Battery Powered LED Strips
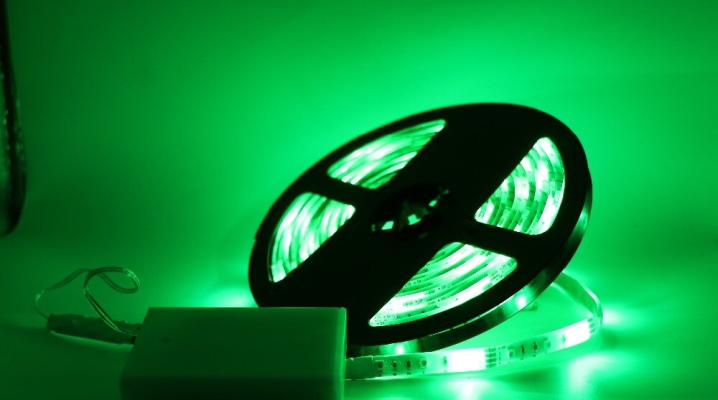

It is convenient to operate LEDs when the power supply is connected to the mains. In 99.9% of cases, electricity is “at hand”. However, in places that are not connected or remote from the mains, battery-powered LED strips are still needed.


Peculiarities
3-volt LEDs connected one at a time will require multiple components.
At 1-1.5 volts - circuits on one or more transistors for "voltage boost"so that from this voltage (one nickel-based battery) the device makes 3.2 volts, without which the LED will not glow. For rare LEDs operating from 1.5 volts, such a circuit is not needed.
If there is an acid battery that produces 1.8-2.3 V - no voltage boost is required for the red, blue, yellow and green LEDs.

They operate at a nominal voltage of 1.8-2.2 V, they can be connected directly, in parallel, in any quantity. The more, the more capacious it should be.
If a lithium-ion battery is used, the colored LEDs are connected in serial pairs. At a maximum voltage of 4.2 V, their glow will reach a level slightly above average (2.1 V per LED). These pairs are connected in parallel to each other. Do not try to connect single color LEDs in parallel without serial pairing - they will immediately burn out.
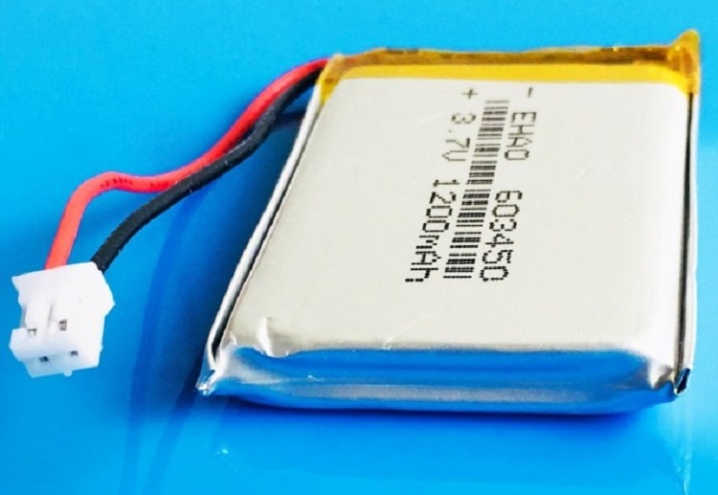

Having a power source at hand, for example, an external battery with a 5 V smartphone, neither color nor white LEDs can be connected directly: they will immediately burn out. Here you need a regulated DC voltage converter - these are stamped in China by the millions a year. It is easy to order the required one and set the input and output voltages using the tester. The disadvantage of DC voltage converters is low efficiency: losses can be up to 34%, depending on the input and output voltage.


12-volt clusters will require not one, but several batteries. For 3 lithium-ion batteries, the voltage ranges from 9 to 12.6 V - the cluster will not be overloaded if you turn on not 3, but 4 LEDs in series (operating voltage does not exceed 12.8 V). The commercially available industrial assemblies, unfortunately, despite the presence of current-limiting resistors in each cluster, have exactly three, not four LEDs. Here, there is a violation of the correctness of the calculation for the sake of economy: less LEDs are spent, but they quickly burn out, which forces the consumer to change them regularly. In the case of red ones, for example, for rear sidelights (brake light), it would be more correct to connect exactly 6 LEDs for 12 V (the assembly voltage would be 13.2 V). But the savings and the desire for light super-profits make manufacturers recruit not 6, but 5 LEDs to each cluster. When exposed to voltage from a freshly recharged battery, the LEDs overheat and burn out prematurely.

For 24-volt tapes, the above power ratings are doubled.
Conclusion: in order not to overload the LEDs, calculate the circuit parameters carefully. The white LED quickly burns out when the voltage is above 3.2 V, the red one - when the value is higher than 2.2. It is easy to calculate for nickel or lithium batteries - some give 1-1.5 V, the second - 3-4.2. Try to calculate the circuit so that only one battery cell (one "bank") works: two or more wear out always unevenly, and an overrun occurs due to the non-use of their resource in full.

When are they needed?
Single LEDs and light clusters (as part of light strips) are needed in several cases.
-
Illumination in places where wiring is not suitable, or, for example, in a country house where there is no power supply (or it was cut off for a long non-payment).
-
Illumination on hikes, where there is no opportunity to connect to a household or industrial power supply.A common case is the illumination of a bicycle, an electric scooter or an electric scooter, a tent.
-
In cases where the unique design does not want to be spoiled by the wiring, there is no way to hide it together with the power supply.
-
When performing work in a place where the area of \ u200b \ u200bthe room is not important, and therefore, power. There is light wherever you are, wherever you go - a headlamp (or spotlight) is ideal for light ribbon clusters. He will only shine next to you when needed. This makes it possible to save on light bulbs and network light strips, lighting of the space that is absolutely unnecessary at the moment.


The disadvantages of this solution are the inability to use light strips on batteries at a height, for example, the decor in the kitchen under the ceiling, which can be effectively illuminated.
This disadvantage can be easily turned into a plus with the help of solar panels that charge the built-in battery during the day.
With the onset of dusk, the photodiode or photoresistor, which is part of the ambient light sensor, independently turns on the lighting. The energy accumulated in the battery over the entire daylight hours is spent on the glow of the light-cluster LEDs. Transportable tapes do not have to be self-adhesive - they use an outer protective sheath made of transparent plastic or silicone.


How to connect?
Connecting LEDs with your own hands is carried out according to the simplest scheme - a battery, a switch and an LED assembly. Separately, for recharging the battery, additional terminals (or connector) are used, which can be brought out to connect the charging adapter.
The whole structure is placed in a small-sized case with a diffuser (or, conversely, with a lens focusing the light flux). Observe the polarity of the light tape and the power source: a tape connected "backwards" will not glow - it is not alternating, but direct current, always passing in one direction.
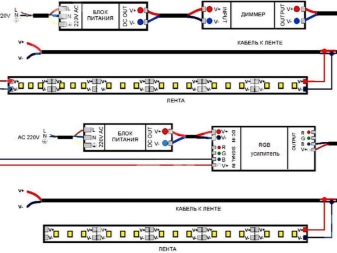

In damp places, connect tapes of waterproof class IP-68: its electrical materials and light elements will not fail under the influence of dampness.
Although voltages up to 12 volts are considered harmless even for wet hands (if the skin is not damaged), the entire structure (circuit) must be reliably protected from moisture condensation and splashing water. If no prefabricated light elements with full moisture protection were found, fill the assembled contacts with hot glue or rubber sealant. Do not use epoxy if the assembly is very thin - one crack and the conductive tracks could be torn. The device "cast" with epoxy is not repairable.


It is not recommended to use colored LEDs in places of critical work. The fact is that red, for example, will distort the colors of blue and green objects in semi-darkness, passing them off as black or brown. Likewise, red objects will appear lighter in red than they are, while not standing out against the background, for example, of whites, also colored with a red glow in the same color. Similar restrictions apply to yellow, green and blue LEDs: objects and substances of the same color will completely disappear.
The most suitable color for everyday use is yellow. So, in yellow glasses, this light is practically not emitted, which gives an anti-glare effect to such a lantern or light tape.

It can be obtained by turning on the red and green LEDs at the same time - illumination with a yellow-orange tint is formed, which is practically safe for the eyes.
Red, green and blue LEDs can be used at the same time if there are no white ones. The fact is that different-sized light will create comfortable lighting reminiscent of "warm", "neutral" or "cold" white light flux.



For a LED strip controlled by a wireless device, the following components are required:
-
remote control - source of infrared radiation;
-
port - a receiver of the same infrared rays;
-
a relay unit or a key on a transistor - a power switching device;
-
the simplest microcontroller - controls the operation of the switch key.
The remote itself will require separate batteries. A similar scheme has found application in the conditions of apartments, when the centralized power supply is temporarily turned off.

How to power up?
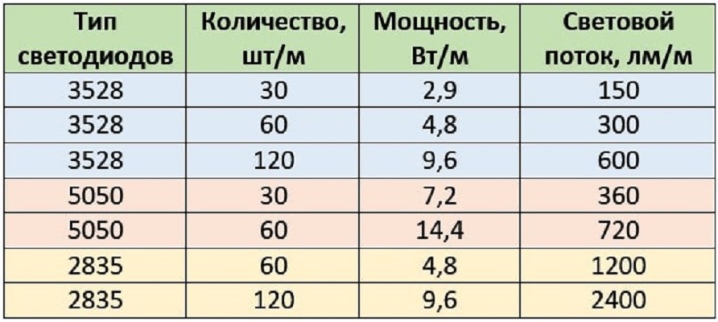
To calculate a diode strip or a luminaire that can work in almost continuous lighting mode for more than one year, use the characteristics of LEDs, batteries and limiting resistors (or reducing the supply voltage of diodes), DC converters (converters, for example, 1.5V-3V), presented above. Your task is to coordinate the power supply as much as possible so that the LEDs work for the stated period from 25 to 50 thousand hours, as indicated in the advertisement. Hasty actions will lead to low luminosity or to their premature burnout due to the peak brightness mode.
When supplying light strips for indoor lighting without an outlet, it is preferable to use rechargeable batteries. Not a single today's user in their right mind, having at least some idea of batteries, buys disposable batteries for constantly and many working devices, be it even a single LED in a small-sized flashlight.
Batteries are the lot of consoles and wall clocks, where electricity consumption is so negligible (measured in microamps per hour) that it is not possible to use them as a source of any significant current that has practical application.



However, only rare batteries are suitable for the street - for example, nickel-cadmium batteries, charging even at negative temperatures, which makes them indispensable in the Far North.
Try to keep the wires as short as possible. This will save you from unnecessary loss of current in them. The light strip, which can be placed in a secluded place, should be in close proximity to the batteries. If a case is used for the tape, then it is advisable to place a battery in it, the switch itself and the terminals for recharging such a device. Some craftsmen place a rechargeable battery, for example, in a piece of hose with a larger diameter, put on a protective coating of a waterproof tape - from one of the ends where there are terminals for connection.
See below for battery-powered LED strip.













The comment was sent successfully.