OLED TVs: what is it, an overview of models, selection criteria

The TV is one of the most popular electronic devices and has not lost its relevance for many decades. Since the sale of the world's first copy, dated July 3, 1928, the television receiver has been modernized several times and has undergone a number of serious design changes. The newest development to date is OLED is a technology that has revolutionized the modern view of image quality and quickly gained recognition around the world.



What it is?
The history of introducing OLED matrices into modern TVs began in 2012, when two world giants LG and Samsung introduced several innovative designs to the market. OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) technology was so popular with the consumer that a couple of years later, Sony, Panasonic and Toshiba began producing superdisplays.


The principle of operation of OLED TVs is based on the use of a special matrix consisting of LEDs, each of which is made of organic materials and endowed with the ability to glow independently. Thanks to the autonomous illumination of each LED, the television screen does not require general backlighting, and the image does not blur or freeze, as happens with liquid crystal models due to a rapid picture change.
The use of organic crystals provides instant image change due to their high speed of color change.
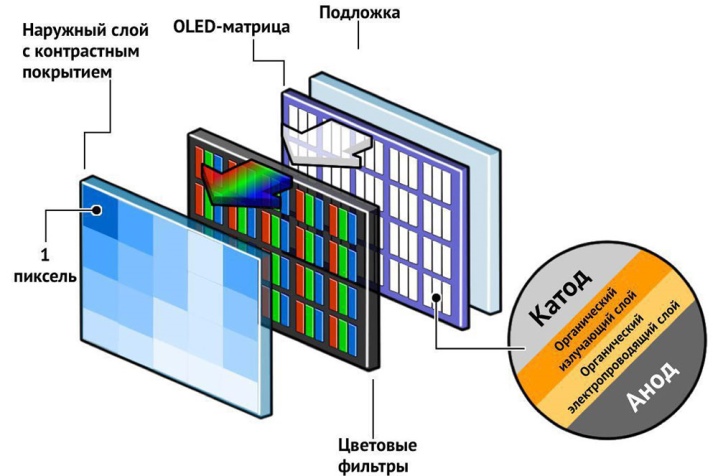
Due to the independent illumination of each pixel, the image does not lose its brightness and clarity from any viewing angle, and carbon LEDs form flawless shades and convey the contrasting depth of black. Self-illuminating pixels work together using phosphor combining techniques to produce more than a billion shades that no other system is capable of today. Most modern models come in 4K resolution and HDR technology, and some of the TVs are so thin they can be simply wall-mounted or rolled.


Most OLED TVs have an average lifespan of 30,000 hours. This means that even with a daily 6-hour viewing, the device is able to function properly for 14 years. However, this does not mean that after the resource is used up, the TV will stop working. The fact is that the matrix of an OLED device consists of pixels of three colors - blue, red and green, while the durability of blue is 15,000 hours, red - 50,000 and green - 130,000.

Thus, the blue LEDs are the first to lose brightness, while the red and green ones continue to work in the same mode. This can lead to a deterioration in picture quality, a violation of the color gamut and partial loss of contrast, but the TV itself will not stop working from this.
You can extend the service life of the device by setting a low brightness threshold, as a result of which the working life of the LEDs will be much slower.

Advantages and disadvantages
The high consumer demand for OLED TVs is due to a number of indisputable advantages of these modern devices.
- The main advantages of the self-illuminating pixel system are the perfect picture quality., the highest level of contrast, wide viewing angle and flawless color reproduction. The brightness of OLED models reaches 100,000 cd / m2, which no other technology can boast of.
- Compared to other TVs OLED receivers are considered the most environmentally friendly and quite economical. The power consumption of such a device is 40% less than, for example, plasma devices that do not have an LED system.
- Due to the fact that the display is based on the finest plexiglassOLED TVs are lightweight and thin. This allows the production of models styled as a sticker on the wall or wallpaper, as well as specimens of curved shapes and displays rolled into a roll.
- TVs have a stylish look and easily fit into all modern interiors.
- The viewing angle of such models reaches 178 degrees., which allows you to watch them from anywhere in the room without losing image quality.
- OLED models are characterized by the shortest response time, which is 0.1 ms versus 7 ms for other TVs. This parameter affects the quality of the image when the color changes quickly in vivid and spectacular scenes.



Along with many obvious advantages, OLED TVs still have disadvantages, and the most significant of them is the price. The fact is that the creation of such displays requires high costs, which is why the cost of OLED TVs is much higher than the cost of devices with LED matrices and ranges from 80,000 to 1,500,000 rubles. The disadvantages include the high sensitivity of the devices to moisture, when it gets inside the device instantly breaks down.
And also the limited working life of blue LEDs should be noted, which is why, after a few years, the colors on the screen begin to display incorrectly.


Varieties
At the moment, there are several types of displays made on the basis of OLED technology.
- FOLED screen is considered the most flexible of the entire OLED family and is a metal or plastic plate with hermetically sealed cells placed on it, which are in a special protective film. Thanks to this design, the display is as light as possible and as thin as possible.
- PHOLED screen built on a technology based on the principle of electrophosphorescence, the essence of which is to convert all the electricity entering the matrix into light. This type of display is used for the production of large-sized TVs and giant wall monitors used in large corporations and public spaces.
- SOLED Displays have a higher resolution, which is characterized by the highest level of detail in the construction of the image. The excellent picture quality is due to the vertical arrangement of the subpixels, each of which is a completely independent element.
- TOLED technology it is used to create transparent displays that have found application in store windows, car glasses and simulation glasses that simulate virtual reality.
- AMOLED displays are the simplest and most common system of organic cells that form green, blue and red colors, which are the basis of an OLED matrix. This type of screens is widely used in smartphones and other gadgets.

Popular models
The modern market offers a sufficient number of OLED TVs from well-known manufacturers. Below are the most popular models, most often mentioned on the Internet.
- LG OLED55C9P 54.6 '' TV 2019 year of manufacture has a diagonal of 139 cm and a screen format of 16: 9. The 3840x2160 model is equipped with stereo sound and Smart TV function. Distinctive features of the device are a large viewing angle of 178 degrees, and built-in memory with a capacity of 8 GB. The model has the option of protecting against children, can be controlled by both the remote control and the voice, and is equipped with an automatic volume leveling function. The device is capable of working in a “smart home” system, is available in sizes 122.8x70.6x4.7 cm, weighs 18.9 kg and costs 93,300 rubles.


- TV Samsung QE55Q7CAMUX 55 '' silver color has a screen diagonal of 139.7 cm, a 40 W audio system and a resolution of 3840x2160 4K UHD. The model is equipped with a VESA wall mount measuring 7.5 x 7.5 cm, has a curved display and is endowed with Smart TV and Wi-Fi functions. The device is manufactured in dimensions 122.4x70.4x9.1 cm (without stand) and weighs 18.4 kg. The cost of the TV is 104,880 rubles.



- OLED TV Sony KD-65AG9 belongs to the premium class and costs 315,650 rubles. The diagonal of the screen is 65'', resolution - 3840x2160, format - 16: 9. The device has an Android operating system, Smart TV, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth functions, and the size of the built-in memory is 16 GB.
The TV can be placed both on the wall and on the table, it is produced in dimensions 144.7x83.4x4 cm (without a stand) and weighs 21.2 kg.



Difference from LED
In order to understand the difference between LED and OLED TVs, it is necessary to take a closer look at the features of the first technology and compare them with the characteristics of the second.
So, LED devices are a type of liquid crystal panel equipped with LED backlighting. The main function of the LEDs located either on the edges of the panel (Edge LED version) or immediately behind the crystals (Direct LED) is to illuminate the LCD matrix, which independently adjusts the level of transmitted light and simulates the picture on the screen. This is precisely the main difference between technologies, since in OLED systems, LEDs are part of this very matrix and emit light on their own.

The difference in technology entails a number of differences that the consumer should focus on when choosing a particular TV model.
- Sharpness of the image, brightness of colors and their contrast OLED displays are much better than LEDs. This is due to the organic nature of LEDs and the peculiarity of building black. In OLED matrices, when broadcasting a picture with black elements, the pixels are simply turned off, thereby forming a perfect black color, while in LED models, the matrix is illuminated continuously. In terms of uniformity of the screen luminescence, OLED samples win, since the contour illumination of the matrix in LED samples is not able to uniformly illuminate the entire display area, and when the panel is completely darkened around its perimeter, illuminated areas are visible, which is especially noticeable in the evening.
- Viewing angle is also the hallmark of OLED systems. And if in LED devices it is 170 degrees, then in most OLED models it is close to 178.
- Pixel response time OLED and LED systems also differ. In liquid crystal models, with a sharp change in color, a barely noticeable "trail" often occurs - a phenomenon in which the pixels simply do not have time to instantly react and change the color brightness. And although in the latest LED TVs this effect is minimized, it has not yet been possible to get rid of it completely. OLED systems do not have such a problem and respond to changes in brightness instantly.
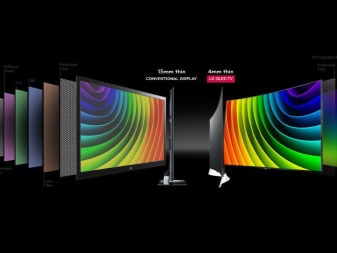
- As for the dimensions, here OLED devices are the absolute leader. The minimum thickness of such panels is 4 mm, while the thinnest LED TV is 10 mm thick. Weight of the thinnest 65-inch OLED model'' is only 7 kg, while LCD panels of the same diagonal weigh more than 18 kg. But the choice of screen sizes for LED-models is much wider than that of OLED. The latter are produced mainly with a 55-77 display'', while the diagonals of LED screens on the market vary from 15 to 105''.
- Energy consumption is also an important criterion, and LED samples are in the lead here. This is due to the fact that the consumption of electricity in such TVs is more stable and depends on the brightness of the backlight set initially. OLED systems are another matter, in which the power consumption depends not only on the brightness settings, but also on the picture. For example, if the screen is broadcast at night, then the power consumption will be lower than when showing a bright sunny day.
- Life time Is another indicator by which LED receivers are noticeably superior to OLED systems. Most LED receivers are rated for 50,000-100,000 hours of continuous operation, while the average lifespan of OLED displays is 30,000 hours. Although nowadays many manufacturers have ditched the "red, green, blue" (RGB) pixel system and switched to white LEDs, thereby increasing the life of the devices to 100 thousand hours. However, such models are much more expensive and are still produced in small quantities.



Criterias of choice
There are a number of important things to consider when shopping for OLED TVs. For example, you should definitely take into account room size, into which the TV is purchased, and correlate it with the diagonal of the device. Most modern OLED systems come with a large screen, which is rather inconvenient to look at in a small space.

Another parameter that you need to pay attention to when buying is price... An OLED TV cannot be cheap, so the low cost of the device should be on your guard. Prices for such models start at 70 thousand rubles, and if it is much lower, then, most likely, the characteristics of the TV do not correspond to those declared, and the device does not have an OLED matrix. A suspiciously cheap receiver is not worth buying, and in this case it is better to pay attention to LED models that have been proven over the years.
In addition, when buying a TV, checking the accompanying documentation and the warranty card should be mandatory. The warranty period for most models from well-known manufacturers is 12 months.



Review overview
Users generally appreciate the performance of OLED TVs. They note high contrast, richness of colors, sharpness of the picture and a huge number of shades. but most experts consider the models "damp", requiring improvement. Manufacturers listen to the opinions of consumers and experts, constantly improving their products.
For example, a few years ago, many owners complained about pixel burnout when watching the same channel with the logo always present in the corner of the screen, or when the TV was paused for a long time while playing video games.


Organic light-emitting diodes on statically luminous areas quickly burned out, and after changing the picture they left characteristic traces on the screen. Although, for the sake of fairness, it should be noted that, unlike plasma models, the prints of the previous pictures disappeared after a while. Burnout was due to flaws in RGB technology used in the early years of such TVs. There were many negative reviews about the short lifespan of OLED TVs, which made their purchase unprofitable.
To date, taking into account the comments of consumers and specialists, manufacturers have saved their devices from the burnout effect, worked out the system of glowing pixels and increased the working life of the matrices to 100,000 hours.

The next video will tell you which TV shows better.













The comment was sent successfully.