When did the world's first TV appear?

Despite the fact that now televisions are slowly but surely becoming less and less used, their invention, and later unprecedented popularity among the people, has become almost a symbol of a large segment of modern history. The very essence of broadcast television is to convert light waves into electrical signals, which are later decoded into pictures. It took a lot of effort and time to invent such devices. Televisions have come a long way from a black and white screen the size of a matchbox to a wide range of modern models and huge screens that are used for large-scale shows. It is about this important period of time, which continues to this day, read in this article.

The history of the emergence of televisions
The first camera obscura, which was the earliest prototype of a television, was created in the Middle Ages. She could convert light into an optical image. However, the creation of a full-fledged TV was predetermined only with the invention of the first radio. Officially, the creator of the latter is Marconi; in the domestic territory, Popov is considered him. However, there is ample evidence that a number of other scientists were involved in this event.
A similar situation occurs with the name of the creator of the TV. However, it should be noted that the development of this idea took place in stages. Officially, Zvorykin is considered the inventor of the first television. His home country is the Russian Empire, after the revolution in which he immigrated to the United States. And the various components of the apparatus were created by many scientists from various countries. Here is a list of important discoveries, key figures and their inventions, without which it would be impossible to implement the idea of television broadcasting.
- In 1817 in Europe, thanks to the discovery of selenium, they learned to convert light into electricity.
- In 1856 Geisler created an inertialess tube that converts electricity into an optical image using gas.
- In 1880 Bakhmetyev proposed a technology for transmitting images over a distance based on perspective.
- In 1889 Stoletov created the famous photocell. It was based on a discovery by Hertz called the photoelectric effect. It describes the effect of light on electricity. Albert Einstein was also engaged in research on this topic at one time.
- German scientist Nipkov came up with a disk of the same name, which scanned and transmitted images to a special receiverj. In fact, this device was capable of reading the image line by line. With the rapid rotation of the disk with holes, the light passing through them merged into a single image. In order to get a picture the size of a matchbox, it was necessary to use a 40 cm Nipkov disk.
- Exactly teacher from St. Petersburg Permsky During one of his performances he gave this device its modern name - "TV".
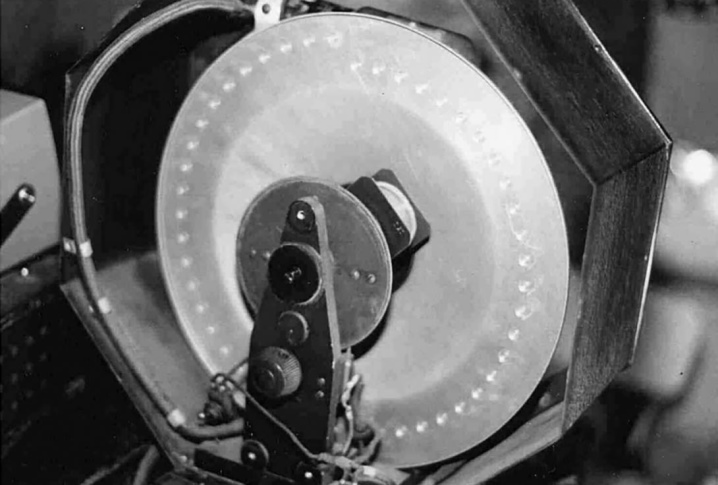

Mechanical
The Scotsman Loughy, with the help of the Nipkow disc, first demonstrated the movement of the silhouette on the screen. It is believed that it was he who made the first mechanical television. The frame rate of his device is 5 pieces per second. However, it later emerged that the mechanical TV was a kind of "dead end". It was impossible for him to increase the image resolution.


Electronic
At some point, it became apparent that mechanical television is a dead end. It was then that they began to look for a direction for the further development of this device. Thus, after a series of experiments, the Russian scientist Rosing soon became the creator of the world's first electronic TV set. He is considered him after the creation of the famous CRT (cathode-ray tube), which he called an iconoscope.

Research on this topic continued scientist Campbell-Swinton... Despite the fact that he did not succeed in making a serious breakthrough in this area, he made a significant contribution to the theory of the development of television.
In 1927 Japanese Takayanagi demonstrated to the world a television system in 100 lines using a cathode-ray tube and a Nipkov disk.
Kataev, being a follower of Rosing, created a "radio eye", which was similar in its structure to an iconoscope.
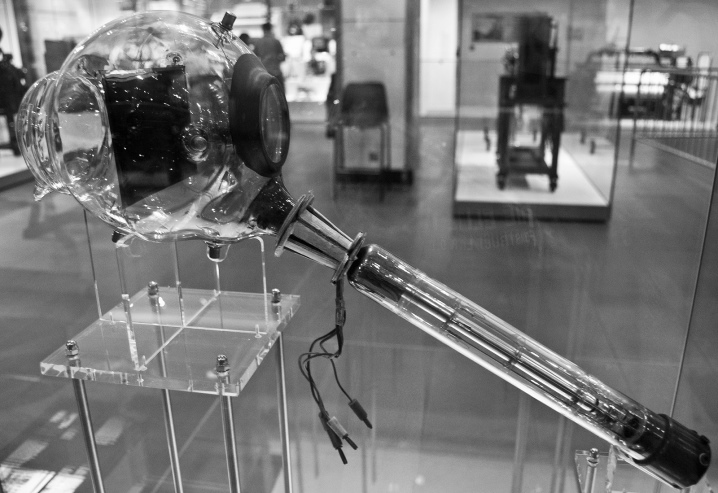

At the end of the 20s of the last century Scots Byrd for the first time presented a device that looks like a modern TV.
And finally, in 1935 already in the USA Zvorykin received an official patent for the world's first iconoscope, which he invented three years earlier.
Thanks to this invention, the first television was later released. This significant event took place in the 20th century.


When did you appear in the USSR?
In 1931, the first TV broadcast was carried out in the USSR. Around the same time, the magazine "Radiofront" began to publish diagrams of TVs for self-assembly. Nipkov's discs, which were on the free market, were connected to neon lamps. Later, radio receivers were connected to them to supply sound. It is noteworthy that at the time of the first television broadcast, televisions were not produced.
The year 1939 is considered the beginning of mass production of televisions on a large scale. The Leningrad plant "Komintern" was engaged in serial production. The first such devices only remotely resembled their real counterparts. They were radios with a pen and a small screen. The latter was 3x4 cm in size, and the device itself had to be connected to a radio receiver. Sound and video were broadcast separately from each other. Television programs began to air around the same time. They were broadcast only by one channel - "First". He temporarily interrupted his work during the Second World War, but then resumed it and is still broadcasting. After this period, another channel also began to air.
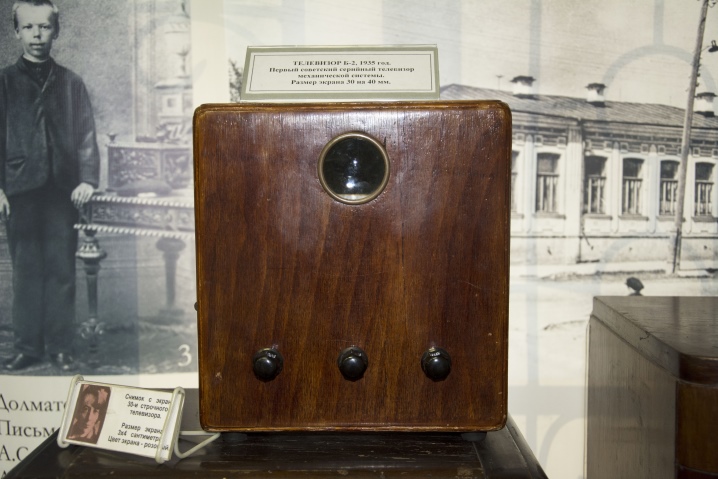

In the USSR, in the period from 1946 to 1949, several engineers (Kenigson, Varshavsky, Nikolaevsky) invented the T-1 TV. Its other name is KVN-49. The device received its name in honor of the first letters of the names of the inventors, and "49" is the date (year) of the beginning of its mass production. It became a truly "people's TV" because it was actively produced and sold. Got a bad name - often its abbreviation was deciphered as "Bought - Turned on - Doesn't work" due to the fact that almost every second device had to be repaired before the end of the warranty period. It looked like a wooden box with a small screen. The dimensions of the screen were 10.5 × 14 cm. The device weighed 29 kg. The model came with a lens that was used to enlarge the image. It was filled with glycerin or distilled water. Some of the models that have survived to this day continue to work, receiving broadcast signals.
From 1953 to 1955, the USSR produced a TV called "Rainbow". It was equipped with an 18 cm picture tube. As it becomes clear, production ended quickly. This device was already much more like a modern television.
Obviously, each of the listed devices broadcast only a black and white image.


The emergence of color television
Color TV was a logical continuation of the development of this technology. Successful experiments with the invention of color television were carried out by Hovhannes Adamyan, but the work of John Loughie Byrd is considered a truly valuable contribution. True, his TV could only broadcast images in three colors - blue, red and green. Moreover, the latter was formed directly on the screen during the broadcast of the image. And also his system was unable to combine these three shades with black and white colors.
In 1900, Polumordvinov applied for a patent. His television system was also tricolor and called "Telefot". Despite all efforts, the color broadcast of the image did not find its popularity at that time and attracted little interest. As it turned out, back then, people were satisfied with a black and white image.
Only after the end of the Second World War there was an invention called "Trinescope", which was a color TV. This happened in the USA. With the invention of this device, televisions began to be improved for use by the civilian population.
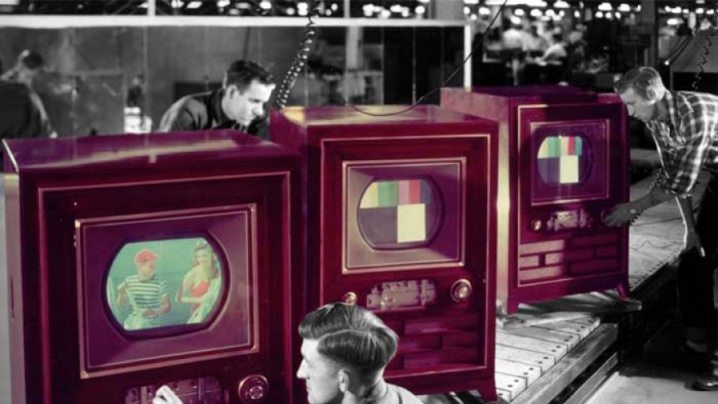

The first color television broadcasting was produced by Leningrad Television in 1952. But in the USSR, mass production was established much later, only by the 70s of the XX century - since 1967, various models of color TVs began to be produced.
Until that time, televisions were very rare and had a high price, they were practically inaccessible to ordinary people. For example, by the beginning of the Great Patriotic War, only about 2,000 television sets were produced on the entire territory of the USSR.
Among the models produced in 1967 were "Rainbow 403", "Ruby 401", "Record 101". The first color TV of them was "Ruby". The sizes of their diagonals were from 59 to 61 cm. However, at that time, black and white devices were still being produced. They were finally withdrawn from production only in 1977.
From the same year, the broadcasting of programs became completely colored.


In Russia, as in other countries of the Soviet space at that time, everyone could afford to buy a TV only closer to the 80s, while in the USA, already in the 20s of the last century, it was possible to go to a specialized store to buy such equipment. It could even be arranged on credit. Such a large temporary difference between the start of mass sales of television devices in the United States and the USSR is most often explained by the internal policy pursued by the leadership of the USSR. For a long time it was believed that radio is a cheaper, and therefore accessible, means of campaigning.
Almost every building was equipped with a radio socket. And also research in the development of televisions for a long time was not supported by the government of the country.

The invention of plasma models
The first plasma devices were not developed as recently as it might seem, already in 1964. The first plasma TV was assembled with one cell. This was done by American scientists at the University of Illinois Slottow and Bitzer. However, they returned to the further development of this invention many years later, and even when it became clear that the CRT system needed to be replaced. This was due to the fact that digital television appeared, and the kinescope was not the best translator.
Plasma TV cells are filled with gas. They are located between glass surfaces, located opposite each other. Every plasma TV is now equipped with millions of cells.
Officially, the first "flat" TVs were introduced by Panasonic in 1999. Their diagonal was 60 inches.


Later, liquid crystal analogs were invented, which began to supplant plasma ones. The main part of such models is a liquid crystal matrix. The space between glass or polymer panels is filled with liquid crystals. Themselves as liquid crystals were discovered in the final period of the XIX century.
In 2010, CRT TVs were almost completely removed from storefronts.Modern models combine several functions - this is not only the ability to watch movies through different media, but also an Internet connection, cable or satellite TV. And also TVs are used as music players. Some of them are equipped with 3D video viewing.
At the moment, the closest possible event in the revolutionary branch of the development of televisions is a complete transition to a ubiquitous holographic image.

The brief history of the invention of various televisions may seem confusing, and indeed it is. In the heyday of discoveries and many technical developments (19th century), many talented scientists simultaneously worked on several important inventions, among which were television and television broadcasting. Like any creator, they worked chaotically, made various discoveries, sometimes jointly, and sometimes, independently of each other.
Television now has a symbolic meaning and for the most part has already moved into the Internet space. It, just as in the years of its creation, is used to impose ideas, which affects world politics. But now - to a much lesser extent.
As for TVs, they are still in almost every family and continue to be actively used, remaining an integral part of modern life. And thanks to the creation of the TV, the invention of both the computer and the smartphone became possible.













The comment was sent successfully.