Greenhouses for growing vegetables all year round: arrangement options
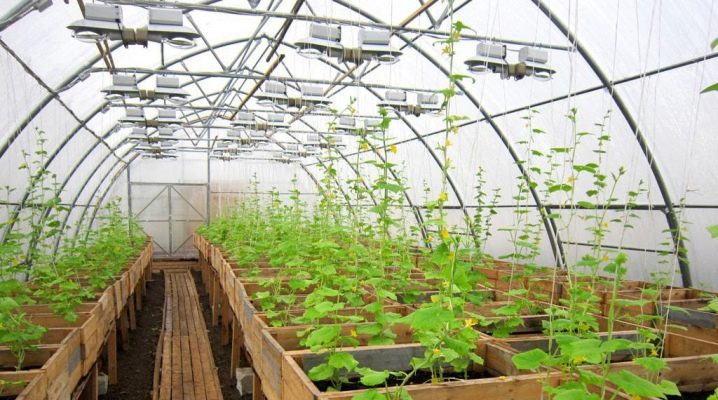

Even if you have a small greenhouse on your garden plot, you can grow crops not only in the spring-summer period, but also throughout the year. It is always pleasant when fresh crispy greens, cucumbers, fleshy tomatoes are served to the table, and if they can be grown on your site and get a year-round harvest, then this is doubly pleasant. Under favorable conditions in greenhouse structures, you can achieve a good microclimate, which allows you to use it throughout the year and get a harvest of fresh vegetables and fruits.



Peculiarities
For many summer residents, greenhouses are familiar, inside which temperature drops are felt. For greenhouses that are located in the ground, these disadvantages do not exist. In such buildings, the walls work like a thermos, so you can not spend a lot of money on heating and electricity. A thermos greenhouse allows you to get a harvest of fresh juicy vegetables and greens all year round.
Underground structures are suitable for growing annual plants and perennial crops. Small decorative and exotic trees and shrubs can be planted in the greenhouse, as well as the production of roses or other flowers. Such a year-round greenhouse will allow you to regularly collect vegetables, fruits, herbs and citrus fruits not only for your own use - horticultural products can be sold on the market, thereby creating your own small business.



Views
In order to have a harvest of fresh vegetables and fruits all year round, use:
- single-slope structures;
- gable;
- arched;
- block structures.



The area and location of the structure depends on which form is chosen for the greenhouse.
A lean-to greenhouse can be called the simplest structure. Such greenhouses can often be seen attached to the main residential building.
Shed greenhouses have the following advantages:
- the design is inexpensive;
- has good thermal insulation properties, since the main wall creates an additional source of heat;
- there is no snow cover at the sharp corners of the slope.


Single-slope greenhouses are used only for home use, where you can grow fresh greens for the table or equip a winter garden all year round. They are not used for industrial buildings.
Gable greenhouses are located from north to south. They are a free-standing structure with different lengths and widths up to 12 meters.
Such a structure has its advantages:
- used in a small farm, suitable for private use;
- can have different sizes: from 30 to 300 sq. m, which reduces heat loss in the room;
- building with good thermal insulation and illumination.


Among the shortcomings, one can single out the fact that intermediate racks interfere with the establishment of a mechanized process. The design has a small slope angle, so manual snow removal is required.
The hangar greenhouse is a gable or arched structure with a maximum width of up to 25 meters. Due to the fact that there are no racks inside the greenhouse, you can make the most of the space inside the structure. Hangar greenhouses have a large width and an angle of inclination of the roof up to 30 degrees, due to which additional costs will be required to carry out heating. For coating, they often take a reinforced film or polycarbonate.


Hangar greenhouses have the following advantages:
- due to its design, the plants receive the maximum amount of illumination;
- there is an opportunity to use mechanics for maintenance;
- it is not necessary to remove snow from arched structures manually, as it comes off by itself.
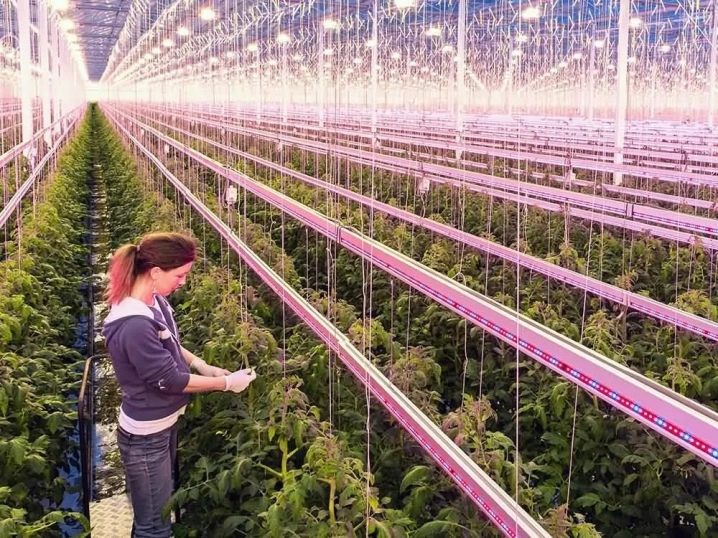

Such structures will require high costs both for construction and during operation, so it is advisable to use them for commerce.
Block structures are a series of greenhouses that are connected at the sides. At the joints, a support stand is placed, due to which the costs will be lower. The roofs are divided into separate sections with gutters for water drainage. Block structures can have different lengths - sometimes it reaches more than one hectare, so this type of greenhouse is used only for industrial use.
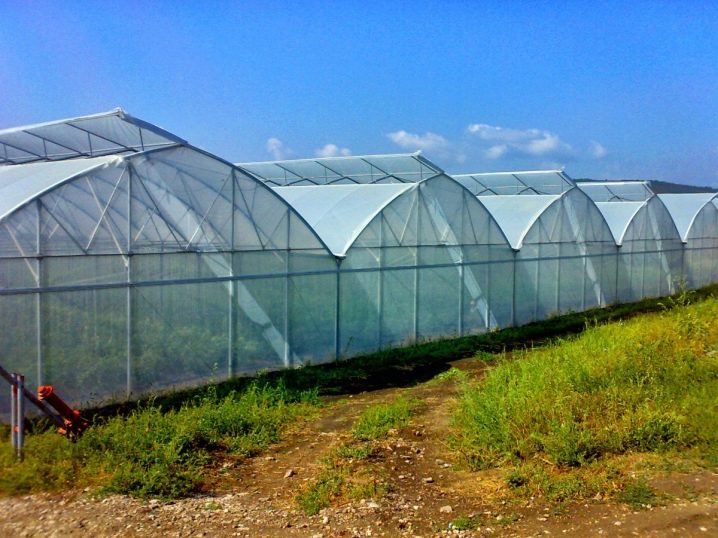

Of the advantages, the following positions can be distinguished:
- the cheapest design for industrial needs;
- has high resistance to wind and snow cover;
- excellent illumination on all parts of the greenhouse;
- all systems can be easily placed for functioning: heating, irrigation, lighting;
- the greenhouse is easily ventilated through the roof, on which the vents are placed.


The disadvantages of this design can be considered the fact that only up to 70% of the area is used. In addition, melt and rainwater begins to accumulate in the recess on the roof, which requires an additional system for melting snow and melting melt water. Block tables are used only for industrial needs - they are not recommended for use in private households due to their size and cost.

If the greenhouse is planned to be built on a small plot of land, underground or buried buildings are best suited, although greenhouses built in the form of a house or an arched structure are familiar to many. If you build structures of this type, then the plants will receive sunlight from 20 to 35%, and when cold weather sets in, it will be quite cold in them.
School physics teacher Ivanov proposed a different version of the building with a lean-to roof, which has a slope of 20 degrees and a tightly closed wall at the back, which allows you to use the energy of the sun to the maximum. Thanks to this design, you can get the harvest much longer.


The construction technology is called Scandinavian, since residents of Europe with a more severe climate began to use it. This unique design has virtually no drawbacks. Its main feature is that, due to a certain slope of the roof, the sun's rays do not slide over the surface, but fall perpendicularly - this allows you to harvest much earlier.

For many crops, fruiting in the greenhouse begins 20 days earlier than usual. This energy-saving design, also called a vegetarian, allows you to get an order of magnitude higher yield than under normal conditions.
Choice of design
Many gardeners believe that by planting plants in buried or underground greenhouses, they will not receive the necessary amount of sunlight. But this is not so, because a large amount of sunlight enters the plants through the roof, which ensures their good growth.
When choosing a design for a greenhouse, one of the options is chosen: underground or buried.


An underground greenhouse is characterized by the construction of walls that are placed underground. They are usually built large and adapted to grow annual and perennial crops and trees. The depth of the structure also depends on how deep the underground waters will run.


With a recessed structure, only a part of the wall up to 60 cm is in the ground, the above-ground part is up to 110 cm above the ground. The recessed structure is built quite simply, although less heat will be retained in it.


In the cold season, precipitation in the form of rain and snow accumulates on the roofs of earthen greenhouses, so they must be removed regularly, otherwise the structure may collapse. However, these greenhouses are resistant to wind gusts.
Semi-underground greenhouses allow you to grow plants that will be heated by the ground, which will save money. The greenhouse-dugout will allow you to keep heat without heating, which will be stable throughout the year.
It is very important for plants that in a year-round greenhouse there is regular watering with sufficient soil moisture, as well as good illumination.
For regions with harsh climates, it is better to use heating in greenhouses. An autonomous greenhouse with heating will allow you to get a stable harvest for the entire period. Different options are used to heat greenhouses that operate all year round.


With electric heating, the following are selected for operation:
- convector;
- electric cable;
- heating mat;
- heat gun.



Often gardeners use stove heating., while the stove is often installed next to the entrance. When choosing this heating method, good ventilation should be done. The advantage of this method is that the stove can be heated with various waste or wood - this can reduce the cost of heating.

Self-construction
In order for the independent construction of a greenhouse to be successful, you need to think through everything in advance. At the initial stage, it is necessary to make drawings and choose a location for the location of the building. On the sketch, you need to accurately indicate its parameters, as well as the place where the structure will be located.
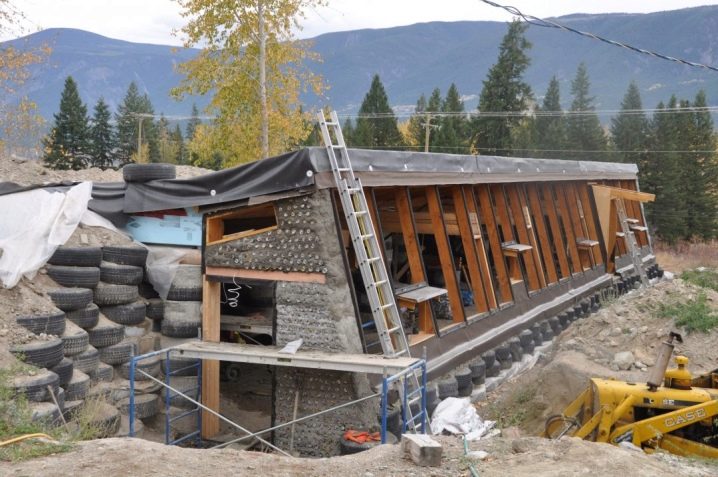

When choosing a place to build a greenhouse with your own hands, you should take into account such factors.
- Sunlight. The plants in the greenhouse need the maximum amount of daylight. The most convenient for this will be the location of the building from west to east.
- Wind protection. When constructing a greenhouse, protection from strong winds can be made.
- Convenience in approaching the building. Adequate operating space should be prepared to allow trolleys and buckets to drive up to the greenhouse.

Before starting construction, it should be taken into account at what depth the underground waters lie. In the event that they are very shallow, the construction of a greenhouse will be difficult.
When starting construction, a pit should be dug - its depth should be at least 2 m. When choosing a size, it is taken into account that the length of the structure can be arbitrary, and the width should not exceed more than 5 meters. If you choose other parameters, for example, build a structure 6 meters deep, then the heating of such a structure will be uneven, which will greatly increase heating costs.
The edges of the pit should be leveled for subsequent pouring with concrete. The frame of the future greenhouse structure is installed on the concrete foundation. When the work on the construction of the foundation is completed, they proceed to the construction of the foundation for the structure, thermal insulation is fixed on top. A polycarbonate roof is installed on a metal base.


To keep the internal heat, the walls should be covered with thermal insulation.
If the greenhouse is installed in the northern regions, then foil is used to insulate it, with which the walls are covered with several layers. Such insulation is done only in the cold season.
If you make warm floors, then you can install heating in a greenhouse. In the greenhouse, the optimum temperature for plants should be maintained from 25 to 35 degrees Celsius, while the humidity in the greenhouse should be taken into account. A prerequisite should be constant ventilation in the room. If all requirements are met, optimal conditions will be created for the functioning of the greenhouse all year round.


When installing a roof, polycarbonate is more often used - with a sheet length of 12 meters, a flat surface is created, which eliminates the appearance of joints, as a result of which drafts will not appear in the room. To prevent corrosion, all fastening parts are pre-lubricated.

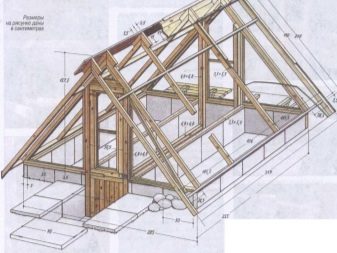
Advantages and disadvantages
Before starting construction, a scheme for construction should be developed. If you plan to grow a winter garden, then you need a certain temperature regime, thanks to which it will be possible to grow tropical plants. For any structure, if it is created by hand, a solid foundation and a reliable frame are required.
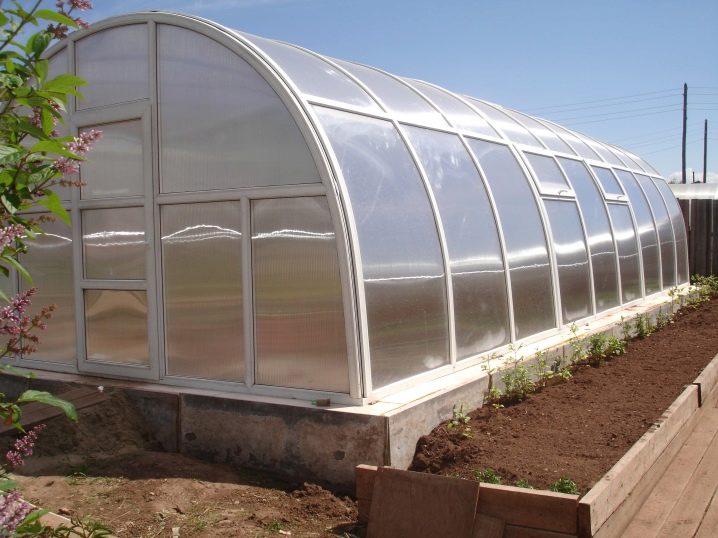

Greenhouses designed to be used all year round have advantages and disadvantages:
- vegetables and fruits are grown in a trench greenhouse all year round;
- the underground structure is characterized by a cool temperature on a hot day, which is necessary for most plants;
- these types of structures can be done independently using a diagram or drawing;
- have a low cost - during construction, you can use budget building and finishing materials.


Hangar models covered with polycarbonate are especially popular - this is evidenced by the reviews of the owners.
These greenhouses have many advantages:
- low cost;
- ease of assembly;
- excellent protection from snow and rain;
- plants receive the maximum amount of light.
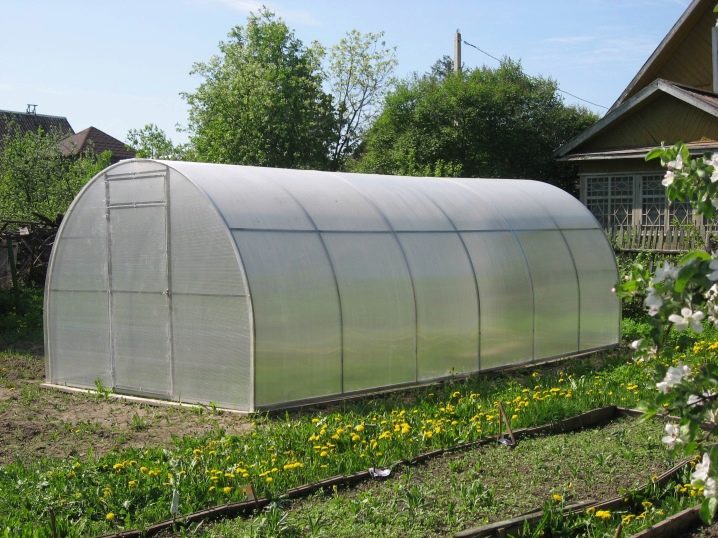

Polycarbonate for building a greenhouse has excellent thermal insulation properties, it is very flexible, which allows it to be used for an arched greenhouse. Polycarbonate is a very light material - it is 16 times lighter than glass.
Can be used for construction and metal-plastic. Although the independent construction of a metal-plastic greenhouse is not an easy task, they usually resort to the services of specialists for this. For such structures, the frame is better made to order - as a result, a not very profitable building in financial terms may turn out.


Examples for inspiration
Many gardeners dream of building a real greenhouse on their site - this is a place where you can grow not only the usual greens and vegetables, but also all kinds of exotic plants and berries, as well as get inspiration by producing magnificent roses, carnations or rare orchids.



A brick building is more suitable for a greenhouse - such a capital structure will be a real home for plants. Although more modern materials are used for greenhouse buildings, greenhouses are still built using metal-plastic and cellular polycarbonate, and a brick structure remains the most reliable.
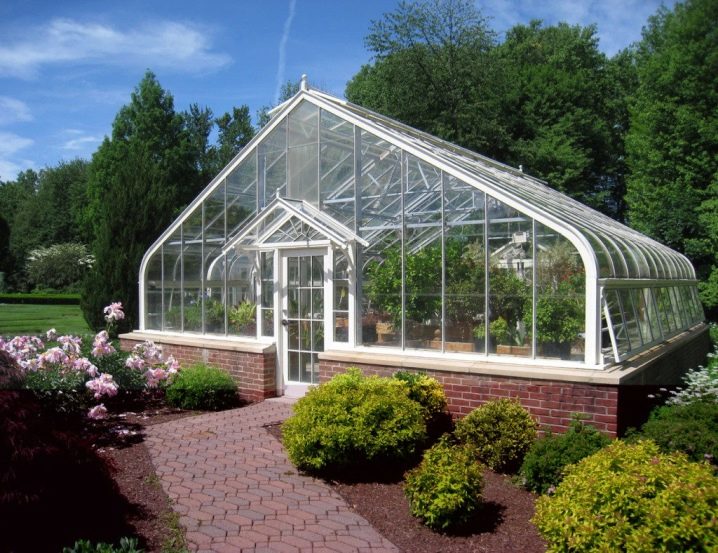

If the owners of the site have at least minimal skills in laying bricks, then you can build a greenhouse with your own hands - such construction will not be very economical and will require an investment of money, even if all the work is done independently and outside workers are not involved.
First of all, you should purchase the necessary material for construction:
- bricks;
- mineral wool;
- cement and sand;
- board, timber for rafters;
- roofing material;
- window, door.



These are the main materials, in the course of construction the list may be replenished.
A brick building differs from other buildings in that it consists of two rooms and a vestibule, where a heating system is installed in the form of a boiler or stove and all sorts of accessories for caring for plants and the main room are stored.


For the vestibule, small sizes are chosen, for example, 2x2 or 2x2.5 m. For the main room, the dimensions can be any. A capital partition with a door is placed between the vestibule and the main room. Usually, windows with transoms are made in a brick greenhouse.
Starting the construction of a brick greenhouse, the strip foundation should be poured. If the masonry is in one brick, the foundation is poured with a depth of half a meter.In order for a lot of light to enter the greenhouse, windows are made for fresh air and transoms are installed.


The roof is made transparent with a slope of 30 degrees, a gutter is mounted at the edges to drain melt and rainwater.
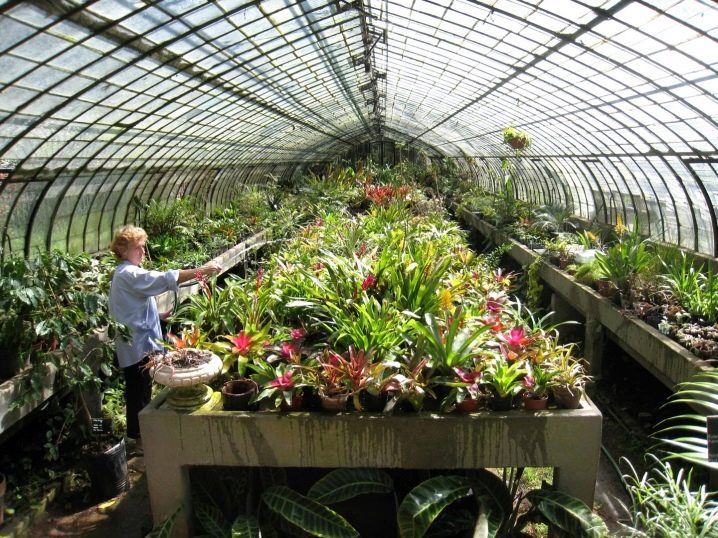

In a heated greenhouse, in addition to flowers, you can grow greens and vegetables.
If you give preference to vegetables, then experienced gardeners recommend growing:
- cucumbers;
- tomatoes;
- peppers, sweet and bitter;
- leaf salad;
- Beijing cabbage.
Any dish will not do without spicy dill, aromatic parsley, cilantro, basil, green onions. A thermos greenhouse will allow you to add greens to your favorite dishes all year round.

In order to have a good harvest all year round, the plants should be constantly looked after. Particular attention is paid to soil preparation - the best for plants is considered a light, fertile soil, which has all the substances necessary for plants. Regular watering and feeding is important for vegetables and herbs.
If all the conditions are met, you can build a greenhouse on the site for growing vegetables all year round and get a good harvest, which will provide vitamins and essential minerals.


Building a greenhouse can be a stepping stone to starting a home business for the cultivation of vegetables, fruits and herbs. Exotic fruits and vegetables, as well as fresh flowers can be especially relevant for sale.

For information on how to build a winter greenhouse, see the video below.





























































The comment was sent successfully.