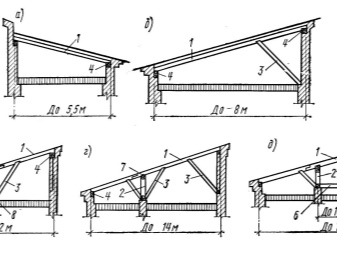
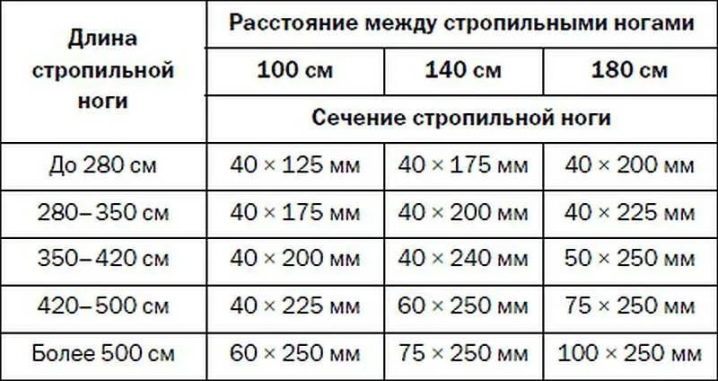
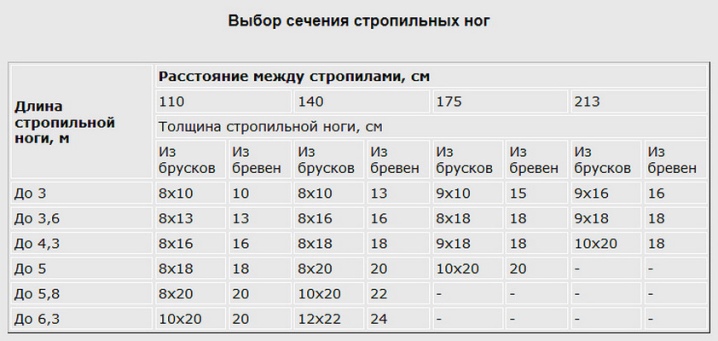
Distance between rafters

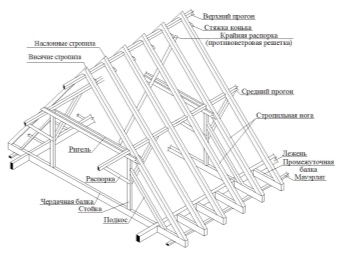
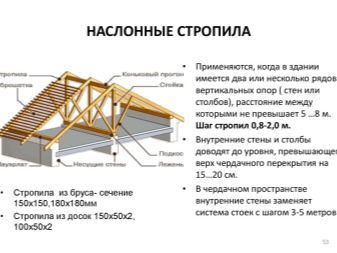
Along with the permissible load on individual elements - Mauerlat, horizontal, diagonal and vertical girders, one of the most important parameters is the step (span) between the rafters. The combination of the optimal values of the entire structure is the key to its durability and strength.


Step taking into account the material
Each of the types (or each of the varieties) of building materials used as a base and covering for a roof has a number of characteristics and notes. The most leading ones include the following.
- The thickness and shape of the corrugated board varies widely. The bend resembles a trapezoid, from which the bottom or top side has been cut off.
- Ceramic tile has a wide choice of shape and texture. Most often it is made in 12 colors.
- Metal tiles - compared to ceramic, this building material is half the price. The advantages are similar.
- A soft roof such as ondulin serves as a noise insulator against rain. According to this parameter, it is close to slate.
- Slate sheets have a round wave, noise insulation from rain. They are cheap, but can break down with intense exposure. It is not recommended to walk on them, it is impossible to put stairs and other sharp devices on the slate roof.


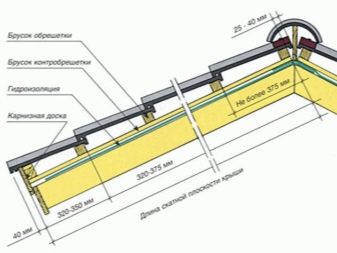
For corrugated board (sheet metal profile), the pitch of the rafters is determined by the dimensions of the steel sheet. Roof frame beams for profile decking, according to standards and according to SNiP, GOST, vary within 6-9 dm. With an increase in this distance, the span between the rafters may contain inserts in the form of a board with an increased section. For corrugated board, the section of the board or timber is from 50 * 100 to 150 * 150 mm. The lathing is built from boards with a cross section of the order of 3 * 10 cm, and the span is about half a meter. The final values are determined by the brand and thickness of the sheet metal profile, the angle of inclination of the roof (in relation to the horizon).
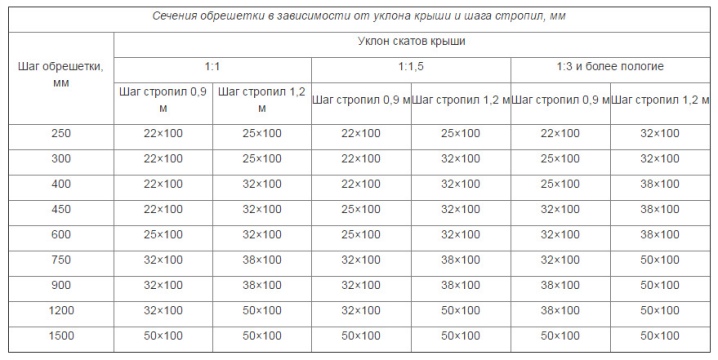
For example, the roof, inclined by 15º and lined with C-10 corrugated board, is installed on the crate without gaps. For profiled flooring, the clearances of the lathing are equal to 3 dm. The largest-wave corrugated board - C-44 - is installed on the crate with a step of 50-100 cm.If the house provides for the construction of a chimney with a stove, an exhaust hood, then the gap under it increases - for fireproof lining of the chimney with non-combustible materials.
Certain features are important for ceramic tiles, for example, the weight of a given roof. The ceramic tile is made mainly of clay fired at an especially high temperature, due to which the material is up to 10 times heavier than the metal tile.
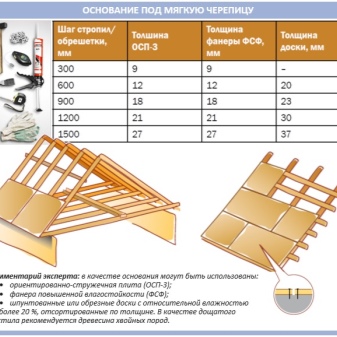
The weight of such tiles has a high specific load - up to 60 kg / m2. The material of the beams - wood - must be thoroughly dried. The cross-section of the rafters is from 50 * 150 to 60 * 180 mm.
If the roof is tilted 15º to the earth's horizon, then the longitudinal gap between the rafters ranges from 80 to 130 cm. When determining the pitch, consider the length of the beam. With an extremely high length, the clearance between the rafters is minimal. The reduced length of the rafters increases the elasticity - the span reaches the maximum mark, depending on the specific value. If the personnel serving it regularly pass on the roof, then the span between the rafters must not be expanded to more than 8 dm.
The dimensions of the ceramic tile elements play an important role in calculating the span of the crate. Ceramic tile has a length of 4 dm. Installation is carried out with an overlap of 5-9 cm.When calculating the pitch of the sheathing, the overlap strip is subtracted. The remaining laying step takes a distance of 30.5-34.5 cm.


In the case of lining a roof with a single slope on a house whose walls are built of profiled timber, it is easy to calculate the spans between the rafters and the elements of the sheathing. On a roof with several slopes, the distance between the rafters is calculated separately for each step of the battens. By using a cord on the opposite side of the ramp, marking the gaps between the rafters is simplified.
The method of work does not depend on the type of premises - bedroom, kitchen, hall or veranda; the layout of the house with non-bearing partitions does not matter for the calculation of the rafters.
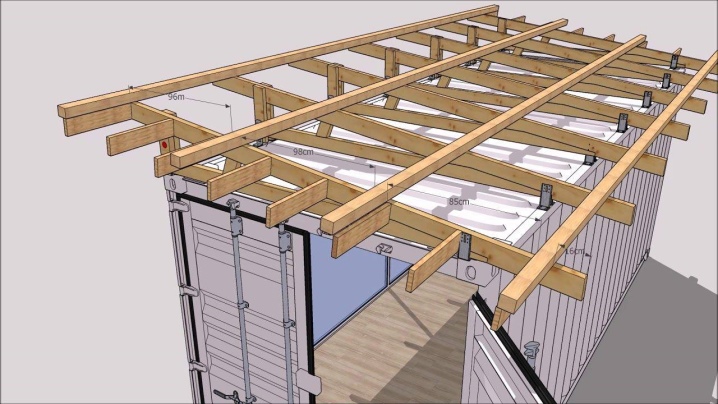
If the roof is lined with metal tiles, then its installation is simplified - technically. The metal tile has a weight of up to 40 kg / m2. It becomes possible to lighten the weight of the rafters by using beams with a smaller section. The pitch between the rafters varies within the range of 6-9 dm. The section of a bar or board is from 5 * 15 cm. When the attic is insulated with 15 cm thick mineral wool, the attic is used as an attic. High reliability of insulation is achieved with the use of mineral wool from 200 mm. Minvata also has its own weight - the safety margin of the rafters and other elements should be enough for it.


The roof frame for metal tiles in terms of parameters does not differ much from the frame for profile decking. The only difference is that the supporting elements are fixed to the ridge girder in the upper part, and not from the sides, as in other cases.
If masters use ondulin as a roof covering, then the house should be built from glued beams or similar materials. Ondulin looks like a repainted slate, but it is lighter in weight. The number of storeys of a house or building does not matter.


Rafters for ondulin are installed at a distance of 6-9 dm. The rafters can be made of coniferous beams, the dimensions in the section are from 5 * 15 to 5 * 20 cm. A smaller cross-sectional area is not recommended. The rafter lathing is installed mainly from a material with a cross section of 4 * 5 cm. The step is 6 dm. Ondulin is attached with an overlap of 3 dm. Fastening of ondulin is carried out with special nails that come with this building material. As for polycarbonate, its unsurpassed lightness will help to reduce the cross-section of the rafters by about 1.2 times - compared to ondulin.

Slate coating is used for private (suburban) buildings. Its advantage is its low cost and easy installation. The cross section of the rafters is from 5 * 10 to 5 * 15 cm, the span size is 6-8 dm. The elements of the lathing have a cross-section from 5 * 5 to 3 * 10 cm. The installation step of the elements depends on the angle of inclination of the slope. Mono-slope pavement of increased steepness - in relation to the earth's horizon - about 45 cm.
There are 4 elements per slate sheet. A pitched roof of reduced steepness will require a span of about 63-65 cm, while no more than 4 elements are consumed per slate sheet.

The span of the rafters under the slate coating depends mainly on the roof structure. Non-residential buildings predominantly use a lean-to roof.
What should be the different types of roofs?
The shape of the roof determines the required safety margin. This margin determines how much distance is applied between the rafter legs.
Single slope
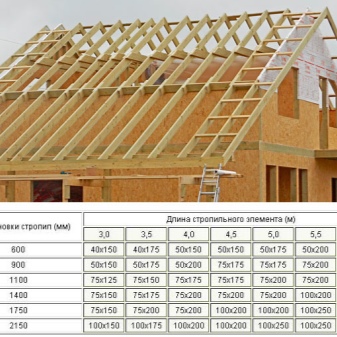
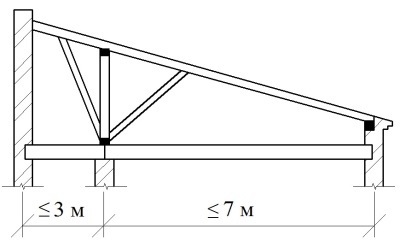
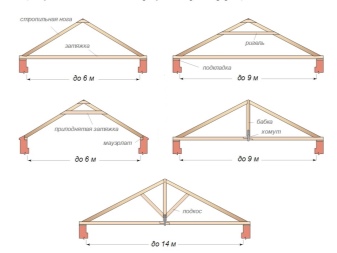
With a pitched roof, strength and ease of installation are at a higher level. The thickness of the rafter system is calculated depending on the type of wood, its strength and specific parameters inherent in a particular technical solution. The span between the rafter legs ranges between 6 and 14 decimeters. The use of insulation determines how this span is comparable to the width of the insulation.
The slightest discrepancy between the width of the insulation and the span will immediately noticeably worsen the thermal insulation properties of the insulation layer.
The thickness of the rafters is considered according to the parameters of the ramp. A slope of 15-20º requires a cross-sectional area of 50x100 mm. A 45º slope will require significantly thicker rafter beams - about 50x150 mm.
Gable
A gable roof cannot do without insulation. The span width is adjusted to the width of the mineral wool. The setting of the overhang of the future roof depends on the step size. The standard pitch ranges from 1 to 1.2 m.
When calculating the span between the rafters using slopes that do not correspond to the number of slopes, the roof will move to the side, and excessive weight will cause the entire structure to bend and weaken. If the distortions have affected the entire rafter system, then an urgent alteration of the attic-roof structure will be required.
Incorrect calculation of the rafter spans will either overload the roof or lead to its premature subsidence.
At the hipped roof of the extension, the distance between the rafters can be ambiguous. If the rafters converge in the center (cone), then the distance between the rafter legs is considered at the base (mauerlat), and not at any point of the rafters.
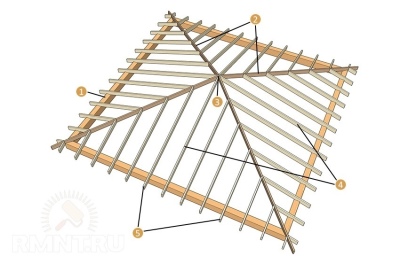
How to calculate correctly?
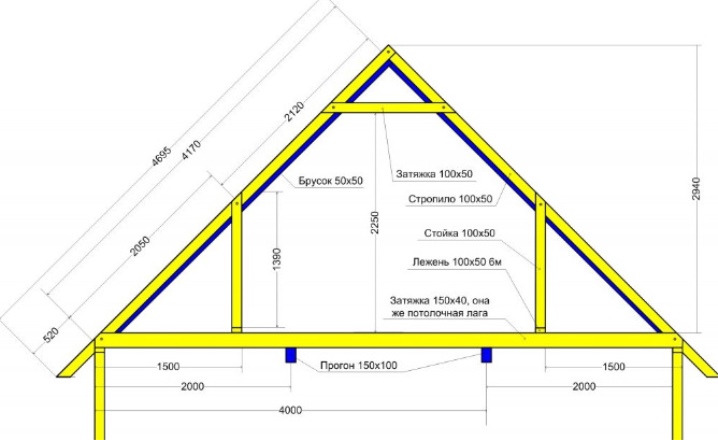
The calculation of the rafters - as the elements that are the basis - is done by assessing the impact on each of the beams. The goal is to calculate the minimum allowable and average cross-section. The calculation formulas are as follows.
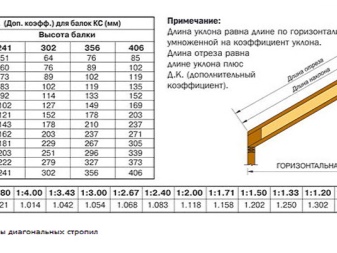
The distributed load per meter of rafter molding, equal to a certain number of kilograms per meter, is equal to the product of the distance between the rafters and the total load. The unit of the latter is kilograms per square meter. The minimum allowable cross-section of the timber from which the rafter is made is determined according to the standards of GOST No. 24454-1980, which reflects the dimensions of coniferous sawn timber.
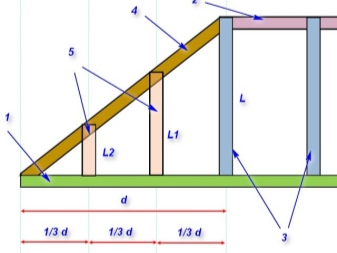
With the help of standard scatter of values, the cross section is concretized for each specific case. The section height is equal to the square root of the ratio of the distributed load per linear meter of the rafter to the product of the section width and the value of the beam resistance to bending, multiplied by the rafter's working area and the value in the range of 8.5-9.6. For pine or spruce rafters, the flexural resistance reaches the following values:
- 140 kg / cm² (premium wood);
- 130 kg / cm² (second-rate);
- 85 kg / cm² (third-rate).
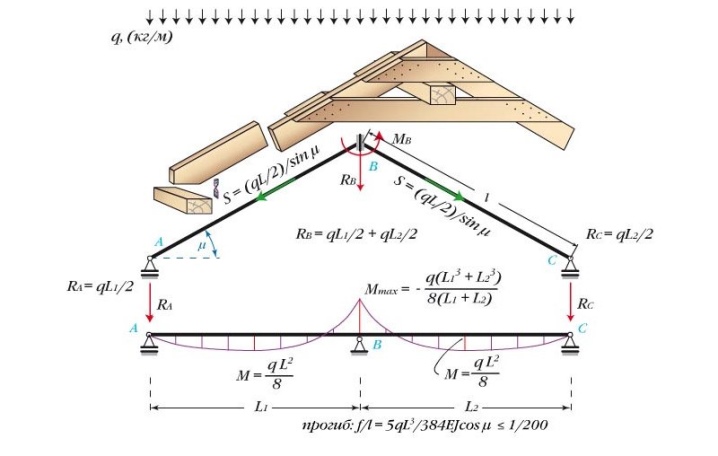
Then the compliance of the deflection value with the standard value is checked. The length of the flange, divided by 200 units, is a kind of limiter for the amount of deflection. This equality is valid only if the inequality 3.125 · Qr · (Lmax) ³ / (B · H³) ≤ 1 is satisfied, where:
- Qr - distributed load per linear meter of rafters (measured in kilograms of weight per meter of length);
- Lmax - the working area of the rafters of the maximum length;
- B - width;
- H is the height of the cross section (in centimeters).
If the last condition is violated, parameters B and H must be increased.
As an example, the slope of the roof covering is 36 °, the span between the rafters is 80 cm. The length of the rafters (active section) is 280 cm. First-class pine with a bending resistance of 140 kg / m is used. Cement-sand tiles have a weight of 50 kg / m2. The total load per square meter of the roof is 303 kg / m2. The thickness of the timber for the rafters is 5 cm.
According to the above formulas, the calculation showed that the load per meter of timber is 242 kg / m. The height of the cross-section of the rafter in this case turned out to be 15.6 cm. The nearest tabular value is 17.5 cm. Checking the conditions for the above inequality, it was confirmed that it was met. The correctness of the calculations is the key to the strength of the roof for many decades. Construction practice shows that the typical distance between the rafters is not less than 60 cm and not more than a value slightly exceeding 1 m.
To prove that the calculation is correct, the length of the slope is measured from below - along the outer length of the wall. The recognized value is divided by the distance between the rafters. 1 is added to the resulting value, and this amount is rounded up. This allows you to calculate the number of rafters per slope.The length of the slope, divided by the number of rafters, will eventually give the amount of span between the rafters.
So, it is easy to determine that 44 rafters will be required for a 25-meter roof. But this method does not allow us to estimate exactly what kind of roofing material to use so that the roof is strong enough. Nevertheless, other calculations, the methodology of which is given above, will help to completely solve this issue. The only ambiguity is, for example, a chimney that heats up to hundreds of degrees and requires a larger span so as not to set fire to the rafters and crate.













The comment was sent successfully.