All About CNC Lathes

Knowing everything about CNC lathes is important for both ordinary users and heads of large enterprises. It is necessary to deal with models for metal and wood, desktop machines for work and other varieties, with collet chucks for them. It is also worth exploring the nuances of processing on mini-machines and other target aspects.

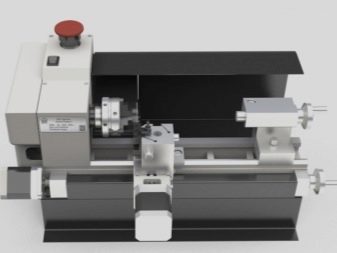


Design and principle of operation
When characterizing CNC lathes, one cannot ignore how this very numerical control works. Knowledge of its features is no less important for competent processing than mastering the basic principles of cutting and operating modes. Large industrial devices are controlled by a PC. The work of ordinary household level machines is usually coordinated by built-in electronics. The difference between the models may also be whether they can accept a standardized G-code or not.
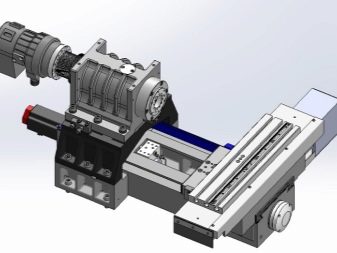

A specialized high-level device can apply a variety of software packages, use the data obtained through three-dimensional modeling. This equipment is abbreviated as CAD / CAM. A number of relatively simple programs have been developed, suitable even for inexperienced users.


The G-code has been in use since the 1970s, it is well mastered and will not cause any problems in use.
A kind of "translator" between the CAM and the machine is a special program - a subprocessor. CNC turning equipment can have several axes of movement. The movement itself along them goes either along a straight trajectory, or with a turn. In some cases, the developers provide for both of these modes. When laser or waterjet cutting, systems are usually bypassed with a pair of linear axes, but milling equipment most often has at least 3 axes; pivot directions can be added to these.



Almost all CNC controllers are capable of confidently working out only straight and circular movements. In this case, the movement along a circular line is limited by the main planes of the coordinate axes. Each movement along the pivot rail is evaluated by the technique as a linear move, but instead of a distance, there will be degrees. Interpolation of linear and rotary axes is allowed in some cases. 100% of them are normally synchronized, which is an extremely difficult task - even with the current level of technology - task.
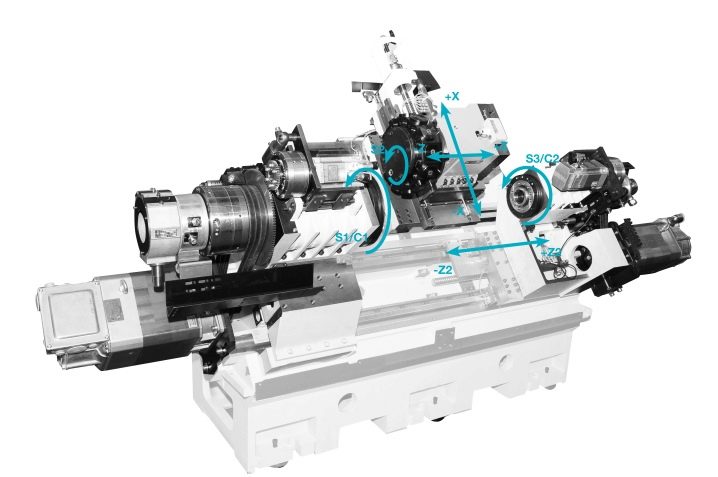
The principal prototypes of lathes appeared in the 18th century. Despite the significant development, the main, fundamental points in the work remained unchanged. The main units include the headstock. This part is predominantly cast from first-class cast iron. Inside there are a device that switches speeds, and a spindle (shaft, made in the manner of a metal tube).
On top of the headstock, a blank of the created part is fixed. The rotation of the workpiece is due to the gearbox. A thread is formed in the end part of the shaft, which allows the chuck to be fixed. An important point in the classification is just the design features of the cartridge or its replacement with a faceplate. Be sure to add a tapered slot to allow the front center to be set.
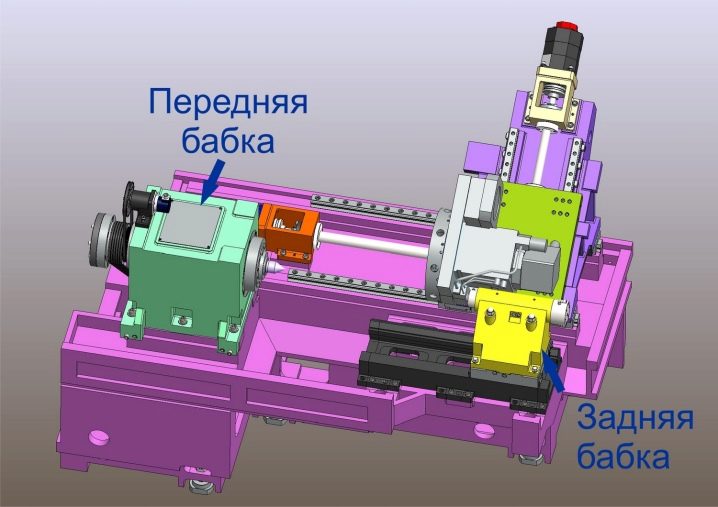
Normal spindle movement would be impossible without the use of backlash-free bearings. Usually a couple of similar elements are used.The peculiarities of the pitch when receiving grooves are set using the guitar of replaceable wheels. The role of the apron is also significant - thanks to it, turning the stroke shaft turns into a movement of the caliper, which is realized in two directions.
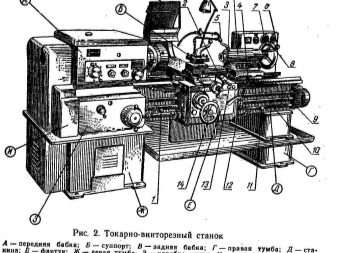

The bed, traditionally for heavy machines, is made of durable metal (most often cast iron).
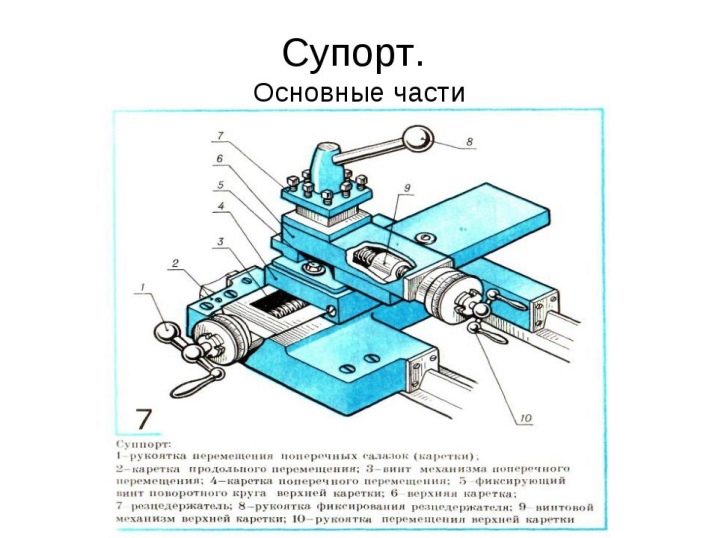
The machine is necessarily equipped with a support. Without this component, turners would have to hold the tool with their hands, and there would be no need to talk about high productivity, acceptable accuracy of the technique. The caliper has a complex structure. It includes:
-
cross slide;
-
carriage;
-
the apron mentioned above;
-
incisor sled;
-
cutter holder.
Rotary drawing plays an important role in the operation of CNC turning equipment. This is the name of the technique for manufacturing hollow elements of rotation on the basis of a sheet or hollow workpiece. An alternative name is roller pressing. Rotary hoods require hydraulic or electro-hydraulic supports. The shape of the part changes locally, and its wall becomes thinner.
The direct version of the hood is needed to obtain cylindrical structures. The linear dimensions of the products will be very large, and their walls are not too thick. The outer contour of the mandrel should be the same as that of the broached workpiece. Reverse pulling implies the opposite (in relation to feed) movement of the roller mechanism.

It is allowed to use mandrels that are inferior to the part in size.
Such techniques are suitable for the production of:
-
jet engines;
-
searchlight buildings;
-
screens of powerful lighting lamps;
-
tapered exhaust pipe segments;
-
bearing housings;
-
rear shrouds of compressors;
-
other tubular parts of large mass with variable thickness.




Tailstocks allow you to fix the free ends of large metal parts. Drills and other auxiliary tools are fixed on them. The built-in middle spins sometimes, although a simpler execution is possible; rotation, on the other hand, allows for increased productivity. The box with electrical filling includes keys, handles and toggle switches. Along with the listed details, may also be present:
-
collet;
-
faceplates;
-
clamps;
-
lunettes;
-
mandrels.





The main practical characteristics are:
-
the largest section of the processed blanks;
-
the distance between the centers of the workers' attendants;
-
the limiting thickness of the workpiece placed over the support.

Drive belts can be made on the basis of:
-
tarpaulin tapes;
-
rubberized fabrics;
-
other durable materials.

Appointment
The main difference between different lathes is what material the cutting element is designed for. The most common systems that work with metal or wood. It is categorically impossible to confuse them and consider them mutually replaceable. Generally, turning is practiced for workpieces that have the shape of bodies of revolution. We are talking about rollers, bushings, semi-finished products for gears and so on.


The parts to be machined rotate, and the cutter moves progressively (as the professionals say, this is the feed movement).
The main working manipulations are:
-
end surface treatment;
-
threading;
-
turning grooves;
-
end face processing;
-
drilling;
-
countersinking;
-
hole pattern (and this is not a complete list).




To perform such work, use:
-
sweep;
-
countersinks;
-
dies;
-
taps;
-
drills and other devices.
Type overview
Positional
Such devices can cope with any kind of workpiece. They are designed to work according to the point method. Movement is provided in two mutually perpendicular directions. The positional mode is also used in more advanced devices - but not during the main activity, but when moving the working part.

Contour
This option is not very autonomous.Despite the CNC equipment, constant human intervention is still necessary. The trajectory is set by the operator himself. A characteristic feature is the coordinated movement in two or more directions in the coordinate system. All axes travel at balanced speeds.

Universal
They are also called adaptive systems. Such a device can simultaneously replace contouring and positioning equipment. This level of functionality is charged accordingly. Such a perfect technique is needed mainly for large enterprises that perform a significant number of types of work.

At home and ordinary workshops, a simple desktop mini-machine will be more preferable.
Another classification
By spindle placement
The horizontal mounting method is chosen if the priority is the processing of grooves with both finger and disc cutters. A feature of this method of organization is the ability to move in three mutually perpendicular directions. The vertical type allows you to work with large parts. Moreover, they can have a large diameter, but a relatively limited length. Horizontal apparatuses usually include an arched column that does not twist when a load is applied along the spindle axis.


By the location of the guides
For this indicator, the technique can refer to:
-
vertical;
-
horizontal;
-
oblique (but the gradation is far from complete).



The screw-cutting lathe is considered a universal piece of equipment. It is widely used in serial and local production. Such a device will be able to cut a thread and perform other types of processing. Turning and carousel models work with large-sized workpieces. They cut grooves, sharpen surfaces, grind and mill.

The turret lathe works only with calibrated bars. They can be turned, bored or countersunk. Deployment and rifling are also allowed. Turning and milling machining centers, as the name implies, perform both turning and milling manipulations. There are also sliding head machines and multi-spindle turning machines (the latter type copes well even with complex workpieces).

Stepless drive systems allow the spindle speed to be continuously varied. Inside and out, workpieces are perfectly processed - and at high speeds. The stepless equipment has a long service life and is not subject to malfunctions. Pipe-cutting systems are only capable of working with steel billets.

Additionally, a gradation is distinguished according to the degree of accuracy: from the most accurate to normal and having a relatively high error.
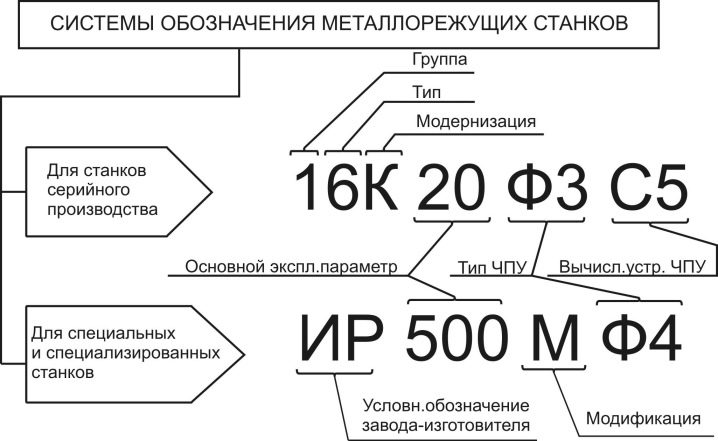
Marking
Alphanumeric markings of CNC lathes are built according to the following structure:
-
the first character is the belonging group (always the number 1);
-
the second character is the manufacturer or generation of the equipment;
-
next is the type of machine;
-
starting from the 4th character, the individual key parameters of the machine are marked;
-
after the numbers there is a letter indicating the modification or the accuracy category (this is not always present).
Popular models
Among modern lathes, it stands out favorably Jet BD-8VS 50000911M... Such a miniature device has a 0.6 kW drive. The spindle can rotate at speeds up to 2500 turns per minute. The current speed is indicated on the display. A typical set includes a 10 cm 3-jaw chuck.
A pair of automatic longitudinal feeds is provided. From 1 to 4 incisors are placed in the holder. The gears are manufactured from premium hardened metal. The length of the working area is 40 cm. A good protective screen is provided.

Proma SM-300E 25951830 operates at a mains voltage of 220 V and has a power of 0.3 kW. The spindle can rotate at speeds from 100 to 2500 rpm. The cross spindle moves 6.5 cm. No cooling.The mass of the device is 40 kg.
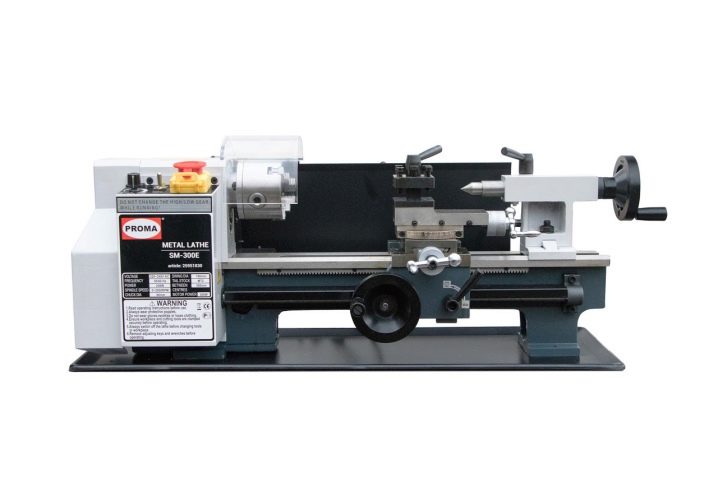

For woodwork, you can use "Enkor Corvette-74"... This lathe weighs 77 kg and is quite stable. The spindle is capable of turning at a speed of 500-2000 turns per minute. Compact workpieces can be manipulated with a faceplate. The headstock turns as needed.
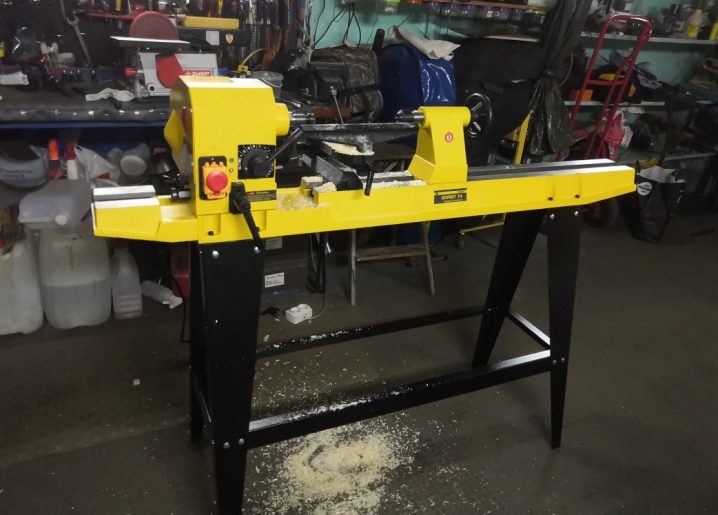

Among the equipment of Russian production, stands out model "Kraton" MML-01 "... Such a machine is designed for workpieces with a circular cross-section. The design operates from a voltage of 220 V. The spindle speed is adjustable. When rotating it, you can use the reverse mode; thanks to the robustness of the device, it is quite reliable.
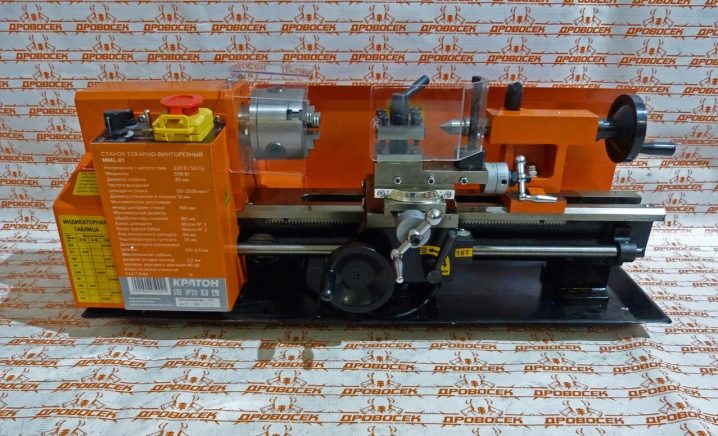

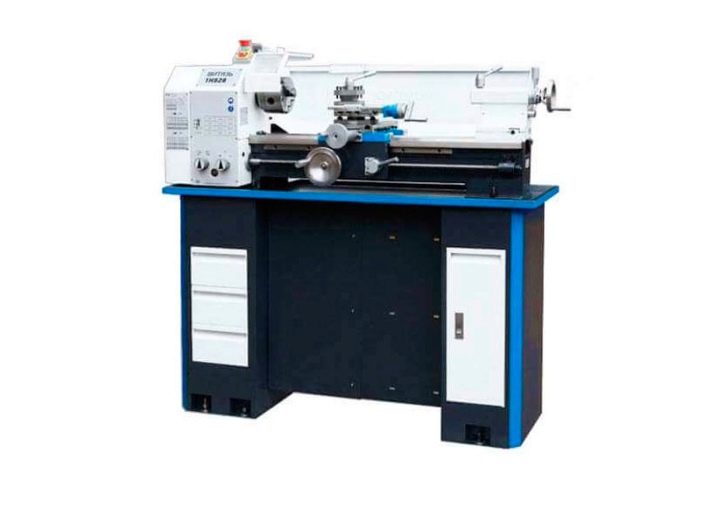
The products of other manufacturers from Russia are also noteworthy. A good example is the benchtop screw-cutter apparatus "Vityaz" 1N628V... The electrical system consumes 1.1 kW of current. The bed is equipped with hardened metal guides. The model can vary the rotation speed from 50 to 2200 rpm.

Accessories and accessories
CNC lathes are traditionally equipped with various fixtures. Noteworthy:
-
cams;
-
lunettes;
-
combined center drills;
-
cartridges;
-
centers.





Traditionally, cutters are used for the lathe. They differ in the direction of supply and the range of tasks to be solved. Some products create threads, others separate areas from the rods, and others allow you to chamfer or perform other work. The power tool is evaluated by materials (their characteristics largely determine the parameters of the finished product and its functionality).
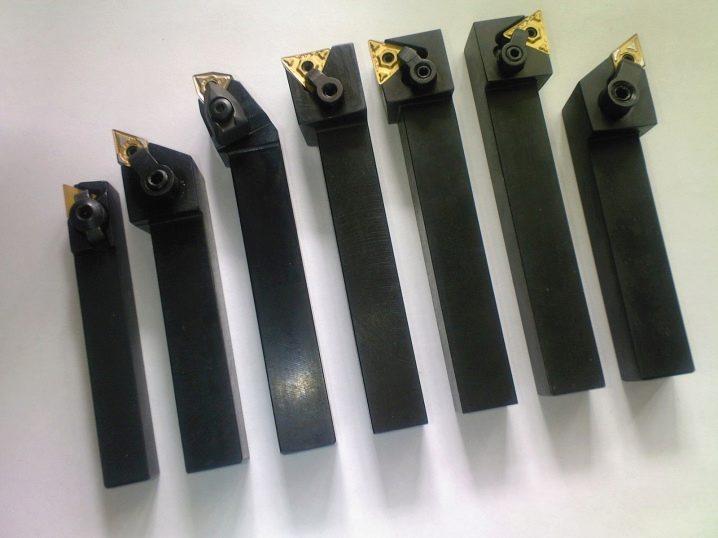

Collet chuck (aka collet chuck) provides quick fixing and dismantling of various auxiliary products.
It is also necessary to mention such blocks and additional equipment as:
-
taps (especially important for threading);
-
dies (forming the thread from the outside);
-
countersink;
-
drill;
-
soldering (increasing the strength of other tools);
-
turret, grinding and milling heads;
-
threading heads.





Nuances of choice
For the overwhelming majority of customers, high precision machine tools will be sufficient. But if a responsible production is organized or it is planned to produce precision products, technology with increased accuracy is already needed to ensure maximum compliance with the parameters. It is imperative to pay attention, of course, to the target material to be processed - including specific types of wood or types of metals and alloys.

Having decided on these indicators and having studied the reviews, you can proceed to assessing the technical parameters.
Desktop miniature machines are compact and lightweight. They consume a maximum of 0.4 kW, but at the same time they do not allow processing massive parts. Such equipment is eagerly bought for home or small services. A wider range of operations can be performed by a semi-professional apparatus with a power of 0.5-1 kW. With such a device, it is already possible to deploy small-scale production.
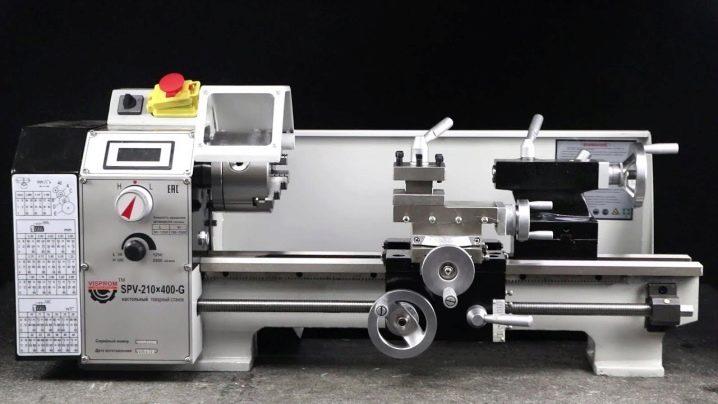

For factories and factories, they buy the largest and heaviest samples. They can guarantee the highest product excellence on a large scale. It is also necessary to pay attention to:
-
mains voltage (in some cases, powerful systems can only operate at 380 V);
-
the diameter of the workpiece processing above the bed;
-
the length of the parts to be fastened.


Programming
The process of setting up and setting up a CNC machine without defining a program or several programs is almost impossible. Manual programming implies the preparation of the text code of the program, which is then transferred to the device memory using data storage devices or cables. You can also use command racks (to set more complex typical modes). The most advanced solution is the use of integrated automation systems. They should cover the entire production cycle.
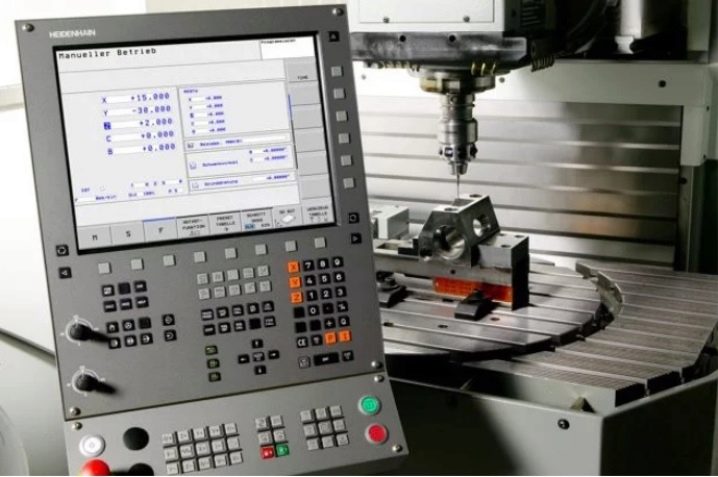

The programs must contain:
-
parameters of workpieces;
-
coordinate systems;
-
zero points;
-
selection of surfaces to be treated;
-
calculation of passes;
-
cutting data bookmark.

Safety at work
It is very important to wear protective clothing (which must be worn correctly). Before starting the lathe, the reliability of fastening of all parts and the quality of the grounding should be checked. There must be no foreign objects on the machine and its work table.
Do not go close to rotating parts or bring any part of your body. All measurements are carried out only in advance.
The working tool must be strictly in place. Sleeves should be tucked up or buttoned up, hair should be cropped and tucked under the headdress. Do not work on the machine if the case is damaged or the insulation of the wires is broken. If you notice any malfunction, you must immediately notify the foreman or repair service, until the problems are eliminated - work cannot be resumed.

Other nuances of safety precautions:
- use only serviceable tools and equipment;
-
lift weights over 16 kg only with lifts or with the assistance of assistants;
-
exclude installation and maintenance of the machine during operation;
-
remove chips from the machine only with a special device;
-
exclude cluttering of the aisles;
-
prevent the floor from flooding with coolant and oils;
-
adjust electrical equipment only after stopping the machine;
-
urgently stop work in case of arcing;
-
carefully regulate lighting;
-
stop the machine at the shortest, even idle time;
-
work as carefully and accurately as possible, without unnecessary haste.















The comment was sent successfully.