What are the machine guides and how to choose them?
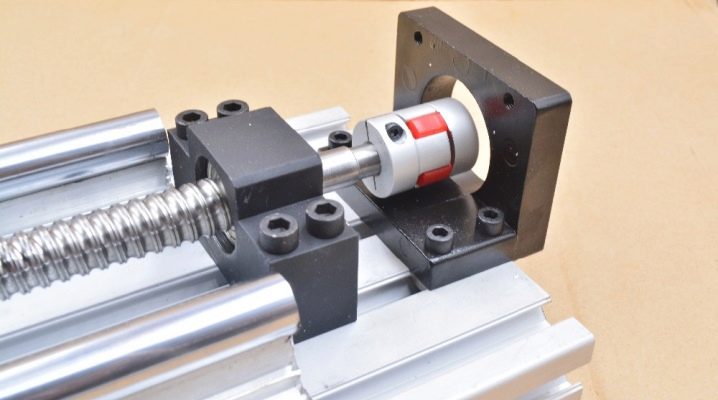

Guideways are the most important part of machine tools, as the accuracy of the tool movement depends on them. From the article you will learn what are the circular and linear guides for CNC machines, which is better to choose - roller, ball or other aluminum guides.


general description
Any mutual movement of the workpiece and the tool occurs along guides - a kind of rails. The working body of the machine or a device with a workpiece fixed in it walks along them. And since these movements directly affect the quality of the product, the guides must meet a number of requirements.
-
Rigidity and hardness. In metalworking, large cutting forces occur - 100 kg or more. It is impossible to allow the working body of the machine to "walk" more than the specified quality. Therefore, the guides are made of alloy steel grades - ШХ-15, 95Х18, followed by heat treatment, as well as various types of ceramics.
-
Low friction force. When machining complex parts on CNC machines, the tool moves with jerks and accelerations. And due to increased friction, the accuracy of its movements is lost.
-
Resistant to wear and tear. In simple models of woodworking machines, the guides are cast in one piece with the bed, and in CNC machines they are mechanically connected to it. But in all cases, repair is a difficult and responsible business.
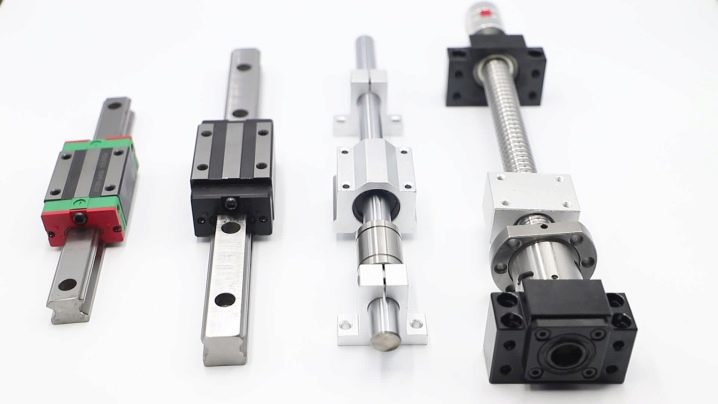

Since there are many types and models of machines, the guides for them are different.
Views
The shaping movements of any machine are rotation and linear movement. They need the appropriate guides.
-
Round tables are often used in rotary tables where the workpiece is machined from all sides. They are found in milling and 5-axis machines.
-
Power heads and calipers of lathes and multi-operation machines with CNC move along linear vertically and horizontally.
-
Inclined are needed for specialized machine tools.

The easier it is to make guides, the cheaper they are, but they do not always give the required accuracy of movements. Therefore, it is necessary to correctly choose the shape of the cross section.
-
Rectangular, cast at the same time with the bed, the simplest. Often found in inexpensive bench-top machines.
Due to their large bearing area, they cope well with static loads, but have a high frictional force.
They do not differ in high accuracy of work, because due to wear, a play appears between the rail and the bushing. But they can be repaired, they are easy to polish.


- Triangular or prismatic, more precisely, because thanks to the beveled edges, there are no gaps. They were widely used in machine tool building, but are now gradually being replaced by other types.
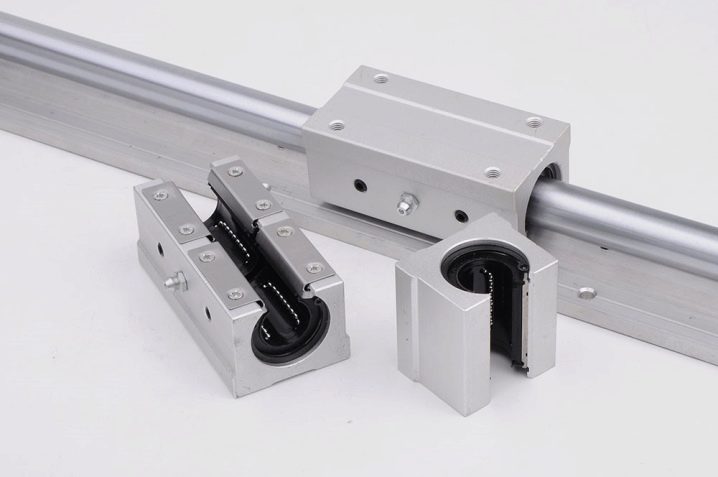

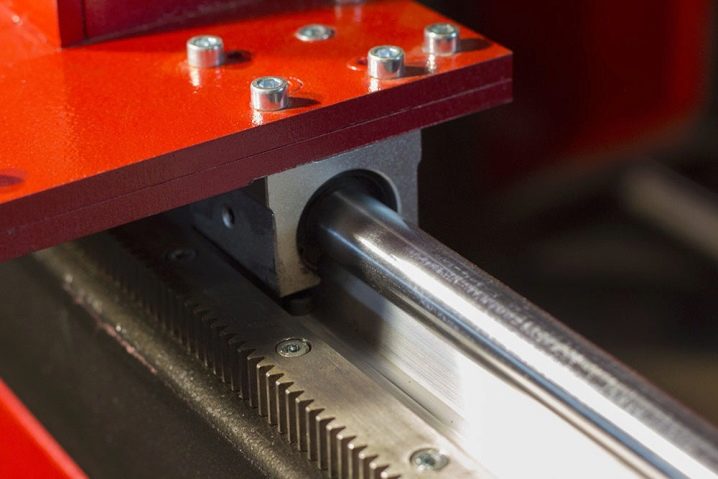
- Polished cylindrical shafts - simple and common, easy to install on the machine or replace. Induction hardening and surface finish ensure wear resistance and low coefficient of friction. But there is a drawback - fastening along the edges leads to sagging under its own weight or under the mass of the caliper. A little, but already leads to product errors. Therefore, such guides are not made longer than 1 m, and the ratio of the diameter to the length of the shaft should be at least 0.05, and preferably 0.06-0.1.
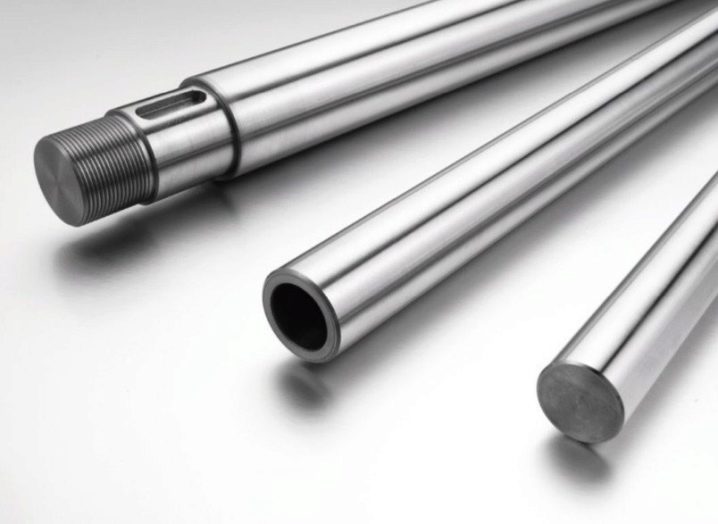

- Splined shafts better resistance to bending and twisting. And the bushing, which travels along the shaft, cannot turn on its own, which adds rigidity to the entire machine. The cons of spline shafts are the same as those of polished shafts.And one more thing - the splined shaft is difficult to install correctly on the machine, so they are rare.


- Cylindrical rail - these are ordinary round guides, but along the entire length they are welded to the prismatic support. This increases the rigidity. When the machine is working with large workpieces, these guides are bent with the bed, so the relative position of the tool or workpiece does not change. This means that the accuracy increases. And such rails are inexpensive.


- "Dovetail" used in heavy machine tools that require rigidity and stability under alternating and static loads. They are cast in one piece with the bed, making them difficult to repair when worn. Only a manufacturer or a very discreet person who will work by hand will be able to grind the planes along the entire length. But such rails serve for a long time.
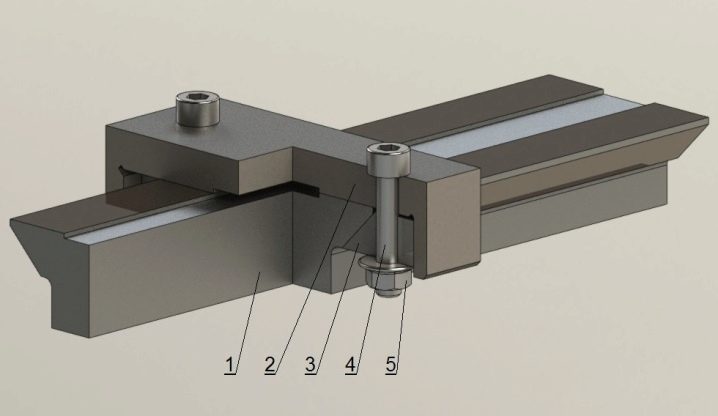
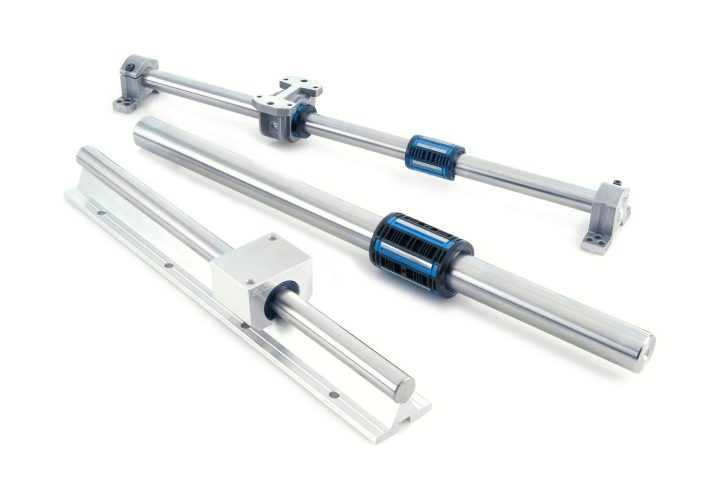
- Steel aluminum profiles - the most reliable in work. Thanks to the grooves along which the balls or rollers move, such guides hold the load well, do not play, do not twist or bend.
But they are expensive, because they require especially high-quality processing during manufacture. And they are also difficult to install on the machine, since high accuracy and alignment of the fasteners is required.
The quality of the machine is influenced not only by the rails themselves, but also by their mating sleeve. In mechanical engineering, they are combined into one term - guides. Friction, positioning accuracy and everything that affects movement depends on the design of this pair. Therefore, the guides are made different: sliding, rolling and combined.
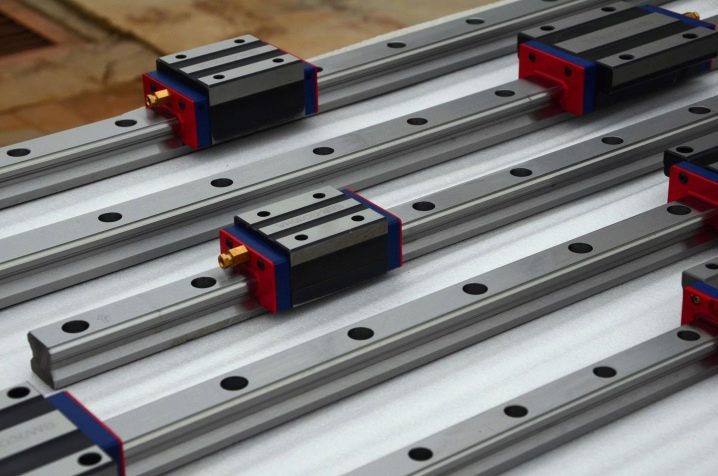

Rolling guides
In them, the caliper bushing on balls or rollers travels along the rail. Special screw grooves are made on the sleeve, thanks to which the balls, when they reach the edge, return to their original position. It resembles a bearing. This solution has many advantages.
-
Good dynamic properties and low friction - the caliper can quickly accelerate and stop. This is essential for precision machining of small parts such as cutouts and grooves.
-
Low heat dissipation - the rails are not deformed due to thermal effects. This is especially good for high precision (precision) equipment.
-
Easy to maintain - when worn, it is sufficient to replace the balls. They are softer than the guide rail and therefore wear out faster.


But there is a drawback - a small damping ability. This means that vibrations generated during cutting are invariably transmitted to the bed. This will reduce machining accuracy and lead to scrap. Vibrations occur, for example, when the stock is uneven in roughing operations.
The roller guides are slightly different in design. They are roller and ball.
-
Roller ones withstand higher loads than ball ones. But the friction that occurs at the ends of the rollers reduces the dynamic properties.
-
Ball bearings are better suited for precision work, but do not tolerate high cutting data.


For difficult conditions, other constructions are needed.
Slide guides
In them, the sleeve slides along the rail along the lubricant layer. Due to the large support area, they can withstand serious loads, including shock loads, therefore they are widely used in the initial processing modes. But in these guides, the static friction force is much higher than the motion friction force, therefore, at low speeds, the nodes do not move uniformly, but in jumps.


To compensate for this, various technical solutions are used.
-
Hydrodynamic ones have a simple and reliable design. In them, oil is drawn in through the lubrication grooves between the rail and the bushing, which separates the rubbing surfaces. These grooves are located along the entire length of the rail. These guides have high rigidity and good damping properties. Disadvantages - they work well only at high speeds, otherwise there is no hydrodynamic effect. In addition, operating conditions deteriorate during acceleration and deceleration.These guides are widely used in planing and carousel machines.
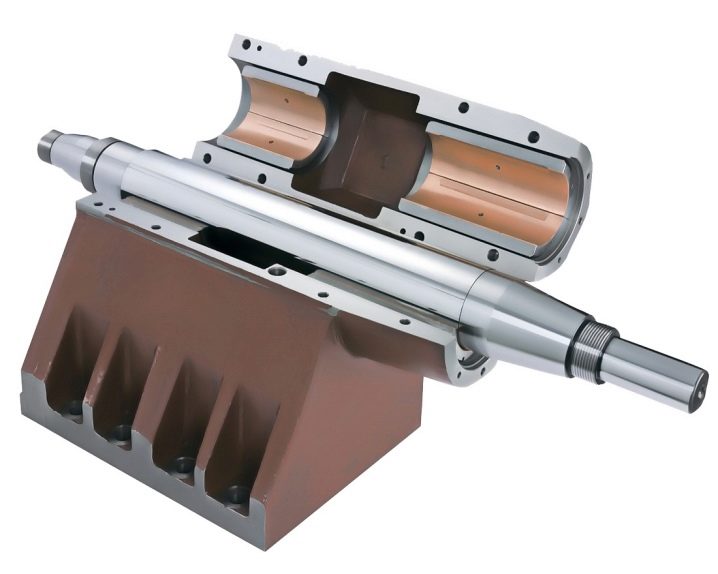

- Hydrostatic ones are devoid of these disadvantages. In them, lubrication is supplied under pressure from a pump, therefore, on the surface there is always an oil film with a thickness of 10-50 microns, and sometimes 100 microns.

But they have serious drawbacks - they need equipment for circulating and filtering the oil, heating occurs during operation, and special devices are needed to fix the caliper in the desired position. In addition, the system is difficult to maintain.
Hydrostatic guides are widely used in heavy and unique high precision CNC machine tools. They are open and closed. Open-ended (without strips) are simpler in design and are used under stable operating conditions and a large caliper mass. Closed ones are better at resisting bending and tipping, but require careful and expensive construction.
- Aerostatic ones use air instead of oil. Therefore, they have low friction, high precision and durability. And if you remove the air supply, the caliper will be securely fixed, unlike hydrostatic devices. But their rigidity and dynamics are worse, moreover, due to the low air density, fluctuations appear. Also, the air passages must be cleaned regularly.
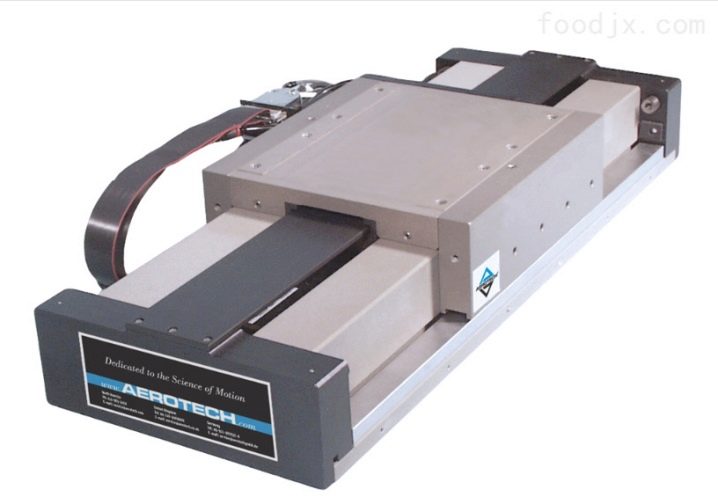

These guides have proven their worth in lightweight machine tools. They are used in coordinate measuring machines, PCB machines and similar equipment.
Structures are often used that combine the positive qualities of different types of guides.
Combined
Semi-fluid or liquid lubrication, mixed rolling-sliding friction and other solutions are used. They provide high rigidity and smooth operation. But they have a short lifespan.
As perfect as the equipment is, it requires protection from damage and regular maintenance.
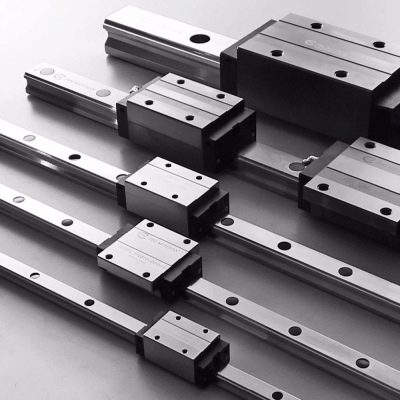

Accessories and consumables
The main task is to make sure that there is nothing but oil between the rubbing parts. For this, the guides are protected with special devices.
-
Rubber corrugated protection will not give coolant (cutting fluid) get on metal products, it will protect against dust and small debris. But it will not cope with sharp chips or large objects, for example, if the workpiece falls on the bed.
-
Roll protection is more reliable. When the caliper moves, it rolls up, and on the other hand, on the contrary, unfolds. Therefore, the guides are always covered with a metal tape, albeit a thin-walled one.
-
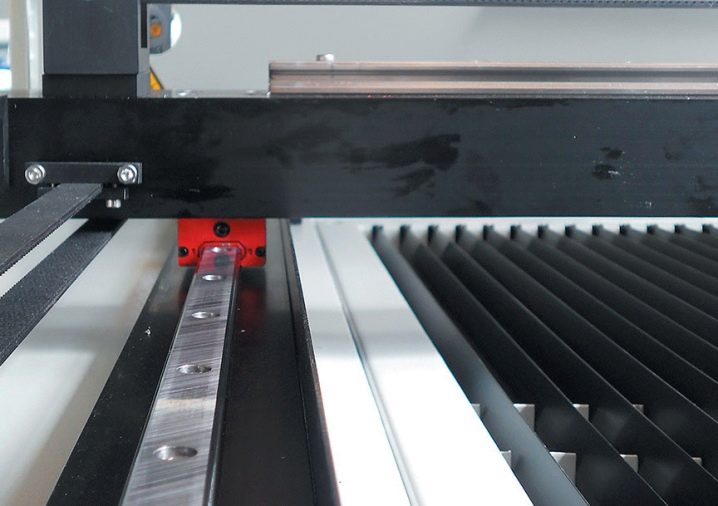
Telescopic is the most reliable. The thick box expands to the full length of the guides and closes them on all sides.

But keep in mind that the more massive the protection, the more effort it takes to fold it. And the stronger the friction. Therefore, you should not take the telescopic version for weak or precise machines that need high dynamic qualities. But it is not recommended to save on protection either.
-
Guides sometimes need to be cleaned by hand. This requires a scraper.
-
And if too much debris is generated during operation, then it is advisable to fix the wiper on the caliper.

And the tech loves grooming.
-
A rag is ideal for removing dirt and old oil from surfaces.
-
And oil for lubricating surfaces protects parts from corrosion. In addition, periodically you need to rinse the guides in oil to clean them of oxides.

But if these tools don't work, you can always buy new guides.
Features of choice
When repairing, you can simply buy the same guides. Or you can upgrade the machine. Just consider a number of points.
-
The guides are preloaded. It is regulated by the diameter of the balls or rollers in the carriage. For example, for lathes with CNC in the X and Y axes, the interference force should be 0.08C. And for the Z axis, it should be 0.13C. Then the high rigidity of the entire structure is guaranteed.
-
The guides must match the accuracy class of the entire machine.

Determine the type of product.
-
For soft workpieces less than 1 m long, polished shafts are suitable.
-
To sharpen metal or large pieces of wood, you need profile rails.
And finally, buy components only in trusted stores.
There are often fakes that not only spoil the workpieces, but also break the contract. And to prove your case, shoot the unpacking of new guides on video in one take without editing.













The comment was sent successfully.