What are rafters and how to install them?
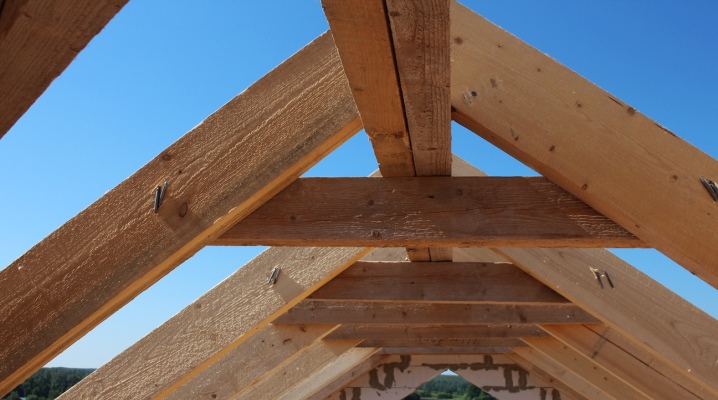

Many people very vaguely understand what it is in general - rafters, how the rafter system is fastened. Meanwhile, there are different types of rafters, and their device can be different - hanging models differ markedly from layered samples and from sliding rafters. Their specific dimensions also introduce significant specificity.
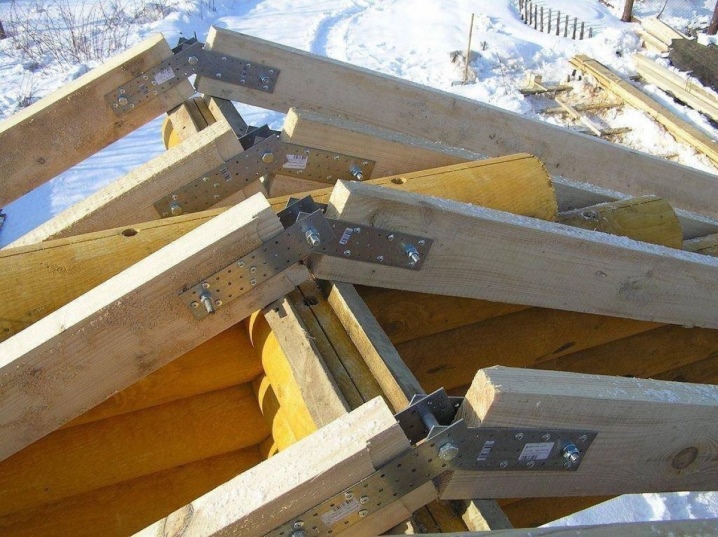

What it is?
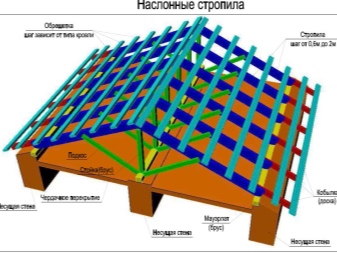
Rafters are one of the most important types of building structures. They are used in any pitched roof. The system includes inclined rafter legs, vertical struts and inclined struts. As required, the rafters are "tied" in the lower part with horizontal beams. The structure of the rafter elements varies greatly in individual cases; the method of "support" differs depending on the material of the building.
Similar structures are equipped on pitched roofs. As all designers strive for maximum stability, they prefer to use a triangular design.

Each particular type of rafter has its own strengths and weaknesses. The difference between them is primarily due to the method of support and the place where this support is made. They certainly also look at the main material of the building, which largely determines the choice of supports for the roof and their organization.


The choice of format is also influenced by:
- financial constraints;
- the intended use of the house itself and especially its upper part (attic or attic, and sometimes their absence);
- the intensity of precipitation and its distribution by the seasons;
- wind loads.


Species overview
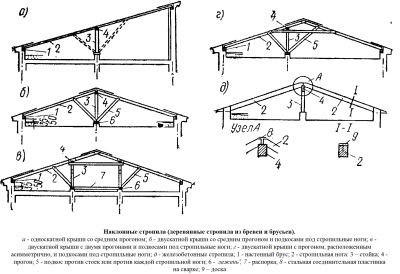
Fortified
Such a rafter system is mainly used when arranging load-bearing walls inside a building. Installation is relatively easy, as the more support points, the easier the installation. The amount of materials used is relatively small (when compared with other types). The main point of support is the skate board. Everything rests on it.
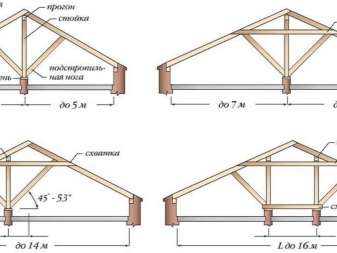
It is worth noting that non-thrust layered systems have three particular types:
- with fixation of the upper sections of the rafters on the ridge (sliding) points of support and with a cut in the bottom into the Mauerlat (additional reinforcement - brackets or wire);
- with undercutting from above at a given angle (joining occurs due to steel plates);
- a rigid connection at the top, made through the bars or a processed horizontal board (the ridge girder is clamped between the rafters connected at an angle themselves).
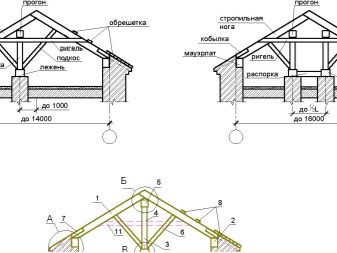
Sometimes layered rafters are made with a spacer system. The lower edge is firmly attached to the Mauerlat.
The resulting side loads are corrected by adding braces and braces.
Strictly speaking, this is the so-called complex, not purely layered version... It contains some of the features of hanging systems.
Hanging
This method is usually resorted to if there are no capital partitions inside the house that could be used as a support. At the same time, the distance between the side load-bearing structures is at least 6 m, and sometimes even more than 11 m. Leaning the roof structure on the load-bearing walls is not the worst solution, but a powerful spacer load appears.
The introduction of puffs or crossbars helps to slightly reduce such stress. They can be fastened at any point, regardless of the height of the rafter assemblies. Most often, a board with a section of 5x20 cm is used, but it is still more correct to proceed from an individual calculation for a specific project.

Sliding
Rafters of this type have only one anchor point. Most often, she is chosen as a skate. Additionally, a sliding support is used, that is, a Mauerlat. This solution is typical for timber houses that are prone to shrinkage. An attempt to use rigid structures will inevitably result in only destruction and weakening of the ligaments with any noticeable temperature fluctuations.
The structure of the rafters varies flexibly depending on the type of roof.


In the single-pitched version, the roof of a small structure rests on rafters, which are supported by the front wall and the wall opposite to it. The slope is formed due to the difference in the height of these walls. But when the gap exceeds 6 m, such a solution is unacceptable. In this case, you will have to use retaining posts; on equally high brick walls, support structures are often placed, completely made of timber or logs.

In case of a long break, the system includes:
- struts;
- legs and racks holding them;
- skate runs;
- mauerlat;
- lie down.


It is assumed that the rafters are supported on a pair of load-bearing walls. Important: these walls must be the same height. A pair of rectangular slopes can represent a triangle with different or identical sides. The difference in sides is good in that it provides easy snow melting from one side of the roof. Most often this is the leeward area; the pediments are sheathed with boards or lined with bricks so that they visually continue the wall.
For a multi-gable roof, you need rafters with high strength and load-bearing capacity. It is immediately assumed when calculating that it will be subject to extreme influences, including an almost hurricane wind. The skate is placed high - this is also taken into account when planning.


In the main buildings with a multi-gable roof, the layered structure of the base is preferable, in the auxiliary ones - the hanging version.
The attractive hip roof also poses a number of challenges when fitting out rafters. The calculation of the cross-sections, again, predictably, must be carried out very carefully. The bottoms of the legs can rest on the beams or contact the Mauerlat. For a bunch of corners and extreme parts of the ridge girder, it is necessary to use diagonal rafter components. The formation of the hip planes is achieved with the help of the so-called napkins.


For half-hip roof assemblies, both layered and suspended support structures can be confidently used. Mounted versions are necessarily attached to the main and auxiliary supports. The trusses are shaped like the letter A or an isosceles triangle. If the ramps are relatively short, side runs can be avoided. But braces, beds and crossbars, other auxiliary elements must be used without fail.

Special attention should be paid to the arrangement of the rafters under the valley. Correctly and clearly lay them there only when forming the girders.
A butt joint, or the convergence of the ends at an angle, means the need for additional calculations for this particular node. An overlap scheme helps to simplify the clarity of the connection of nodes. The lathing at the junction is formed in a strictly continuous way and necessarily also provides for waterproofing.
In some cases, the roof is supplemented with one or more bay windows. The arrangement of the rafters then also has its own characteristics. 3 center intermediate rafters are fixed at each corner of the ridge beam. Corner - they are also oblique - components are located in the corner parts of the frame. So-called intermediate products are placed between the central nodes.
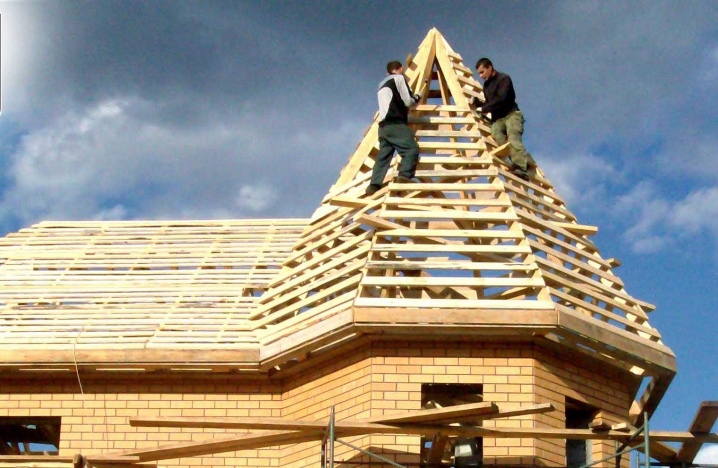

Manufacturing materials
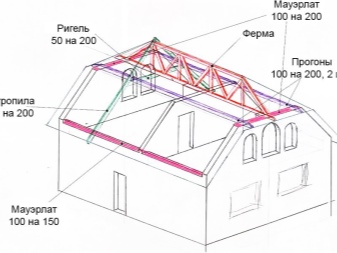
In residential private houses, wooden truss systems are mainly used. Structures based on metal blocks are in demand mainly with a significant amount of spans and with powerful roofing loads. This is rather a feature of a production facility. The cost of metal structures is quite high, but in terms of reliability they greatly outperform their wooden counterparts. Most often, channels are taken as a basis.
Roofing complexes made of wood are usually performed on the basis of edged boards with a section of 15x5 or 20x5 cm.

The reason for their popularity is their cost-effectiveness and ease of production. In some cases, logs produced from trunks with a cross section of 10 to 20 cm are taken as a basis (the tree is pre-cleaned and processed). For reasons of strength, sometimes glued laminated timber rafters are also used, which in the plan resembles a rectangle or square - such a structure simplifies laying on the crate.

Calculation of the aggregate loads
With such a calculation, you must first determine the mass of all materials used - for each of them it is recalculated per 1 sq. m. Take into account:
- interior decoration;
- the actual rafters;
- insulating parts;
- isolation from water, wind and water vapor;
- lathing and counter-lattice structures;
- roof coverings.
It is advisable to add another 10%. Then even an unexpected change or excess of purely roofing loads will not be fatal for the rafter system. Snow, rain and wind effects are calculated according to the standards set for a specific region. There will be nothing bad if you add another 10-15% to these indicators. A professional approach also requires paying attention to the load arising from the regular maintenance of roofs, communications and communication systems installed on them, and other infrastructure.
Additional elements
In the descriptions of the arrangement of the roof, the use of fastening reinforced corners 100x100 is sometimes mentioned. But experienced carpenters and roofers never use this method, because such supports are frankly unreliable and impractical. A truly professional approach is to use special staples. They have been used for many decades, and, despite all the latest technological solutions, such a step is fully justified in the 21st century.
In some cases, metal studs are used. This means that metal reinforcements cannot be dispensed with. Some craftsmen prefer galvanized metal nail strips. Rows of teeth approximately 0.8 cm high are their main characteristic feature. Nail strips are very reliable and practical.


How to do it?
When arranging rafter systems with your own hands, it is very important to correctly determine the parameters of the materials used.
The size of the boards is critical. You cannot use a board less than 5x15 cm.
Large spans require even more massive elements. For small outbuildings, the thickness of 3.5 cm is quite worthy; in the case of residential buildings, you need to be guided by at least 5 cm.
Requirements (concerning also logs):
- for 1 m - no more than three knots;
- high-quality drying (up to a moisture content of 18% and below);
- inadmissibility of through cracks.

Elongation
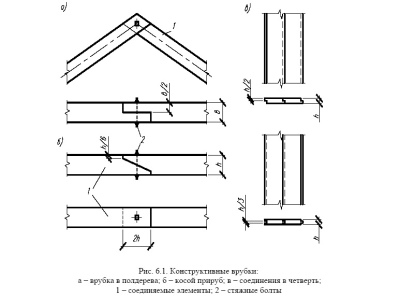
The maximum length of suitable planks is not always sufficient. And it is not very convenient to use very large blanks. The solution is this: take shorter products and carefully connect them along the length of each other. This approach also allows the use of many boards with a length of 3-5 m, which remain during construction as waste. To do this, apply:
- oblique cut;
- butt joint;
- overlap joint.
How to file?
The technology depends primarily on the angle and dimensions of the structure being formed. The length of the rafters is calculated using the Pythagorean theorem. A triangle is formed from the tree with the same angle at which the structures will be filed. Homogeneous sawing should be done exclusively according to the template.The marking is carried out directly on the roof, and not on the ground; Do not cut too deep because this negatively affects the strength of the system.
Fastening
If you need to mount the rafters on a pitched roof, they are usually installed on load-bearing walls. This path reduces the consumption of lumber.
Important: the load-bearing wall in this case should be located at the level of the roof itself. Otherwise, such an installation is not feasible.
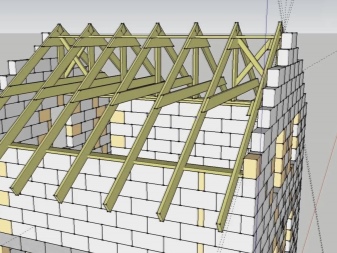
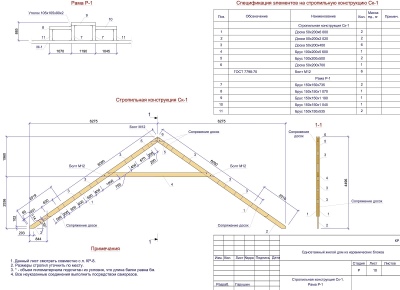
A more traditional approach is to design the truss in the form of a triangle containing posts and beams; all farms can be pre-assembled on the ground according to a template.
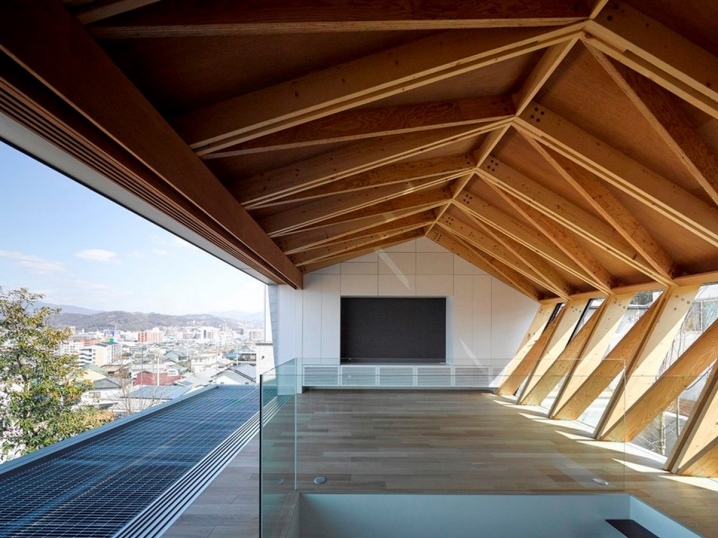

Fastening of rafter complexes is made according to various schemes:
- with Mauerlats;
- on beams (as they say, on the floor - or, more professionally, with the support on the floor beams);
- using puffs;
- by connecting to the upper crown (if log cabins are constructed from beams);
- top strapping (when using frame technologies).
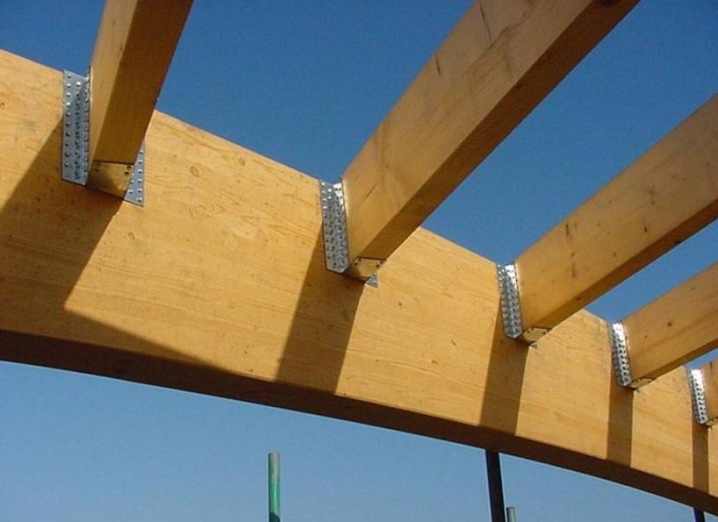

It cannot be assumed that only one or two options can be placed correctly. In fact, you need to adapt to the specific situation. The recesses in the Mauerlat do not always have to be done. It is advisable to make an incision in hard wood. But the coniferous tree allows you to refuse such a step.
To install the structure correctly, you need to cut out the connectors in the rafter legs:
- due to a tooth with an emphasis (if the mounting angle is more than 35 degrees);
- with 2 teeth (if a sloping roof is installed);
- in stops - with or without spikes.
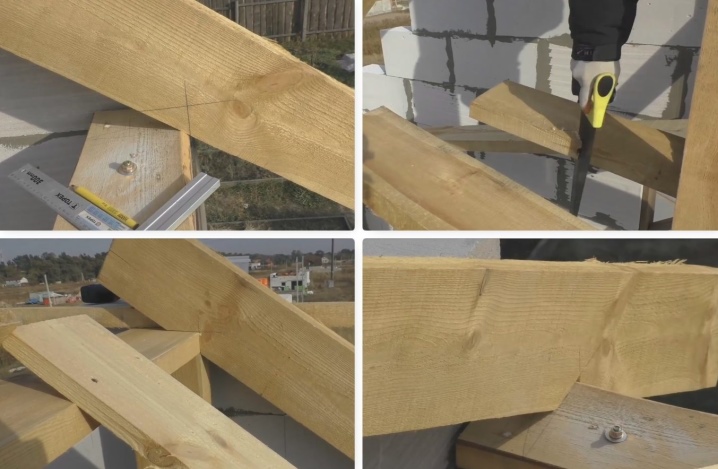

Supporting the floor joists means powerful, precise loads. This solution is most typical for wooden houses. Pressure is dispersed using a Mauerlat, which is made on the basis of a thick (approximately 15x15 cm) bar. The beams must be laid out on the same Mauerlat and thoroughly fixed.
The rafter legs are attached to the beams to increase the area of the attics or to unload the rafters themselves.
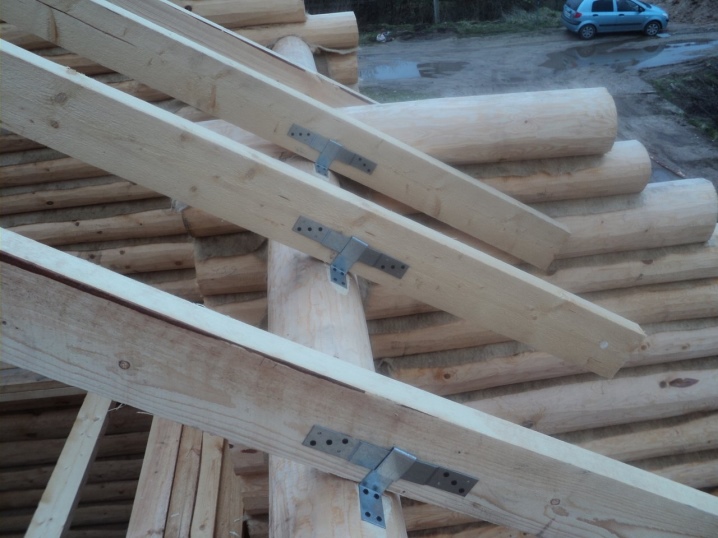

The easiest way is installation with special fasteners. The leg is cut from the end at an angle. The angle value is the same as the slope of the ramp. Such a solution will give a significant increase in the area of support under the foot. Serrated plates are hammered in at the butt sections, and perforated plates are placed on top of the same places.
Sometimes the connection to the wall is done using struts. Adding them changes the type: there was a beam with one span, and after the introduction of the brace, it is divided into two spans. Overlapping with one beam becomes possible at a distance of up to 14 m. At the same time, the diameter of the rafters is reduced. Attention: the struts must be docked with the rafters strictly so as to exclude a shift.
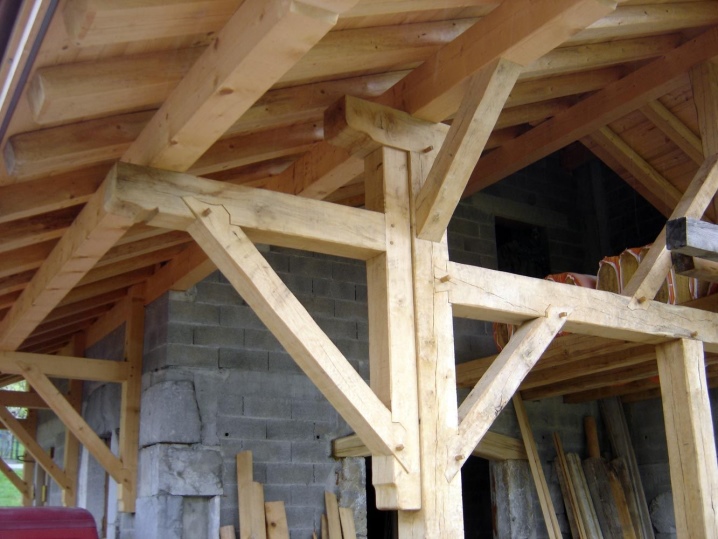

When drawing up a work plan for the installation of rafters for a four-pitched roof, it must be borne in mind that complex and long work will be needed. The hip version implies the design of the central segment according to the same system as for the gable roof. Lifting of the assembled farm is possible either by a large team (3-4 people at least), or with the help of a crane. In areas where hips are equipped, diagonal rafters are needed, which necessarily require reinforcement, because the load on them is 50% higher than on neighboring elements.
The main nodes of both layered and hanging rafters must have the most reliable connections. From a technical point of view, these connections are also nodes. On long aisles, load-bearing parts located under the rafters must be used. They are especially important in layered format.
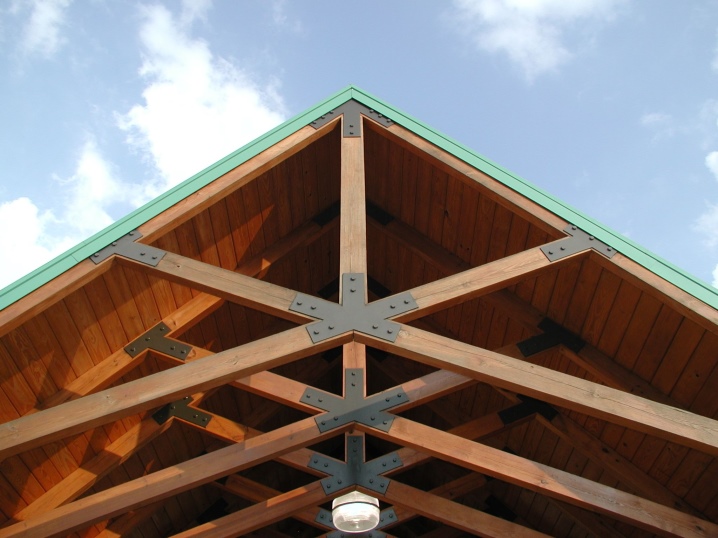

Deflections can be trimmed only if the undercut is less than the support diameter; if this requirement cannot be met, it is necessary to build up the structure with rafter trimmings.
When installing rafter complexes for a gazebo, it is also necessary to carefully maintain the distance between the individual parts of the structure according to the project, as in the arrangement of residential buildings. Even the simplest visual methods require following the drawings. Most often, the arrangement is carried out according to the lean-to method, which has proven itself many times.It is advisable to drill holes for fastening in wood in advance in order to exclude cracking when driving nails into the ends of the posts. If the roof of the pergola is horizontal, the rafters should have a long overhang or be placed in pairs.
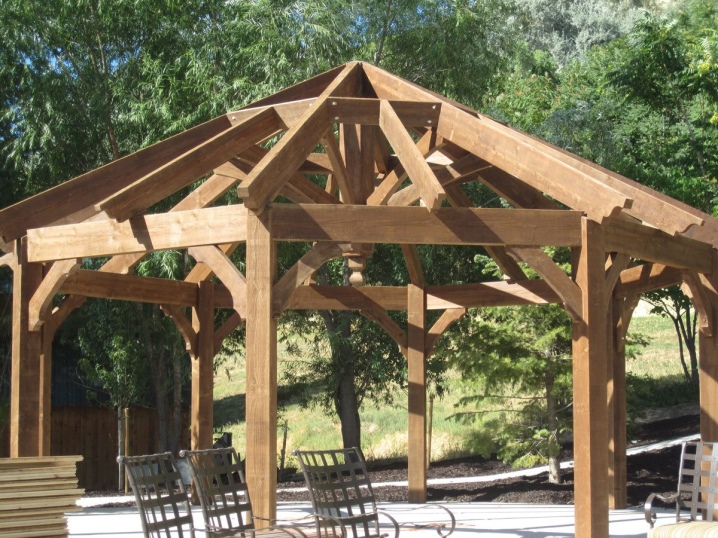

Extendable models expand the attic. The support will be on the beams of the upper floor. When building a roof with a cuckoo, it is necessary to remove the more rafters on the slope, the larger it is. The easiest way to do this is on a gable version. And, of course, everything should be set strictly according to the level; it is useful to try on structures during installation, before attaching them completely - in order to avoid mistakes.

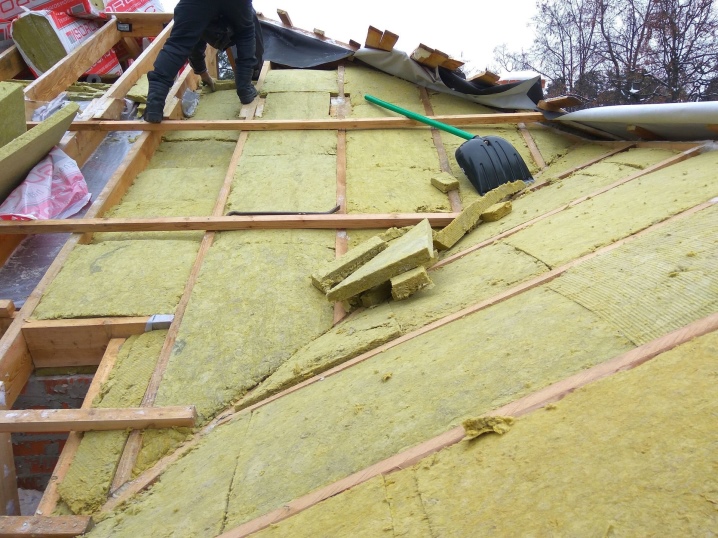
Warming
The connection to the log is usually provided with a crossbar. The crossbar itself should be positioned as low as possible in relation to the ridge. The rules of the insulation itself:
- insulate with strictly one material;
- from the side of the room, the insulation should be denser;
- when choosing a method, they are guided by the specifics of construction and the peculiarities of the weather;
- if possible, it is necessary to insulate from the inside so that it is less dependent on the weather;
- rafter legs should be 3-5 cm wider than the insulation.

Advice
Most often it is advised to treat wood with alkyd enamel. When choosing other antiseptics, one should be interested in antiseptic characteristics. If possible, the wood should be soaked in advance in the chosen composition. The coatings are applied in layers at half hour intervals. For your information: not all antiseptics are designed for wood moisture in excess of 20%.
How to install the rafters, see below.













The comment was sent successfully.