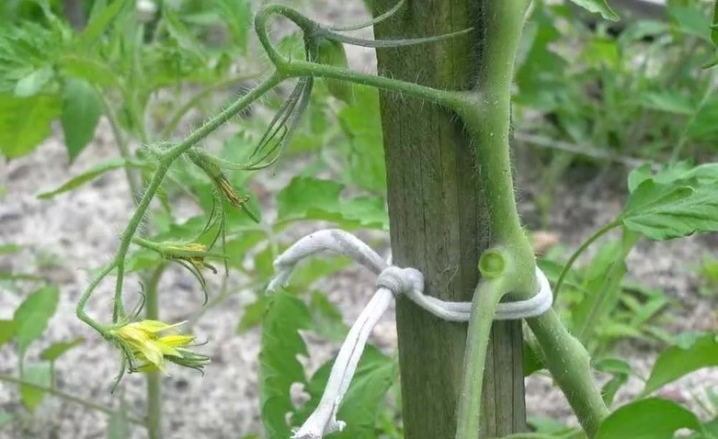
Tying
Tying the bushes is also a necessary procedure when growing tomato crops. This manipulation may differ depending on the type of plant. Tie the stems of tomato crops to the frame or to the trellis. Dense knots on the trunks cannot be made. The thread must be twisted around the trunk several times, making the fixation not too rigid.

Schemes by number of stems
Before planting seedlings in the ground, it is necessary to decide according to what scheme the bush will be formed. The distance between the holes will be planned according to this rule. Breeders have developed several schemes for the formation of culture: one main stem, two main shoots, 3 and 4 stems. For proper formation and obtaining an excellent harvest, you must follow the step-by-step instructions.
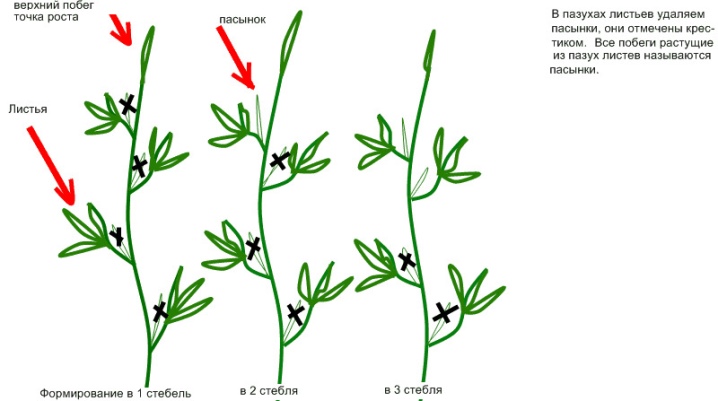
IN 1
The main bush grown in one stem is represented by one thick lash, on which tomato clusters are densely placed. This method of shaping will help save space on the site and get large tomatoes. Step-by-step instructions for forming:
- all extra stepson's processes are removed;
- the main shoot is tied to a trellis or other support;
- at the beginning of ripening, unnecessary leaves are removed;
- the top of the bearing stem is pinched about 40-50 days before the end of the growing season.
The distance between the bushes formed according to this pattern should be 40-50 cm.

IN 2
The two main stems are formed mainly by tall varieties that grow in open ground, as well as determinant greenhouse species. The distance between the bushes formed according to this scheme should be more than 50 cm. To form two stems, a strong young shoot must be left under the very first flower ovary. Upon reaching the required size, it also requires tying and removing all lateral stepsons on it, excess lower leaves, pinching the top.

AT 3
In this way, undersized greenhouse varieties are usually formed, as well as determinant tomatoes for open ground. For the formation, it is necessary to leave one more strong stepson, which is located under the flower brush. More space is needed for the arrangement of such bushes so that the seedlings receive sufficient lighting.
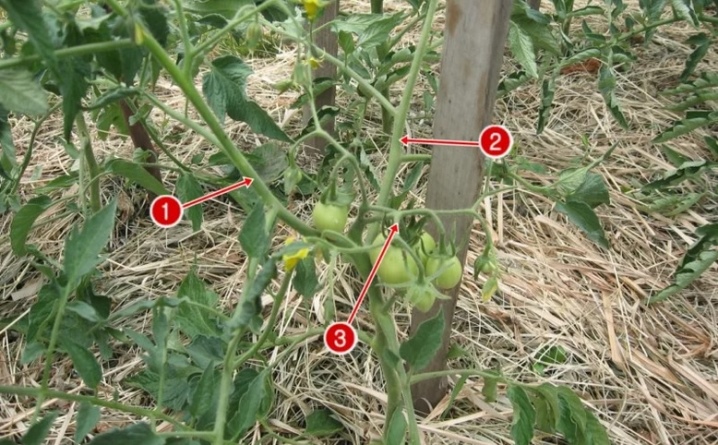

AT 4
The formation of a four-stem bush follows the same pattern as the formation of three stems. It differs only in that 3 stepsons are left. This scheme is recommended mainly for low-growing tomatoes.

The nuances of formation, taking into account the growing conditions
To choose the correct scheme for the formation of a bush, it is necessary to take into account the conditions in which the plant will be grown: in a polycarbonate greenhouse or in the open field. To form tomatoes in the open field, you need to focus on the type of bush, plant variety, as well as the degree of formation of stepchildren.
To grow tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse, you also need to pay attention to the type of plant, the degree of illumination, and the area of the greenhouse.












The comment was sent successfully.