Folk remedies for late blight on tomatoes
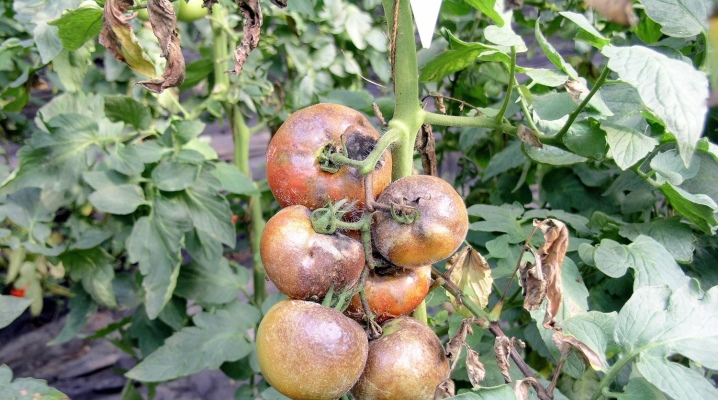

Late blight, known to many as brown rot, is a fungal disease caused by Phytophtora Infestans. The disease is notoriously familiar to most gardeners. It affects tomatoes, potatoes and other crops, preferring plants grown in greenhouses and ruining up to 70% of the crop. Some gardeners, noticing the appearance of phytophthora, immediately rush to the store for special means, others resort to folk methods. About them, their pros and cons, and will be discussed.

Advantages and disadvantages
Before starting treatment, you first need to deal with the symptoms of the disease. Phytophthora is a fungus, respectively, multiplies by spores. These spores are easily carried by water and wind, adore moist environments and are highly frost-resistant. Fighting them is very, very problematic, especially if the moment is missed, because late blight is called a "plant eater" for its rapid development and fatality.
Here are some reasons to raise the alarm:
- the appearance of brown spots and stripes on the leaves and stems;
- white fluffy bloom on the underside of the leaf after rain;
- rotting of brown marks at high humidity, drying out - in dry weather;
- rotting fruit, even if they looked healthy when picked;
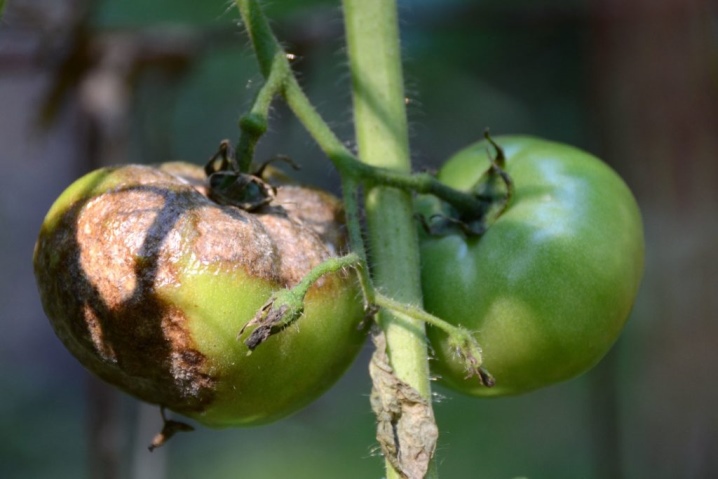
- spreading brown spots under the skin of the fruit.
The disease manifests itself on tomatoes in the third decade of July. Fighting with her is to wage a constant war, since it is almost impossible to completely eliminate disputes. Preventive measures are needed. Greenhouses should be treated for late blight in the spring, as soon as the air temperature reaches +10 degrees - it is at this temperature that spores are activated.
If you decide to fight late blight with folk remedies, you need to imagine their pros and cons.

Pros:
- in most folk methods, powerful pesticides and other substances that can harm the health of humans and domestic animals are not used;
- homemade formulations are often cheaper than purchased ones;
- many folk recipes have been tested for decades of use;
- some remedies that help treat phytophthora are also an excellent top dressing for tomatoes (iodine, kefir, potassium permanganate, ash, etc.).
Minuses:
- the effectiveness of the funds is by no means always confirmed by science;
- some of the components can still be dangerous if they are in excess or incorrectly used;
- if the recipe you have chosen suddenly does not work, there is a risk of wasting precious time and losing the entire harvest;
- a number of recipes require a certain skill, experience and very careful following of the instructions when preparing.
Thus, we can conclude that it is better to leave complex home remedies for late blight for experienced gardeners, and for beginners - turn to simple recipes or ready-made remedies.

What can be processed?
If you decide to treat late blight with home remedies, here are some of the most popular and proven ones. Some of them are easy to make, while others will have to tinker with.
Milk whey and kefir
A liter of kefir diluted in 5 liters of water is the most elementary way to prevent late blight. They just need to spray the tomatoes a couple of weeks after planting and repeat the treatment weekly.
A well-known recipe for gardeners with milk whey (you can use kefir instead) and iodine. Ingredients: 1 liter of whey, 15 ml of hydrogen peroxide (3%), 40 drops of iodine per 10 liters of water. The whole plant should be sprayed with the prepared mixture.Milk whey will act as a shield against spores, forming a film on the tops. Another similar option is to dilute kefir or whey one to one with water, strain and, again, spray the tomatoes with the mixture.
The disadvantage of all methods based on sour milk is fragility, they will not survive even a mushroom rain, which means that such processing should be carried out regularly. But this is an environmentally friendly and safe option.

Salt
For protection (specifically for protection, not for treatment!) From late blight, saline is well suited. Once on the plant, it forms a film that does not allow spores to pass through. The recipe for the solution is as follows: for 10 liters of water, 1 glass of table salt is needed. The resulting liquid must be sprayed on the plant, removing the previously affected fragments, if any.


Vinegar
The use of a 9% vinegar solution is no less effective. Dissolve 100 ml of vinegar in 10 liters of water and regularly process tomatoes with this mixture.

Hot water
However, water can help without additional additives. With the help of hot water, already harvested green tomatoes can be saved from late blight. You just need to remember that the method works against those disputes that have not yet managed to penetrate deep into the fetus.
The course of action is as follows:
- remove cuttings;
- rinse the fruits under running water;
- pour water heated to about 60 degrees into a saucepan, bucket or basin (not boiling water!);
- immerse the fruits in a container;
- hold the tomatoes in water for about 2 minutes;
- quickly transfer the tomatoes to cold water;
- dry the fruit.
These simple manipulations will allow the tomatoes to ripen calmly and get to your table, and not to the trash bin.

Garlic tincture
A cocktail of garlic and iodine is another home remedy for late blight. A vigorous mixture is prepared according to the following recipe: 200 grams of water is 20 grams of iodine, 200 grams of chopped garlic, 30 grams of laundry soap. First, garlic is added to the water. It should be infused for a couple of days, after which the composition should be filtered and diluted in 10 liters of water. After that, you can add the rest of the components. The recipe is interesting, although many gardeners strongly recommend adding significantly less iodine to it or completely abandoning it in this mixture.

Zelenka
To 5 liters of water, you need to add 20 drops of brilliant green and, if desired, 5 drops of iodine. The volume of brilliant green and iodine is best measured with a pipette. The resulting mixture of seedlings should be processed two weeks after moving to open ground or a greenhouse, and the procedure must be repeated every 14 days. This method is one of the controversial ones, since it is not entirely clear how exactly brilliant green affects tomatoes. But even children know how she colors everything that she touches. The marks you get when preparing the mixture will stay with you for a long time.
Experienced gardeners use the recipe only as another preventive measure.
Potassium permanganate
The second antiseptic used in the fight against fungus is potassium permanganate. It works well on plants, and its constituent potassium and manganese help plant growth. When using potassium permanganate, the recipe must be strictly observed so as not to damage the plant.
With potassium permanganate, you can process tomato seeds by lowering them for a couple of minutes in its solution (1 gram of potassium permanganate per liter of cold water), or you can spray the plants themselves with a solution. This should be done with a pale raspberry or pink, but by no means purple solution in late spring - early summer and in mid-July, if there is no intense heat. From the moment of precipitation until the moment of spraying, the funds must have elapsed at least a day.

Tomato fruits and leaves are sprayed once every 7 days with a mixture of 3 grams of antiseptic per 10 liters of water. In addition, to combat a disease that has already manifested itself, a mixture of potassium permanganate with garlic is used - 100 grams of ground garlic is insisted in a glass of water for a day, keeping in a place protected from direct sunlight. Then a gram of potassium permanganate is added to the infusion.Before use, the concentrate of the composition is diluted with 10 liters of water and used every 10-15 days.
Many gardeners process already harvested fruits with potassium permanganate in case of danger that phytophthora will kill them before they ripen. Tomatoes are kept in warm water with potassium permanganate, dried and wrapped in paper. In this form, they are left to ripen.

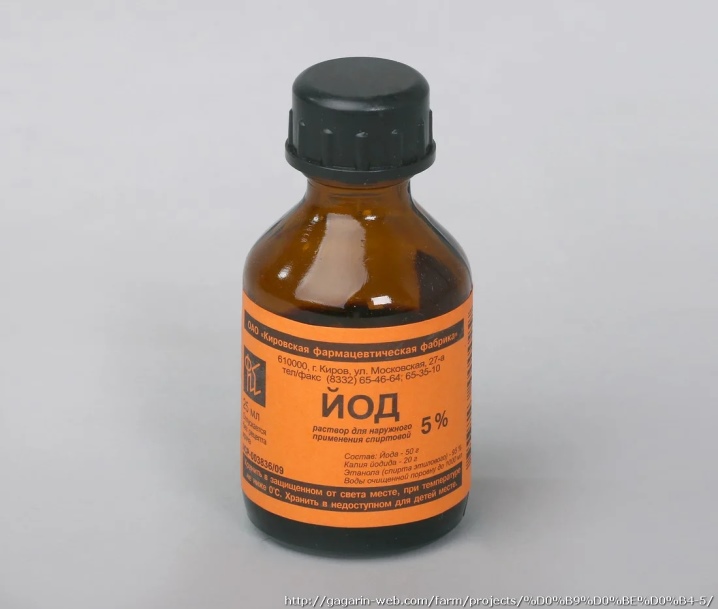
Iodine
You will need to dilute 4-5 drops of iodine in 10 liters of water. Iodine is an excellent disinfectant, known to everyone and everyone, and is also a useful fertilizing for plants. The solution obtained from it, infused for 6 hours, should be sprayed on the bushes every 15-20 days. Best the enemy of the good. The concentration of iodine in the mixture can be increased only when feeding during the fruiting period, however, here the opinions of gardeners differ, since there is a risk of burning the plant.

Calcium chloride
The next remedy is a method of dealing with already a strong defeat of the fungus. It will need a 1% calcium chloride solution. And since a ten percent solution is sold in pharmacies, you will have to spend a little time diluting it by dissolving 200 ml of the substance in 2 liters of water.
With the finished composition, you need to process the bushes, carefully pour it on the stalk - the key carrier of the disease from bush to fruit.

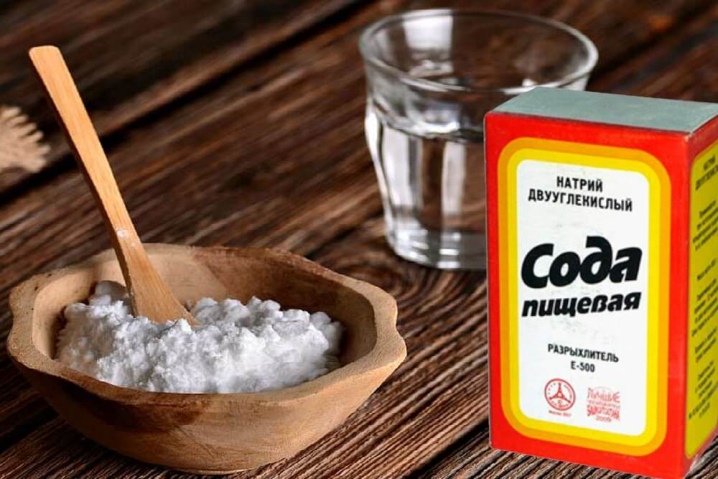
Soda
Soda solution is one of the simplest protective methods. In 10 liters of water, you need to dissolve a glass of soda and spray the tomato bushes with this liquid 10 days after they are planted. You can add grated laundry soap to the soda. By the way, soda, dry or dissolved in water, is an excellent remedy for ants and aphids. But it is dangerous to sprinkle powder on young shoots or water the roots of tomatoes abundantly with a solution - there is a great risk that the plant will die along with the pests.

Ash
Simple wood ash is not only a good fertilizer, but also a help in the war for the harvest with late blight. Dissolve 5 liters of ash in a bucket of water and let it brew for 3 days, stirring occasionally. Drain the infusion and add water to a volume of 30 liters. Fill in 35 grams of soap, pre-grind it.
You need to use the composition 10 days after planting seedlings, before flowering and after the appearance of ovaries.

Toothpaste
Gardeners call a mixture based on a whitening toothpaste among the effective methods of combating late blight. A tube of paste must be diluted in 2 liters of water, then add water to 10 liters when the paste begins to dissolve. It is necessary to spray the soil and the plants themselves with the composition - both healthy and already diseased.

Herbal infusions
Even dry grass can help protect tomatoes. Pour a kilogram of hay with 10 liters of water, add a handful of urea and let it brew for 3-4 days.
Infusion of tomatoes should be sprayed every 2 weeks.

Tree tinder fungus
For this mixture, you will first need to find a tinder fungus, which will not be difficult in most regions of Russia and the CIS. Fresh mushroom (100 grams) must be chopped, dried, and then minced. The resulting powder must be dissolved in a liter of boiling water, allowed to cool and strain. It is necessary to spray the plant with this liquid once every one and a half weeks. Processing should be done in calm weather, in the morning.

Bordeaux mixture
This method can be called a transitional link between folk remedies and special ones presented in stores. In order not to harm either yourself or the plants, the spray mixture must be prepared and applied strictly according to the instructions, accurately observing the dosage. If you are not confident in your abilities, purchase a ready-made drug. If you want to do everything yourself, then you will need to buy quicklime and copper sulfate. Bordeaux mixture is used in 3 concentration options: 0.75%, 1% and 3%.
The ratio of ingredients should be as follows:
- 100 grams of copper sulfate, 75 grams of lime, 10 liters of water - 0.75%;
- 100 grams of vitriol, 150 grams of quicklime, 10 liters of water - 1%;
- 300 grams of copper sulfate, 450 grams of lime, 10 liters of water - 3%

An example of a recipe for a mixture.
- Pour 2 liters of hot water into a non-metallic container with a volume of 10 liters.
- Add 100 g of vitriol to the water.
- Mix.
- Pour in another 3 liters of water.
- Prepare a solution of lime in the ratio of 150 g per 1 liter of water.
- Prepare a container with cold water (4 liters).
- Pour diluted lime into cold water.
- Mix.
- Strain the mixture through cheesecloth.
- Carefully pour in a solution of copper sulfate.
- Mix.
- Dip a metal object into the solution. If it turns red, add a little more lime.
The solution consumption should not exceed 2 liters per 10 squares. When processing, spray especially thoroughly on damaged plants. During the season, tomatoes should be sprayed with the product 4 times.
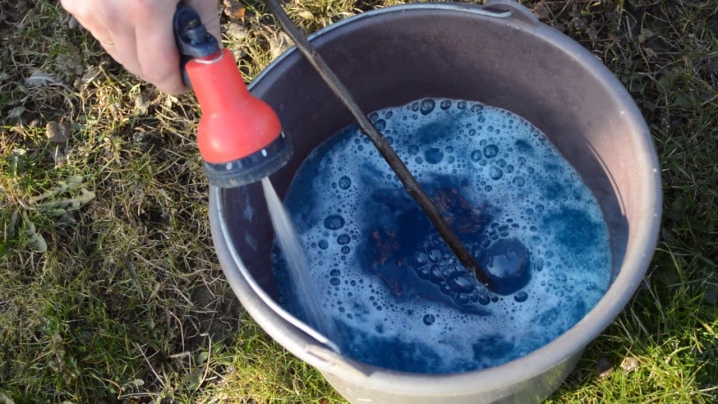

Do not under any circumstances process plants with fruits. This can be hazardous to your health. This method requires special attention and care, but it is one of the most effective and efficient.
Precautionary measures
Although most methods seem completely harmless, letting things go and forgetting about safety rules is the last thing to do. Even the usual iodine, potassium permanganate, brilliant green and peroxide do not cease to be drugs just because we are faced with them since childhood. And almost any medicine, as you know, quickly becomes a poison, if you do not care about the dosage. What can we say about lime or copper sulfate.
So, when preparing solutions and using folk methods of waging war with phytophthora spores, you need to follow the following rules.
- If the recipe contains pharmaceuticals, insecticides or other chemicals, you should work with them with gloves and a respirator.
- The room where the mixture is prepared must be well ventilated.
- Finished medicines must be stored in signed containers, out of the reach of children and animals.
- It is important to strictly follow the recipes and not experiment with their composition and ratio of components.
- Be careful! Not all products can be used on those tomato bushes where fruits have already formed. An example of such a composition is Bordeaux mixture. It is strictly forbidden to work with its components without gloves and breathing protection!
- Do not smoke while preparing and using Bordeaux liquid.
- Drinking or eating during the manufacture of most drugs and working with them in the beds is also not recommended. The same mixture of vitriol and lime is the strongest toxin.
- If after treatment you experience symptoms of poisoning, shortness of breath or discomfort in the eyes, consult a doctor immediately.

But don't be intimidated by the complexities. Recipes with kefir, salt, soda, ash, etc. are completely harmless, effective and easy to implement, they will help get rid of the disease at the initial stage. You can start with them, and then, if preventive measures to combat the infection did not have the expected effect, it is up to you to decide. You can, strictly following the rules, continue the fight with folk methods, choosing the ideal one, or you can go to a gardening store and choose from ready-made tools. Good luck!

For folk remedies against late blight, see below.













The comment was sent successfully.