How to build a greenhouse made of wood?

A greenhouse is the only way to guarantee the cultivation of heat-loving crops even in the middle lane (not to mention more northern latitudes). In addition, greenhouses facilitate the preparation of seedlings and the cultivation of early varieties of plants common for the Russian climate. The only problem is that it can be quite difficult to correctly make the greenhouse itself. There is one attractive solution to this problem - the use of wood. But here there are subtleties that must be taken into account in order to achieve success and get a stable rich harvest.






Peculiarities
An element such as a greenhouse must necessarily be in any summer cottage. Anyone can make it with their own hands, deservedly proud of the result obtained, and in addition, individual work makes it possible not to adapt the dimensions of the building to ready-made standards. There are many samples on the market, including polycarbonate, but with all the advantages of this material, it is not warm enough and costs too much.
Before starting work, you need to pay attention to:
- exact location;
- illumination level;
- the required area;
- material type;
- financial resources that can be spent on the construction of a greenhouse.




The service life of high-quality wood is quite long, and you can buy suitable material in all hardware stores. Or even use the materials left over from the previous carpentry and locksmith work. All work is easy to do with your own hands without any special and especially complex tools.





Comparison of materials
Wood is better than other materials because:
- it is environmentally friendly;
- under the influence of strong heat or ultraviolet radiation, toxic substances do not appear;
- work can be done with standard joinery elements;
- the design is always the best in terms of the ratio of lightness and strength;
- if something goes wrong, some part will fail, replacing the problematic part will not be difficult;
- a frame made of timber or boards allows you to mount additional devices and working elements;
- costs are noticeably less than when using metal, agrofibre.

Even an untreated tree will quietly serve for 5 years, and if the frame is made according to all the rules and is well protected, there is no need to fear for its safety in the next decade.
Interestingly, even the weaknesses of wooden structures, done correctly, can be turned into strengths. By choosing the most competent location of the greenhouse on the site, it is possible to minimize the negative impact of the shadow. Due to special processing, the susceptibility of wood to harmful insects and fungi, to fire and dampness is sharply reduced.


Ready-made greenhouses are mostly made from other materials, but the good thing about wood is that it allows you to get away from standardized patterns.
Anyone can use round timber or processed sawn timber at their own discretion. Extension of the service life of wooden structures is achieved by placing them in special metal sleeves.
In the opinion of professionals, the most promising species are larch, pine and spruce, which themselves rot only slightly and are very strong.Oak, teak and hornbeam wood is too dense and difficult to work with, it is unlikely that it will be possible to prepare the necessary structures without an electric tool in an acceptable time frame. In addition, the cost of such a tree is higher than that of a conventional one.


The pine massif is popular due to its hardness and low likelihood of decay.
It is not difficult to find such material, although it can hardly be called very cheap. Larch rots even less than pine, and this difference is due to the increased concentration of resins. And the larch massif only gets stronger over time. Only the part that will directly touch the ground needs to be processed in a special way.
Regardless of the specific breed, the material should be selected very carefully. Knots and chips, blue areas and cracks should not be too numerous. For work, it is permissible to use wood with a maximum moisture content of 20%, otherwise no attempts to improve it will lead to success.


Types of structures
Single-slope greenhouses can be either attached to the main building or stand-alone structures. It is not difficult to recognize gable greenhouses - they are all rectangular and the roof slope exceeds 30 degrees. According to experts, the arch format is not only exquisite in appearance, but also creates optimal conditions for growing plants. As for polygonal round structures, an attractive design will not hide from an experienced eye the need to equip additional vents in order to improve ventilation inside.



As it is easy to see from this information, the types of floors in greenhouses are very different in design. And they differ significantly from each other. So, single-slope solutions are recommended in cases where there is an acute shortage of space on the site and you need to use it as rationally as possible. It is advisable to orient the roof slope to the south, although, depending on individual considerations, builders may choose another option. Shed roofs are predominantly covered with glass or plastic elements.


A sufficiently high-quality and original version of a wooden greenhouse is assembly according to Meatlider. It differs from classic greenhouses in the original arrangement of ventilation. The upper segment of the roof is equipped with transoms to help the warm air escape. The inflow of fresh air occurs through door openings or special windows located below the roofing parts. The frame of the mitlider greenhouse is very strong, because the beams are installed more often than usual, supplemented with spacers.


Such a solution is reliably protected from wind and hail, and if necessary, the structure can be moved to a new place if bolts or screws are used during the construction. Ventilation flaps face south to avoid cold northerly winds. The main structural parts of any greenhouses according to Mitlider are made of wood, this prevents the formation of condensation.
When calculating the need for arcs, it must be borne in mind that such greenhouses are large in size:
- Length - 12 m;
- Width - 6 m;
- Height - 2.7 m.
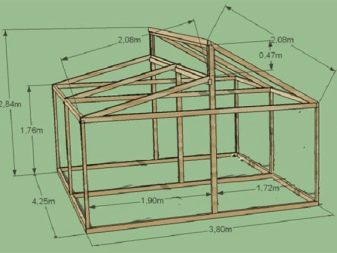

Such a solution allows you to maintain an optimal climate in the greenhouse and reduce temperature drops compared to changes in the external environment.
Theoretically, it is possible to reduce the size of the structure, keeping only the basic proportions. But then you have to come to terms with unpredictable heating and cooling rates. The roof should have two slopes, dissimilar in height. No less often, a greenhouse is created in the format of an arch, also equipped with a two-level roof.
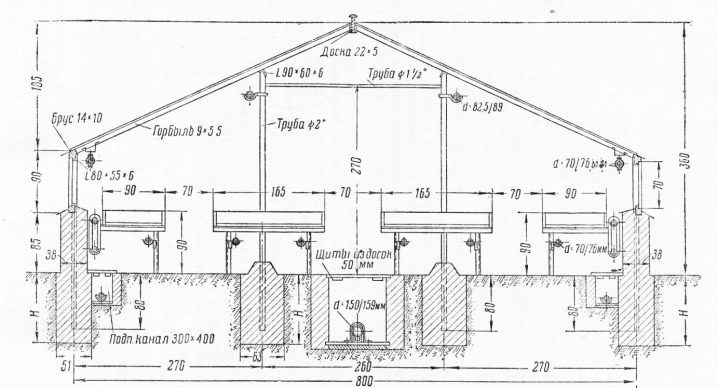
It is possible to set up a greenhouse according to the Mitlider scheme only on a flat, sunny place. If you have to work on a slope, you need to form a terrace with reinforced ledges. The frame is made of a bar with a section of 10x10 cm, the length of the central posts is 305, and the side ones are 215 cm.When assembling the lower straps and spacers at the corners, boards with a size of 2.5x20 cm are used. Skates and guides for beams should be made of wooden beams.

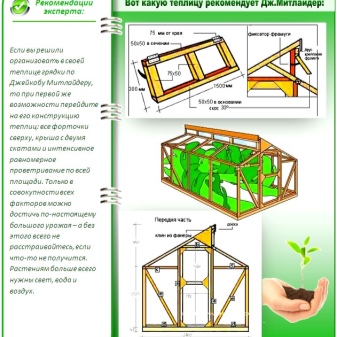
Although the frames of the greenhouses along the Meathlider are quite reliable, it is recommended to initially make the foundation so that the structure would stand in one place for many years. Beams with a length of 3 m and a section of 10x10 cm are placed on the perimeter of the structure, the corner joints are fixed with self-tapping screws.
Immediately after that, the diagonals in the rectangle are additionally verified, which must be equal. The entire base is knocked out with pegs; self-tapping screws will help to hold them. The walls at the ends are made of timber with a section of 5x7.5 cm, the gap between them is 70 cm.
In the mitlider scheme, a pair of windows is placed, which are held on the frames by clamps and awnings. When assembling the doors, a 5x5 cm bar is used. The base is supplemented with 7 mm wedges, they must be placed at the corners one by one and in pairs where the door frame is connected to the bar. When it comes to the roof, the northern slope is necessarily steeper than the southern one with an elevation of 0.45 m.


A subspecies of a gable greenhouse is considered to be a "Dutch woman" with inclined walls. With its help, it is easy to expand the area for planting. It is quite difficult to make a round wooden greenhouse, because there will be a lot of parts, and there will be even more joints. The appearance of the structure is, of course, spectacular, but in order to rationally use the territory, you will need to make curly beds or put up racks. But during the whole daylight hours the level of insolation will be the same.
The semi-circular format is preferred because it:
- versatile;
- easy to maintain;
- it will be easy to cover the plants due to the exclusion of corners;
- light is distributed uniformly throughout the space;
- resistance to wind load will be very high.


Arched greenhouses cannot be assembled from wood simply because it does not have a sufficiently high elasticity. Buried greenhouses with one roof above ground level often have wooden rafters. Such a solution requires thorough antiseptic impregnation and regular coloring. In the summer months, the covering is supposed to be removed, a building of this kind is suitable only for preparing seedlings.

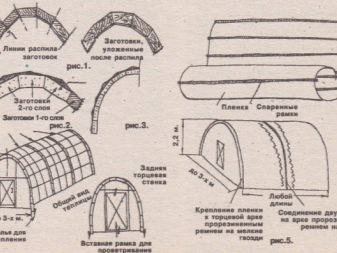
Self-construction
Before installing the greenhouse, it is necessary to analyze not only the level of illumination on the site, but also how far it will be to the water source, what is the terrain, the level of wind load and the type of soil. Without understanding these key points, there is no point in moving on.


Structures with one slope are oriented along the east-west axis, with two - along the north-south axis.
It is undesirable to place the greenhouse directly next to trees, with high fences. But next to shrubs that do not become an obstacle to light, it is quite justified to build a greenhouse. It is imperative to build a greenhouse with enhanced wind protection. As for the size of the building, there are no universal recipes.
You need to focus on:
- the amount of the crop;
- total area of the territory;
- type of crops grown;
- material opportunities.
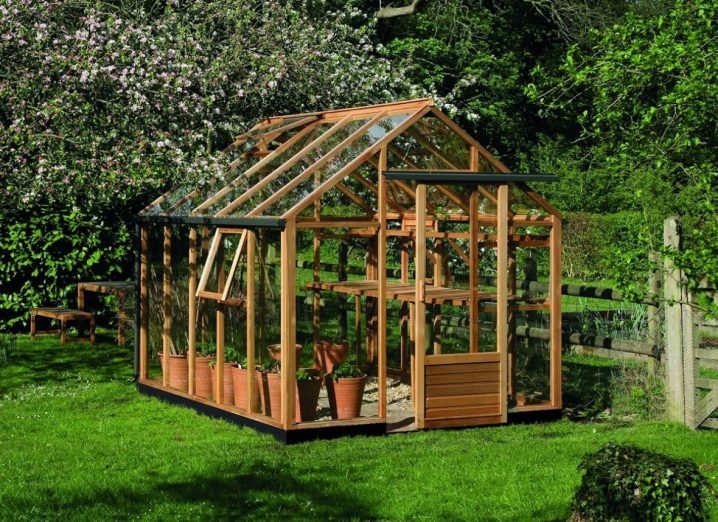

Most gardeners limit themselves to greenhouses of 3x6 m, which allows a balance between the occupied space and the total number of fruits. Since not all plants can be grown in one room, there is no need to try to make the building larger.
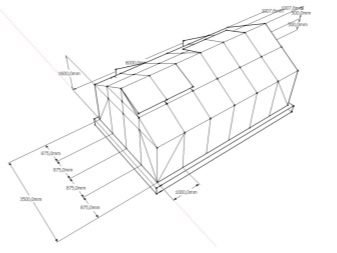
If you plan to heat the greenhouse, you need to put pipes under the beds in perfect order from the very beginning. For the manufacture of the foundation, it is recommended to take a beam with a section of 10x15 cm.
You cannot build a greenhouse without a foundation if:
- it comes close to living quarters;
- the beds are below the freezing height of the soil;
- construction will be carried out on a hillside;
- it is required to give the maximum strength to the structure.
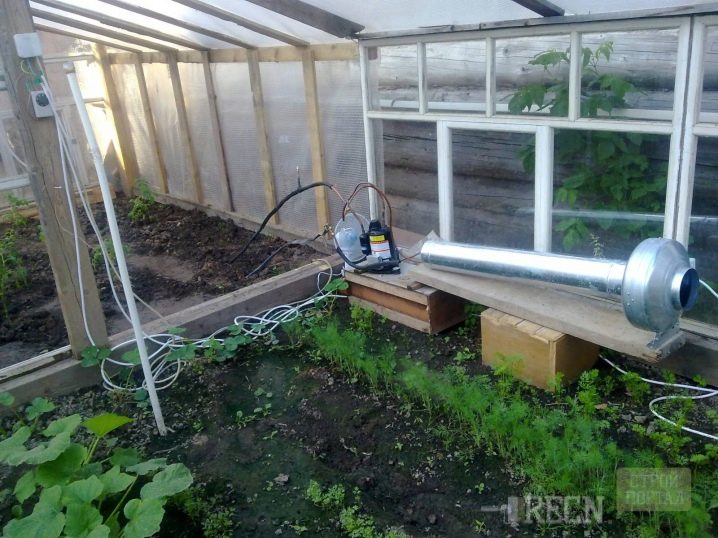

Calculations and drawings
Even the best step-by-step greenhouse building instructions cannot be followed properly if a large dimensional diagram is not properly drawn up.
A competent drawing should display:
- walls;
- foundation;
- rafters;
- skates and strapping bar;
- racks for placing containers with soil;
- racks for displaying shelving;
- gaps from shelving and solid structures to walls;
- chimney (if a heating system is installed).
In most cases, the foundation is made of a tape type with a tab of 0.4 m. Windows are trying to be mounted both on the sides of the structure and on the roof. The overwhelming majority of designers opt for stove heating, chimney pipes are placed under internal shelves and racks (so that they do not spoil the appearance). If it is necessary to save money, it is better to abandon the recessed structures, especially since they are quite laborious. And a large deepening is unacceptable if the groundwater level is very high. In this case, they can provoke serious trouble.

On a greenhouse, whose length does not exceed 4 m, it is permissible to make a pitched roof - lowered at the rear wall and raised above the entrance door. Then the rainfall flowing down from above will definitely not pour on those entering or leaving, creating an unpleasant puddle at the entrance.
CD profiles are widely used in design, they are needed as rafters, rafters and skate beams, as well as for the preparation of diagonal braces in sections. Horizontal parts are mainly made of UD profiles, their size is selected individually.
The standard distance between the profiles is 1 m, the covering elements are overlapped with a mutual overlap of 30 mm or more. Subsequently, each joint and seam should be covered with silicone sealant so that less dust and foreign liquid from the outside penetrate.
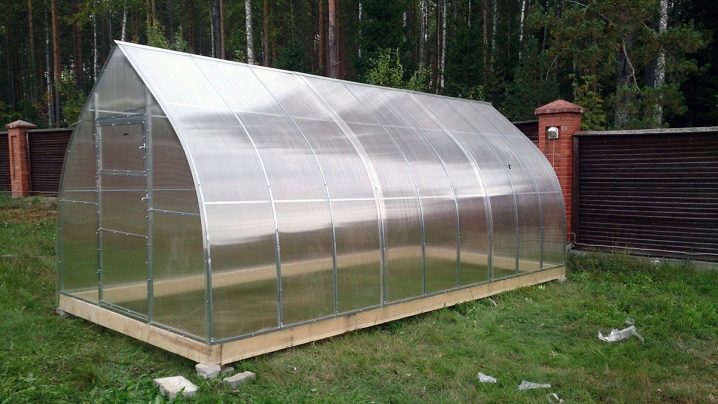

Manufacturing process
The workflow when creating a greenhouse is always built according to a uniform scheme, regardless of whether they do it themselves or hire specialists additionally.
The sequence of steps is as follows:
- foundation creation;
- fixing the carrier bar;
- frame preparation;
- arrangement of rafters;
- installation of skates and wind boards;
- preparation of vents;
- creating an entrance;
- external cladding with decorative materials.


It is impossible to build a greenhouse made of wood if the work area is not properly prepared, it is not strong and stable enough. The soil is leveled, beacons are placed on the perimeter of the site, after which they dig a trench 10 cm deep and 0.2 m wide. Most greenhouses stand on a brick or reinforced concrete foundation. The trench is equipped with formwork and poured with a layer of concrete. Brick can be laid only after the final drying of the poured layer.
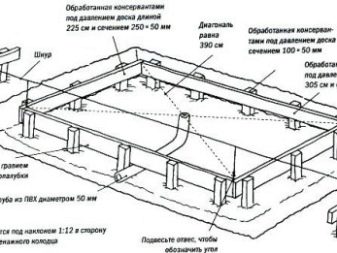

As for the location of the greenhouse, in the opinion of experienced gardeners, it is best to bring it closer to the house. Some novice builders are trying to make the gap between them larger, so as not to create an obstacle and not to occupy the most promising territory in the center of the site.
But practice shows that it is more difficult to maintain greenhouses remote from residential buildings, the preparation of communications becomes more complicated and more expensive. It is advisable to choose a place that is as gentle as possible in order to simplify the work.
It is unacceptable to undertake the manufacture of a greenhouse in a swampy or sandy areaas the tree will quickly be destroyed by the accumulating water. Clay soil is compacted by adding gravel, on top of which fertile black soil is poured. When choosing an orientation to the cardinal points, they are guided not only by the illumination, but also by the "wind rose" so that in spring and autumn less heat is blown out from the inside. Construction can help reduce wind loads by building a hedge or by attaching the greenhouse directly to the walls of houses.
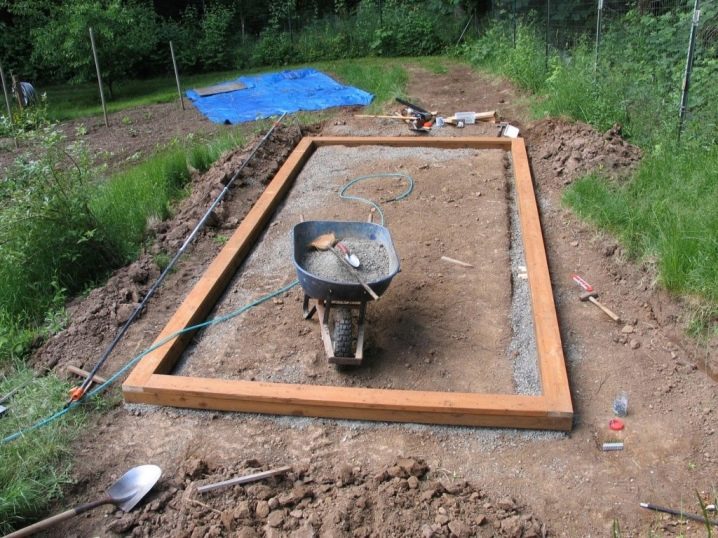

You can not put the frame directly on the soil, even in the driest areas, the wood will quickly rot.
To protect the greenhouse from such an ending, you need to use a columnar foundation, which is made on the basis of:
- pipes filled with concrete from the inside;
- fragments of piles;
- bricks (perhaps even battle);
- reinforced concrete products.


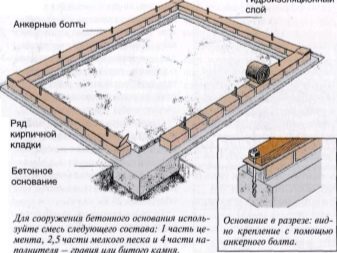
The pillars can be placed by yourself, maintaining a distance of 100-120 cm, after which the frame of the beams is laid. If the strapping is not provided, the posts will have to be made under all the racks. An alternative to the columnar base is a tape base, during the preparation of which it is necessary to free the site from accumulated dirt and thoroughly level it. Standard belt widths range from 300 to 350 mm.
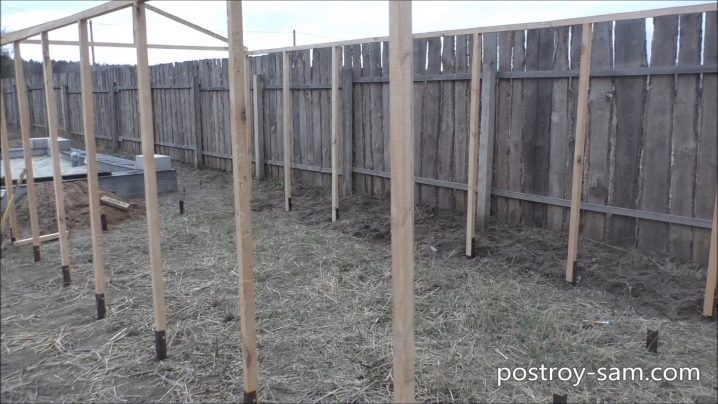

At the bottom of the trench (0.3 m), sifted sand 100 mm thick is poured. Wooden planks 20 mm thick allow for formwork, which should rise 0.25 m above the ground. Ties and jibs are used to connect the side parts. The line for pouring concrete is determined by the hydraulic level. A standard reinforcing belt is constructed from a steel rod with a diameter of 0.5-0.6 cm with a grid spacing of 0.2 m.
When the trench is filled with concrete, it is leveled strictly according to the previously made markings. Then the foundation is left alone for 14-21 days. If the weather is hot, water it regularly to avoid cracking. As soon as the time comes to remove the formwork, processing is performed using gypsum mastic or roofing material to increase the resistance to moisture. Then a homemade greenhouse is built under a film or with a polycarbonate work surface.


Wood must be impregnated with antiseptic mixtures. The harness should be made of solid elements. If you use the segments, the strength will be unsatisfactory.
Wooden parts for side walls are formed according to the following criteria:
- length - 540 cm;
- height of a separate rack - 150 cm;
- the number of crossbars on one side is 9.


To transform disparate parts into a monolithic canvas, it is recommended to use grooves. To connect the walls with the rafter system, ceiling joists and door blocks, self-tapping screws and metal corners are used. In most cases, rafters with a length of 127 cm are enough, and only if tall people are using the greenhouse, this parameter increases to 135 cm.All these indicators are calculated for wooden greenhouses with sides of 6 m, if it is necessary to build another structure, they are recalculated.
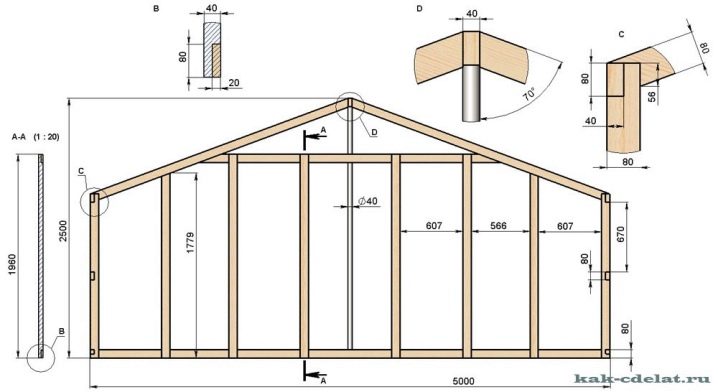
Based on the declared values, the total length of a pair of side struts and a pair of legs for rafters will be approximately 580 cm, that is, there will be no wood processing waste. The final stage of the work is naturally the installation of the roof and door.
First of all, rafter pairs are mounted; a solid bar is used to make the ridge of roofs and wind boards. Then they prepare the frame and create a frame for the vents.
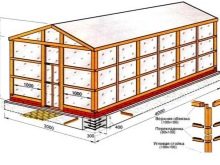
There is a more complex option for building a greenhouse. In this case, the standard foundation is always tape, the optimal dimensions are 360x330 cm, the height of the central passage is 250 cm. The technology for preparing the foundation is the same as before. When it is ready, the side, front and rear front walls are assembled. The sides are made of seven racks of 85 cm in size, to which they attach parallel straps of 3.59 m each; self-tapping screws are used to hold them.

The stern wall is made of six supports and a pair of straps of 310 cm. Once the walls are assembled, they are installed on the foundation and screwed to each other using anchor bolts. To connect smaller parts, corners and self-tapping screws are used. Roof blanks on a flat solid base are pulled together with similar self-tapping screws, but only through the mounting plates. It is necessary to carefully assess the strength of the structure and consistently attach its fragments to the assembled frame.
To install the roof, first use a ridge beam, the length of which is 349 cm. Then the rafters are prepared (from bottom to top).Their parts are connected using plywood overlays. The frame is painted and impregnated with protective mixtures. It is imperative to insulate the structure, for this they use foam or mineral wool. You can make the greenhouse more protected from the cold if you equip the entrance with a kind of vestibule where no plants will be grown, but due to the additional layer of air, heat loss will decrease.

Foam insulation implies the layout of its sheets along the walls (from the inside). An alternative material is bubble plastic. Experts recommend wrapping the polystyrene in plastic wrap, then even dampness will not be scary.
It is impossible to guarantee the maximum life of a greenhouse if it is not properly prepared for use. You should not rely on the beautiful appearance of timber and boards, even if they were bought in a reputable store or sawmill. Be sure to brush it so that there is no dirt and a layer of sand, wash the material and wait for it to dry. Then the tree is cleaned with medium-sized emery or wet abrasive. If cracks appear in the painted greenhouse, they must be painted over immediately to avoid rotting of the building.
It is also necessary to pay attention to very important points - lighting and heating in the greenhouse complex. The exact need for lighting is not the same for every crop and even different varieties.
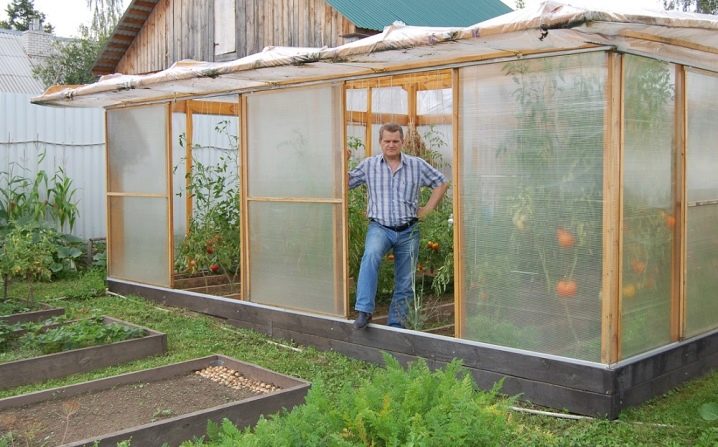

Everything that is grown in an ordinary garden requires lighting in one way or another, especially for peppers, eggplants and other nightshades. If a culture is called upon to produce flowers or fruits, it needs more light than for those that value nutritious leaves.
Contrary to popular belief, monochrome lamps cannot be used because they make the crop tasteless. It is necessary to highlight the plants with the whole spectrum at once. For forcing individual crops, incandescent lamps can be used, which are suspended 0.5 m above the plants themselves.
Fluorescent energy-saving backlight - the best in quality and value, especially in a small room. But regardless of the type of lamp chosen, it is worth consulting an electrician. If the wire is laid in a trench, its minimum depth is 0.8 m, and intersections with drainage systems are unacceptable. All electrical appliances, wiring and connections must be designed for high humidity and temperature conditions.


Special heating needs to be taken care of if you have to organize a winter garden or grow fresh herbs in the coldest months. Not everyone is so “lucky” that a heating main is located right under the greenhouse, but there are a number of workarounds that are designed to solve this problem.
So, solar accumulators are shallow pits covered with heat-insulating material, on top of which is located wet sand of a coarse fraction. Air heating involves the installation of steel pipes, one end of which is placed in a fire or outdoor stove.
If a scheme with periodic heating with gas cylinders is chosen, then in addition to observing safety requirements, it will be necessary to allocate a special place for the heating boiler and take care of enhanced ventilation. After all, oversaturation with carbon dioxide and water vapor will have a bad effect on any plants.


Beautiful examples
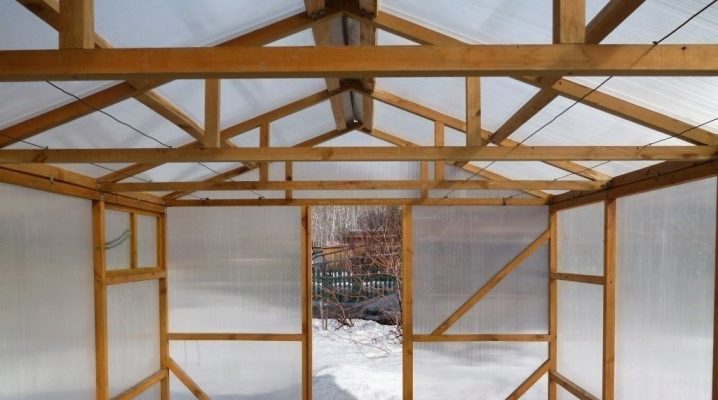
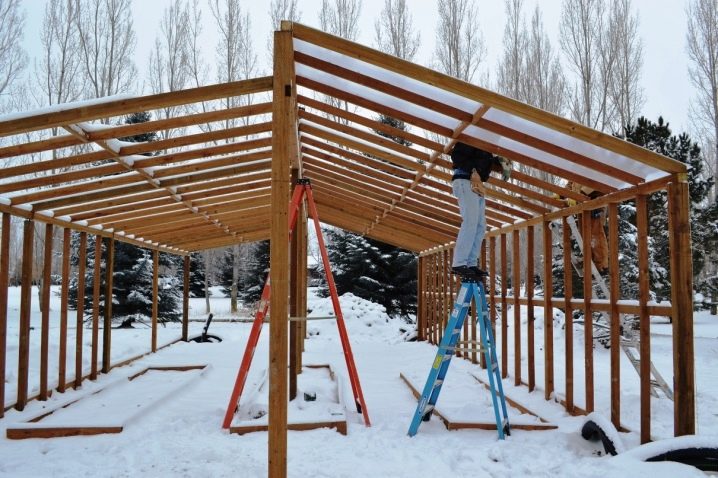
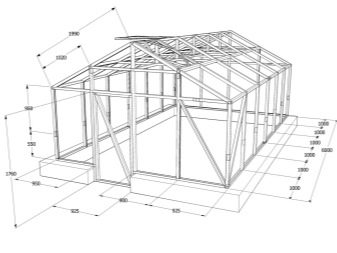
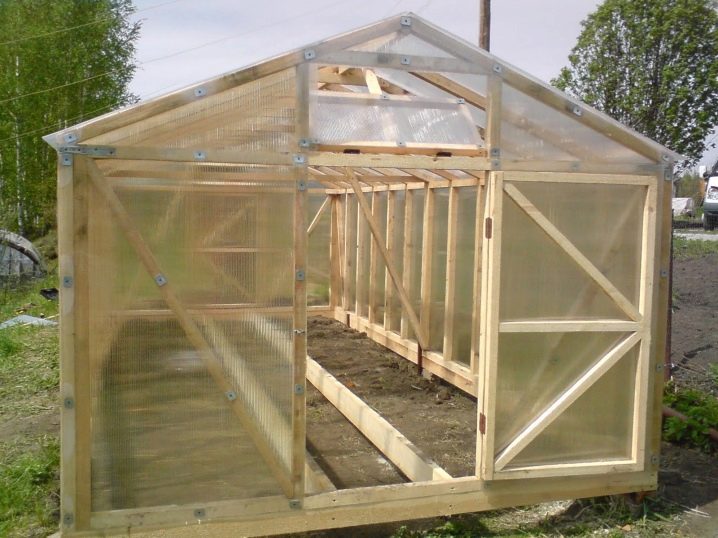
At the dachas, you can find not only ordinary greenhouses, but also those that really delight connoisseurs. This photo shows the frame for the greenhouse, which has yet to be completed. And already now the contours of the gable roof are guessed.
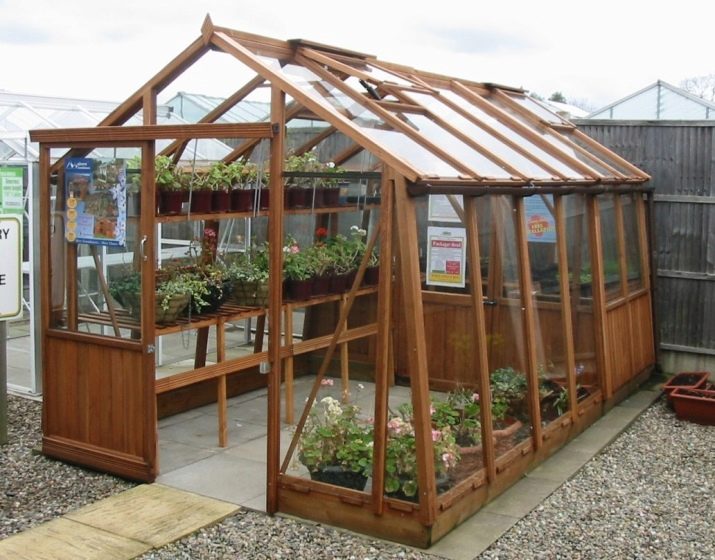
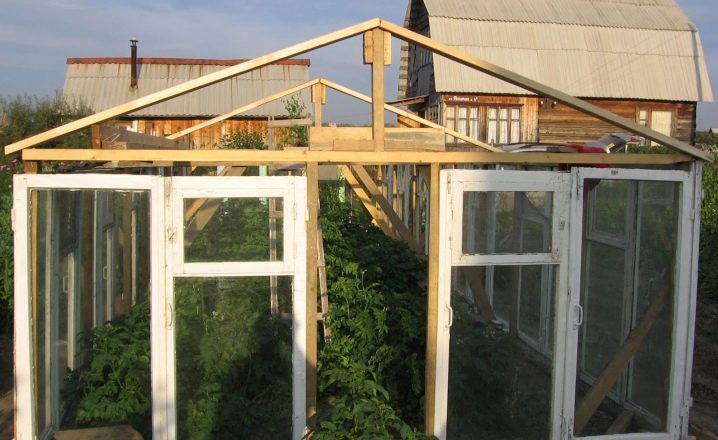
The authors of this project have chosen a similar structure, where a wooden frame is also ready.



For information on how to build a wooden greenhouse with your own hands, see the video below.





























































The comment was sent successfully.