All About Archive Racks
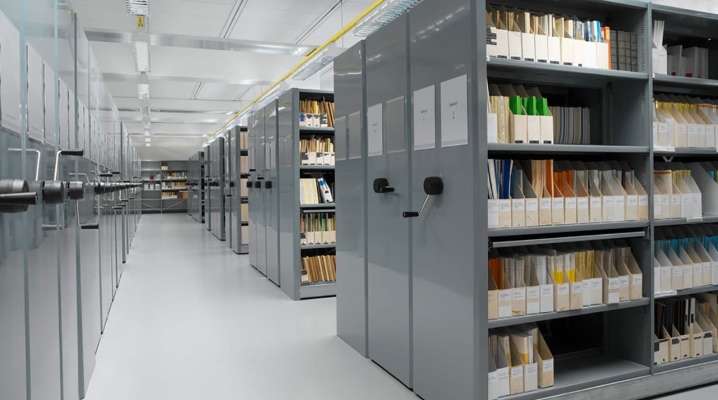

Only certain racks are suitable for storing archival documentation - with a sufficient carrying capacity, with perforations so that air can freely enter the papers, of the correct configuration. We figure out what types of shelves and cabinets are best suited for storing important documents written off to the archive in them.
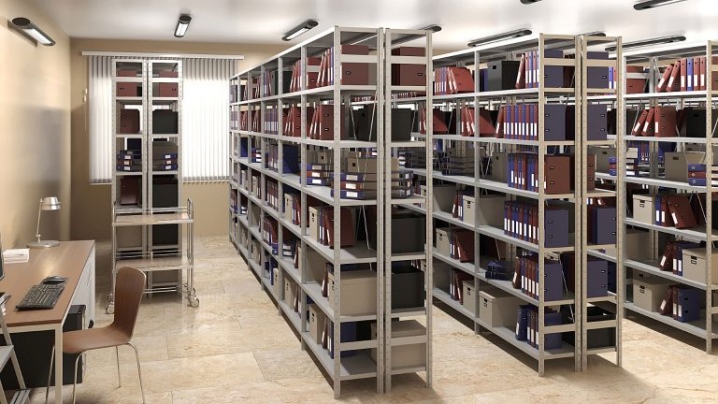

Description and purpose
Shelves are called special devices, the purpose of which is storage. They perfectly organize the space and, of course, are available in a wide variety of types and configurations.
Their purpose is to store both current and archival documentation. Archival shelving structures can be used not only for this, but also for placing and storing any other suitable size and type of things, be it materials or equipment.


Each rack is a structure that is assembled and adjusted using bolted connections. High-strength steel is used to create each rack on the rack structure, making them both strong and durable. Those models that are collapsible are easy to adjust (for example, increase or decrease the height of the shelves), you can quickly add sections, shelves, side walls to them and also quickly remove each of the listed elements.
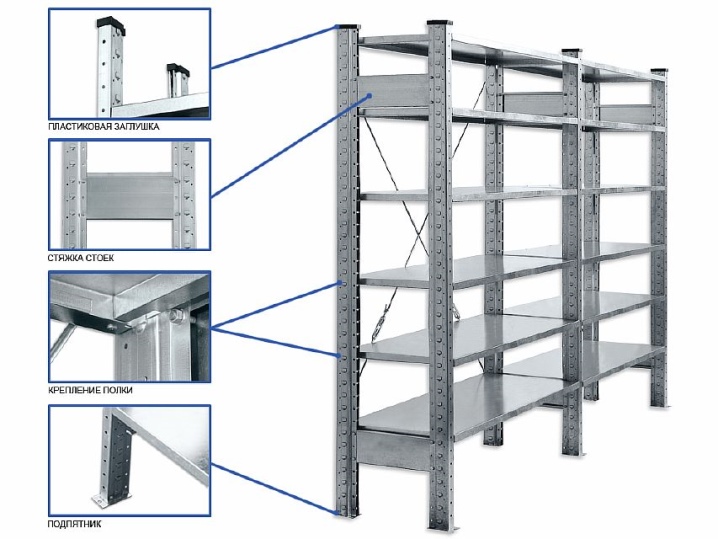
Basically, the racks consist of 4 perforated racks. Shelves are bolted to the uprights. There are also corners on the products.
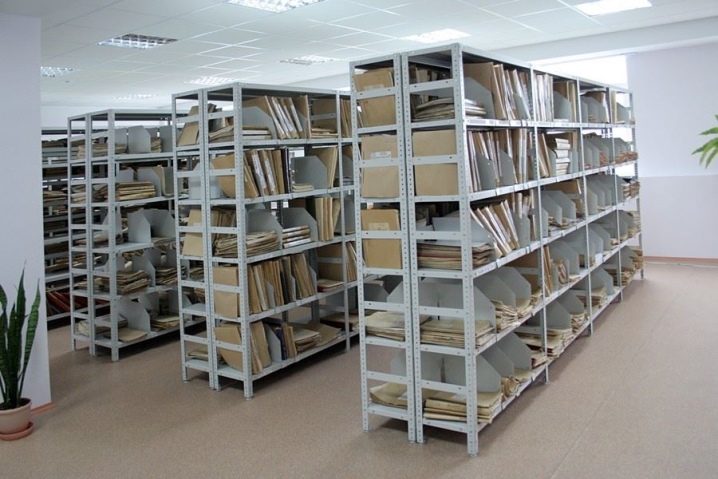

Primary requirements
Archive racks are manufactured in accordance with GOST R 56356-2015. It contains all the requirements that apply to these products (provided that they are made of metal). The production of shelving structures (including archival ones) is now very large, because complex equipment is not required for this, especially if you are dealing with collapsible structures. But wherever and whoever makes such products, the end result must fully comply with the requirements of GOST.

Wooden cabinets for storing archival documentation are also produced and are quite in demand among consumers, however, it should be remembered that such cabinets can store archives of those organizations that do not fall under the mandatory requirements for archives equipment. It is legally established that archival documentation must be stored in metal racks, cabinets and safes, and this requirement is one of the mandatory ones.


Species overview
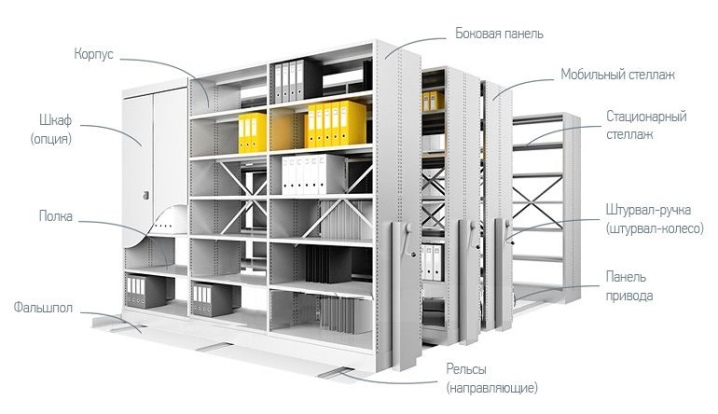
The main criterion for the classification of racks is the ability to move them. Depending on this criterion, two large groups are distinguished - stationary and mobile (mobile) products. Both have their own merits and demerits.




Stationary and mobile
Let's start with the stationary ones. Usually, they have a rather low weight, they are not difficult to assemble even for a person who does not have much experience in assembling furniture. It is also easy to dismantle them. As a rule, such products are relatively inexpensive, while being excellent for placing and storing office or archival documents in them. But there is also an inconvenience - a stationary rack, once assembled, without dismantling, can be installed in only one position.
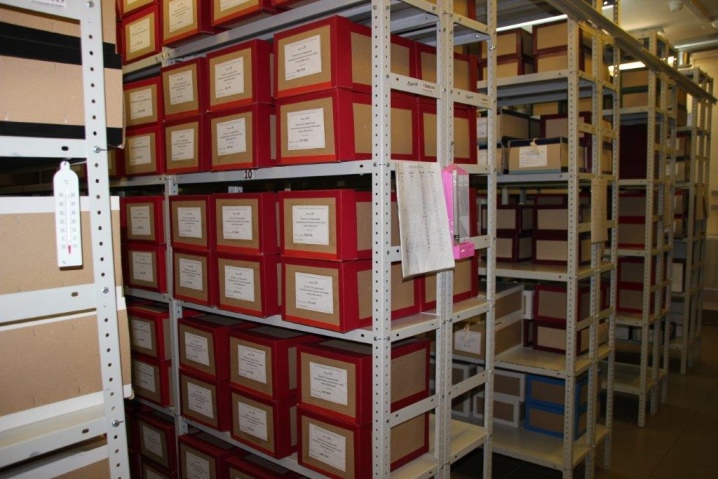

Mobile cabinets can be easily moved along the floor surface to any point in the room. Thanks to their mobility, you can find the desired document without lengthy searches, simply by accessing the required section. However, in order for mobile shelving to really move easily on the floor surface, strong rails are needed, i.e. additional equipment. In addition, it is also required to install specialized mechanisms on the racks themselves that will help the movement. Also, side walls and locks can be installed on such products. Then the archival documents will be preserved and their safety ensured.
The disadvantage of mobile devices is the need for a perfectly flat floor, only then is it possible to install rails. And, of course, the price - for mobile products, it is always much higher than for stationary ones.
Welded and prefabricated
In accordance with the method of fastening the elements, rack structures are subdivided into prefabricated and welded. Prefabricated models outperform stationary ones in terms of convenient transportation, the ability to quickly mount and dismantle. In addition, such models have an attractive and modern appearance, very often they are equipped with wheels and therefore are mobile and can be moved to the desired place.
Previously, it was believed that welded racks are more stable, that collapsible structures are inferior to them in this parameter. However, modern fasteners and materials make it possible to create collapsible models that have even greater reliability and stability, because of this, welded structures have ceased to be in demand, and many manufacturers have refused to release them.

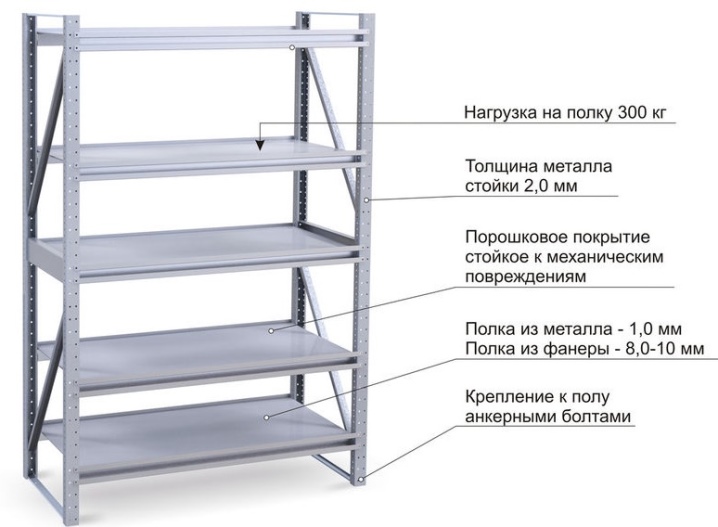
A reinforced rack can withstand a load of up to 900 kg per one of the sections, that is, if there are 4-5 shelves in it, then the shelf can withstand up to 200 kg. The shelves can be adjusted in 25 mm increments. Like a typical one, a reinforced rack can be additionally equipped with shelves, walls, and locking equipment.

Corner
The corner shelving structure allows the most efficient use of office and archive space, especially since the archive is often allocated the smallest room in the organization. Corner shelving can be placed where the straight line simply does not find a sufficient number of square centimeters. Using the corners, you can put in each of the shelves and thereby place more documents than if they were stored in one, but straight.


Dimensions (edit)
Archive racks are the most compact. They are used to equip archives, offices, libraries, book depositories, warehouses, etc. It is convenient to place printed materials on them, mainly in A5 (notebooks and books) and A4 formats (a typical album sheet, this size is suitable for storing folders and papers).




A standard archive rack has the following dimensions - height 1500-2500 mm, shelf length - 700-1500 mm, shelf width - 300-800 mm. That is a construction with dimensions of 2000x1000x500 mm, and 2200x1000x400, 2000x1000x400, and 2000x1000x300, and 2500x700x500 will also be standard. If we talk, say, about the size of 600x400x2000 mm (for 4 shelves), it is designed for storing documents that are not formatted in height.
Experts note that the assembly of multi-section archival racks is advisable if complete sections are connected. Then the load characteristics are not reduced, in addition, each section can be supplied separately. But you can reduce the number of racks if a multi-section rack is being assembled. Then you can save a little on the purchase of rack equipment. It is allowed to alternate full sections (that is, those that have all four racks) with additional ones (which have two racks). It is also possible to install a section without posts at all between four post sections.
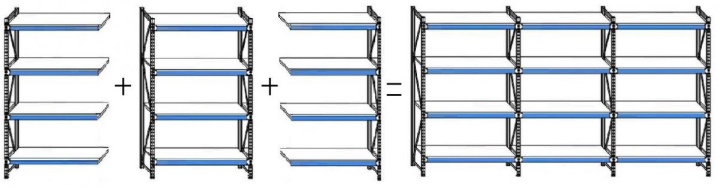
If a two-section line is assembled, 6 racks are enough for it instead of 8 if separate sections were connected. If a three-section line is assembled, 8 racks are enough instead of 12.
The one-piece metal archival shelving unit with a height of 2000-2500 mm has a load capacity of approximately 700 kg. The multi-section has less, only 550 kg. The load on the shelves must be distributed strictly evenly, on a single-section, the top shelf will withstand a maximum of 60 kg, on a multi-section - 30 kg.
Nuances of choice
Which racks will be installed in the archive - each organization decides independently. The choice does not depend on one parameter. Since the legislation establishes requirements not only for shelving, but also for the archive room, it must be isolated. Therefore, every organization in which there is a certain amount of archival documentation (and which does not submit it to a centralized archive) is faced with the need to organize the premises in which it will be stored.




The choice of shelving structures depends on some parameters.
- The area of the room and the height of the ceilings in it. If both are small, then perhaps it makes sense to use corner structures in order to occupy the area as efficiently and rationally as possible. In a long narrow room, you can place racks along the perimeter along the walls, in a wide one - arrange them in several rows.
- Collapsible structures are preferable where, for example, doorways do not allow carrying and delivering a welded model.
- The dimensions of the shelves in the rack and the height depend on the amount of documentation that needs to be placed, its format - A4, A3, A2, etc.


As for the purpose, modern archival racks are quite universal and can be used both as archival and warehouse, and even as warehouse. It all depends on what will be placed on the shelves. The rack can be 4 shelves, 6 shelves, 7 or 8 shelves of different heights and widths. Interestingly, for most collapsible structures, in order to install an additional shelf or side wall, you do not need to completely dismantle the product and reassemble it. That is why collapsible racks are so popular, they can be used everywhere - in shops, offices, warehouses and libraries. The service life of such racks is quite long, because archival racks are made of metal, most often of stainless steel.




To restrict access to documents of particular importance, it is necessary to purchase racks equipped with special locks.


Rules and methods of placement
The legislation imposes a large number of requirements on the archive as a place. One archive should be clearly isolated from another, be fireproof, have ventilation, heating or climatic systems so that air circulates around the room 2-3 times per hour, and much more. Documents must be stored in accordance with storage rules, temperature and humidity conditions, sanitary and hygienic regimes, security regimes, etc.
It is permissible to place only metal shelves in the archives. If auxiliary storage facilities are required, then it is permissible to use cabinets (large format) and metal safes.


Cabinets should also be arranged in a certain order. If the shelving structures are stationary or sliding, then they should stand at an angle of 90 degrees to the wall with a window. If there are no windows in the archive, then the arrangement takes place as required by the features of the room and equipment in it. Shelves should not be installed directly against the outer walls of a building or near heating appliances.


The racks in the archive room should be located at a distance of 1200 mm from each other. The aisle width between the rows of shelving structures should be 750 mm. The same distance should be between the outer wall and the rack parallel to it. With regard to the distance between the outer wall and the rack structure from the end, it should be 450 mm. The bottom shelf of the rack must be at least 150 mm above the floor.The installation of archival metal furniture equipped with pull-out sections, drawers or doors takes into account what type and size of materials will be stored in them.













The comment was sent successfully.