Overview of fiberglass profiles
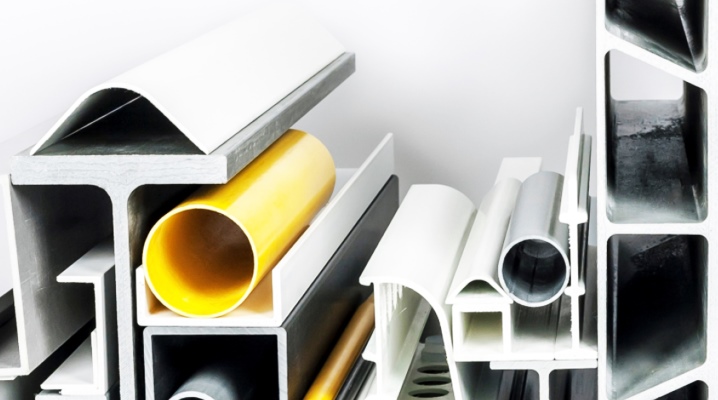

The article provides an overview of fiberglass profiles. Describes composite building profiles made of fiberglass, pultruded from fiberglass. Attention is also paid to the specifics of production.
Advantages and disadvantages
In favor of fiberglass profiles are evidenced by:
-
long time of use (at least 25 years) without noticeable loss of technical qualities and appearance;
-
resistance to adverse environmental factors;
-
resistance in a humid environment;
-
relatively small costs for the arrangement, maintenance and repair of fiberglass products;
-
low energy costs during movement and installation;
-
no risk of short circuit and accumulation of static electricity;
-
comparative cheapness (in comparison with other building materials of the same purpose);
-
lack of any fragility;
-
transparency;
-
low susceptibility to powerful loads in statics and dynamics, to shock effects;
-
the ability to maintain the original shape after applying mechanical force;
-
low thermal conductivity of fiberglass modules.


But these products also have weak points. So, glass composite material is characterized by low wear resistance. Its elastic modulus is small. It is very difficult to make high-quality material and strictly adhere to the necessary requirements. Therefore, the choice of high-quality fiberglass is rather difficult.
It is also worth noting:
-
anisotropic change in basic properties;
-
uniformity of the structure, due to which the penetration of foreign substances into the thickness of the material is simplified;
-
the possibility of obtaining only products of a straight geometric configuration.
Compared to plastic, glass composite material lasts longer and is mechanically stronger. It does not need to be reinforced with metal at the time of profiling. There is no release of poisonous vapors.
Unlike wood, pultruded fiberglass cannot:
-
rot;
-
crack from dryness;
-
deteriorate under the influence of mold, insects and other biological agents;
-
light up.
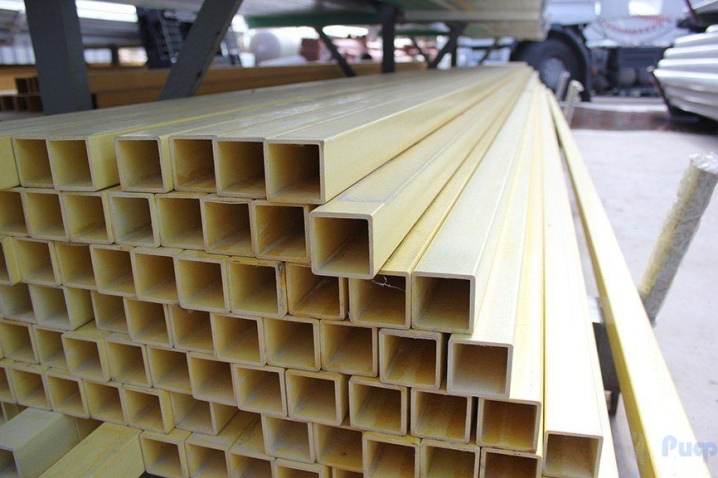

Fiberglass differs from aluminum at a more favorable price. It also doesn't tend to oxidize like a winged metal. Unlike PVC, this material is completely free of chlorine. The glass composite profile is able to form an optimal pair with glass due to the identity of the coefficients of thermal increase. Finally, plastic (PVC), like wood, can burn, and fiberglass absolutely wins by this property.
Profile types
The differences between them are expressed mainly in the color of the material. According to the geometry of the profile and other properties, it is divided into types:
-
corner;
-
tubular;
-
channel;
-
corrugated tubular;
-
square tubular;
-
I-beam;
-
rectangular;
-
handrail;
-
lamellar;
-
acoustic;
-
tongue-and-groove;
-
sheet.




Application
Before characterizing it, it is necessary to tell a little about the profiles themselves, or rather, about the process of their development. These elements are obtained by pultrusion, that is, broaching inside a heated die. The glass material is preliminarily saturated with resin. As a result of thermal action, the resin undergoes polymerization. You can give the workpiece a rather complex geometric shape, as well as very accurately observe the dimensions.

The total length of the profile is almost unlimited. There are only two restrictions: customer needs, transportation or storage options. Installation costs are kept to a minimum.The specific use depends on the performance. Thus, fiberglass I-beams become excellent load-bearing structures.
With their help, the soil is sometimes fixed on the perimeter of the mine shaft.... By no means deeper - there the load and responsibility are too great. Fiberglass I-beams become excellent assistants in the construction of warehouses and other hangar structures. With their help, the use of technology is minimized or completely excluded, since the structures themselves are quite lightweight. As a result, overall construction costs are reduced.
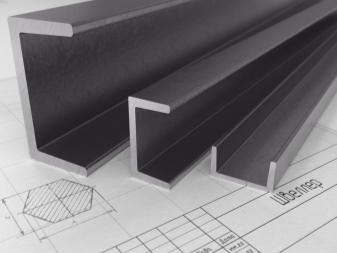
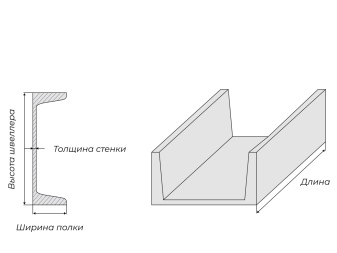
Fiberglass channels are quite rigid. And they transmit this reserve of rigidity to the structures inside which they are placed. Such products are applicable for frame parts:
-
cars;
-
architectural structures;
-
utilitarian buildings;
-
bridges.
On the basis of fiberglass channels, bridges and crossings for pedestrians are often made. They are quite resistant to moisture and even exposure to aggressive substances. The same designs are used in the design of stairs and landings, including at chemical industry facilities. Composites are increasingly being used in hangar furnishings. When creating them, an important role is played by increased durability (20-50 years even without prophylaxis and restoration), which is not available for other massively used materials.
A number of industries use fiberglass corners. For a number of characteristics, they are even better than steel counterparts.... With the help of such corners, rigid frames for buildings are prepared. It is customary to divide them into equal and unequal types. Fiberglass can also be used to equip technological sites where reinforced concrete and steel cannot be used.


But this material is also becoming an excellent option for the formation of building facades and fences. After all, the surface of fiberglass can be painted in a variety of colors. The use of a variety of textures is also allowed. These properties are highly prized by architects, decoration specialists. As for square pipes, they do well with both horizontal and vertical loads.
The scope of such products is incredibly wide:
-
bridges;
-
technological barriers;
-
stairs on objects;
-
platforms and platforms for servicing equipment;
-
fences on highways;
-
restriction of access to the coasts of water bodies.



The rectangular fiberglass pipe has in general the same purpose as the square models. Round tubular elements are quite versatile. They can be used both independently and as connecting links in other elements.
Other possible areas of use:
-
power engineering (insulating rods);
-
antenna stands;
-
amplifiers inside various structures.
Other areas of application include:
-
the creation of handrails;
-
railings;
-
dielectric stairs;
-
treatment facilities;
-
agricultural facilities;
-
railway and aviation facilities;
-
mining industry;
-
port and coastal facilities;
-
noise screens;
-
ramps;
-
suspension of overhead power lines;
-
chemical industry;
-
design;
-
pigsties, cowsheds;
-
greenhouse frames.












The comment was sent successfully.