Old TVs: what were they like and what was valuable in them?
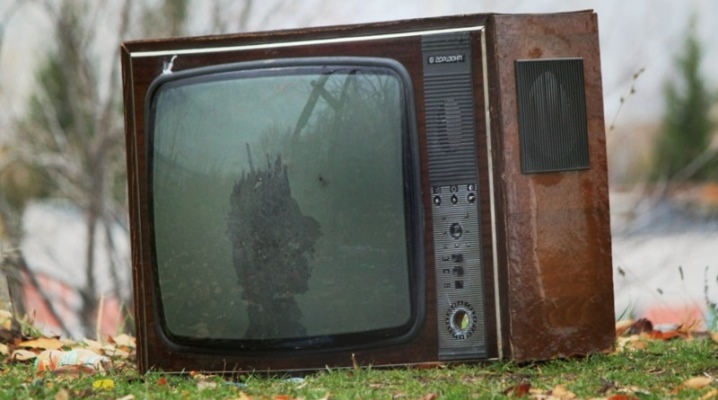

TV has become the main item in any family since the days of the Soviet Union. This device was the main source of information and collected Soviet families in front of its screen in the evening. Despite the fact that today TVs made in the USSR are outdated, they still work well in some places. And if they break and it is not possible to repair them, then they should not be thrown away, because they can still be used. More precisely, a lot of useful things can be learned from them. And these are not only radio components. Parts of televisions from the times of the USSR also contain metals, among which there is even gold.


History
In the USSR, tube TV became a common device somewhere in the early 60s of the XX century, although at that time it can still be called a rather rare novelty. Most often, in the entrance, where there were a dozen or two apartments, only 3-4 residents had this device. When there was supposed to be some kind of broadcast or event on television, the apartment of the owner of the TV could accommodate all the neighbors in the house.
But since that period, TVs have become more and more. Although the first models began to be produced in the 1930s, they were, as a rule, very small batches of devices that had rather unassuming characteristics and practically did not hit the market. But after the 1960s, a whole industry was formed in the USSR, which produced a fairly large number of models, which included both black and white and color devices.
By the way, color TV in the USSR was also a very rare phenomenon for a long time, but by the end of the 1980s it had already become widespread.


Features and working principle
Considering that televisions in the Soviet Union in the vast majority of cases were lamp, then such devices should be considered through the prism of the fact that these are radio receivers that can receive electrical signals, amplify them, and transform them into images and sound.
TV transmitter emits electrical signals - radio waves, which excite high-frequency oscillations in the receiving television antenna, they go to the TV channel via the antenna cable, amplify, divide, detect, amplify again and go to the loudspeaker, as well as the electric ray tube, which receives it.
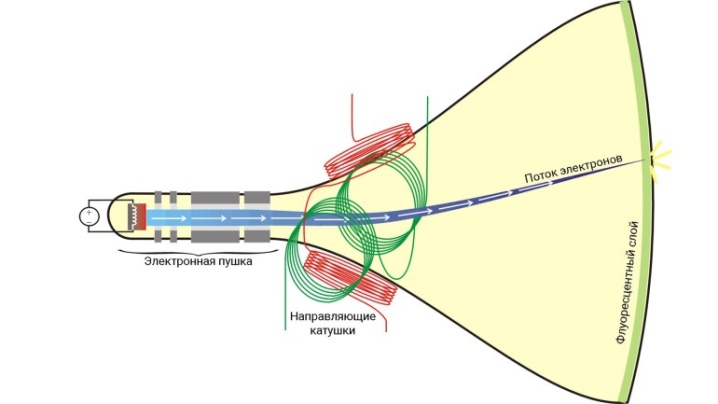
At the bottom of a flask made of glass, which is located in the receiving tube of a black and white TV, is phosphor - a special layer that serves as a screen. Its chemical composition is quite complex, it has the ability to glow under the influence of electrons that fall on it. Their source will be electronic tube spotlight... To get a picture, the beam must move across the screen. receiving tubes... To do this, the device contains generators of vertical and horizontal scans, that the generation of a sawtooth current is carried out. This is what allows the beam to be set in motion at a constant speed along the lines of the screen while simultaneously moving down the frame.
The beam moves at high speed, which is why, due to the inertia of visual perception, the entire screen surface appears to be luminous at the same time. Although at any moment only one dot is lit.
That is, from individual points that glow with different brightness, and a complete image is obtained on the screen.This is how almost any Soviet TV works.

Overview of the most popular brands and models
If we talk about the most popular models and brands of Soviet TVs, then there are a lot of them: "Ruby", "Electron", "Spring", "Dawn", "Youth", "Photon", "Coves", "Rainbow", "Temp", "Shilalis" and many others.
Models "Ruby" became the first mass and "popular" devices. They began to be made in the late 1950s, their feature has always been a relatively affordable price. It's about the device Rubin-102which produced just under 1.4 million units. In the 70s, a color version of such a TV was released, which was no less popular than black and white. It's about the model Rubin-714, of which for 10 years of creation from 1976 to 1985, a little less than 1.5 million copies were created.


TV brand "Electron" produced at the plant of the same name in Lviv. The devices were especially popular in the 1980s thanks to the very user-friendly color TV model. "Electron Ts-382"... This model was distinguished by the highest image quality for its time, excellent reliability, advanced design and low power consumption.
The popularity of this device was so great that during this period every fourth TV set in the USSR was produced by this very enterprise.


The next fairly popular brand of TVs is "Dawn"... It was especially popular in the mid-1970s. To be more precise, we are talking about the fact that in the days of color television sets, black and white models were made. Dawn 307 and 307-1. There were about 8 million of them in total, which was explained by the highest reliability and a very affordable price compared to the color models common at that time.


The line of TV receivers was no less interesting. "Spring", that was produced at the enterprise of the same name in Dnepropetrovsk, which was popular from the late 1970s to the early 1980s. The most famous and widespread device has become "Spring-346"which was also sold with the name "Yantar-346".
It has been produced since 1983 and has proven to be very successful in terms of reliability, affordable price and functional features.


TV models such as "Youth". Especially when you consider that they were the only ones in the niche of portable TVs. Many people wanted to have just such a TV set, which they could always take with them. Similar devices from other manufacturers had low reliability. But "Yunost" just stood out against their background, because it broke down extremely rarely and had a higher image quality than similar solutions from other Soviet manufacturers.
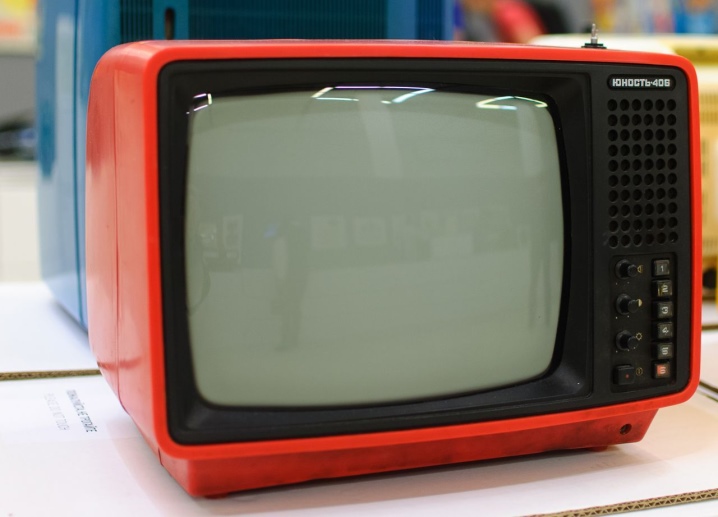

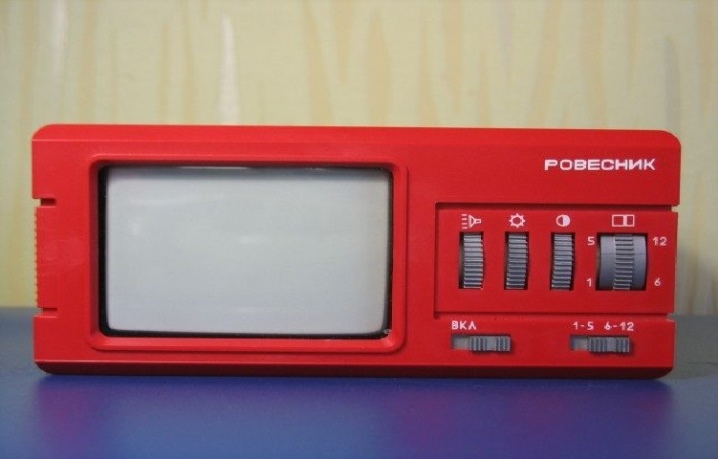
Since we were talking specifically about portable TV models, it should be said that the TV was a pretty good device. "Peer". It was the smallest TV receiver that was produced in the vastness of the USSR. Its distinctive feature was that it could be purchased either already assembled or as a designer and assembled by yourself according to the instructions.
Its distinctive features were low weight - without a battery, it was less than 1.5 kilograms and a screen with an 8-centimeter diagonal.

At the end of the review of the most popular models and brands of Soviet TVs, I would like to say more about brand models "Record" and "Horizon".
TV receiver "Record B-312" was a very popular black and white model and was produced around the same period as "Dawn 307". It was produced in 2 types of finishes: wood grain with a glossy surface and coated with textured paper. Many people remember it because it was extremely difficult to turn the toggle switch there, especially if the channel selector knob was lost. Therefore, many Soviet people used pliers.
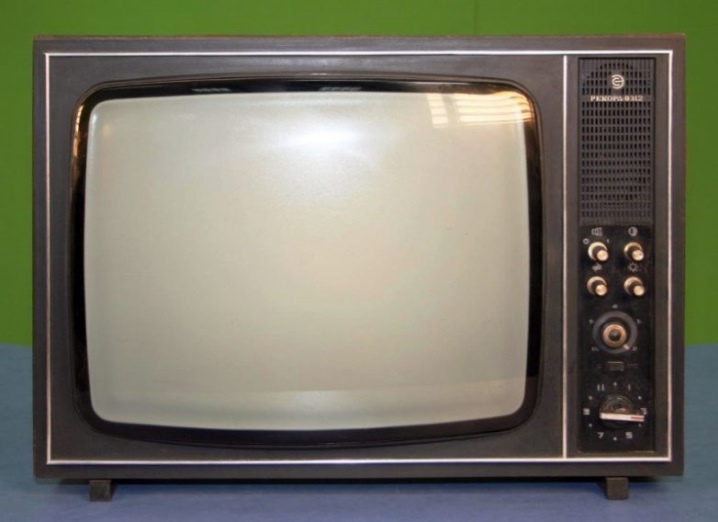

And here is the TV "Horizon C-355" was the pinnacle of dreams of a Soviet person and was created at the radio plant in Minsk since 1986.Its characteristic feature was the presence of a Japanese picture tube of the Toshiba brand, which had a radial deflection angle of 90 degrees.
For this reason, there was no need to additionally adjust the image, and its reliability was significantly higher than domestic models.

What is valuable in old TVs?
Now let's figure out what valuable parts can be taken from Soviet televisions. In addition, it should also be said that precious metals can be found in models of the Soviet period. True, the content of precious metals in models of different brands will be different. In models produced before the 1980s, gold could only be found in radio tubes that were located on a mesh next to the cathode.... The most interesting thing is that if you look at the TV box of this period, you can find there information about which precious metals and in what quantity are present in the device. When transistors were very popular, gold could be found on their substrate, as well as on the contacts of the TV channel switch. In addition, gold can be found on items such that you can pull out:
- switches;
- terminals;
- diodes;
- connectors.


It should be said that sGold made it possible to make TVs of high quality and more reliable, which made it possible to significantly extend the period of their operation. After all, gold does not corrode and does not oxidize. In addition, microcircuits, UPCHZ coils and other elements are of a certain value. And not only because of the gold. It is also in them, but not in such quantities.
It is now very profitable to rent TV sets to special factories that process them, extract useful elements and which can use them to create new parts for various equipment.


By the way, you can also find a lot of useful things in the CRT. It contains metals such as lead, barium, strontium and mercury. Also of value are elements such as wires that are coated with a layer of insulation. They are accepted at scrap metal collection points, because under a layer of protection materials such as aluminum and copper can be found. Various boards, as well as relays, will also be of value to the receiver of the radio-breaker. After all, they contain solders from aluminum, tin and lead... There are also veins made of gold, palladium and silver.


The only thing I want to say is that it is quite difficult and troublesome to pull out the metals on your own, because in one TV there is very little of all this, less than tenths of a gram. Yes and improper technology for obtaining these metals and elements at home can cause certain harm to health, for which reason you should be careful. Moreover, it takes a very long time.
At the same time, handing over televisions made in the Soviet Union to special factories is not a bad decision.


Watch a video on what you can get out of your old TV.













The comment was sent successfully.