Tobacco mosaic of tomatoes: description and treatment of the virus
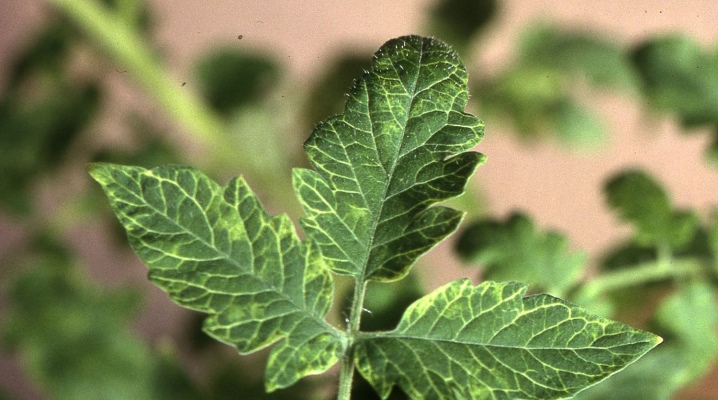

Every gardener dreams of laying the dinner table with the best and healthiest vegetables grown on their site, for example, tomatoes. These are beautiful, healthy and tasty vegetables. However, growing them is far from easy. Often on the way there are various diseases, for example, tobacco mosaic of tomatoes. This article will focus on the virus that causes this disease, the treatment of the disease on the leaves and fruits, as well as measures to combat yellow spot and the peculiarities of growing tomatoes in greenhouses.

Description of the disease
Many vegetable growers grow tomatoes in their summer cottages or greenhouses, while they often encounter tomato mosaic of tobacco. This disease is caused by the rod-shaped virus Tomato mosaic tobamovirus, known since the last century. At that time, entire tobacco plantations perished from it.
The mentioned virus is persistent and tenacious, it is difficult to fight it. When it gets into the soil for 3-4 years, it remains dangerous for many plants, affecting, in addition to tomatoes, cucumbers and peppers. Treatment of diseased plants is possible only in the early stages, therefore it is very important to recognize the virus as early as possible. In the future, you have to destroy them, pulling them out of the garden and burning them. A withering shoot indicates the presence of a disease, while the fruit looks ugly and spoiled. And also such signs include a distorted shape and rot in the pulp.

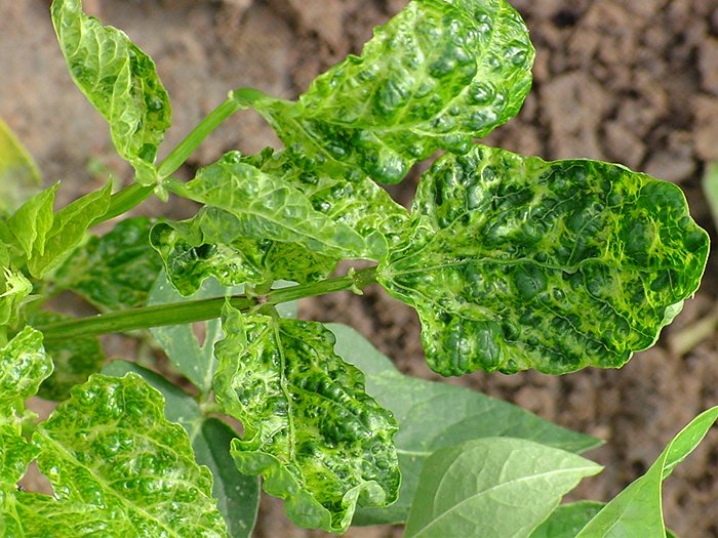
Signs of defeat:
-
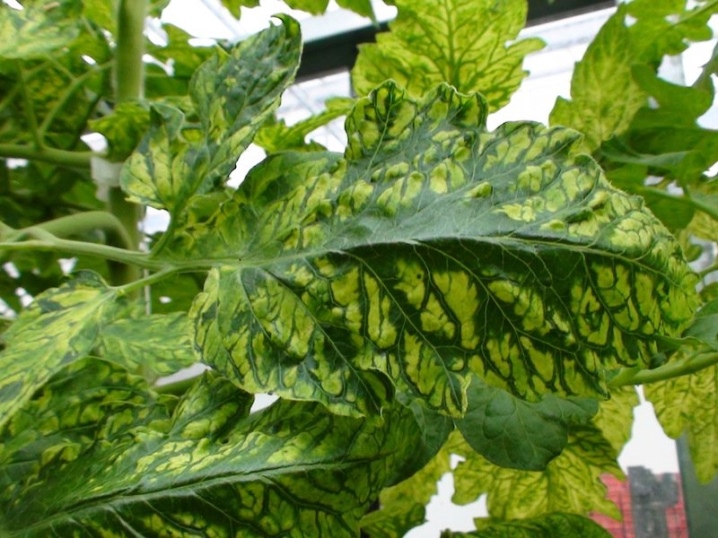
spotting on tomato leaves, alternation of lighter color with a darker one;
-
the presence of leaves with a wrinkled surface;
-
the edges of the sheet plate are deformed and dry out.
Already in the first days, a viral infection leads to wilting of plants. Their color becomes pale or colorless. Tomato leaves form numerous folds, have different sizes, and sometimes become filamentous. The affected parts are clearly visible on the fruits, their outer color is bright yellow, darkening is noticeable in the inner part. It begins with a cup, gradually expanding to the top of the berry. The process ends with the death of the tissue. In this case, the fruit is covered with a brown mesh.
The peel of such tomatoes bursts, and the seeds, along with the pulp, fall out. The disease begins with the upper shoots, further covering the bushes completely.
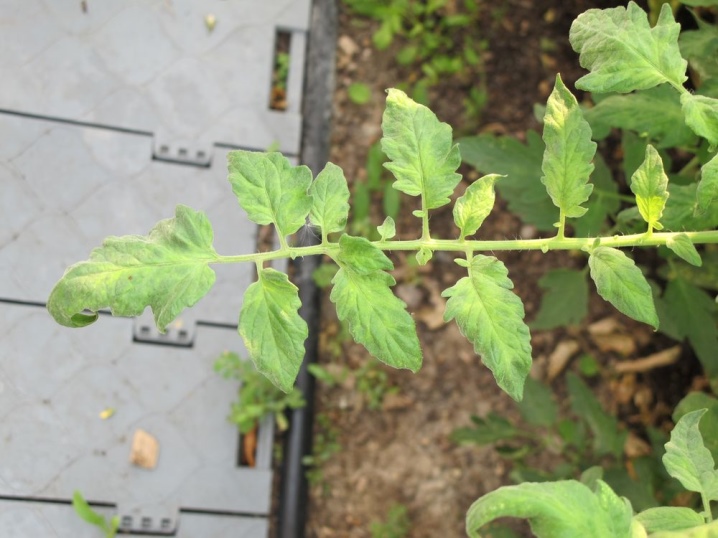

Reasons for the appearance
There are many reasons contributing to the defeat of tomatoes by tobacco mosaic. Several factors become the cause of the appearance:
-
contaminated soil;
-
the infection is spread by pests - ticks, aphids, beetles;
-
the virus can get to the site together with the acquired infected seeds or planting material;
-
the disease is also transferred if the juice of a diseased plant gets on a healthy tomato.
Most often, tobacco mosaic affects plants that are grown in seedlings. The reason here lies in agricultural technology with the use of a large number of different operations, which often contribute to the spread of the disease.
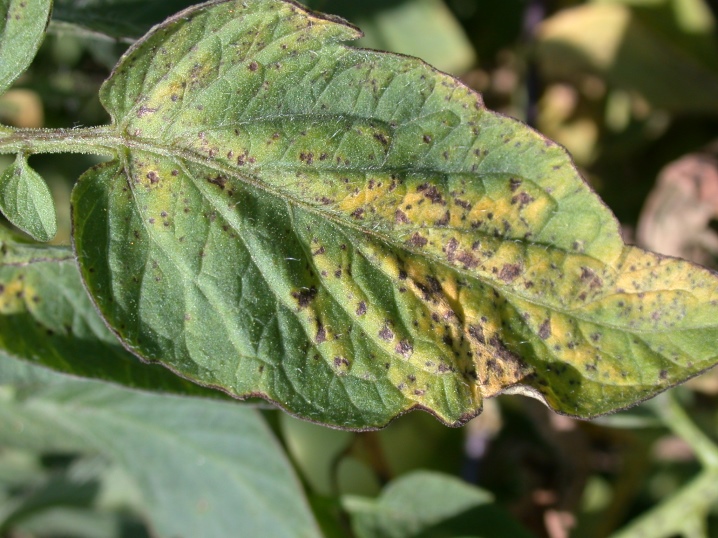

Bushes that are grown both outdoors and in greenhouses tend to ache with tobacco mosaic.
Certain errors in agricultural technology contribute to this:
-
waterlogging of the soil due to excessive watering;
-
mechanical damage to the shells of plants, opening the way for the penetration of infection;
-
high thickening of tomato bushes when planting;
-
poor ventilation of the bushes.
An increased moisture content, a sharp change in temperature, as well as weeds left on the beds under the bushes, stimulate the infection of tomatoes with the virus. Using garden tools without disinfecting treatment is also a possible way of spreading the infection to other areas, which can lead to wider infection.
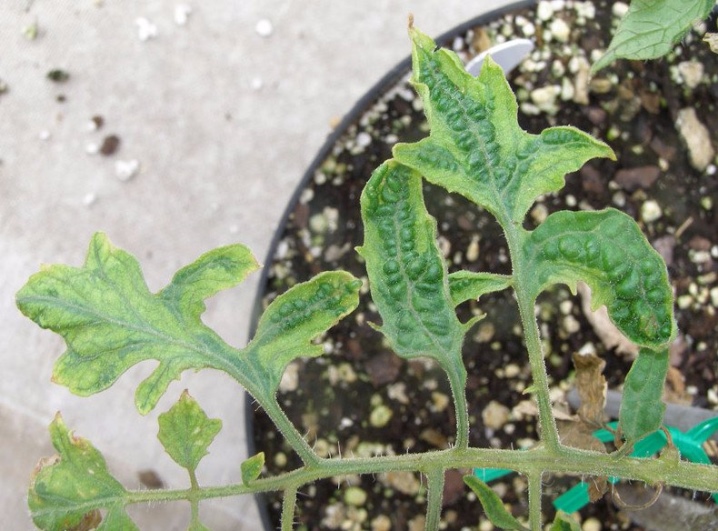

Treatment methods
Immediately after the virus hits the tomatoes, it begins to progress, therefore, the plants need to be treated immediately. It is difficult to combat tomato mosaic tobacco because the virus is very persistent.
-
Having noticed the first signs of the disease in the form of mosaic spots, it is necessary to immediately destroy the affected plants or separate them from healthy ones.
-
The affected areas are trimmed to healthy tissue, and the sections are treated with potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide or chlorhexidine.
-
At the initial stage of plant disease, the plantation can be treated with "Karbofos" - this will help protect healthy plants, since pathogenic microflora will cease to form. To prepare such a solution, 75 g of the drug is dissolved in 10 liters of water. Re-processing is carried out after a decade.


A more radical way is to use a variety of fungicides and drugs that can cope with most viruses. Gardeners more often than others use "Maxim" or "Lamador". When using them, it is important not to forget that these are toxic chemicals. When working with these drugs, it is important to adhere to the instructions, use individual protective equipment in the form of glasses and gloves.
In order not to abuse chemistry, you should water the tomatoes with a milk-iodine solution. To prepare it you will need:
-
milk - 1 liter;
-
iodine - 10 drops;
-
water - 10 liters.


Plants are treated with this solution twice, with an interval of a week. Under the influence of iodine, bacteria die, and milk contributes to the formation of beneficial microflora.
Prevention measures
When starting to grow tomatoes, it is important to remember that it is easier to prevent the disease on the beds than to fight it later. That is why it is so important not to forget about prevention. You need to start with proper seed preparation. An effective means of combating mosaic is to soak the seeds for a couple of hours in a weak solution of potassium permanganate. After that, the seeds are removed and washed in clean running water. All this is done immediately before planting in the ground.
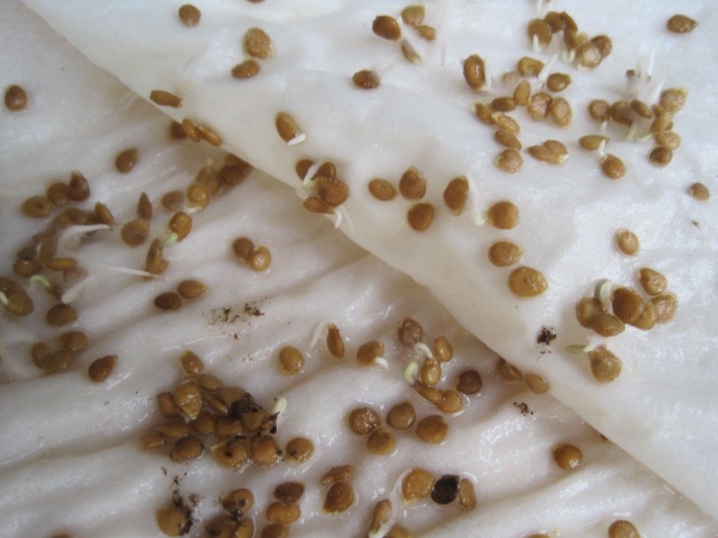

Since the virus can be in the ground, antibacterial soil cultivation is carried out. If the soil is taken for growing seedlings, it must be heat treated in an oven with a temperature of at least 70 degrees.
The next stage is planting seedlings in open beds. In the selected area, you should dig up the ground and fill it with a disinfectant solution. To prepare the solution, use:
-
boric acid - 1 tsp;
-
10 l. water.
Potassium permanganate can be added to the solution so that the liquid becomes pale pink.
When planting seedlings, you should keep the distance between the plants, the bed should not be densely planted. The optimal distance will be half a meter between the bushes. It is also important which crops will grow in the neighborhood. So, the neighborhood with nightshades or cucumbers is undesirable.
2 weeks after planting the seedlings in the ground, you can start preventive treatment. First, it is sprayed with 2% copper sulfate, or 5% Bordeaux liquid. Spraying is repeated after a couple of weeks. This will protect tomatoes not only from tobacco mosaic, but also from other diseases.
If in previous years there was an outbreak of tomato mosaic on the site, it is recommended to replace the top fertile layer, removing the old one by at least 10 centimeters, while peat and humus should be added to the fresh soil. You will have to work hard, but there is no other option for getting rid of the sore.

To completely exclude the disease, you must:
-
sterilize instruments;
-
timely destroy weeds;
-
regularly carry out pest control.
When choosing seedlings or seeds, it is better to use varieties that are resistant to tobacco mosaic, such as Pasadena, Lord, Zozulya. However, it is worth knowing that these varieties do not guarantee 100% resistance to the virus. There are no drugs that give an absolute result, which means that it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the plants, and if an infection is detected, start a fight.














The comment was sent successfully.