Treatment of tomatoes with boric acid during flowering

The value of a summer cottage or garden is not only in its area and competent planning. The main criterion is the fertility of the land, because depleted soil will not give a good harvest. But the soil can be fed by making efforts to restore the mineral balance in it. Particularly important in many cases, for example, for tomatoes during flowering, is considered boric dressing, which involves the use of boric acid.

Benefit and harm
It is difficult to find boron in a natural environment; plants usually remove it from the salts contained in the soil. And this is important, because boron helps to better assimilate useful components. Without boron, tomatoes, and many of them are considered the most important and valuable crop on the site, will have a difficult time growing and developing.
What are the indisputable advantages of boric acid as top dressing:
-
ensuring flowering productivity;
-
help in reducing the number of barren flowers;
-
increasing the resistance of fruits to aggressive external conditions (for example, if humidity rises in the greenhouse);
-
the sugar content in fruits decreases;
-
the risk of tomato infection with late blight also decreases, as opposed to feeding powdery mildew and spotting;
-
tomatoes are stored better and longer after harvest.

Boron may be present in the free (that is, undiluted) fertilizer composition. But it is still easier, more convenient and more rational to use boric acid. And this should be done more often, because boron is not particularly well absorbed in the soil, therefore regular spraying is required.
Of the disadvantages of boric acid, one can note the risk of getting burns if the dosage is violated, as well as death with preliminary deformation of the bush with an excess of feeding. The fact that there is an excess of boron can be judged by the unnatural glossiness of the leaves, the domed shape of the plate. The boron balance in the earth can be restored with potassium.
Usually, tomatoes are treated with boric acid several times per season. It makes sense to process the seed material with it before planting, which will strengthen the immunity of future seedlings. Foliar acid treatment will enhance flower growth and prevent shedding.
Top dressing during the fruiting period will protect the tomatoes from spoilage, accelerate their ripening, improve the taste and, of course, the aesthetic appearance.
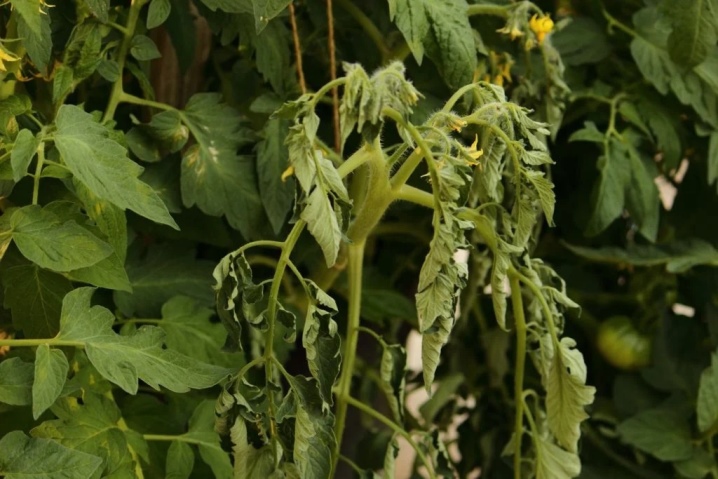
Tomatoes should be fed with boric acid if:
-
the stems have become brittle;
-
the leaves are curled around the edges;
-
the leaf plate turns pale;
-
the upper shoots dry up;
-
the veins on the leaves become dry, turn black or turn yellow;
-
brown or light spots appear on the tops;
-
the base of the stem darkens;
-
the flowering of the plant is insufficient;
-
flowers, ovaries crumble.
Most often, boron deficiency occurs on sandy and sandy loam soils. This trace element does not linger in them, which must be taken into account by the owner of such a site.

How to breed?
Boric acid needs to be bought in a store for summer residents, gardeners, farmers. The packaging always contains detailed, understandable instructions. The main thing to remember is that acid does not dissolve in cold water, it only needs hot water. If the crystals of the substance do not completely dissolve in water, the culture may get burned after such spraying.
The preparation of a solution for different purposes has some differences.
-
Seed treatment. For 1 liter of warm water, 0.2 g of boric acid is taken. The solution is poured into a convenient container. On top of this liquid, gauze or tissue identical to it is placed, on which the seed is poured.So the seeds remain lying for a day. Before they go to the ground, the procedure is repeated.
-
Land cultivation before planting seedlings. The acid is diluted in a ratio of 2 g per 10 liters of water (warm, previously boiled).
-
Watering. To carry out root dressing, take 10 g of boric acid per 10 liters of water. At first, the earth is plentifully, not sparing, watered with water. Top dressing is carried out only in wet soil.
-
Spraying. This procedure is considered to be more effective than root feeding. It is easier to make it with a fine spray gun. Flowers, ovary and leaves should be sprayed. First, the beds are treated with a weak manganese solution, a week later it is replaced by a boric acid solution, and a week later - an iodine solution. If the purpose of spraying is to protect tomatoes from late blight, 1 teaspoon of acid is diluted in 10 liters of water. If the task of the acid is to preserve the flowers and ovary, 10 g is diluted in the same 10 liters.


It is important not only to properly dilute the solution, but also to find the right time for processing. There are no special subtleties here, but there is a list of rules, the implementation of which guarantees the result.
Application
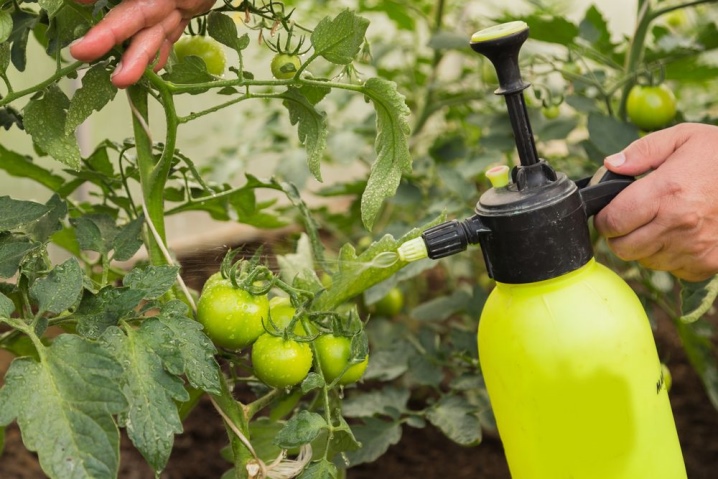
Spraying is the effect of feeding on the plant itself, its aboveground part. It is considered more effective, but also more dangerous, in the sense that the risk of crop burns with this treatment increases predictably. But you should not disdain root feeding, complex actions will give results.
Spraying
The first rule is that tomatoes need to be treated with boric acid 3 times a season. The first time at the end of June: the solution perfectly accompanies the appearance of ovaries on the bushes, which will be a certain guarantee of good fruiting. To be more precise, it will give weighty prerequisites for this. The very first treatment will become a kind of vaccine for tomatoes, which will protect them from late blight.

Attention! The first spraying is carried out no earlier than 2 weeks after planting the seedlings in the ground. This applies to both the greenhouse and the open field.
Spraying number two is the budding period, but the third time the plant will receive boric acid during the period of active flowering.
What rules still apply for spraying:
-
before feeding the bushes, the beds are watered abundantly;
-
spraying is carried out only in the early morning or at sunset;
-
solution is the only possible form of using boric acid, dry powder is never used (it will simply burn the plant);
-
after spraying, it is important to leave the greenhouse door open;
-
watered bushes, which are still slightly wilted, cannot be sprayed - the turgor must return, and only then the plant is ready to receive feeding.
Sprinkling with a spoon or even picking up the solution in the palm of your hand (albeit with gloves) is not a tactic to follow. Only in a bottle that works like a spray bottle (or is). This ensures the safety, uniformity and quality of the procedure.

Under the root
Root feeding is a delicate moment, because during it it is advisable not to touch the green part of the tomatoes. A stream of water with boric acid diluted in it should be directed strictly into the ground, namely in the root zone.
Here are the features of root watering.
-
In the seedling phase, as well as at the beginning of flowering, it is most useful to feed the plant with boron - precisely in the form of root influence.
-
The frequency of watering depends on whether the seedlings were grown at home, or the bushes were purchased from the market or from a store before planting. If this is a home seedling, watering occurs 3 times per season - twice when processing the seedlings and 10 days before flowering. If these are acquired bushes, then you need to feed the roots only before budding begins.
-
Watering tomatoes with an acid solution should occur at intervals of a month. This is if watering is carried out with a concentrated solution.If the solution is ordinary (we can conditionally say - weak), then no earlier than 2 weeks after the first feeding, the second should be carried out.

An important and dangerous moment is an overdose. It often happens when a caring farmer decided to fertilize black soil or salt marshes "just in case". So the soil will contain boron in excess, which is dangerous for the culture growing in it. Surpluses also occur with the wrong dosage, using a concentrated solution more often than it should. An overdose will automatically make the plant toxic.
Boric acid is not particularly dangerous for humans. The solution that gets on the skin is not likely to cause burns or irritation. But the substance will accumulate in the body (if you work with it carelessly, without gloves), and leave it for a long time. A high concentration of the substance is dangerous for pets.


And, of course, you need to control your own work: after the first feeding, observe the tomatoes. If their appearance has deteriorated, it is possible that the method of preparing the solution is violated, or the plants are too actively processed. It makes sense for novice gardeners to keep a diary with entries (you can electronic), where the dates of fertilizing and some moments of observation of the growth and development of plants will be entered.
Successful path to the harvest of your dreams!
How to process tomatoes with boric acid, you will learn from the video below.













The comment was sent successfully.