Using boric acid for tomato ovary

Growing any fruit and vegetable plants in a greenhouse or garden beds is a long and rather laborious process. To get the desired result in the form of a good harvest, you must follow many rules and follow a variety of procedures. One of them is feeding with the help of various fertilizers, since plants need some trace elements to ensure active development. When it comes to growing tomatoes, boric acid is one of the most common and effective dressings.


Peculiarities
Boric acid has the chemical formula H3BO3. In nature, it is included in the composition of a substance such as sassolin. It is a mineral found in some mineral waters and natural hot springs. Boric acid can be obtained from this mineral by hydrolysis or by mixing acid with borax.
Boron takes an active part in the development of the educational tissue of plants; it has a stimulating effect on cell division. This helps in active growth.
The importance of boric acid as a plant fertilizer can hardly be overestimated. Although, in fact, tomatoes do not specifically require the acid itself, but its main constituent part, namely boron. The trace element is included in many industrial fertilizers sold in specialized stores. However, many gardeners still prefer to use boric acid. This substance is very useful for the rapid growth and active development of plants, because it helps in the assimilation of other nutrients and trace elements from the soil. Boron has a positive effect on tomato seedlings, improves its nutrition. Thanks to this, a rather favorable basis for the further growth of tomatoes is formed.

Boric acid solution is useful in that it promotes the active growth of tomato bushes and reduces the risk of contamination of tomatoes with various diseases, such as late blight.
And also, thanks to spraying tomatoes with such a solution, metabolism is normalized and activated. Boric acid has a very beneficial effect on the tomato ovary, ensuring its normal development and preventing possible shedding. In addition, it helps to increase the number of flowers - accordingly, the number of future fruits will be greater. And also this is a fairly effective means for ensuring the safety of fruits during overflow: the decay process will not develop if excessive moisture is observed. Feeding tomatoes for ovary with boron improves the taste of the vegetable, due to the fact that the level of sugar content in the fruit increases. And this is due to the activation of the intake of carbohydrates in the fruits.

Boron shortages are especially noticeable in the first weeks of growth. If you do not feed the plants in time, then you can not hope for a good harvest. Boron deficiency is not at all difficult to determine. It is necessary to carefully examine the bushes. The appearance of the plant will perfectly speak for itself. Top dressing using boric acid is required if:
- dry spots appear on the fruits of tomatoes;
- leaf petioles are uneven and too brittle;
- flowering is not strong enough;
- ovaries fall off in large quantities;
- old leaves quickly turn yellow and die off;
- many thin and weak stems grow from the root;
- from above the shoots die off;
- despite flowering, ovaries are not formed;
- there are no new shoots that come from the main stem.


Of course, tomatoes must be fertilized, but a certain measure must be observed in everything, and when spraying with boric acid for the ovary of tomatoes, you cannot overdo it either. Not enough boron is bad, but too much boron is also harmful. To understand that the plant is oversaturated with boron, you need to see if the following symptoms are observed:
- small specks of brown color can be seen on the leaves, and over time they grow to the entire leaf, as a result of which it simply dies off;
- the leaves bend and begin to resemble a dome in their shape;
- necrosis is noticeable on the lower leaves, they become yellow;
- the leaves of the bush acquire a noticeable glossy shine.


It should be noted that boron saturation depends on the type of soil on which the tomatoes grow.
For example, on acidified and swampy soil, boron is likely to be insufficient. There is also a small trace element in calcareous alkaline soils, calcareous and sandy soils. However, on loamy and clayey soils, there is almost no significant boron deficiency. When deciding on spraying tomato beds, the type of soil must be taken into account. This will help avoid boron deficiency or excess.

How to prepare the solution?
Boric acid is sold in the form of a white crystalline powder that is odorless. In such a powdery form, it is categorically impossible to use it as fertilizer and top dressing. It is required to prepare a solution from the powder using the most ordinary water. During the preparation process, it is necessary to ensure that the boric acid crystals are sure to completely dissolve. If the prepared solution contains powder granules, then the plant may suffer damage in the form of chemical burns.
The recipe for the preparation of the solution depends on the purpose and the period of its use.
- In order to soak tomato seeds in one liter of water, it is necessary to dilute 0.2 grams of boric acid. In this case, the water should be hot enough (approximately 50-55 degrees Celsius).
- For the purpose of spraying according to the developed feeding plan, the solution is prepared in the following proportion: approximately 1/2 teaspoon of powder (if the soil contains little boron, then you can take 1 teaspoon), add to a container with 200 grams of boiling water and carefully dissolve the crystals of the powder there. After the final dissolution, the resulting liquid must be cooled and 10 liters of water must be added.
- To set fruits, boric acid is required to dissolve as follows: add approximately 1 gram of white powder to 1 liter of hot water. You can use the prepared mixture for spraying as soon as it has completely cooled down. For high-quality processing of a plot of 10 sq. m of beds with tomatoes, you need to use approximately 1 liter of the prepared solution.

Processing nuances
When growing tomatoes, regardless of where they grow - in a greenhouse, on beds in the open field or in an apartment - boric acid is used as the main top dressing. It is especially useful for plants that grow in apartments. Nowadays, it is not uncommon for several tomato bushes to grow on the balconies or windowsills of city apartments. But such plants are rather weak, because they do not have enough space, nutrients and sunlight. Apartment tomatoes without feeding, without a sufficient amount of nutrients, will not bring a harvest, or it will be quite insignificant.
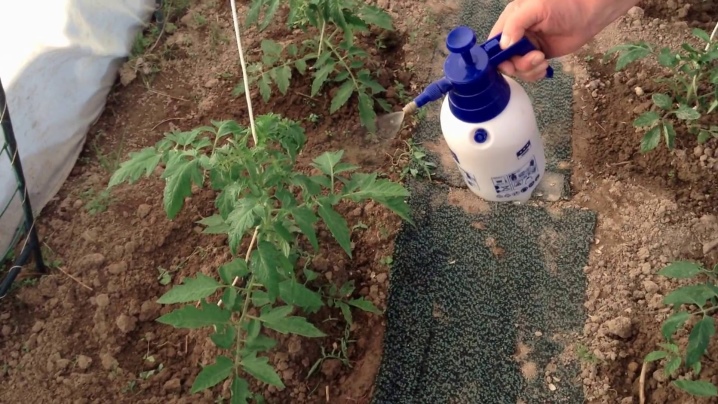
Usually, foliar feeding of tomato bushes is used. It gives a more effective result, because boron is characterized by a very rapid leaching from the soil, it does not stay in it for a long time.Because of this, when the solution is introduced under the root of the bush, the useful composition does not have time to reach the plant directly. Therefore, root feeding will not be effective enough. It is possible to water the ground with a solution, but then more solution will be required than when spraying. Therefore, it is better to evenly process the entire bush. Spraying should be carried out from a spray bottle on all stems and buds, leaves, flowers, fruits should be treated.
The result can be noticed quite quickly - within 3-4 days after the processing process, it will be visible.

It is necessary to spray tomatoes with fertilizer only in the morning or evening. It is allowed to use it during the day, but only in cloudy weather, since immediately after treatment the bushes should not be exposed to direct sunlight. If this happens, then severe burns may occur, which, in turn, may even lead to the death of the bush. Do not process in the rain.
To get a large crop of tomatoes, you will have to process tomatoes with boric acid solution not once, but several times. First - before planting, then - when buds begin to form, during flowering, during the beginning of fruit formation, and additional feeding is also possible.
The first time you need to use fertilizer before planting. To do this, it is recommended to soak tomato seeds in a solution for about one day. Seeds can rise to the surface, and this should be avoided. Therefore, it is best to dip the seeds into the solution in gauze bags. Thanks to this soaking, germination can be improved, in addition, this procedure will strengthen the protective functions of the plant against damage by various diseases.

2 weeks after planting tomatoes on permanent beds, it is worth doing the prevention of late blight and other diseases. And additional use of boron solution may be necessary if there is a noticeable lack of boron. You can spray as needed, but this procedure cannot be performed more than once every 10 days. In order not to harm the tomato bushes, too large doses of fertilizer should not be applied.
Correct feeding assumes an even distribution of the mixture throughout the bush. Boron does not have the property of spreading from one point throughout the plant, so the entire plant should be sprayed - each stem and leaf should receive its own rate of useful composition. With inaccurate distribution of fertilizer, one part of the bush will receive an excess of boron, and the other will not receive it at all. Naturally, such feeding will not bring the desired result.
Another nuance that must be taken into account in order to properly feed the tomatoes is the temperature of the boron mixture when spraying. A solution that is too cold or too hot will not be effective enough.
The temperature of the boric acid solution should be approximately equal to the ambient temperature.

Without treatment, tomato bushes are at risk of falling ill with late blight, powdery mildew and other diseases. Late blight is especially dangerous for tomatoes. It is a fungal disease that most commonly affects plants that are already bearing fruit. Signs of this disease:
- dark spots located on the stems and individual leaves;
- the flowers dry up before the fruit is created;
- whitish bloom on the shoots;
- brown spots on fruits.
Boric acid is good for coping with this disease and getting a bountiful harvest. For a successful fight, you need to use iodine, potassium permanganate and boric acid. In the prevention of fungal diseases, the dosage is 1 teaspoon of powder per 10 liters of heated water. This solution is used for processing tomato bushes. To maximize the prevention effect, it is recommended to spray with a weakly concentrated solution of potassium permanganate a week before boron spraying.To consolidate the result obtained, it is worth treating the plants in a week with an iodine solution.


Precautionary measures
Use boric acid as a top dressing for the ovary of tomatoes with great care. Despite the usefulness of this fertilizer, the bushes can be irreparably damaged if used improperly.
The most common mistake is the wrong preparation of the solution. If boric acid is added to the water in the wrong proportion, then instead of a useful fertilizer, a harmful mixture will turn out. And also it will not be possible to achieve the desired effect if the composition is introduced into an alkaline soil. The bush will not be able to get as much boron from this type of soil as it needs.

Despite the fact that boric solution is considered useful and even necessary for the ovary of tomatoes, you should not use it thoughtlessly.
You need to focus on the reaction of the plants themselves. If after the first treatment a good reaction was noticeable, then further treatment with this preparation is quite appropriate. If the plants reacted badly, then it is better to refuse this drug in favor of other types of fertilizers.
Boric acid can be purchased not only in the form of a powder with white crystals. A 3% alcoholic acid solution is sold in pharmacies. It is sold in bottles of various sizes (10 ml, 15 ml, 25 ml and 40 ml). The alcoholic solution is used for medicinal medicinal purposes as an antiseptic. As for the use of this particular form of boric acid for feeding tomatoes, this is unacceptable. First of all, the concentration of the acid itself in the pharmaceutical solution is very insignificant, only 3% in 70% ethanol. That is, to prepare a mixture of the required concentration from an alcohol solution, it will take about 350 milliliters. In addition, alcohol can only have a negative effect on the plants themselves.

Helpful hints
Boric acid is an excellent fertilizer for a variety of vegetables, including tomatoes, to make plants stronger and increase yields. The main useful recommendations when using boric acid for the purpose of ovary and active growth of tomatoes:
- only powdered boric acid should be used;
- completely dissolve crystals in heated water;
- feed the plants with a solution of ambient temperature;
- more effective foliar feeding;
- spraying with boric acid solution can be carried out several times;
- the distribution of the composition over the plant must be uniform.


Observing all the above recommendations, fertilizing in time and carefully observing the reaction of tomatoes to feeding, you can get a bountiful harvest of juicy sweet tomatoes.
Boron is an essential element for the ovary of tomatoes, it stimulates the formation of flowers and ripening of fruits. The use of boric acid helps protect the plant from harmful diseases and increase yields. Tomatoes respond well to such fertilization.
Bushes in the beds bloom profusely, many ovaries are formed on them, you can get a rich harvest.


For information on how to properly prepare a boric acid solution, see the next video.













The comment was sent successfully.