All about boring machines

Boring machines are one of the most common groups of machine tools in the metalworking industry. They are universally in demand in individual, small and large-scale production. A characteristic feature of such units is the ability to carry out metal-cutting manipulations in the most difficult-to-reach areas of the workpieces being processed.


Device and purpose
Boring machines are classified as universal equipment. On such units, it is possible to carry out almost all complex machining with perforation while maintaining maximum accuracy. The design of any boring machine provides for the inclusion of a horizontal or vertical spindle - it is a shaft equipped with drills, cutters, as well as taps and cutters. Such devices allow fixing the cutting tool and its movement along the main axes corresponding to linear directions.
The equipment allows you to perform the following types of operations:
- boring of internal surfaces;
- threading;
- drilling;
- turning the outer covering of bodies of revolution;
- countersinking;
- deployment;
- face milling.


All boring units on the market differ in the following parameters:
- dimensions of the machine and its weight;
- power characteristics of the motor;
- spindle speed range;
- modes of working feeds;
- maximum movement along the axes;
- limiting dimensions and weight of the processed element;
- desktop area;
- the size of the rising spindle.
Most boring machines are universal equipment. That is why the price for them can be from a couple of hundred thousand to tens of millions of rubles. The cost of such units directly depends on the technical and operational characteristics and operating condition of each specific working model.

Varieties
Depending on the design features and the mechanism of operation, there are several grounds for the classification of boring machines.
By design
At manufacturing enterprises, three types of finishing boring machines are used:
- horizontal boring, including boring and surfacing;
- jig boring;
- diamond boring.
The first two options are in maximum demand, they can be stationary and portable. In all versions of the equipment, the spindle is responsible for the movement of the tool.
At the same time, when carrying out manipulations associated with the processing of metal parts, different tools are used - reamers, drills, countersinks, a cutter can also work.



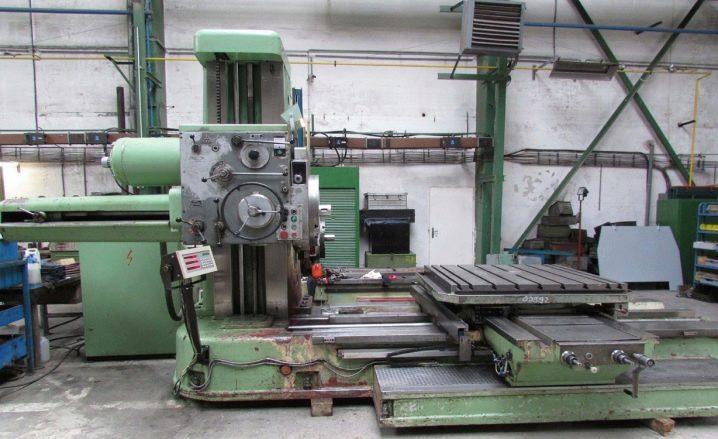
Horizontal boring
The main structural difference of such machines is the horizontal arrangement of the spindle. Due to this, perforations can be created even in hard-to-reach areas and bulky elements of metal structures. The movement of horizontal boring units is carried out in a rotational-translational pattern and is carried out by a spindle. Moreover, in such machines, it is not just a working tool that moves, but also a workpiece.
It is possible to switch the high-speed processing mode and the feed system. Horizontal models are widely used in the field of working with cast iron and steel elements.

Jig boring
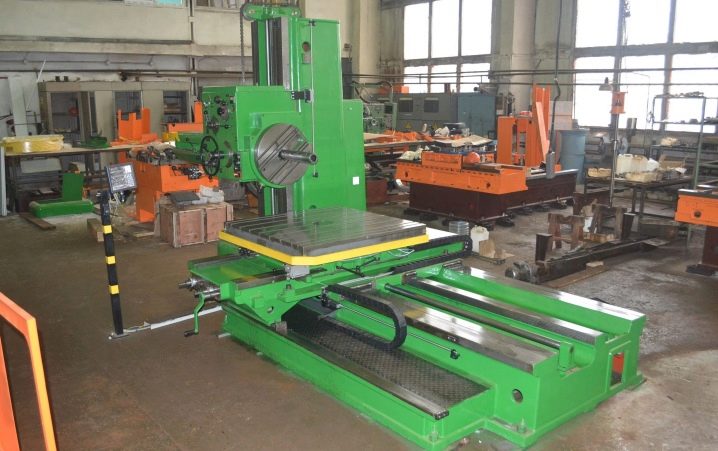
Machines of this type are in demand when drilling perforations according to strictly defined parameters. Such manipulations can be performed on various types of workpieces - body blocks, jig plates and some others. The presence of mechanical, optical and electronic modules in the design of these models provides increased processing accuracy.
Such units are equipped with rotary tables - this helps to form perforations in polar coordinate systems, without displacing the part. The use of coordinate boring machines makes it possible to process holes with precise holding of the given center distances between them. It is in demand when it is necessary to orient the holes in relation to the base surfaces - in this case, the counting is performed within a rectangular coordinate system. No additional mechanisms for guiding the working tool are provided here.



Jig boring machines have found application in both single-piece and in-line production. The following types of work are performed on them:
- rough and finish drilling;
- boring perforation;
- external turning of cylindrical surfaces;
- reaming holes;
- countersinking the ends of the holes;
- thread design;
- milling of flat elements.
In addition, coordinate units allow making holes in hull blocks and conductors, where the main factor is the accuracy of their location relative to each other. Such machines are much lighter than horizontal ones, so they can work as a mobile version of the equipment.


Diamond devices are used much less often horizontal and coordinate.
The scope of their application is limited to boring connecting rods, all kinds of cylinders, bushings and other engine elements.

By layout
Boring machines are relevant when it is necessary to process workpieces with a complicated configuration, which have many ledges, grooves and holes. In this regard, according to the layout, all the equipment presented is divided into several categories.
Units with a spindle section of less than 100 mm - such installations allow processing workpieces of compact dimensions. The work table here moves along two main axes, and the boring head moves vertically.
Units with spindle diameters ranging from 100 to 200 mm - these units are needed for processing workpieces of medium and large sizes. Their desktop moves only in one plane.
Machine tools with spindle from 150 to 350 mm - these installations are relevant for the processing of large-sized items. Their desktop is static.

Boring machines with numerical control are distinguished into a separate category. These are the most modern units that have a lot of advantages over traditional ones. Any work carried out in them is controlled by software, which makes it possible to achieve the level of maximum productivity and maximum accuracy.


Rigging
The work of horizontal boring machines requires equipment.
The basic working element is incisors. Depending on the shape of the head, they are divided into round, square, and rectangular. Depending on the processing options, such cutters can be scoring, threaded or through. For boring perforations over 20 mm in size, plate cutters are used.
An important element of the rig are reamers. They can be with non-adjustable as well as adjustable knives. These consumables are needed for finishing the holes after pre-boring.
To carry out manipulations with workpieces located at an angle to each other, angles are used.


The entire cutting tool is fixed using two support and cantilever mandrels, as well as chucks. The need for them is due to the fact that technologically it is not allowed to fix the cutter in the radial slide or in the boring spindle.
The jig boring equipment is different. Their design provides for the inclusion of special devices for high-precision work.
A universal tool holder is used for boring holes and cutting ends during the movement of the spindle, as well as for radial feed of the cutter. Its body fixes the spindles.
To align the edge of the workpiece with the axis of the spindle, as well as to place the vertical surface of the workpiece parallel to the movement of the table, use a center-finder microscope.
A shank is provided in the body of such a microscope; it is attached to the tapered hole of the equipment spindle.


The optical elements of the microscope are mounted in the housing. These include lens, mirrors, eyepiece and crosshair reticle.
To align the perforation of the workpiece with the spindle axis, as well as to align the perpendicularity of the end face of the elements of this axis, use a center finder with an indicator.
An obligatory tooling element is a horizontal rotary dividing table. Its functionality is associated with an accurate reading of the angular parameters of rotation - this allows processing in a polar coordinate system.
Interchangeable collets, a drill chuck, a set of adapter sleeves, a spring core, a box table, boring bars and other consumables are used as auxiliary tools.


Popular models
One of the most popular models of boring machines is the equipment of the Maikop machine-tool plant, brand 2E78P. The machine has been produced since 1982 and is the choice of large metalworking companies to this day. Allows to perform machining on steel and cast iron parts, as well as non-ferrous metal workpieces.
Provides the formation of holes with a diameter of 30 to 200 mm. The drilling section reaches 15 mm. In this case, the limiting dimensions of the processed parts are 75x50x50 cm, and the weight reaches 200 kg. Spindle speed 25-130 rpm. Power parameters of the drive 2.2 kW.



Another popular Russian-made unit is the 2A622F4, which is produced by the Leningrad Machine-Tool Plant. This is a modern device, equipped with a CNC module, due to which its optional capabilities are significantly expanded.
Such an installation provides automatic movement of the main working tool along four axes. Possibility of control through the remote control is provided. The unit is equipped with an electronic monitor, which displays basic information about the performance of the machine.


It bores holes in the range from 15 to 250 mm, while drilling forms a diameter of up to 50 mm. The mass of processed products can be up to 5 tons, and their maximum dimensions are 100x100x120 cm. Spindle revolutions in the range from 4 to 1250 rpm, drive power 20,000 W. The working table has dimensions of 125x125 cm.
These are large units for industrial use. They are intended for serial production of products. The machines are heavy, their weight is 20 tons.
The advantages of the unit include the presence of hydraulic clamps that automatically fix the workpieces, the use of telescopic guides and the operation of the spindle assembly on precision bearings.
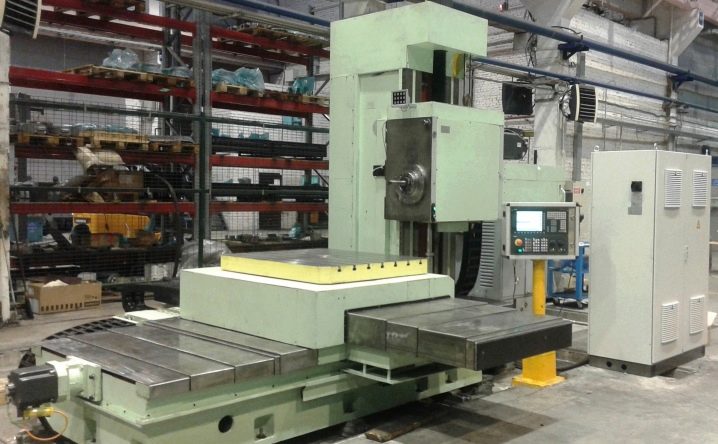

Operating rules
Boring machines are complex and very expensive equipment. That is why, when operating it, it is important to adhere to the basic rules of work. Equipment maintenance includes several measures:
- regular cleaning;
- lubrication of all technological units;
- inspection of the performance of all blocks and parts.
The operator should take care of the coolant supply module and promptly eliminate any minor malfunctions.
The operation of automated plants usually includes their maintenance and adjustment. The latter is performed by the fitter, and the adjustment is performed by the machine operator. The machine operator's functionality includes:
- acceptance of workpieces, their installation;
- implementation of operational management and regular monitoring of the condition;
- replacement of the cutting tool;
- crumb removal.
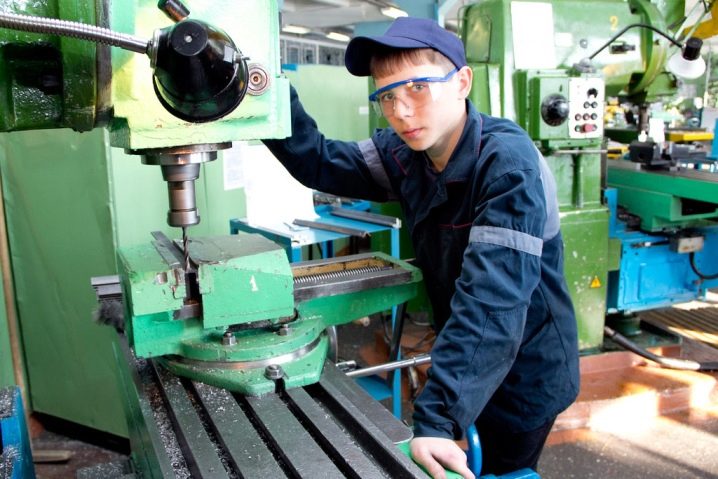

Pay special attention to the hydraulic system. Caring for it involves controlling the heating of the oil in such a way that the temperature does not rise above +50 degrees. Usually, the first time the oil is changed after a month of operation - this allows you to remove all the lapping products of the working mechanisms. Subsequently, the oil change frequency is once a quarter.
The piping should be checked periodically to prevent airborne particles from entering the hydraulic system. It is important to clean the filters in a timely manner. From time to time, the device drives must be lubricated. At least once every 6 months, the polarity of the functional contacts of the switches, as well as the buttons used in the DC and AC circuit, should be changed. If metal droplets are found on the contacts or burns, they should be cleaned with a velvet file. Usually, all operational requirements for machines are indicated in the user's manual and are standardized by the current GOST. Strict adherence to these rules allows you to ensure uninterrupted and long-term operation of the equipment.















The comment was sent successfully.