What do beets look like and how to grow them?
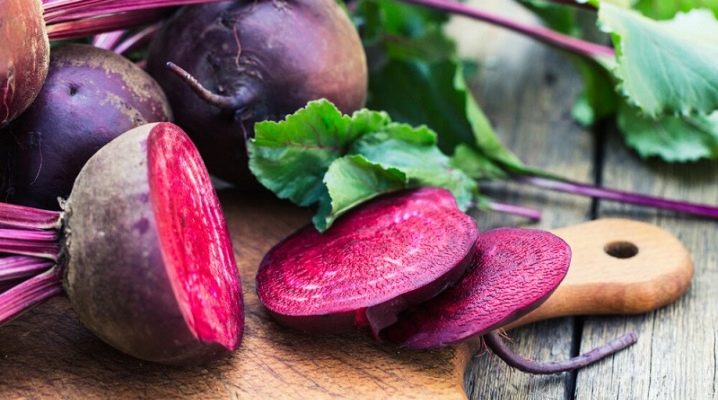

Beetroot is one of the most popular crops grown in vegetable gardens and home gardens. Nevertheless, you cannot call it completely unpretentious, and in order to obtain sweet juicy fruits, certain rules of agricultural technology must be observed.


general description
Beetroot can develop as an annual, biennial or perennial herb.... However, the life expectancy of most varieties is still limited to two years. The vegetable belongs to the amaranth family and is a representative of the dicotyledonous class. In Belarus, Ukraine and some regions of Russia, the plant is known as beetle, or beetle. The appearance of farmed beets is slightly different from those found in the wild. For example, the wild annual form has a thin root, while the garden one has a more powerful tap root system. The characteristic of the structure of the plant indicates that in the first year it only forms a thick, powerful root crop, which outwardly looks like a turnip.
Its base color is burgundy but can also be white or yellowish. The root crop appears accompanied by a rosette of long leaf blades sitting on petioles. It is formed from the head, neck and root. The next year, the culture from the middle of the outlet grows a stem, erect, branched and reaching a height of 50 centimeters to 1.25 meters. Alternate leaves have a lanceolate shape, and can also be smooth or wavy. Spikelet or paniculate inflorescences are collected from small white-green bisexual flowers.
The peculiarities of the development of culture indicate that flowering can last from July and practically to September. The fruits of common beet are compressed single-seeded nuts, growing together in 2-6 specimens.


Origin
It is quite difficult to determine where the beets come from. Wild beetroot was found and is found to this day in Iran, India, China, as well as near the Mediterranean and Black Seas. History testifies that Ancient Rome may also be the homeland of cultivated beets, because it was there that not only root crops, but also the tops of plants were already eaten.
Nevertheless, it is known that in Russia, ordinary beets appeared already by the X-XI centuries AD, having got there from Byzantium. In 17th century Russia, sliced root vegetables were served before dinner, and greens were used in soups. In 1801, the manufacture of sugar from beets began in Moscow, and in 1802 the first sugar beet factory was launched.

Types and varieties
According to the classification, the species group of common beet includes 3 varieties: feed, sugar and table... Unsweetened fodder beets form large, smooth root crops weighing up to 10 kilograms. Sugar beets are high in sugar and low in juice. A cone-shaped root vegetable with white flesh and a rough surface weighs about 300-600 grams. Finally, beetroot produces common dark red fruits. She, in turn, has 4 varieties: Egyptian, Bordeaux, Eclipse and Erfurt.
One of the more popular beet varieties is early maturing "Valenta" with dark red flesh, characterized by frost resistance and good immunity. Gets good reviews mid-late "Ataman", whose roots reach a weight of 300 grams. The burgundy pulp has a sweet, pleasant taste. Mention should be made of the mid-late variety called "Cylinder"... Its bright red elongated fruits reach a weight of 0.5 kilograms.
For cold regions, "Podzimnyaya" is recommended, the weight of root crops of which varies from 200 to 400 grams.


Landing
It is customary to plant beets in open ground in spring, when the ground temperature at a depth of 10 centimeters warms up to +8 degrees, and the air temperature will be approximately + 15 ... 18 degrees. Such conditions are usually typical for mid-May. A variant with the April sowing of non-germinated grains under a greenhouse is also possible. If the cold days have dragged on, then you can postpone the planting to a later date, but give preference to early ripening varieties.
Winter beets are sown at the end of October with dry material, always having time before frost. The garden bed, where the beets will be located in the future, must be dug up and fertilized in the previous fall. For culture, organic matter is suitable - compost or manure, deepened into the soil by 30-35 centimeters. To normalize acidity, dolomite flour, wood ash or crushed egg shells are introduced into the site. Again, in the fall, you can fertilize the garden with mineral components such as superphosphate and potassium sulfate. In the spring, the earth is dug up and mulched with peat or rotted sawdust.
The crop requires a spacious and well-drained area near an irrigation source. It is necessary to observe the rule of crop rotation, that is, do not plant the crop twice in the same place. Good precursors for beets are onions, garlic, carrots, courgettes, and nightshades, and bad precursors are cabbage.... Before planting, the seeds are checked for germination by immersing them in a glass of salt water and removing the ones that have surfaced, and they are also quenched by alternating hot and cold water. Disinfection of the material is carried out in a weak manganese solution. You can also soak the seeds in a stimulant and germinate them if you plan to grow seedlings.
When planting is carried out immediately into open ground, it will be necessary to prepare grooves 3-5 centimeters deep, 20-30 centimeters apart from each other. The distance between the holes is kept equal to 5 cm, and between the seedlings of seedlings - 20 cm... Winter crops are necessarily deepened by 10 centimeters. In a cold or dry spring, crops are covered with a transparent film, which is removed when the first shoots appear.


Care
Caring for beets is impossible without timely watering and feeding the crop. The plant also needs thinning, carried out in several stages.
Watering
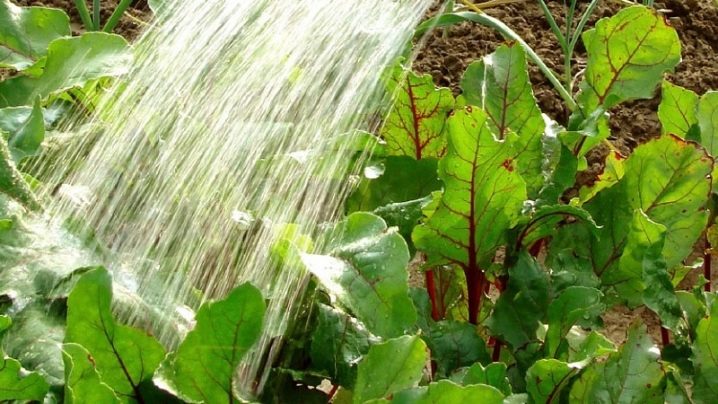
When the culture germinates, it will have to be irrigated every 6-7 days, alternating the procedure with shallow loosening that does not affect the roots. The first watering is organized only after the first thinning from the watering can into the aisles. For each square meter of planting, from 10 to 12 liters of water should be poured.
Hilling the vegetable is not required, but it would be nice to form a groove between the rows, along which excess liquid will go away. If the soil is eroded, then the beds are sprinkled on top with a thin layer of humus. For the crop, mulching of row spacings with layers of chopped dried grass is shown. Irrigation stops 10 days before harvesting.

Top dressing
Usually the crop has enough mineral fertilizers applied before planting, however, if the plant has deviations in development, then it is worth feeding it additionally... Preventive feeding of beets with diluted herbal infusions or yeast fertilizers is a preventive one. A couple of times per season, beets will need to be irrigated with salted water made from a tablespoon of salt and a bucket of water. The vegetable will react well to the introduction of a mineral complex, for example, "Makbor".It is customary to do the first feeding organic - to breed a kilogram of mullein or chicken droppings in a bucket of water and leave for 3 to 5 days.
Before use, the concentrated mixture is diluted in 10-12 liters of water and supplemented with 1 gram of boric acid. An alternative to such an organic mixture is 200-300 grams of ash or 30 grams of nitrophoska diluted in a bucket of water. After 2 weeks, the beets can be fed with a potassium-phosphorus complex.
When the tops in the aisles begin to close, the culture will again need these components in the amount of 30-40 grams per square meter.


Harvesting
Beets should be dug out in early September, and sometimes at the end of August. It is important to monitor the weather conditions and control so that the roots do not get frozen, otherwise their storage will be difficult. If the autumn is warm and dry, then the harvest can be held in the beds longer. In general, it is recommended to focus on the state of the tops - as soon as it begins to turn yellow, you can start harvesting. The procedure is organized on a sunny day. Rounded root vegetables are carefully removed by hand, while cylindrical beets are best pried with a pitchfork or a shovel. Vegetables extracted from the moist soil are dried, after which they are cleaned with hands from the remnants of dirt.
Harvesting carefully is important. The fruits should not be thrown to the ground and mechanical damage should not be allowed in any way. Root crops with a length of 10 to 12 centimeters, devoid of symptoms of rot, cuts and scratches, have the greatest keeping quality. Before going to the cellar, they are freed from the tops, leaving only centimeter petioles. The sections will need to be dried, which can take from a few hours to noon. The storage location should maintain a temperature equal to + 2 ... 5 degrees, and a humidity level from 90% to 95%.
Possible growing problems
When growing beets, it should be remembered that waterlogging of the soil can lead to decay of the roots or even the development of cercospora. If you overfeed the beets with nitrogen, then its taste will become unpleasantly bitter and even earthy. The appearance of white spots on the leaf blades, as well as curvature of root crops are symptoms of a lack of boron.
We must also not forget that overexposure of beets in the garden can contribute to the accumulation of nitrates in vegetables.














The comment was sent successfully.