How to plant tomatoes in a greenhouse?

The indisputable fact is that tomatoes are one of the most popular plantings in the country. It is hardly possible to find a vegetable garden without beds, which have these wonderful and beloved by many plants. At the same time, summer residents try to get the coveted harvest as early as possible and strive to learn how to plant tomatoes in a greenhouse correctly. It is worth noting that such a process has a whole list of important nuances that must be taken into account.


Suitable varieties
The vast majority of greenhouse plants require minimal maintenance. Moreover, all the necessary activities are standard and simple. The following varieties of tomatoes have recommended themselves as the most suitable for this method of growing.
- "Miracle of the Earth" Is an early ripening and high-yielding variety that is especially popular with modern gardeners. Key features are tall bushes and sweet heart-shaped fruits. Their weight is capable of reaching a record 0.9 kg. These plants are resistant to extreme temperature fluctuations and drought.
- "Major" - a high-yielding variety of an indeterminate type, having fruits with dense pink pulp and a pleasant smell. The main competitive advantages include resistance to adverse conditions, as well as disease.
- "Silhouette" - a high-yielding hybrid from the mid-early family. Its rounded fruits have an unusual flattened shape and are distinguished by their outstanding taste. This tomato variety has increased resistance to adverse conditions.
- "Kohava" - ultra-early ripening tomatoes, characterized by high yields. Flat-round fruits weigh from 150 to 180 g, and the first crop is harvested on the 90th day of the life of the bushes.
- "Gondola" - a mid-season indeterminate variety belonging to the category of hybrids. The weight of fruits with dense, red pulp ranges from 150 to 500 g. Tomatoes are used both fresh and salted, pickled, as well as in various sauces and side dishes.
- Long Keeper - a late variety of high-yielding tomato. The seedlings are medium-sized, the fruits are large enough, round in shape with a weight of up to 300 g. They ripen well in the so-called maturation.
- "Dina" - mid-season tomatoes with high yields. The variety has seedlings of medium height and round fruits, the weight of which varies from 150 to 200 g. They are also distinguished by an unusual bright orange color and sweet taste. Plants are not susceptible to disease and tolerate drought well.
- "Bull heart" - one of the most famous and long-established varieties of tomatoes exclusively from the positive side. Taking into account the species, it can produce fruits weighing up to 300 g of red, black or yellow.
- "Hurricane" - early ripening tomato. The average weight of the fruits is 90 g, and they can be eaten fresh and processed. The first crop can be harvested 90 days after planting in the ground.
- "Lelya" - relatively recently bred by breeders, an early ripening variety of tomatoes with a high yield. The weight of small fruits with bright red flesh reaches only 100 g.


When selecting specific varieties, it is recommended to take into account the following characteristics:
- yield;
- ripening time of fruits;
- taste;
- the size of the bushes;
- fruit weight;
- keeping quality.
Experienced gardeners prefer not to dwell on one or two varieties.As a rule, ultra-early, mid-season and late tomatoes are grown in greenhouses. This approach allows you to ensure the harvest for the longest possible period.

Timing
The disembarkation time is determined by taking into account a number of the most important factors. So, for example, the following signs indicate the readiness of tomatoes to "move".
- The height of the bushes has reached 20-25 cm.
- There are 8-12 developing leaves.
- 1-2 inflorescences are formed.
- The seedlings are about 55 days old.
The timing of planting seedlings in heated and unheated greenhouses depends on soil temperatures and climatic characteristics of the region. In addition, experienced gardeners are also guided by the weather conditions during a particular year. The determining factors in this case will be an early or prolonged thaw, premature and sharp frosts, cold or excessively hot summer, late spring, etc.
In addition, it is worth paying attention to the lunar calendar. So, in the current 2021, the following dates have become favorable for planting tomatoes.
- January 2, 14, 17, 18 and 20.
- From 6 to 9, 11, 12 and 14 February.
- From 7 to 10, 15 and 16 March.
- April 6, 7, 11, 12, 17 and 18.
- 2, 3, 8, 9, as well as from 15 to 18 May.
It has been proven by many years of practice that the seedlings planted taking into account the lunar cycles are distinguished by their increased resistance to diseases and strength. This, in turn, guarantees high yields of the bushes in the future.


What can you plant next to?
Often, even the most daring experiments of gardeners give interesting results. But in this case, we are talking, first of all, about the compatibility of tomatoes and other plants that can be planted in the same greenhouse (greenhouse). So, good neighbors of tomatoes, in addition to eggplants and bell peppers, will be:
- white cabbage and Peking cabbage;
- legumes;
- sweet peas;
- physalis;
- spicy greens;
- sunflower;
- corn;
- radish;
- garlic and onions.
In addition to all of the above, greenhouse tomatoes next to melons and watermelons will feel comfortable. If you need to protect tomatoes from pests, then it is worth placing mint, parsley, as well as anise and celery next to them.

How to prepare a greenhouse?
Regardless of whether tomatoes will be planted in a new greenhouse or greenhouse, or we are talking about a previously used structure, due attention must be paid to the preparatory stage. First of all, it is necessary to make beds, the width of which is most often 75-80 cm. At the same time, it is important to leave paths 30-60 cm wide.Considering that in some regions of the Russian Federation, sudden cold snaps are not uncommon even in late spring, it is better to make the beds up to 40 cm high and arrange from east to west so that in the morning they are as illuminated as possible.
Before planting, the greenhouse must be disinfected without fail. Metal structures can be treated with a bleach solution prepared at the rate of 0.4 kg of substance per 10 liters of water. This mixture should be infused for 5 hours before use, after which it will be necessary to spray everything inside the greenhouse. After two days, the frame is treated with boiling water, and the room is ventilated.
If we are talking about a wooden base, then the processing is carried out differently. It will first be necessary to seal up all the cracks. After that, a metal sheet is placed inside, on which a mixture of sulfur and kerosene or a ready-made sulfur stick is set on fire.
After such fumigation, the greenhouse should be well ventilated, and the frame itself is treated with a solution of copper sulfate.


Soil preparation
As a rule, the soil in greenhouses is changed every five years. As practice has proven, during this time the land is almost completely depleted, despite the regular application of fertilizers. In addition, every autumn it is necessary to disinfect the substrate. Available tools can be used for these purposes, namely:
- 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid;
- copper sulfate;
- dolomite flour.
After such processing, you can proceed directly to the preparation of the greenhouse soil, which includes the following steps.
- Arrangement of the lower layer, which serves as a heater (10 cm of sawdust, straw or dry needles, and 10 cm of rotted compost on top).
- Backfilling of warming bedding is a ridge of garden soil with a thickness of 30 to 40 cm.
- Fertilization for digging.
The features of the last point depend on what kind of soil is used in the greenhouse. For example, in situations with a peat substrate, additives in the form of humus, turf, as well as sawdust or wood chips will be required. After completing all the described procedures, the greenhouse will be completely ready for "moving" the seedlings.


Planting patterns overview
Experienced gardeners always adhere to a certain order of planting young tomato bushes in a greenhouse. It is important to remember the importance of how much space will be allocated to each plant. It is no secret that the planting density of seedlings directly determines the growth rate, development and, of course, productivity. Taking into account the peculiarities of each species, the distribution scheme of young stock in the beds should not be too compacted. Every tomato should be getting enough air and light.
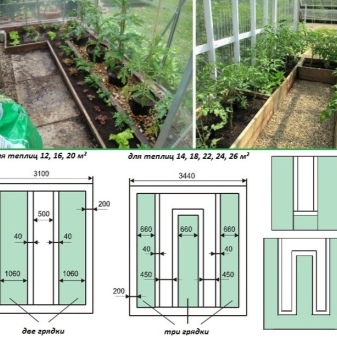
Today, there are several main ways to place seedlings in greenhouse beds. Many people use 3 by 4 or 3 by 6 when planning plantings. Of course, the choice in this case is determined by the characteristics of specific tomato varieties.
- Low-growing types of early tomatoes. The best option in this case is a checkerboard pattern. Given that the bushes lead in 2 or 3 stems, the distance between the rows is 0.5 m, and between the bushes - 0.4 cm.
- Standard and determinant tomatoes (usually in 1 stem). On 1 square meter, you can have up to a dozen of such bushes with a scheme of 0.2x0.5 m.
- Indeterminate, tall varieties. One of the most successful options would be the use of a staggered landing with two rows. It is important to take into account that the distance between them should be 0.8 m, and the intervals between the plants themselves should be 0.5-0.6 m. This is important if the tomatoes will lead to one stem. For situations with two stems, the spacing between the bushes should be increased to 0.7 m.

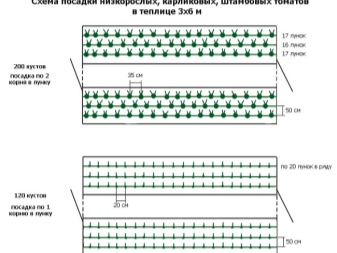
In practice, combined landing methods are often successfully used. We are talking about a productive neighborhood of low-growing early-ripening tomatoes and their tall relatives. This would be a good choice for a standard greenhouse with two wide beds and a relatively narrow aisle. In this case, a number of early low plants are placed along the walls of the structure with an interval between the bushes of 0.4 m, while leading them into the stem. This arrangement provides the plants with maximum light.
The second row of seedlings is planted at the very aisle, and it is created from tall varieties. The gap between them must be maintained 0.6 m and formed in the same way as undersized ones, into one stem. In the intervals between these two species, it is necessary to place seedlings of superdeterminant, standard bushes with an interval of approximately 0.25 m.
If all of the listed plants are formed into 1 stem, then it will be possible to get a record early harvest. However, it is worth considering that it will not be very abundant.

How to plant seedlings correctly?
The process of planting tomato tomatoes in a greenhouse made of polycarbonate and other materials in itself is simple and not too laborious. However, it is highly recommended to follow certain rules, taking into account a number of factors. This approach will provide plants with active growth and appropriate development, and, consequently, a high-quality and rich harvest.
Before planting young tomatoes in the greenhouse soil, the seedlings must be properly prepared. So a couple of days before that, you need to remove a few lower leaves. It is important to remember that when you cut them, small stumps should remain.Such manipulations can minimize the risk of disease.


Not overgrown
Seedlings are considered optimal for planting, the age of which is 1.5 months. The main thing is that the plants are as strong as possible, have sufficiently thick stems, as well as from 8 to 12 true leaves of a dark green color. Another important condition is the presence of developed and powerful roots. Ideally, the height of the seedlings should be no more than 30-35 cm. The very procedure for planting non-overgrown specimens includes the following steps.
- At the preliminary stage, the plants are watered abundantly, which makes it easier to remove them from pots or other containers used for seedling.
- In accordance with the chosen scheme and taking into account the characteristics of the tomatoes themselves, holes are prepared in the beds.
- Each well is spilled abundantly.
- The seedlings are placed one at a time in each groove in a strictly vertical position.
- The bushes are deepened so that the edge is 3 cm above the clod of earth with roots. It is worth considering that additional roots will form quickly enough on the stems located underground, which will strengthen the plant.
- After distributing the bushes in places, they are sprinkled with earth, which should be slightly compacted.
- For the first few days, the seedlings "moved" to the greenhouse are shaded in order to exclude the negative influence of the sun's rays on the seedlings that are still immature and not adapted to new conditions. After that, this protection will need to be removed.

It is important to remember that in the process of transplanting seedlings, fertilizers are not applied if they have already been added at the stage of complex preparation of the greenhouse. The disembarkation of young stock should be carried out with the utmost care. It is highly undesirable to allow the destruction of the earth clod (exposure of the root system) and damage to the stems.
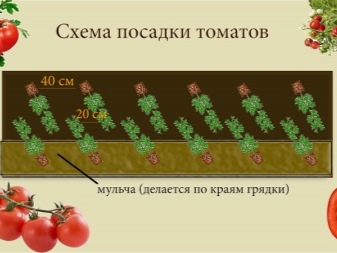
1-2 weeks after "moving" to the greenhouse for permanent residence, the soil around the bushes must be mulched with straw or hay, the layer of which should be 3-5 cm. Due to this, the moisture in the soil will slowly evaporate, which in itself will reduce the intensity of irrigation, and therefore the humidity in the room. Such manipulations exclude the development of late blight, which is the consequence of sharp temperature fluctuations and high humidity.

Overgrown or elongated
Quite often, gardeners do not manage to transfer tomato seedlings to the greenhouse soil in time. Planting overgrown (too high) specimens has its own characteristics and looks like this.
- Make a groove 5-7 cm deep over the entire length of the bed.
- Outline the location of the bushes by placing them reclining.
- Make additional depressions for earthy lumps with roots if the seedlings were grown in pots at the previous stage. This will help avoid injury to the stems at the base.
- Water the landing sites abundantly with warm, settled water (3-4 liters for each bush).
- After absorbing water, place a lump with roots, placing the plant itself while lying down and at an angle of about 30 degrees.
- Sprinkle earth on the part of the stem from which the lower leaves were previously cut.
The described actions allow even very tall seedlings to be correctly transferred into the greenhouse soil. One of the key points in this case will be strict adherence to the landing pattern and control of the density of the arrangement of its elements. Mulching around the planted plants is carried out after their rooting. It is also important to take into account that even the longest stems are not tied up immediately after planting, so as not to damage them.


Follow-up care
After transplanting, tomatoes are given at least 5-6 days to adapt to a new place. After a week, it is necessary to gently loosen the soil around each young bush, which will improve air access to the plant root system. After that, they begin regular care, without which it is impossible to grow a good harvest. We are talking about the following important points.
- The first watering, of course, is performed on the day of planting, and the second time the plants are watered after a week and a half.After that, the growing tomatoes should be irrigated abundantly, but infrequently. This is necessary so that humidity and the risk of developing fungi do not increase.
- At the first signs of the appearance of infectious diseases, watering is stopped and measures are immediately taken to save young tomatoes. Overly affected specimens are removed from the beds, and the remaining ones are treated with fungicidal agents.
- Drying of the soil is unacceptable, which will slow down the growth and development of tomatoes.
- After all watering, it is required to ventilate the greenhouse (greenhouse).
- The feeding of young tomatoes is carried out in parallel with the second irrigation. For this, it will be good to use ready-made mineral complexes. However, gardeners often prefer conventional nitrogen fertilizers (both mineral and organic). It can be manure diluted to a liquid state or saltpeter.
- When growing tall varieties, it is necessary to provide for the presence of a structure for subsequent fixation (garter) of the stems. They should be installed no later than 2 weeks after planting. Low-growing plants do not need all this.
In situations where tomatoes are grown with one stem, it is important to track the appearance of the first so-called stepchildren and remove them in a timely manner. If we are talking about 2 or 3 stems, then you should leave 1 segment under and 2 above the flowering brush.











The comment was sent successfully.