Reproduction of black currant by cuttings
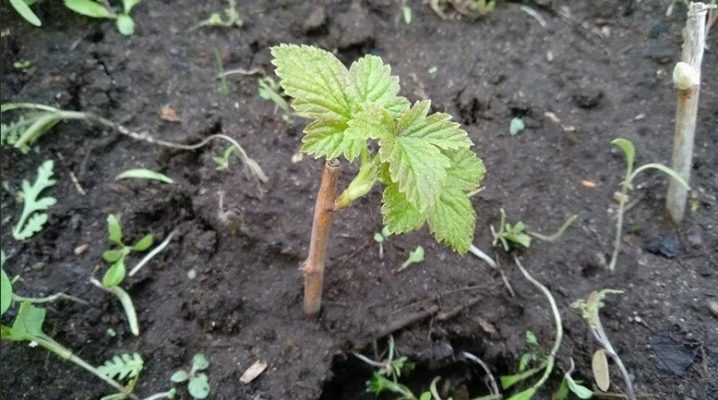

It is not difficult to propagate black currants - one old bush can give life to ten (and more) new ones. In addition, currants are distinguished by their vitality - they take root even in winter conditions at -20. Given time, cuttings you planted in early or mid-fall are almost guaranteed to take root.


Advantages and disadvantages
The reason that will encourage summer residents to propagate currants is obvious: to have a good harvest of this tasty and very useful product (berries) in your garden. Or, when its consumption is prohibited by a doctor due to existing diseases, to sell the crop at a price slightly lower than the market price to neighbors in the quarter, to the village - who does not grow this berry. We list the advantages of vegetative propagation of currants.
- No need to wait for the berry to sprout from seed... Unfortunately, seed propagation of many horticultural crops, including most fruit trees and shrubs, will produce a sour wild taste. And when the crop is ripe, although it will be sweetish, it will turn out to be very small, and its assembly will turn out to be an irrational business. Cutting - with the help of "shanks" - is preferable here: the characteristics of a particular variety will be preserved in full. A cutting branch will pass on to its daughter branches all the hereditary characteristics of the original berry.
- Frost resistance... Quite often there are cases when properly planted and rooted cuttings survive frost up to 20. Of course, certain conditions must be met.
- One large bush gives rise to 10 and newer... If the branches have grown enough, then there will be a decent amount of seed - cuttings. A bush rejuvenated in this way - everything that is cut to the 5th bud from the ground level - is cut into cuttings, depending on its condition, freshness, energy, vitality. The more of them, the more chances, opportunities to successfully propagate the bush.
- Fruiting is actively increasing from the 2nd year from the date of planting of cuttings... With the right care, the harvest will always be large.


It is permissible not to cut currants, but to separate the daughter processes when dividing the root of the parent bush. Each of them sprouts lateral roots - like raspberry sprouts. Then the main root is cut off from the common maternal root - and transplanted directly into the open ground in the area, to an empty place. After planting, a new bush must be carefully looked after.
The disadvantages of vegetative propagation of the currant bush are in the following.
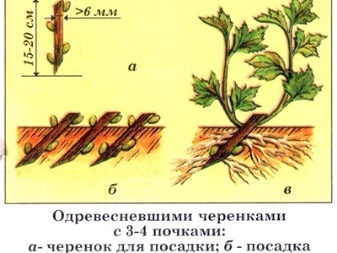
- The cuttings should not be random, namely from 6 mm in diameter. Too small thickness of the cutting requires "greenhouse" conditions and scrupulous saturation with organic matter and minerals of the "planting" soil. Everything that is more than 8 mm, it is advisable to discard or not cut the branches of the bush larger than a given diameter.
- If winter is characterized by prolonged frosts below -20, then currants cannot be grown in the open field.... Build a greenhouse for her. Its internal space should be windproof. In severe frosts, the greenhouse room is heated using electric heaters or a stove-stove.
Violation of the technology of transplantation and reproduction of bushes is fraught with a low survival rate of cuttings. This means that out of 10, for example, only 1–3 cuttings can successfully take root, the remaining 7–9 will simply die before they can take root. This procedure cannot be performed in winter, with frequent frosts: vegetation, which streamlines the growth of new adventitious roots, does not manifest itself at temperatures below +1 in any way.
A stalk that has not established a "food" connection with the ground will freeze, and in the first thaw, being dead, it will simply rot.


Procurement of material
Cuttings for spring and autumn plantings are used lignified. Summer shoots are taken by annuals - and do not grow in the ground, but start up the first roots in the water.
Summer
It is recommended to cut currants in the summer using not a soil, but an aquatic environment... Cut a fresh, non-lignified annual shoot above the level of the bud from which it has blossomed. Dip it in a jar of fresh water. It is advisable to hold the water a little - at least a few hours - so that chlorine and hydrogen sulfide come out completely. This also applies to groundwater pumped out of the well and tap water.
Even if your "vodokanal" purifies water from reservoirs in accordance with GOST and in accordance with all the rules of the sanitary and epidemiological service, it is still recommended to defend it. Shoot length - no more than 20 cm.
To stimulate root formation, you can dissolve a small amount of root (stimulant drug) in water - but no higher concentration than indicated in its instructions.


In spring and autumn
The sequence of actions when breeding white, red or black currants is approximately the same. In spring, cuttings are made in March, before the buds begin to bloom on existing currant bushes, in autumn - at the end of September or at the beginning of October, depending on the region. Material - annual, but lignified shoots. You can also use shoots that are up to several years old, but their survival rate in this case is much lower.
For cutting, use a pruner or a sharpened clerical or ordinary knife. It is impossible to squeeze the bark and other surface layers at the incision site.... The top is cut perpendicular to the direction of growth of the branch from which the cutting is cut, the bottom is cut obliquely, at an average angle of 55 degrees. Cutting is performed on the middle of the branch. If transportation of cuttings is required, then they are wrapped in a damp cloth and placed in a plastic bag.
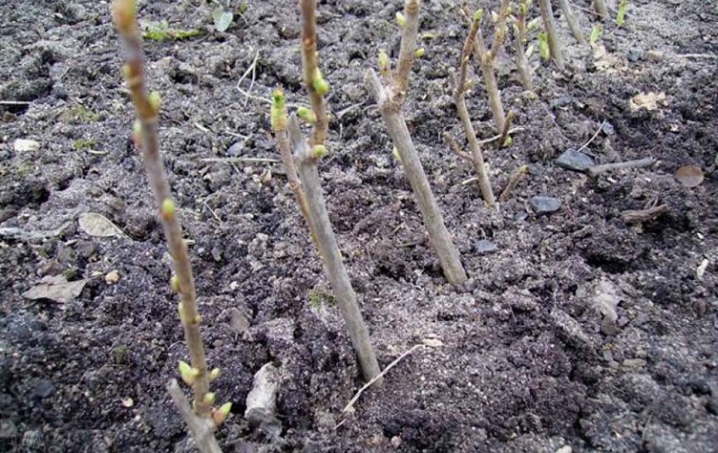

Rooting
If everything is done correctly, then the currant shoot will take root in three weeks. If this did not happen a month later, and no signs of adventitious roots are visible, then the escape in a jar of water did not take root and died. The water in the bank must be gradually replaced, preventing the formation of duckweed from algae. Do not place the container in a place where the sun's rays strike directly: there should be a lot of light, but it is allowed diffused. Or you can replace it with an artificial one - from LEDs of warm colors (but not a red-orange tint).
Rooting in a pot is possible only if the following conditions are met.
- Cuttings 6-7 buds long are stuck into a mixture of peat and black soil so that so that at the top, above the boundary between the land and air, there are only 2-3.
- Poor soil such as clay cannot be used... The soil must be chernozem, and peat and sod are added in order to facilitate it. It is difficult for the embryonic roots to overcome the layer of compressed earth. If you do not mix the soil with turf and peat, then the cuttings will not germinate, but will die.
- Be sure to add sand or vermiculite to the bottom of the jar with holes. The soil layer in the pot must be "breathing" - the roots breathe, since they will die without air at all.
- Treat the cut sites with garden varnish, wax or paraffin... This will prevent moisture loss and decay, turning the shoot into dust.
When everything is done correctly: the cuttings germinate in greenhouse (+ 5 ... +20) conditions, with regular watering, the upper buds will bloom. Avoid blooming and fruiting - the nutrients from the cuttings will focus on the growth of its roots.


Landing
In the spring, in moderately warm weather, rooted cuttings are planted in their permanent place. In order not to transplant them several times, prepare a place on the site in advance by digging up the ground and selecting extraneous wild-growing roots from it. It is allowed to plant currant bushes near fruit trees - so to speak, "cultivated" symbiosis, however, all other crops, for example garden crops, are recommended to be planted away from currants so that they do not fight for nutrients among themselves.
The place must be partially shaded - for the southern regions, in which the summer heat and the temperature in the sun above 40 degrees will burn out the bushes. For the "middle lane", the place where the currants grow should be completely sunny - in most cases there is no such heat there.

Care
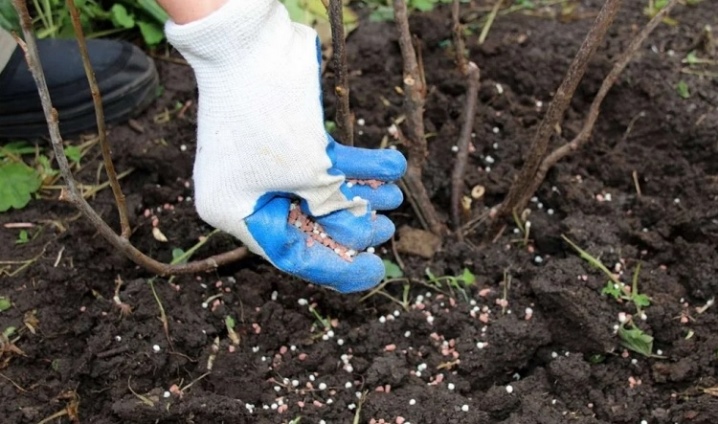
Growing currants, like any other berry crop, is possible only with timely care... The slightest weeds that interfere with cultivation must be destroyed at the root. The cut weeds can be laid under the bush - they will dry out and turn into a sod litter, which will prevent moisture loss even in the heat, after evening or early morning watering of the bushes, and also delay the growth of new weed shoots, depriving the soil of light. Top dressing can consist in adding rotted manure (compost of three years of overexposure), rotting turf during the winter and during the rainy season, applying potash fertilizers once or twice a year (for example, in April and June).
In the southern regions, currants ripen around mid-July. In the spring, in March or April, the first loosening of actively growing bushes is performed. Heavy, finely structured soil - in fact, it is clay with humus - dilute with sand in a 1: 1 ratio.
"Sanding" of heavy soil during digging is carried out once - one and a half bayonets of the shovel deep into the depths.














The comment was sent successfully.