Types of aphids and how to deal with it
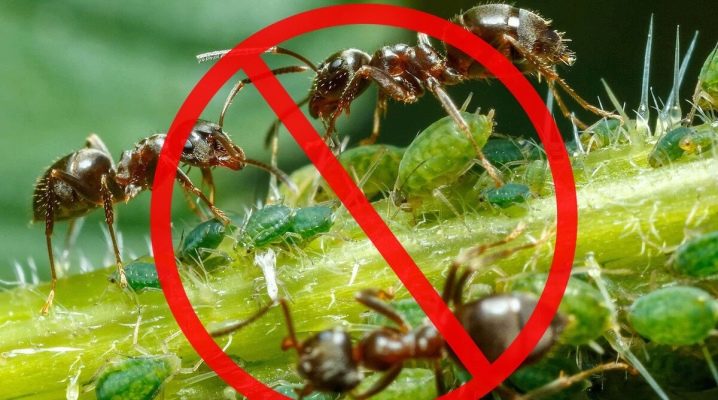

The appearance of aphids in the garden or vegetable garden is called a big misfortune. This insect causes significant damage to the harvest of fruit and berry crops, moreover, it has great potential for rapid development and reproduction. Where does this pest come from and how to treat it in order to get rid of it forever - we will talk about this in our review.
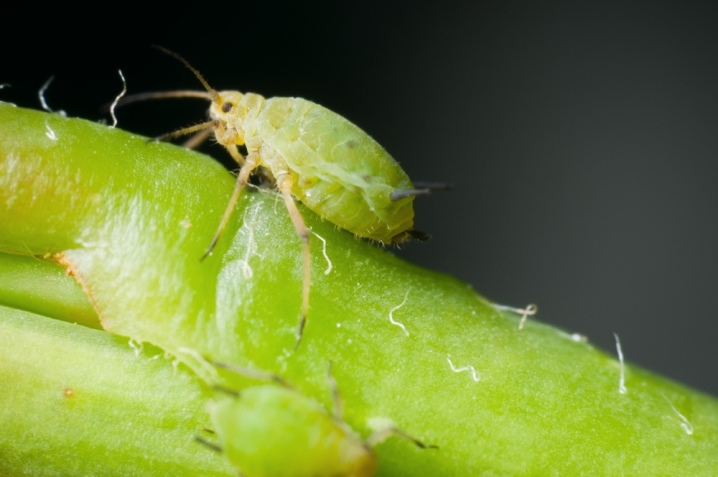

What is it and why is it dangerous?
Aphids are small sucking insects. The body is elliptical, soft. Depending on the species, the insect can look green, brown, black, dark beige and even red. There is a trunk on the head - it can be long or short, sharp or blunt, with which the aphid pierces the succulent tissues of plants.

The winged species have two pairs of wings. Legs are thin, elongated. Females have glands on them that secrete pheromones and attract males. The body is covered with whitish fluff or bumps, this escapes the garden pest from moisture and pollution.

The appearance of an insect poses a great threat to green shoots and seedlings. Aphids parasitize on green tissues, sucking out vital juices and nutrients. This leads to a weakening of landings, which is complex in nature:
- shoots die off;
- green leaves are deformed and wither;
- the growth of crops slows down;
- flowering and fruit formation are delayed.
Through the saliva of an insect, pathogens of fungal and viral diseases are transmitted from one plant to another. According to statistics, 80% of viral pathologies are carried by this particular insect.

The secretions of the pest are the main source of food for ants - using them, they also become carriers of viruses and carry them throughout the district.
Aphids also harm pollinating insects... They mistake her pad for nutritious nectar and die. If you do not take prompt action, then after a couple of generations you can say goodbye to the thought of a rich harvest.
The active reproduction of this pest begins with the arrival of spring heat, when larvae hatch from the clutch laid for the winter. They instantly dig into the green parts of the garden host plants and suck out their life juices. Soon after molting, they transform into wingless females - these are fertile individuals that do not lay clutches, but give birth to live larvae. The larvae that appeared in this way are ready for a new round of reproduction after 10-14 days.
Thus, each of them in 3-4 weeks is capable of giving more than one generation with a total number of up to several hundred thousand new insects.
In the second generation, winged individuals appear that can move long distances. This aphid reproduces on young plantings and settles on related crops. In general, over the summer, up to 15 generations of aphids of all species are born: both winged and wingless.
The colony that appeared in the fall consists not only of females. She is already heterosexual, males can be found in it - they fertilize females. And those, in turn, arrange their clutches for wintering on perennial plants. With the onset of spring, this cycle begins again.

You can identify aphids with the naked eye:
- clusters of small insects are visible on buds, green shoots and leaves;
- the affected areas are sticky to the touch;
- with a large number of pests, a sooty fungus may appear on the leaf plates.
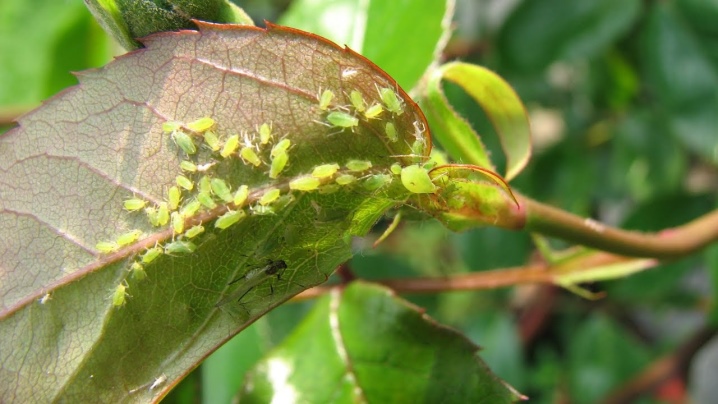

Species overview
In total, there are about 4 thousand varieties of pests on the planet, and a third of them live on the territory of the Eurasian continent.
- Melons - ubiquitous insect 3-4 mm in size. It has a green color and a slightly elongated body shape.

- Leaf gall and red gall - insects measuring 3 mm. Lead to the appearance on the leaves and juicy shoots of swellings of a yellowish or purple color.


- Beetroot - a pest with a length of 3-4 mm. It has an oval shape, slightly widening at the sides. It is most widespread in the south of our country.
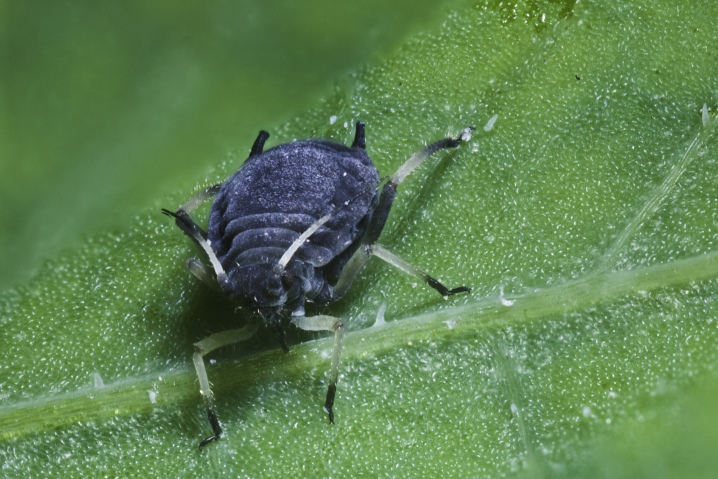

- Cabbage - a pest with an extended oval body. Coloring - green, length - 3-4 mm. It is found in all climatic zones, except for the subtropics.
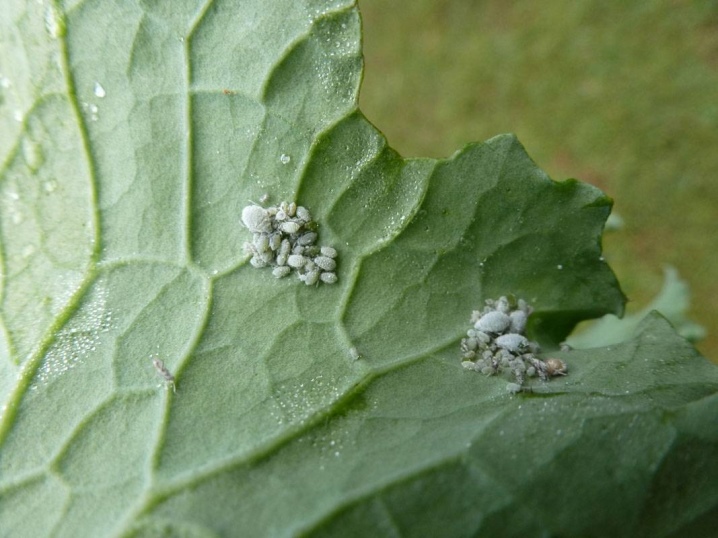

- Phylloxera - attacks exclusively grapes. Leads to the appearance of bloating on the roots and a deterioration in yield. The insect has a yellowish-brown color, the size does not exceed 2 mm.


- Rosanna - aphid of green color, lives in all regions of Russia.
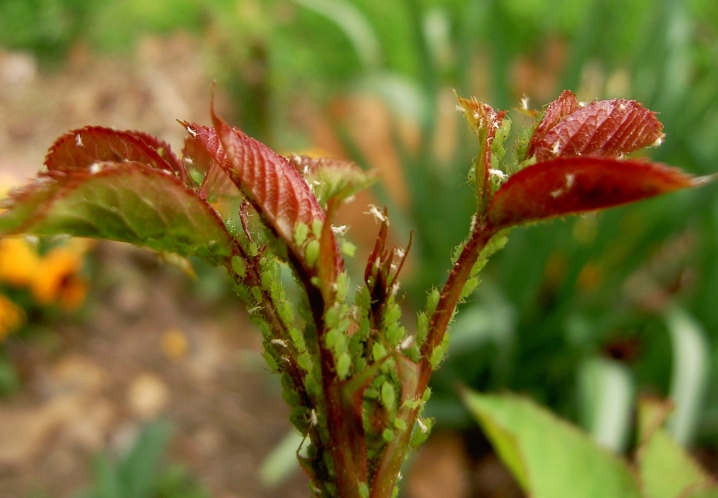

- Plum - lives mainly in the Caucasus and in the European part of our country. It has a small size - only 2-3 mm, pale green coloring and an oval-elongated body.
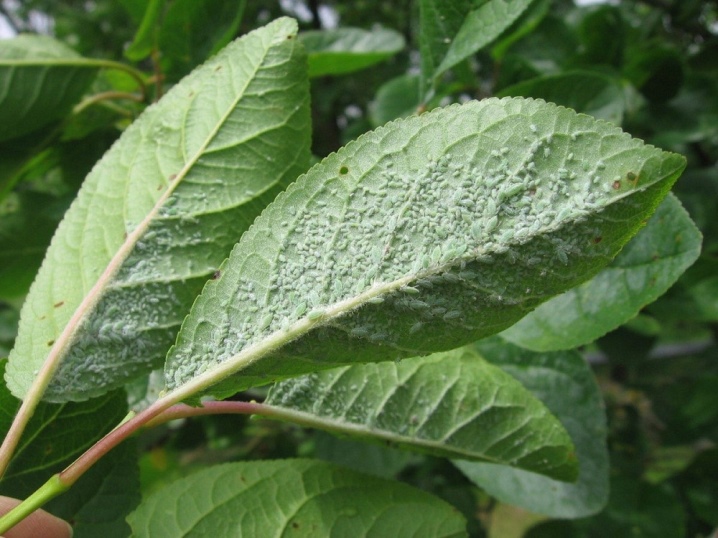

- Yablonnaya - a green pest with a dark red head and black legs. Got spread in Asia and Europe.

- Large potato - can grow up to 3-5 mm, has a green color. It is capable of affecting plants in open areas, as well as in greenhouses.

- Large peach - one of the largest varieties (up to 5 mm long). The body is gray, the head is black. It is a parasite on fruit trees and bushes.
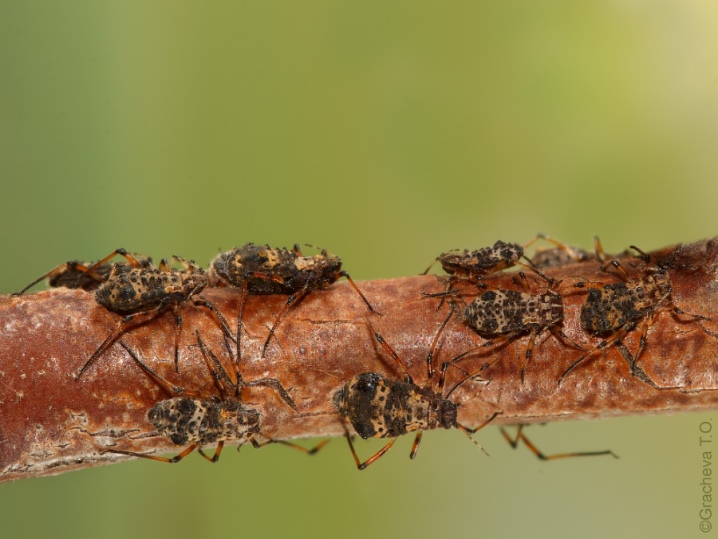

- Cherry - the adult is colored black. In spring, this insect is very active, but with the arrival of summer days, when the young juicy green areas of the plant begin to woody, the bulk of the population dies.
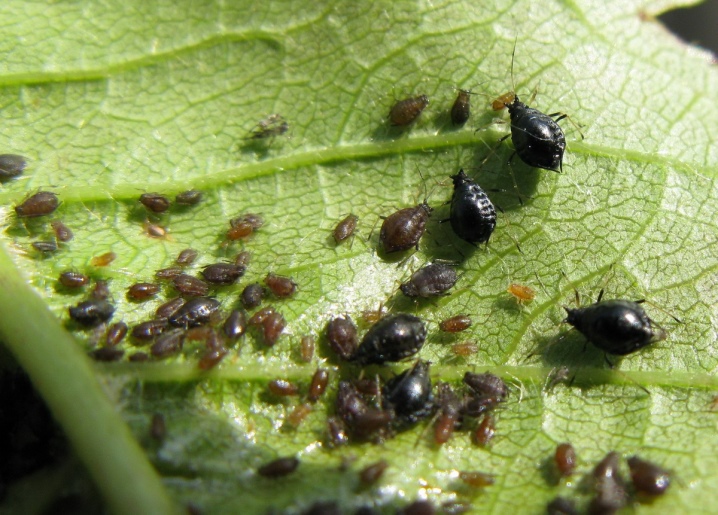

- Floury - aphid dark beige with a whitish bloom and bristles on the sides.
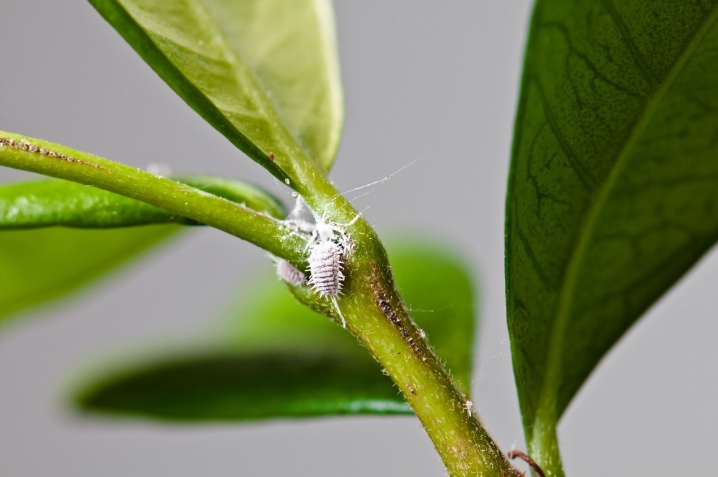

- Home - affects many plants, has black, white, bright red or green colors.
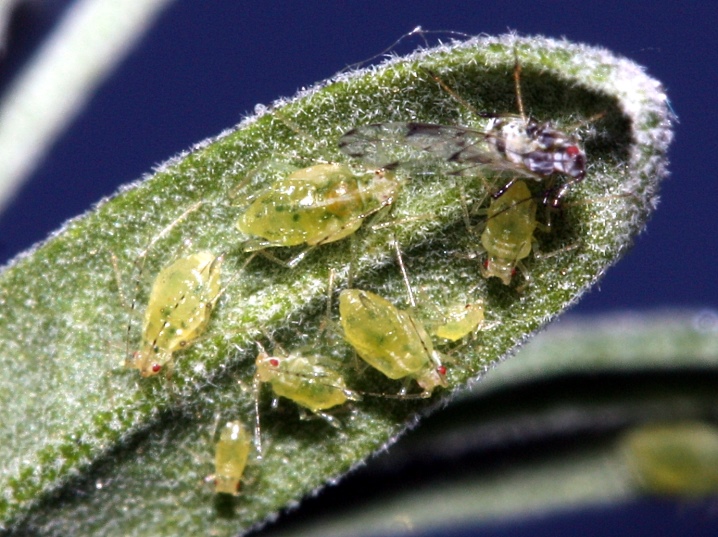

What plants are affected?
Despite its size, this small pest is quite voracious and does not miss a single horticultural crop.
- Gall aphid affects currants and legumes. It feeds on the vital juices of sunflower, beet, peas, beans, as well as viburnum and jasmine.
- Cucumber variety prefers melon plants: watermelon, melon, pumpkin... It can be found in cucumber, zucchini and beetroot beds.
- Cabbage is common on representatives of the cruciferous family: radish, radish and cabbage, as well as carrots.
- Rose aphid causes damage to plantings of apple, pear, raspberry, strawberry, as well as rose hips and roses.
- The apple species actively reproduces on fruit plants: irge, hawthorn, is found on mountain ash, apple trees and pears.
- Plum and large peach aphids settle on plums, cherries, and also on apricot and cherry plum.
- Cherry can be found on cherries, sweet cherries and morel.
- Greenhouse varieties can kill potatoes, bell peppers, eggplants, and herbs: dill and parsley.


Houseplants can also suffer from aphids: dracaena, dieffenbachia, pelargonium, Kalanchoe. The insect infects balsam, violets and begonias.
An overview of anti-insect drugs
There are many methods of aphid control: chemical and biological. The choice of the most effective depends on the growing season of the affected crop.
Chemical
The greatest result in the fight against aphids is given by chemical methods. Modern industry has developed many specialized drugs, this poison helps to remove the insect colony in the shortest possible time. All of them belong to the group of mild insecticides and bring minimal harm to the environment. The use of serious compounds such as acaricides is not recommended.
Depending on the type of working component, all chemical preparations are divided into three groups:
- pyrethroids for intestinal effects: Decis, Iskra and Confidor;
- nicotine formulations: "Vector", "Ratibor", "Bombardier";
- organophosphorus compounds: Aktellik, Fufanon, Karbofos, Aktara, Nurel and Fitoverm.



The group of biological products stands apart "Bitoxibacillin", "Lepidocid", "Bicol", "Batsikol", "Trichopol".

All of these drugs are sold in the form of ampoules or powders. If the dosage is observed, they destroy the population in 3-4 hours.
If the use of insecticides did not give a 100% result and complete disposal of the plant from the pest, re-treatment should be carried out. However, it must be remembered that there are temporary restrictions on the use of drugs:
- pyrethroid formulations can be used no earlier than three weeks after the first treatment;
- organophosphorus - not earlier than in 2 weeks.
The use of chemicals provides high efficiency, but also has its drawbacks. Their use at the stage of bud emergence, flowering, fruit ripening and harvesting is not allowed. However, aphids can grow in the garden and in the vegetable garden at any vegetative stage. It is necessary to deal with it promptly, therefore, in some cases, other means are used.

Biological
At the stages when it is impossible to poison aphids with chemicals, biological means of controlling garden pests come into play. They involve the use of natural insect opponents and do not cause any harm to crops, people, pollinating insects and pets.
- Scarers... In this capacity, plants with a pungent and persistent odor are used. This can be mustard, chamomile, lavender, marigold, tansy, coriander, and fennel. They are planted in places where aphids move as tightly as possible.
- Attractors... The opposite method of influence, it involves attracting aphids to other parts of the garden to crops that do not have a specialized agricultural value. These are nasturtium, as well as mallow and begonia. Such plants are planted in large groups away from fruit crops, it is best to grow them on the leeward side.
- Predators... Of all living things, the garden aphid is at the bottom of the food chain. It has no natural defenses, so it becomes food for many birds and other (larger) insects. Natural enemies of aphids are wrens, bedbugs, as well as ladybugs, hoverflies and earwigs. Small birds can also kill aphids: robins, tits, sparrows. To attract them to your site, you can plant other fragrant plants and equip birdhouses with nest boxes.



Folk remedies
You can remove aphids using folk remedies. They involve spraying the affected areas with broths and infusions. Processing is carried out with regularity once every 7-10 days, you can spray the beds using a manual or professional spray gun. It is advisable to do this in the evening or cloudy weather.

It is advisable to include soap in the working composition. The addition of this component helps to improve adhesion to the surface and thereby provides a prolonged action of the treatment.
Among the most effective recipes, the following are distinguished.
- With onion. 100 g of onion and onion husks are finely chopped and poured into 3 liters of water. Kept in a warm place for 5-7 hours and add 10 g of liquid soap.
- With iodine. 2 tsp iodine is dissolved in 5 l of water and 50 g of soap is added. Use this mixture immediately after preparation.
- With soda... 2 tbsp. l. soda is dissolved in 4 liters of water. Add 20 g of crushed tar soap and stir until complete dissolution. This composition provides effective protection for up to 1 month.
- With chamomile. 200 g of pharmacy chamomile is infused in a liter of water for 12-15 hours. After this time, add another 1 l of water and add 20 g of soap.
- Marigold, dandelion and mint infusions give a good effect. For their manufacture, 300-400 g of raw materials are poured into 1.5 liters of water and 5-10 g of soap is added, preferably with tar.
- With alcohol... To treat trees, 200 ml of vodka is dissolved in 3 liters of water and 30 g of a soap base is added. For ornamental and fruit crops, the volume of the alcohol-containing component is reduced by 2 times.
- With vinegar. 15–20 ml of vinegar essence (250 ml of vinegar 9%) is poured into a bucket of water and 50 g of liquid soap is added.
- With hydrogen peroxide. 50 ml of peroxide is mixed with 2 tbsp. l. alcohol, add 3 g of dishwashing detergent and dissolve in 1 liter of water. You need to use the composition within 15 minutes after mixing.
- With garlic... Finely chop 100 g of garlic cloves, pour 0.5 liters of water and let it brew well for 3 days. After this time, the prepared solution is diluted with water in a ratio of 1 to 2.
- With tobacco. 100 g of tobacco is poured into 3 liters of water, kept for two days. This concentrate is diluted with cool water (the latter should be twice as much) and the affected plantings are treated. A good effect is the addition of 100 g of ash to this solution.
- With needles. 3 kg of pine needles are poured into 10 liters of water and left to infuse for a week with daily stirring. Before use, pour in the same amount of water and spray.
- With citrus... Aphids can hardly tolerate the aroma of citrus. To combat it, you can use any ready-made aromatic oil or tincture of orange peel, lemon. However, such a composition has increased biochemical activity, therefore it must be used in minimum dosages.





Also, aphids are afraid of boric acid.
Prevention measures
To prevent the appearance of aphids in the garden, it is necessary to adhere to the rules of agricultural technology.
- Remove weeds and cut root growth in a timely manner - it is in them that the pest often makes its clutches.
- Destroy anthills, as ants are carriers of aphids. To do this, you need to dig them deeper and fill them with hot water. On the boles of large trees, belt traps are usually arranged.
- Follow the feeding rules. An excess of nitrogen should not be allowed, since the rapidly growing green mass becomes a source of food for the pest.
- And of course, do not forget about mulching, loosening the earth and periodic sprinkling of plantings.... The main part of the aphid colony can be washed away with a jet. However, keep in mind that it is not recommended to irrigate the plants with too cold water - this can weaken the immunity of the crops.

















The comment was sent successfully.