All about Japanese spirea
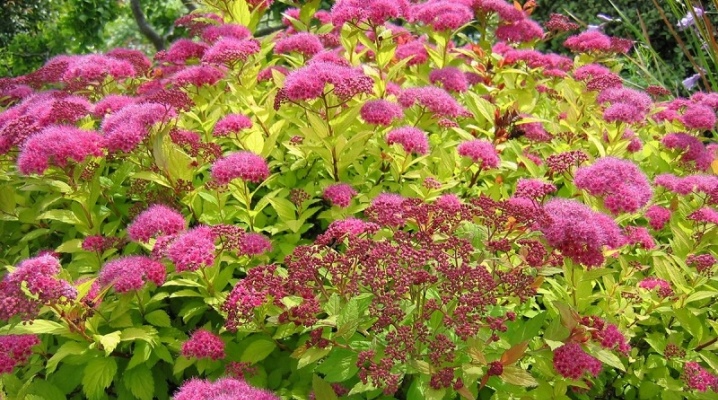

When creating a landscape design for your site or garden, you always want each plant to look harmonious and beautiful. Not all cultures can coexist together, forming an interesting ensemble. However, this does not apply to Japanese spirea - a plant that will perfectly complement any composition, making it truly unique.


Shrub description
The homeland of Japanese spirea is, of course, Japan, although this plant is very popular in some other Asian countries. If you translate the name of a culture, it will become clear that the word "Spirea" looks like a "spiral", and indeed, the branches of the spirea curl interestingly, resembling spirals... The plant belongs to the pink family and is a slow-growing shrub.
In the wild, the height of the shrub can reach half a meter, however, the "home" varieties have a much smaller growth - about 25-30 cm. The main feature of the culture is the unusual leaves. In spring, they can have a wide variety of colors in a warm palette: red, orange, pinkish. With the onset of summer, they become familiar green, and in the fall they return again to the spring shades. The shape is completely different and depends on the variety, but there are always teeth at the edges.


Separately, it is worth talking about the spire shoots. Young specimens are felted, with a soft edge, which they lose with age. At the ends of the shoots are large inflorescences, consisting of many individual flowers. The size of the inflorescences also depends on the variety, and the color, which can be red, white, pink. Nevertheless, all varieties have long flowering, which cannot but be regarded as an advantage.
Japanese spirea belongs to the species that bloom in summer. This process begins around the middle of June, and ends before the onset of cold weather.
In addition, spiraea can bloom and re-bloom. However, it will begin to bear fruit only after 4 years of life.



Popular varieties
Japanese spirea has many interesting varieties, each of which deserves separate consideration.
- "Sparkling Champagne". A tall, meter-long shrub that can reach 150 cm in diameter. It has pink-white inflorescences, and the color of the leaves changes every season. The perfect solution for hedges.
- Frobeli. This variety is also distinguished by its high height. It begins to bloom in June, the inflorescences are pink, heavy, the leaves acquire a green color, beautifully contrasting with the flowers. Turn red in autumn.
- "Jenpei or Genpei". The second name of the variety is "Shirobana". Very beautiful, medium height variety. Unlike many other varieties, the leaves are always dark green in color. But the real "highlight" of the variety will be the inflorescences, which can include as many as three different shades. For this "Shirobanu" is popularly called tricolor.
- Albiflora. This spirea grows up to one and a half meters wide, but does not even reach a meter in height. In summer, its leaves are green and the inflorescences are white. In the fall, the foliage turns yellow.
- Golden Carpet. Dwarf artificially bred variety. The shrub has a round shape, about the same height and diameter - about 30 cm. It does not bloom too abundantly, but beautifully - with small pink inflorescences in the form of a shield. Leaves are bright yellow, golden.
- Magic Carpet. It has a rather dense and dense crown that looks like a carpet.A feature of the variety is the frequent change in the color of the leaves, for which the plant is highly valued in landscape design. The flowers of this variety are small, in pink tones, and the culture grows up to about 50 cm.
- "Nana". Another miniature shrub, reaching no more than half a meter in height. Blooms until September, inflorescences have a bright red color. The leaves change their color from green and red to orange.
- Neon Flash ("Neon Flash"). A very beautiful compact bush, it reaches almost a meter in length and width. The leaves change their color, the flowering is profuse, long-lasting. The inflorescences are saturated, bright, can have shades from lilac to deep red.
- Firelight. A bush of medium height, about 60 cm. Blooms until September, pink inflorescences, cover the culture loosely. The shoots have a burgundy hue, very bright. This is one of the slowest growing varieties.
- Japanis Dwarf. The name of this variety is translated very funny - "Japanese gnome". Height - 30 cm, the crown has a spherical shape. The leaves are deep green, small, and the inflorescences are pink, corymbose.
- "Manon". A compact shrub with a round crown and leaves that change color seasonally. Inflorescences are not too large, bright red.
- Golden Princesses. A very beautiful shrub, also round. Inflorescences are in the shape of a ball, very dense, large. Coloring - from lilac to pale pink.



Growing rules and care features
The main advantage of Japanese spirea is its ease of maintenance. But in order to provide the plant with healthy and harmonious growth in advance, as well as to protect it from diseases and pests, you need to carefully consider all the stages of planting and further care for it.
Timing
Japanese spirea is planted in open ground in spring or autumn. Most experts believe that a spring planting will be more successful. After all, the seedling will have every chance to adapt to new conditions, strengthen the root system, and take root. Besides, spirea will be able to start buds, which in summer will bloom with beautiful inflorescences... Nevertheless, the autumn planting of culture also takes place, but it is advisable to carry it out only in regions with a warm climate.
In addition, it is important to do this before the first frost, otherwise the young plants will die.

Seat selection
To grow spirea, you need to select sunny open areas. In such places, she will show her best qualities. but it should be noted that the shrub will grow in partial shade, but you won't have to expect such abundant flowering from it.
Another nuance is the size of the area. A large area should be allocated for planting the spirea, since the root system needs a lot of space for harmonious development.

Soil preparation
A plant such as spirea does not impose special requirements on the composition of the soil. But it is still better if the land is fertile. It is good if the acidity is slightly above neutral. For those gardeners whose soil is drained, light, saturated with oxygen, it is easiest. They don't need to worry about fertilizer when planting. But if the soil is poor, then first, a couple of weeks before planting, it is fertilized with peat or a complex of mineral dressings.


Landing scheme
Before talking about planting a plant, consider the rules for acquiring planting material. Here you need to be careful, carefully examine the seedlings. They are acquired only in nurseries and primarily look at the roots, which should be slightly damp. Shoots should bend, because this plant is very flexible. If you nevertheless looked at something, then at home, trim the diseased roots with a sterile pruner, the same should be done with too long roots (they need to be shortened without completely cutting them off). Then the roots are placed in a container with a weak solution of manganese - this simple procedure will kill bacteria, if any.
While the planting material is being prepared, you can do the holes. The pits are prepared 3-4 days before planting, and their size should not be much larger than the size of the root system of the seedling itself. The hole is usually about 40 centimeters deep.


Having prepared the pits, they begin planting seedlings. It is best if it is carried out in cloudy but not cold weather. The bottom of the hole is covered with a 15-centimeter layer of gravel or crushed brick. Then the plant descends, the roots will need to be carefully straightened. After that, a fertile mixture is poured, which consists of turf, peat, humus and sand in a ratio of 3: 1: 2: 1. The soil is placed carefully, lightly tamping. The root collar should not be buried.
Once the plant is planted, it needs to be watered. Enough one or two dozen liters per bush. Then experts advise to mulch the trunks with dry peat or sawdust... This will help keep moisture in the soil and further nourish the roots. After a few days, do another watering, but now add a little ammonia to the liquid. This will allow the roots to handle stress more easily. Important: do not forget that the root system of Japanese spirea is quite voluminous. Therefore, it is important to respect the landing interval.
A distance of half a meter must be left between each bush, and 70 centimeters between each row of plantings. If you have taken sprawling, large varieties, keep a distance of one meter.


Watering
Watering is probably the most important aspect of caring for any plant. Particular responsibility should be shown in the case of newly planted spirits. Once every 14 days, the bushes are watered, each one and a half buckets are required. The water should be warm and in the sun.
In hot weather, the frequency of watering can be increased; it is impossible for the plant to need moisture. In cool, on the contrary, the supply of liquid is reduced, watering only when the soil dries up. If the rainy season has begun, you can stop watering altogether. In addition, it should not be sprayed with a spray bottle, nor should it be watered. But it will be useful to loosen the soil after watering, as well as dig up all the weeds nearby.

Top dressing
You can start feeding Japanese spirea already in the first year of life, in the summer. At this time, it is important to use exclusively organic matter. Take a little water, dilute with fresh manure, and then insist in a cool place for 10 days. Then you need to dilute the infusion in a bucket of water and water the culture. This event is done after the pruning procedure. Besides, before fertilizing, you need to water the bush with plain water, loosen, remove weeds... Small plants will require about 1 liter of liquid, large ones will need 3-4.
Mineral complexes can also be introduced from the second year. Unlike organic ones, minerals are used in the spring, before flowering. Fertilizers are suitable for rose crops, which must be applied as stated in the instructions. You can also additionally fertilize the plants with superphosphate, which is applied along with the manure in the summer.
One bucket of infusion will need 10 grams of the substance.


Pruning
Spirea grows well, so pruning is vital for it. The crop is cut in the spring. Initially, in the first three years, regular pruning will be required, in which frozen, diseased and dried branches are removed. The procedure is done in May. A cardinal rejuvenating haircut will require a spire for 4 years. The bush is pruned low, leaving 30 cm. Then top dressing is applied.
Subsequent haircuts are carried out taking into account the purpose of growing the plant, which can be different: hedges, paths, alpine slides, etc. Every 2 years, the shoots are pruned, since only young specimens bloom. After flowering, pruning is not carried out: this is relevant only for spring-flowering varieties of spirea.


Diseases and pests
It is worth noting that spirea rarely becomes infected with diseases. But this happens, so it is important to know in advance how to save and protect plants.If you notice that the leaves of the spirea have begun to dry, curl, turn yellow, and the plant itself has stopped growing, it's time to look for the cause. Viral and bacterial diseases must be "discarded" immediately, since spirea almost never picks up them. Most likely, the matter is in fungal infections, which mainly arise due to the fault of the gardener: excessive watering, non-observance of the distance between plantings, as well as due to external reasons, for example, strong humidity and prolonged showers.
One of the most common and unpleasant infections is verticillosis, which quickly leads to death if the problem is ignored. Sick bushes are sprayed with fungicides, for example, "Fundazol", as well as a solution of manganese. If this does not work, the bush will have to be destroyed.


As for pests, there are more of them than possible diseases. In total, three main parasites can be distinguished.
- Rose leafworm. This is a small moth that does not disdain anything. It harms both in the caterpillar stage and in the stage of an adult insect. Gnaws leaves, drinking their juices. To combat it, insecticides should be used.
- Spider mite. It begins to create its colonies in May, and is fully activated at the end of July. It also gnaws at the leaves, entangling them with a small cobweb. They fight against it with insecticides, "Karbofos" has proven itself especially well. If everything has not been started yet, you can try a solution of laundry soap, which is sprayed on the culture. To do this, mix a quarter of a bucket of water with three tablespoons of grated soap and leave for a couple of days.
- Aphid. A dangerous and very popular pest that drinks all the juices from shoots and foliage. Against aphids, you can use "Actellik", from folk remedies, tobacco, pepper, garlic or soap infusion perfectly helps. It is also recommended to deal with the destruction of ants on the site.
In addition to insects, moles can also cause harm. They gnaw at the roots of the spirea, which causes the plant to dry out and die. Few people will find the strength to catch and kill moles, and this is not necessary. It is much easier to install a tool such as "Krotogon" on the site. It emits special sound waves that moles do not like. Plus, moles hate castor oil.
If you place containers with oil around the perimeter, the animals will have to look for another area to live.


Preparing for winter
Almost all varieties of Japanese spirea are remarkably resistant to frost. Many of them do not need shelter at all, but this does not apply to first-year seedlings. If in doubt, you can cover all plants, even adults, there will definitely be no harm.
How to cover:
- collect the shoots in a bunch and bandage;
- mulch the plant with a 10 cm layer of straw or sawdust;
- bend the bundle and secure;
- cover the plant with leaves and branches so that it is not scattered by the wind;
- with the onset of winter, the spirea is additionally covered with snow.

Reproduction methods
Japanese spirea can be propagated in several ways, each of which has its own characteristics.
Cuttings
Propagation by cuttings is a fairly simple method available to beginners. It is recommended to carry it out in early autumn. For grafting, choose a strong stalk and cut it into 4 parts. Each of them should have leaves. The cuttings should be soaked in water with a growth stimulator for a couple of hours, then planted in the ground, consisting of peat and sand. The container with cuttings is taken to a cool and dry place, covered with foliage and left for the winter.
With the arrival of spring, the material will be ready for planting in open ground.


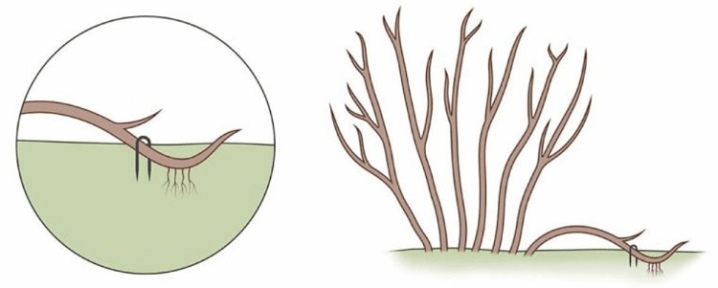
Layers
Another very easy method in which there is practically nothing to do. At the very beginning of spring, before the leaves appear, the branches that are closest to the ground are tilted and bent, securely fixing on the ground. The bent branches will need to be sprinkled with earth and do not forget to water. If everything is done correctly, by the beginning of autumn the spirea will delight you with new bushes.
Seeds
This is a rather unreliable method of reproduction for spirea, since only half the seeds germinate. In addition, the technique is far from applicable for all varieties, so most gardeners do not turn to it. However, if you want to try it, you need to know how to do it right.
In the early days of spring, you will need to prepare boxes with fertile and high-quality soil. They put seeds in it, you can put peat on top. The container with seeds is covered with glass, and when the first shoots appear, it is removed. Water in moderation, protecting small sprouts from drafts and the scorching sun. When two leaves appear, the seedlings dive, settling in separate containers. After a year, the crop can be planted on the site.


Application in landscape design
Japanese spirea is a very decorative, beautiful and delicate plant that will decorate the site both alone and in the company of other crops. In autumn they will delight gardeners with unusual colors of leaves, and in late spring and summer - with airy inflorescences of various shades. Spireas decorate not only plots, but also city parks, walking squares near medical institutions, kindergartens and schools, private estates. These plants are appropriate anytime, anywhere. But they look especially beautiful together with conifers: thuja, juniper, small Christmas trees. No less magnificent compositions can be formed by combining spirea with lilacs, lavender, rhododendrons, hawthorn.
If there is a desire to create spacious, spectacular flower beds, then spirea can be successfully combined with lilies of the valley, tulips, violets, primroses, daffodils... An interesting solution would be a single spirea, in whose near-stem circle periwinkles, lungwort, and cerastium are comfortably located.



And now let's see some beautiful examples of how effectively you can transform a site by just planting a spirea on it.
- Japanese spirea "Golden princesses" in an unusual design.
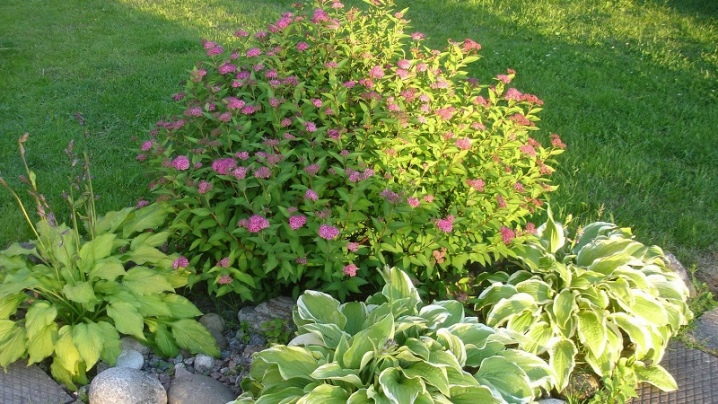

- Circular crop planting is simple and aesthetically pleasing.
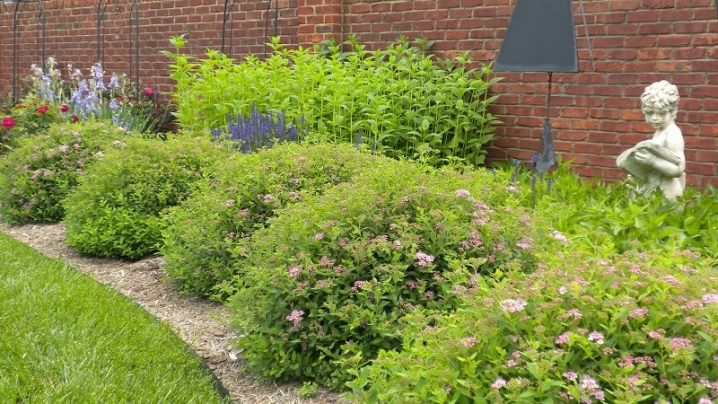

- Elegant walkway decoration with two rows of pink spirits.
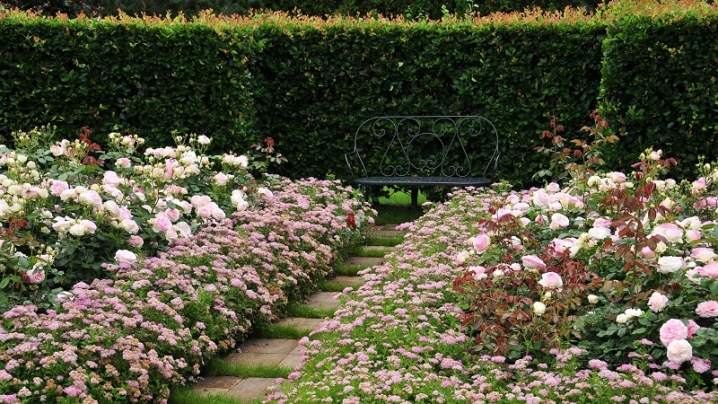

- Low-rise compact "Country Red" within the city.
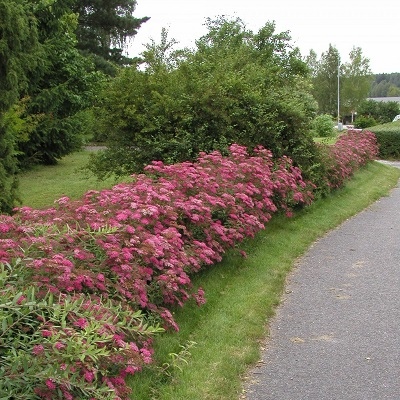

- Amazing landscape of light rose bushes.
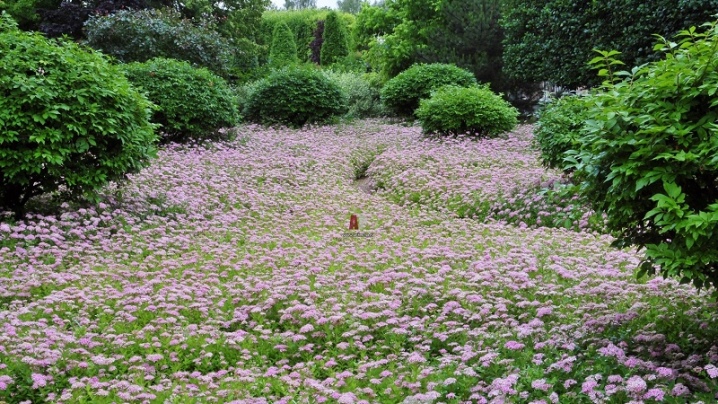

- An airy hedge formed from a large white spirea.
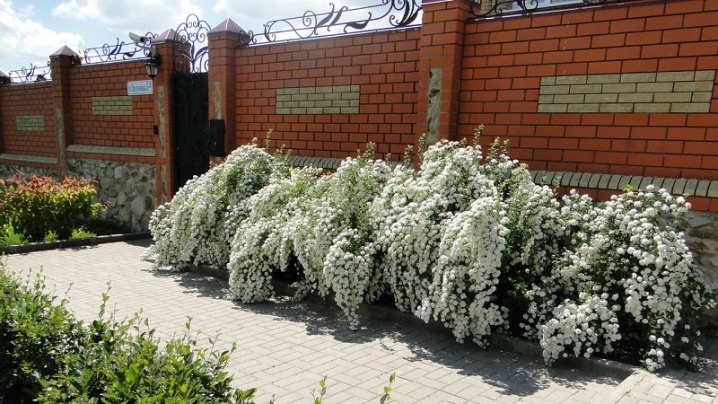

- Compact bushes in the design of coniferous crops are an excellent choice for a private garden.

In the next video, you will find additional information on Japanese spiraeus.



































































The comment was sent successfully.