Nuances of planting red currants in autumn

There are over 150 types of currants in different colors, sizes and flavors. For all shrubs, autumn planting is the most suitable. The article will focus on red currant varieties, the nuances of their planting and further care.


Timing
Many gardeners prefer autumn planting of red currant seedlings for various reasons.
- Summer residents in the fall, after the harvest, are already less busy than in the spring, during the general planting period.
- Nurseries offer a large amount of planting material for autumn planting.
- In autumn, the bushes are transplanted after the growing season, when the plant does not need to spend energy on the development of buds, leaves, and it can give all its strength to rooting and adaptation to new conditions. Therefore, in seedlings of autumn planting, the root system develops faster, the crown is actively growing. During the winter, the bushes will have time to take root in a new place, and in the spring they will begin to release buds, like all perennial plants.
- Having survived the winter, red currants become stronger, frost-resistant and can resist not only cold, but also diseases.
- The melting of snow in the spring becomes good watering for the bushes planted in autumn, with which top dressing, laid before the onset of winter cold, gets into the soil.


The downside of the autumn planting can be the death of the plant due to the wrong actions of the gardener. Before planting seedlings, you need to study the weather conditions. The ideal time for rooting is the period when the growing season is over, leaves have fallen on the bushes, but at least 3-4 weeks before the first frost. This period is enough for the bushes to take root and take root. In places with an unstable and frosty climate in winter, the bushes can be covered with spruce branches or agrotextiles.
It is possible to specify the timing of planting only taking into account the climatic conditions of different regions:
- in central Russia, the Moscow region, they are planting bushes and trees in late September and early October;
- in the northern regions, they are trying to complete planting work before the last days of September;
- in the south of the country, the best months for plant transplantation are October and November.


Sapling selection
To harvest a large harvest of red currants, it will be correct to grow varieties of different ripening periods: early, middle and late. Then fresh berries can be enjoyed for a long time. Up to 17 kg of berries are harvested from one bush of adult currants - provided that seedlings of zoned varieties were used, that is, those species that are most suitable for a specific climatic region.
In autumn, red currants can be planted with cuttings, seedlings and the method of dividing the bush. Any planting material must be carefully examined and sorted out so that diseased and non-viable plants do not get into the soil.

Cuttings
When preparing the planting material, cuttings are pruned on an adult healthy bush. To do this, cut off a twig, remove the upper and lower parts, leaving the middle about 30 cm long. There should be 3-4 buds on the handle. Make sure they are strong, pronounced. A distance of about 15 cm remains from the lower bud to the end of the cutting. The cuts are made in late August or early September (depending on the region). You can immediately transplant the cuttings into the ground, or you can temporarily plant them in pots and wait two weeks before the root system regrowth. Then transplant them into the soil a month before the first frost.
With cuttings grown in greenhouse conditions, before sending them into the ground, a hardening procedure should be carried out, that is, the currants should be taken out in pots every day for several hours outside. In this way, the plants are acclimatized.
The advantages of planting red currants with cuttings are the abundance of material and its survival rate up to 90%.
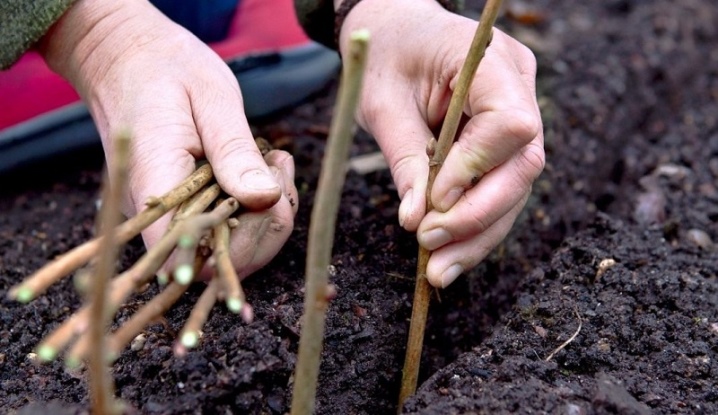

Saplings
For autumn planting, 1–2-year-old seedlings are used (two-year-old will be stronger). The planting material must have a developed root system, that is, at least 3 skeletal roots 15–20 cm long and many small fibrous roots. Yellow, and in the context of the white color of the material indicates a healthy root system, brown shades are found in frozen or diseased currants. If seedlings are purchased in pots, they should be removed and the roots inspected before purchasing. A plant with an earthen lump, densely braided by roots, will take root quickly and will not freeze in winter.
The seedling should contain 3-5 healthy shoots up to 40 cm long, with smooth, uniform bark and well-defined mature buds. You should not take too tall bushes with twigs that did not have time to stiffen, such a plant may not survive the frosty winter. When buying, you need to pay attention to whether the roots of the plants are overdried. It is best to keep them wrapped in a damp cloth until planting. If the seedlings are purchased in pots, they will need to acclimatize for 3-5 days (as described above).

Split bush
Sometimes gardeners in late autumn, when the growing season ends, transplant the bushes to a new place. Having dug up the currants, you can divide it into several bushes, thus obtaining ready-made material with a developed root system.
Such bushes take root quickly and well, since they are outside the ground for a short time. If they are transplanted to the same area on which they grew, they will not have to get used to a different type of soil.


Where is the best place to plant?
A good harvest can only be expected if the plant is planted in a place that is comfortable for it. Experts recommend following the rules below when planting seedlings in open ground.
- Red currants love warmth and light; they must be planted in an unshaded space.
- The bushes are afraid of drafts, it is not bad if at some distance from them there is a fence or a wall of a building that impedes the revelry of the wind.
- Currants do not tolerate moisture oversaturation. It should be planted in an area with groundwater occurrence from one and a half meters and deeper. For the same reason, you should not plant bushes in the lowlands, where precipitation or melted snow will flow.
- Most often, all currants are planted along the garden paths, along the fence, moving away from them by one and a half meters so as not to fall into the shade.
- The plant prefers light fertile soils with neutral acidity. Grows well on black soil, loamy and sandy loam soils. Poorly tolerates heavy clay or excessively sandy soil.
- Do not plant red currants in the vicinity of any plants of the gooseberry family. They have the same pests and diseases that they will share.
Currants feel bad next to trees that have a powerful root system and thick shade, as well as next to creeping shrubs (such as raspberries and blackberries).

Preparation
Preparation for planting should begin 3-4 weeks before the planned action. If cuttings are planted with preliminary growth of roots, they will need 2-3 weeks for their regrowth. The planting pit needs about a month to sit down naturally.
Planting pit preparation
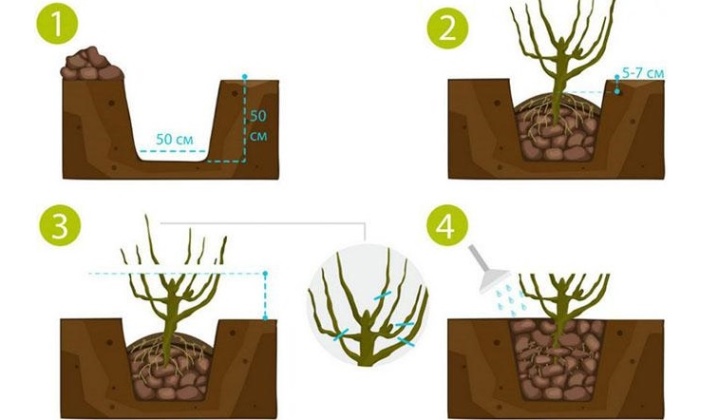
When a place for currant bushes has been chosen, it should be cleared and holes dug according to the number of intended seedlings (40 cm deep and 60 cm wide). The deepening should be twice the size of the plant's root system, as it will be filled with fertilizer and crumble from time to time in anticipation of planting.
At the bottom of the dug holes, a fertile layer 10 cm thick is poured. Then fertilizers are applied.
- Double superphosphate (2 tablespoons in each recess), carbamide, potassium sulfate. Potassium is preferred by red currants over phosphorus.
- A mixture of slurry and ash (1: 2), pouring water over.
Top dressing is thoroughly mixed, covered with fertile soil on top, so as not to "burn" the roots with concentrated fertilizer, then watered with water and allowed to brew for about a month.


Plant preparation
Seedlings with a closed root system are transplanted with an earthen clod. Before planting, they should only be slightly stirred. The open roots the day before planting are soaked in any stimulating preparations ("Zircon", "Kornevin"). And half an hour before planting, they are dipped in a manganese solution to disinfect.
Technology
A little fertile soil is poured into the wells prepared and fed in advance and poured over a bucket of water. Then they wait until the moisture is completely absorbed, and proceed to the autumn planting. Plants with a closed root system, transplanted with a clod of earth, take root better and develop faster. If you plant a bush with open roots, you should place it in the center of the hole and carefully distribute the roots in a circle.
A seedling or stalk should have 6–8 buds. When planting, the lower half of the buds are covered with earth, in the future they will give growth. The upper half remains above the surface of the ground and will turn into bush branches. To make the development of the lower buds more active, the seedling is added dropwise at an angle of 45 degrees. The established plant is sprinkled with soil and lightly tamped, this helps to remove air voids and allows the roots to contact the nutrient soil. Having planted a bush, a small earthen side is made around it, which will not allow moisture to spread, but will redirect it to the roots.
After planting, each seedling is watered with water and sprinkled with dry earth, not allowing the wet soil to gradually dry out and crack.
Follow-up care
If we want to wait for a high harvest, we cannot plant a plant and forget about it. After transplanting, the seedlings require periodic maintenance, it will consist in the steps described below.
- Watering. Immediately after planting the bushes, 3 buckets of water should be poured under each of them. If the autumn is warm and not rainy, the seedlings should be watered every 4–5 days until they take root.
- Mulching. It is necessary to retain moisture, and also protects the plant from freezing during the winter period. Peat, compost, humus are chosen as mulch for red currants, covering the ground under a bush 10 cm thick. The procedure is carried out after watering and drying out the soil.
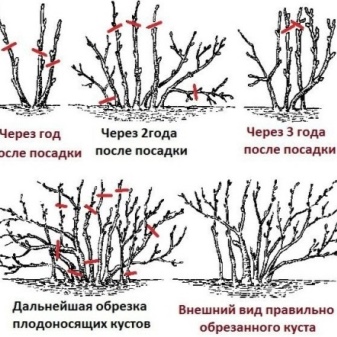
- Pruning. Autumn pruning of bushes is necessary to strengthen the roots. To redirect the forces of the plant to the underground part, the branches are cut, leaving 3-4 buds on each of them. It turns out a small neat seedling, which, if necessary, can be easily covered to protect it from frost.














The comment was sent successfully.