Everything you need to know about lathes

Without a lathe, turning, sharpening, leveling the surfaces of parts cannot be done extremely accurately. Manual work will require several times more time.

What it is?
The lathe works with wood, composite materials, as well as metals and their alloys. This machine produces low-current and high-precision turning of spherical, cylindrical, conical and other parts. The lathe cuts external and internal threads several times faster than a master would do with a hand die or a tap, cuts and rounds the ends of parts, drills and countersinks components for products, and develops technological holes.
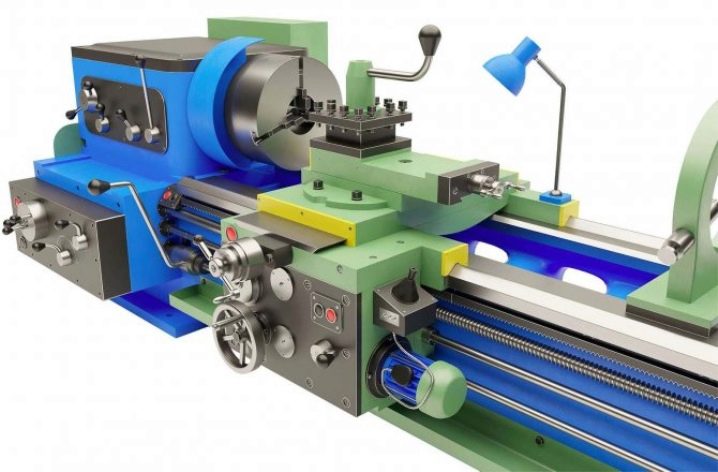

The machine consists of the following components: a bed, a drive with a spindle (the functional unit also includes the front and rear spindle heads), a support, a gearbox, a gearbox (if the device is indirect drive), an electromechanical or electronic control device (one or more control circuits are used based on mono-board or cassette-modular construction), remote control with buttons and switches. The CNC module puts the production of parts on the stream, reducing the human factor to a minimum.


History of appearance
Attempts to create primitive machine tools date back to ancient times. Until recently, which was marked by mass industrialization - first in Western countries, and then in the USSR - machine tools were rather primitive. They are not suitable for large-scale production. Attempts to create a machine for sharpening swords and daggers were not unsuccessful: back in the 4th century BC. NS. the Chinese used devices that gave a relatively straight blade.

The mechanical support as a more effective means of controlling the machine appeared only at the beginning of the 18th century. The machine of that time had a holder for a cutting knife, which, moving by hand, tightly adhered to the workpiece being processed. Threading screw and bolt threads was considered a high-tech skill.
Mechanized devices began to be widely used only at the beginning of the 20th century. The electric motor eliminated the need to use horse traction and combustible fuel on such machines.
During Soviet times, lathes of the 16K20 group, as well as 1K62 devices, spread.
Soviet machines are powerful and reliable, durable devices that, with proper care and replacement of consumables, can last up to 150 years (subject to the rules of operation).
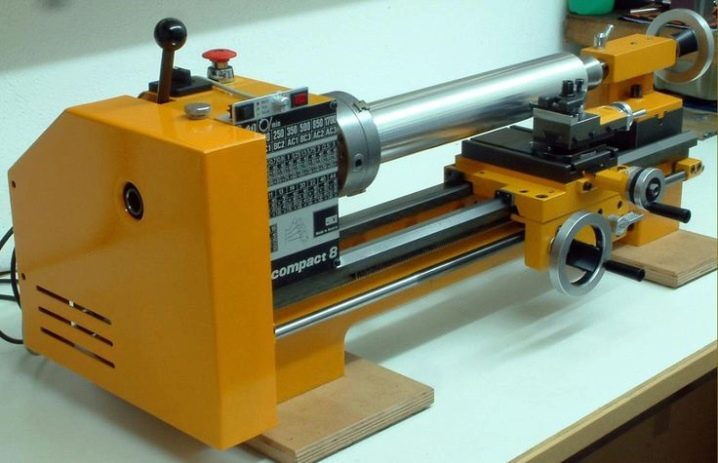

Views
Lathes have reached a certain species diversity: wood and stone working, metal working, glass and composite lathes, etc. A separate variety is decorative gouging machines, which allow, for example, to obtain door handles with a round design.
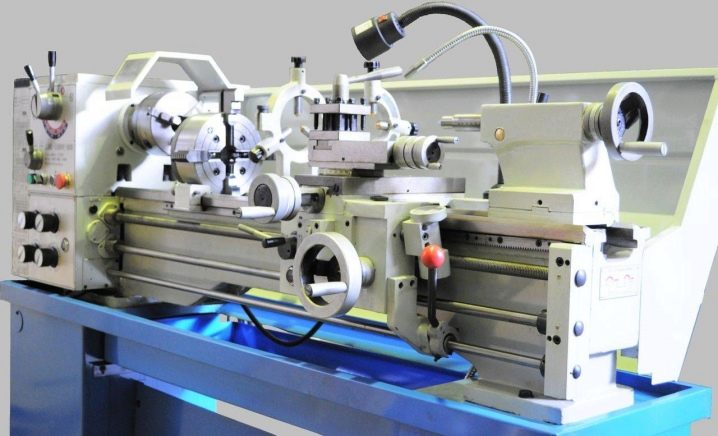

Specific types of machines are presented in the following list.
The screw-cutting lathe is produced for work on ferrous and non-ferrous metal. It grinds tapered parts, cuts metric, inch, modular and pitch threads - and is designed for small batch production. The 16K20 unit is just that.Screw-cutting lathe machines have three classes of accuracy: P - increased, H - normal, B - high, A - ultra-high, C - ultra-precise processing.


For turning and carousel products, the axis of rotation is located vertically. This machine cuts out cylindrical and conical parts, trims the end and groove edges. Thanks to the modernization, it is possible to grind shaped surfaces according to a copy source, and to cut and grind simple products.


The frontal (lobotocar) mechanism is shown when turning large-diameter and shortened parts - it grinds them frontally. Suitable for reworking shortened components with short length and weight over a ton. If the load on the drive is increased, and the relief of the parts is significantly complicated, then the frontal lathes are replaced by turning-boring machines.
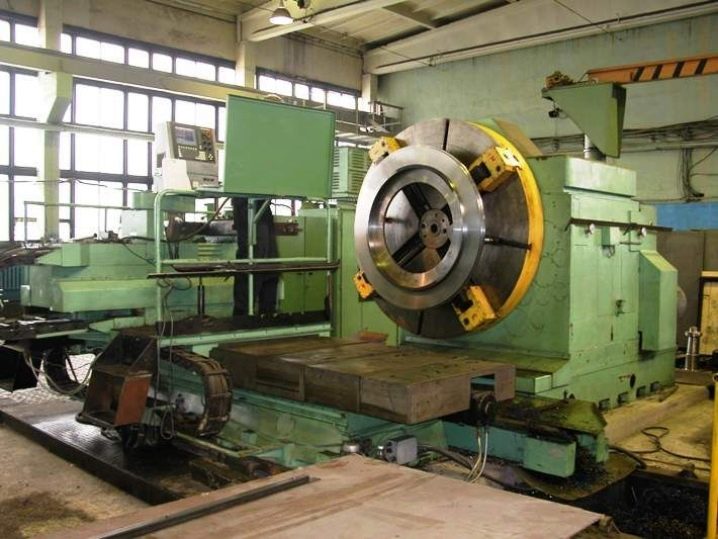

A turret lathe sharpens parts from a calibrated bar, bores, drills, countersinks, unfolds turning for shaped components, cuts threads from the outside and from the inside. It is equipped with a copier and a CNC module.


The sliding head machine grinds parts from cold-rolled bar, profiled steel and wire. Large-scale it works with ferrous and non-ferrous metal, can be equipped with two or more spindles.
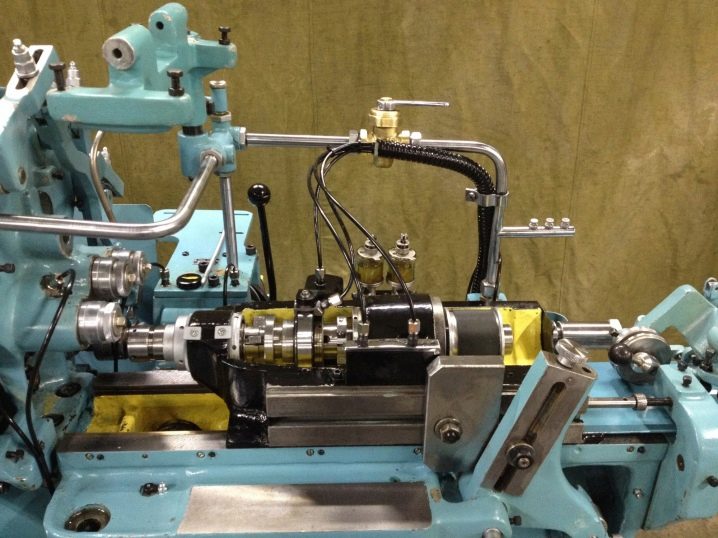
The turning and milling machine is equipped with an automatic cutter changer. It combines simple milling and turning activities for a wide range of applications.


Accuracy class
High-precision machines are designed for finishing, and low-current machines for roughing. The originally named units, according to the kinematic scheme, are equipped with cutters that make grooves in an arbitrary sequence, and low-current ones only perform preliminary cutting and grinding of the surface, allowing, for example, making a spherical or egg-shaped part from a cube.
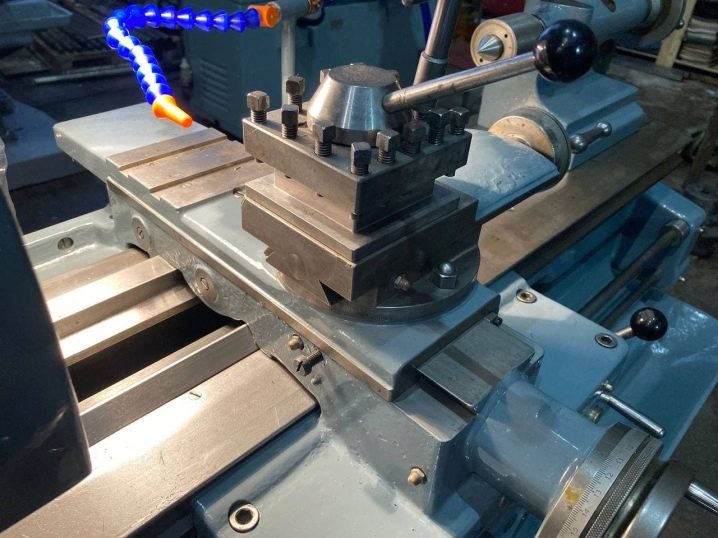

By weight
Portable low-power machines weigh no more than a few kilograms. Easily transported and transported to another workshop. Massive machines - floor-standing devices: there is a separate table or stand, for which it is convenient to work. Product weight - from tens of kilograms to tons.

By the degree of automation
Partially automated machines have only a protective shutdown function - due to overheating of the motor and gearbox. Fully automated ones are equipped, in addition to the numerical control module (CNC), with a safety blocking device for the viewfinder, for example: in the absence of lighting in the workshop and the dangerous proximity of the foreman's hands to the working area.

By the flexibility of the production system
For example, if a machine “knows” how to grind cylindrical and conical parts, but it “is not able to make spherical parts,” such a machine is not quite flexible in terms of repurposing production - without purchasing a more fully functional unit.
Most modern machine tools sharpen parts and workpieces of any shape, perform simplified artistic cutting and turning.

This conversion is not limited to peaceful activities. So, the shipbuilding enterprises of Leningrad and Moscow, which before the Great Patriotic War produced parts for steamships and icebreakers, began to produce T-34 tanks. This is due to the fact that parts for fuel engines were used both in military ships and in tanks.
By special purpose
A lathe, regardless of its classification, can be customized for a specific production. For example, an assembly that makes duplicate keys is equipped with special cutters for common sizes and execution of code recesses that make up the channel code of the key. In order for the duplicate to accurately copy the code of the original key, the turner places this key in the working area - and sets the cutters under its code gaps. Then the wizard inserts a new blank instead of the original key - and grinds the same code on it.


Of course, the spindle drive is capable not only of making keys, but also, for example, grind forks from food-grade stainless steel - all you need to do is change the cutting tools on it, with the help of which cutlery is created.
A fork grinder that makes duplicate keys is unlikely to grind, for example, replacement parts for a car's carburetor, such as valves.
This requires a deeper re-equipment of the unit.


By versatility or narrow focus
A typical example: a machine for sharpening needles, knives, sharpening reusable razor blades and scalpels is not intended for grinding wooden and composite handles for doors, locks and anti-burglar fittings for plastic windows. The machine used for the production of gears will also cope with the turning of parts for indoor and wrist mechanical clocks, metronomes and timers, but it will not be possible to turn out spare parts for carburetor engines of cars on it. All of the above examples are for highly directional machines.

Universal machines have high power, smooth speed control, and can be used with equal success both for sharpening drills, sharpening medical scalpels, and for turning parts for gearboxes and clockwork mechanisms. More expensive models are equipped with several spindles at once, each of which has its own equipment. This approach is applicable for universal craftsmen, who, in the event of a crisis in relation to certain types of products, are redesigned for objects and parts of a completely different kind, which are currently in higher demand.


The best manufacturers and models
Of the machine tools of the times of the USSR, it is worth mentioning the 16K series. Model 16K20 is used for basic turning, regardless of the complexity of the turned parts. Of the more modern ones - for 2021 - the following models are presented.
-
Screw-cutting unit DMTG CDS6250B / 1000 - the power consumed from the network is 7.5 kilowatts, the power supply is from an interphase voltage of 380 volts, the weight is 2170 kg. Designed for processing steel, cast iron and non-ferrous metal parts. Turnover - 2500 every minute.


- Universal unit DMTG CDS6250B / 1500 for turning and screw-cutting works, it operates at a frequency of 2240 revolutions, weight - 2310 kg, other parameters are the same.

- Universal machine CDS6250B / 2000 - the closest analogue of 16K20. It is in demand at most metalworking factories and in car service, works with ferrous metal.

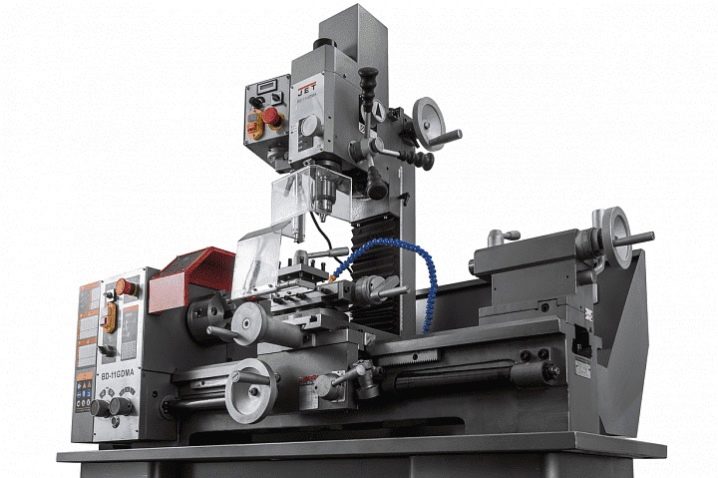
- JET BD-11GDMA - turning and milling equipment. Turnover - 2000, works from a simple single-phase 220 V network, weighs only a quarter of a ton.

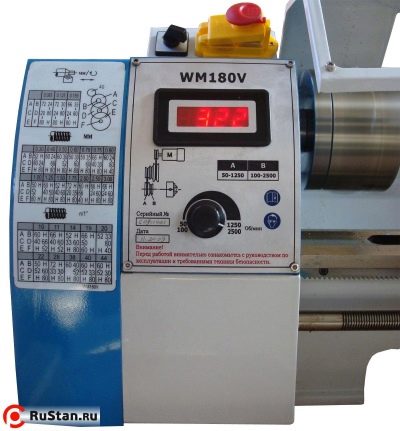
- Model WM180V - 2500 rpm, 600 W, weight - 60 kg. Designed for beginners, works with non-ferrous metal, composite and plastic. Suitable for home or school work in labor lessons.

Users choose a device that can solve most of the most demanded tasks in accordance with the available budget.
Components and spare parts
Before servicing and repairing the machine, it is not superfluous to familiarize yourself with the list of the main components that need to be replaced as their resource runs out.
A drive is fixed on the bed - an engine with a spindle, the headstock and tailstock are combined with it. The spindle allows you to fix cutters (drill, cutter, flat knives) set at the desired angle.
A fully debugged machine, with particularly strong and hard cutters, with regular, systematic lubrication, cuts steel with thin plates - just like a kitchen knife cuts frozen butter.
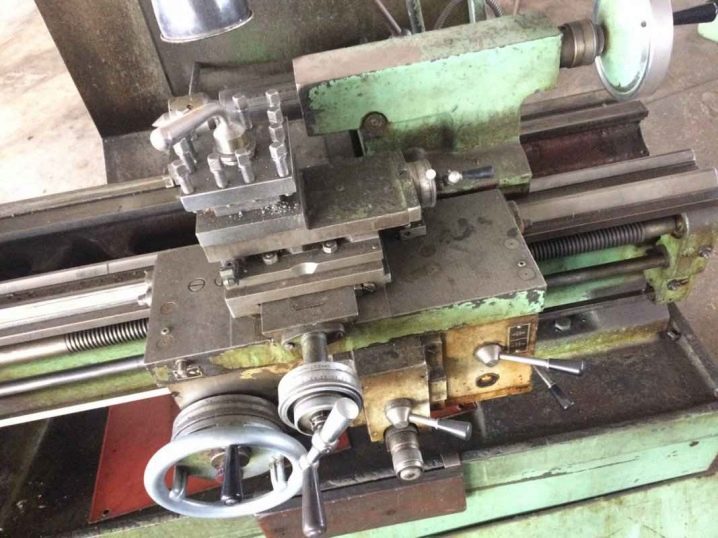

Complete with the drive, the assembly kit for the initial installation of the machine includes a support, an apron, speed and feed switching units, as well as a control panel. Fully functional automatic machines are also equipped with a "brain" - a CNC unit. All of the above nodes are fixed to the frame of the device. Guides (so-called.slide) allow you to move the workpiece strictly within certain projections, not allowing it to deviate arbitrarily, which would immediately lead to damage to the entire workpiece. The tool holder (spindle chuck) reliably holds the cutters used for cutting metals and alloys according to the workpiece drawings.

Selection Tips
When choosing, focus primarily on the power that your wiring will withstand. When selecting a machine that consumes more than 3 kW, it will be necessary to replace 16-ampere machines with 25-, 50- or 100-amperes, as well as replace a meter with a peak throughput power exceeding 3.2 kW.
Beginners who are just mastering the basics of machine tool production stop choosing less high-performance machines: it is important here that a device, in which more than tens of thousands of rubles have been invested, is purchased not just for the sake of a hobby, but would pay off, ideally, bring an income several times higher expense item.
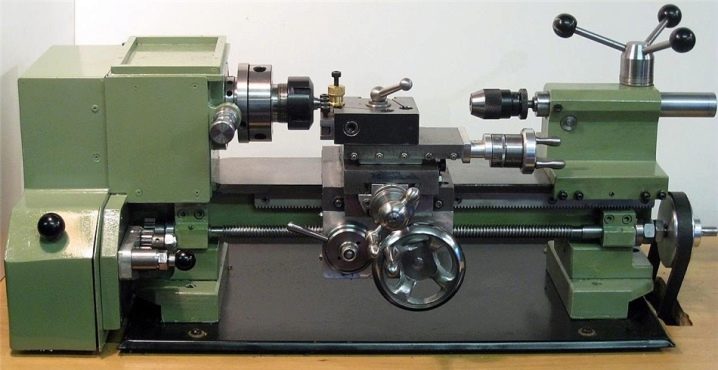
If you are busy with fine processing of workpieces, then you will need a much more resourceful, although not always quite powerful device.
A machine that weighs over a ton may require a reinforced foundation in the room where it is installed. An ordinary wooden floor weighing two or more tons will collapse in a few weeks or months after the start of work.
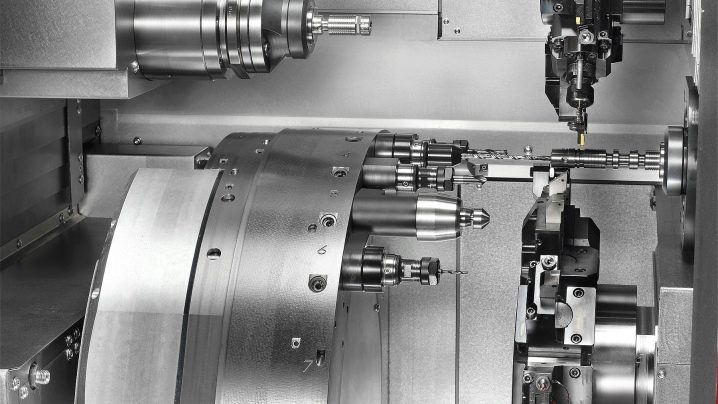
Features of work
The torque from the engine is transmitted through the gearbox, on which the speeds are switched, to the spindle, and from it, with the help of the headstock, to the cutter. The movements of the cutter are controlled by guides that load the workpiece for turning into the working area.
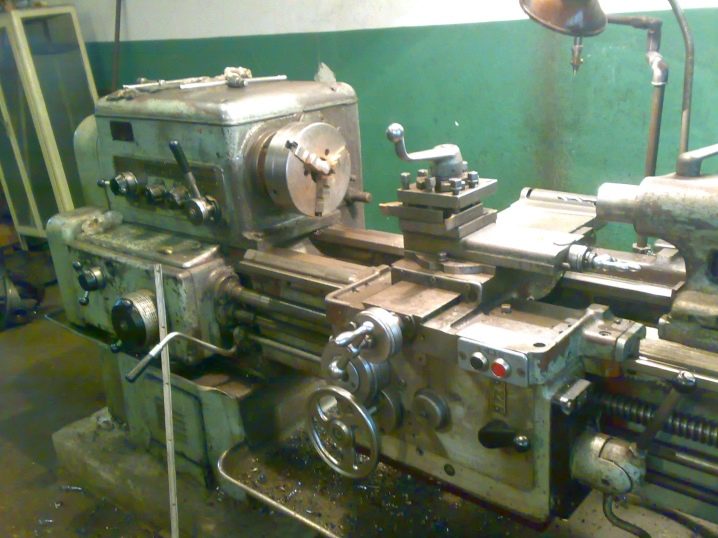

The machine for cutting metal, wood and lumber, composite and glass, according to the classification and its structure, is a device of relatively precise mechanics. When working, it should not unnecessarily vibrate, knock, twitch from side to side - this would worsen the quality of the processed parts tenfold. The drive and the spindle, on which the cutters are fixed, ideally work well, the misalignment of the engine and transmission is practically excluded. Cutters should ideally always be sharp.

If, in spite of the serviceability and operability of the machine, the cut quality remains poor and has inaccuracy, then the cutter must be sharpened, straightened, and, if necessary, replaced with a new one.
Nuances of repair
Lathe malfunctions may include the following:
-
the body has cracks, chips, stripping of threaded connections, non-straightness and violation of geometry;
-
shafts wear out over time, their centering is disturbed;
-
flanges may not fit tightly to each other, as well as show cracks and chips in the holes of the fixing points of components;
-
gears are distinguished by wear of the teeth and the presence of an "egg", from which a radial runout of the transmission element appears;
-
lead screws and pins have thread wear and thinning of the adjoining surfaces.

Routine repairs are carried out when components with rubbing surfaces are worn out. This is the replacement of bearings and brushes of motors, cleaning and lubrication of rubbing units and mechanisms. Overhaul - mainly replacing shafts and gears, repairing damage to the frame or replacing its faulty components.














The comment was sent successfully.