Scheme and rules for planting tomatoes in a greenhouse

Many gardeners place greenhouses and greenhouses of various sizes on their summer cottages. They allow you to grow seedlings for further planting in open ground or early vegetables and greens. Including tomatoes are grown in them.

Peculiarities
If you plan to build a polycarbonate greenhouse on the site for growing tomatoes, then the best option would be to locate it on the sunny side so that the plants receive the required amount of sunlight during their development.
It is best to mount the greenhouse structure along the east-west axis. In this case, the seedlings will be able to receive the maximum amount of light. In addition, the greenhouse should be located in an open area - trees and buildings should not shade it.
Even in greenhouses with a small area, with rational placement, it will be possible to grow a large number of bushes. Often, different varieties of tomatoes are placed in the same greenhouse.

Such designs make it possible to grow both light-loving and shade-loving varieties, early and late-maturing species at the same time.
Indoor conditions, which are created artificially, should have the most favorable effect on the planted vegetables, as well as promote their easy adaptation and full-fledged growth.

How far to plant tomatoes?
Before proceeding with planting, you should determine exactly at what distance the bushes will be located from each other. In this case, plant varieties will play a great role.
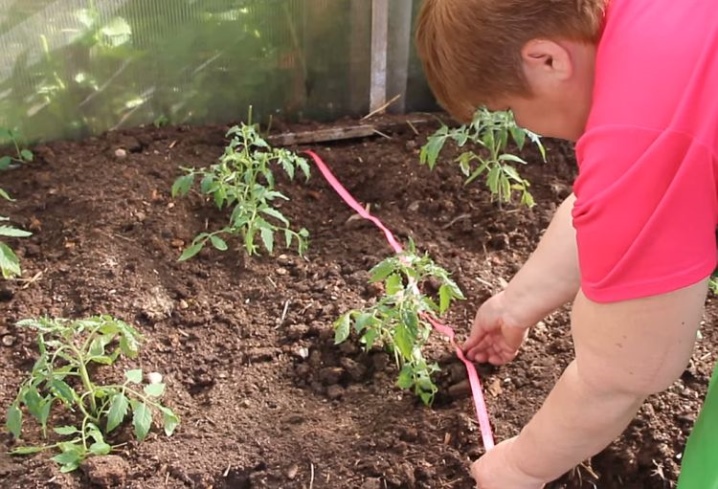

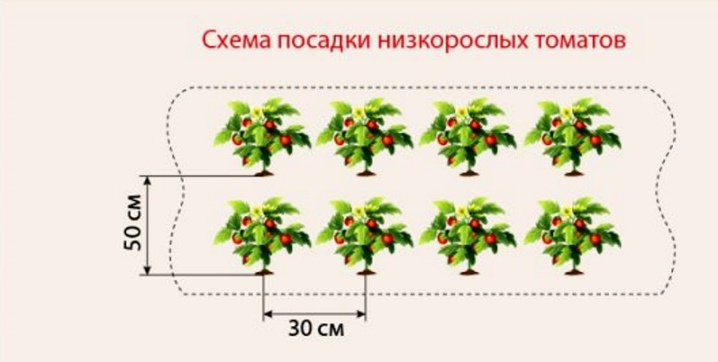
Undersized
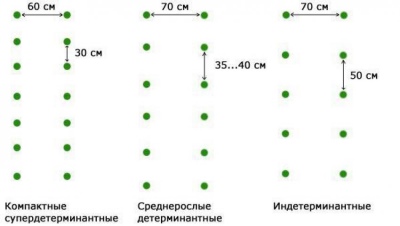
The height of such vegetation, as a rule, does not exceed 50 centimeters. Low-growing tomato varieties usually have a compact root system, a thick and powerful central trunk, strong lateral shoots. They don't need a garter.
These varieties can be planted at the rate of 6 bushes per 1 sq. meter.
Sometimes, when placing low-growing varieties, a special staggered planting is used, which makes it possible to slightly increase the number of bushes by 1 sq. meter (up to 8-9 seedlings).
Medium-sized
The height of plants of such varieties can reach 1.5 m. Medium-sized bushes need to complete the formation, as well as organize a garter. You need to plant only 3 or 4 bushes per 1 sq. meter. If you create the most favorable conditions for growing tomatoes in the greenhouse, then as a result you can get 8-9 kg from just one medium-sized bush.

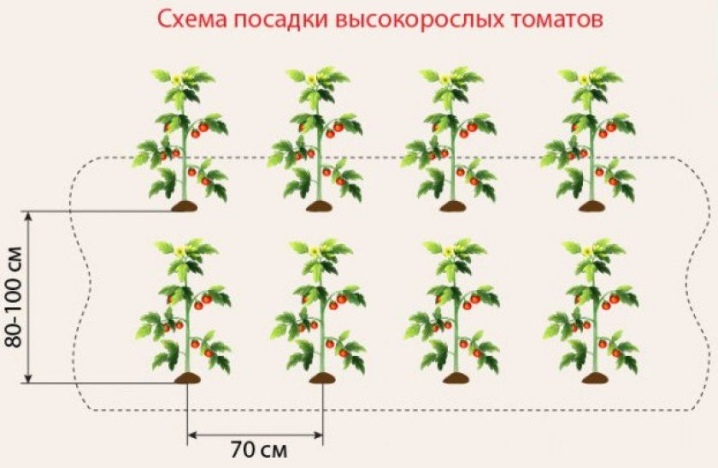
Tall
These plants are characterized by the most intensive growth. Often their height is more than 3 meters. They need a binding garter and constant pinching.
And it is better to plant them at the rate of 2 bush per 1 sq. m. To get a full-fledged harvest in the end, you should not increase this rate, otherwise you can only lose.
On one stem of this variety, up to 10 fruit clusters grow, which need light and relative freedom of development. Thickening the planting will significantly reduce yields and increase the risk of disease.
Boarding density calculation
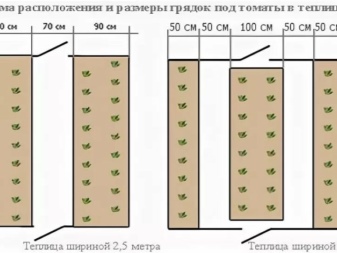
Before planting seedlings in a greenhouse, it is worthwhile to correctly calculate its density. For this, the total area of the greenhouse must be taken into account. Most often 2 or 3 beds are used. This scheme is perfect for structures with dimensions of 3x4 m. In this case, two rows are located along the side walls, the width of which should not be more than 1 meter.
The number of bushes will depend on the variety. If low-growing bushes are planted, then the distance between the rows should be at least 50 cm, but if tall bushes are planted, at least 60 cm.
In greenhouses with dimensions of 3x4 m, three rows are often planted, two of the same size on the sides and one small one in the center. In this case, two passes are formed.

But often the plants that are located in the center do not have enough light.
In larger polycarbonate structures (6x3, 3x8 m), you can organize one small bed on the sides, and make a wide bed in the central part, in which tall tomatoes can be planted. In this case, medium-sized or undersized varieties are placed in the side rows.
The listed schemes are the most common and simplest options that provide optimal planting density.
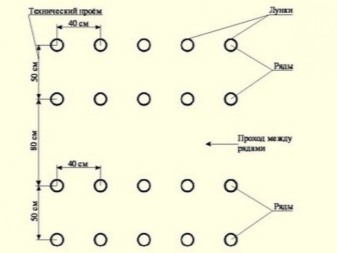
There are many other schemes for planting tomato seedlings in greenhouses of different sizes, so the planting density may vary.
- Chess order. This option may be suitable for low-growing plants. In this case, all the beds in the greenhouse are marked with lines, and then young seedlings are planted in a checkerboard pattern. The distance between bushes in a row should be 30-40 cm, between rows - 50 cm. After planting the first row, you should mark holes for the second. Each hole should be placed exactly in the middle between the planted bushes of the first row. Medium-sized tomatoes can be planted in the same way, but you will need to leave more space between the plants to provide better ventilation.
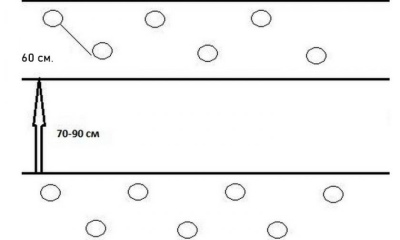
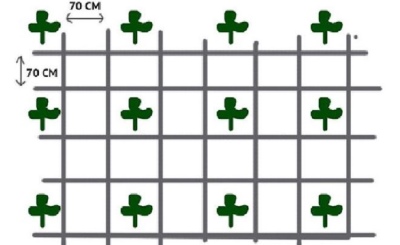
- Square-socket scheme. In this case, each tomato seedling will receive a sufficient amount of light and beneficial nutrients from the soil. However, caring for plants in the future will be more problematic. According to this scheme, planting holes are formed in the corners in a square with dimensions of 70x70 cm. 2-3 undersized or medium-sized bushes are planted in them, and a hole for watering is arranged in the center. Thus, 2-3 plants of different varieties will be placed in one place at the same time. But this option is suitable for large greenhouses.
- Parallel order. This scheme is similar to a simple scheme in rows, but at the same time crops are planted in two rows at once, which significantly saves soil and facilitates planting maintenance. Parallel order is suitable for any variety of tomatoes. The distance between young seedlings should be at least 60-70 cm. Between the belts it will be necessary to leave passages up to 1 meter.
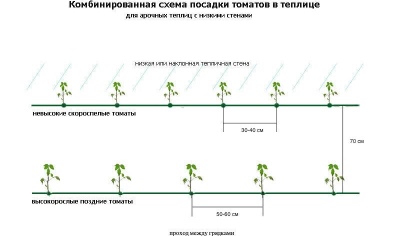
- Combined. In this case, when planting tomato seedlings, several different planting schemes are used at once. In this case, tall varieties are placed mainly in the central part using a three-row planting (2 rows and 1 passage), and undersized varieties are placed along the edges of the central part or closer to the aisles.
What will happen when thickening?
If tomato bushes are planted too close to each other, it will lead to darkening, which, in turn, will lead to a later ripening period. Vegetation with a well-developed root system will inhibit the full development of weaker varieties.
In addition, thickening will significantly complicate the process of caring for the seedlings.
The likelihood of the occurrence of various diseases and the appearance of harmful organisms will increase due to the constant contact of the leaf plates of the diseased plant with healthy bushes.
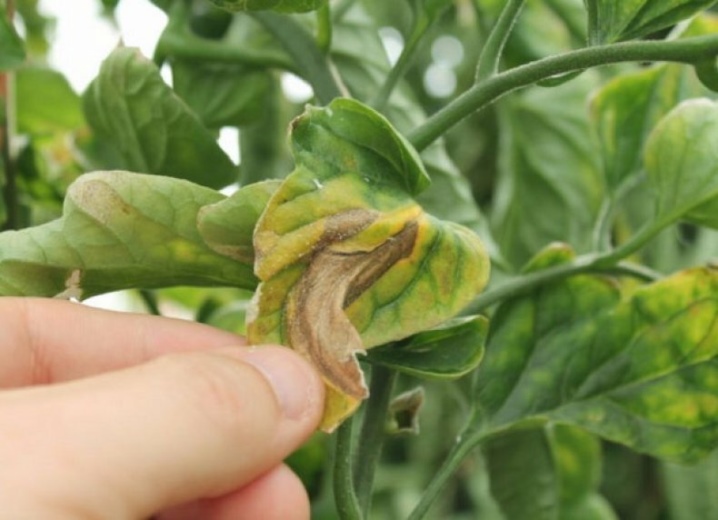

But at the same time, too rare placement of tomato bushes will be irrational, therefore, when buying seed material, you should determine in advance what species the selected variety belongs to. You need to understand that the level of yield largely depends on the correct location of the plants, the distance between them.

Useful Tips
When planning the planting of tomato seedlings in a greenhouse, it is necessary to take into account important recommendations from specialists.
- Before proceeding with the procedure, you should prepare a greenhouse structure. To do this, the soil is carefully dug up in the spring, humus, various mineral fertilizers must be added to the soil (you can immediately use complex compositions).
- 8-10 days before disembarkation, the land should be disinfected. This will destroy the larvae of various garden pests that hibernate in the soil, as well as pathogens of dangerous diseases.
- When planting large beds, it is necessary to accurately calculate the required number of tomato bushes. Most often, pegs, a rope, and a measuring tool such as a meter ruler are used to get the correct markings. If you need to plant a small number of bushes (12-15), then you can do without planning at all.
- When choosing a suitable layout for seedlings, the limited size of the greenhouse should be taken into account, so its entire area should be used as efficiently as possible.
- Too large gaps between vegetation will provoke strong growth of leaf blades, the appearance of a huge number of stepchildren. And also it will help slow down the ripening of vegetables.
- A too tight fit will result in a lack of sunlight and power. This can lead to diseases and even to the early death of plants.
- Before planting, the necessary fertilizers are necessarily introduced into the soil. They will need to be used in the process of further development of culture. Sometimes it is necessary to use special phytohormones.
- It is not recommended to increase the landing area by reducing the area of the passages. This can make it very difficult to care for tomatoes. In addition, too narrow passages will interfere with normal air exchange in the greenhouse, which will certainly affect the development of plants and yields.

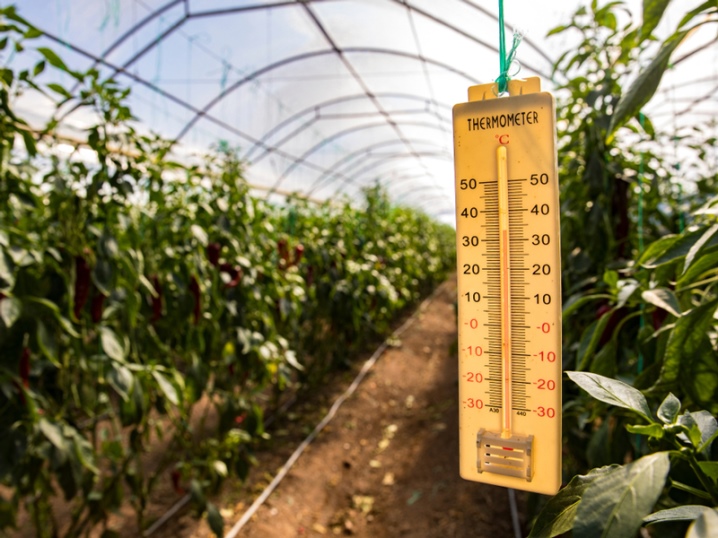
It is better to evenly place several thermometers in a greenhouse at once. This will make it easy to control the temperature regime in different parts of it.










The comment was sent successfully.