All about black currant

It is extremely important to know everything about black currant for any summer residents and gardeners. It is useful to understand for general development with the life form and family of this plant. But for practical purposes, it is much more important to find out where the bush grows, familiarize yourself with the description of the fruits, with the characteristics of the leaves and root system, with other basic nuances.

Description
It is difficult to find people who have never heard of black currant. Nevertheless, knowledge about it is rather scarce. Therefore, it is worth starting with a basic botanical description. This is a representative of the class of dicotyledonous plants. It belongs to the order of saxifrage, and within this order to the family of gooseberry plants.
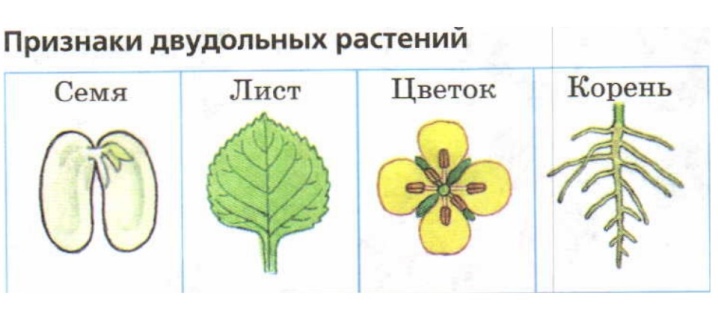
There are no other genera in this family.
Within the framework of the botanical order, the "relatives" of black currant are:
-
Kalanchoe;
-
rhodiola;
-
wolf leaf;
-
urut;
-
pion;
-
astilba;
-
saxifrage;
-
tetracarpea.




The life form of black currant is a deciduous shrub. The usual plant height is from 1 to 2 m. At the very beginning of vegetative development, the shoots are fluffy and have a pale color. Strengthening, they turn brown. Black currant leaves usually reach 3-5 cm in length and width, and the largest specimens can reach up to 12 cm.
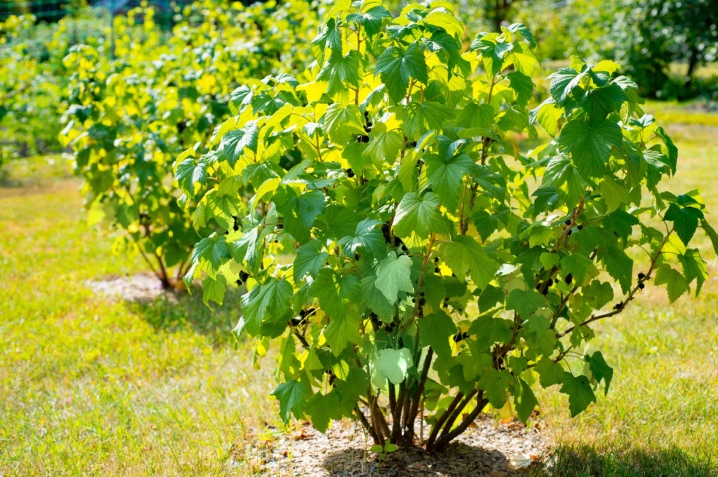

Speaking of foliage characteristics, it is also worth noting:
-
jagged edges;
-
the presence of 3 or 5 blades;
-
veins containing golden glands;
-
blades in a wide triangle format most often;
-
dark green color;
-
almost complete absence of "cannon" (observed only from below on the veins).

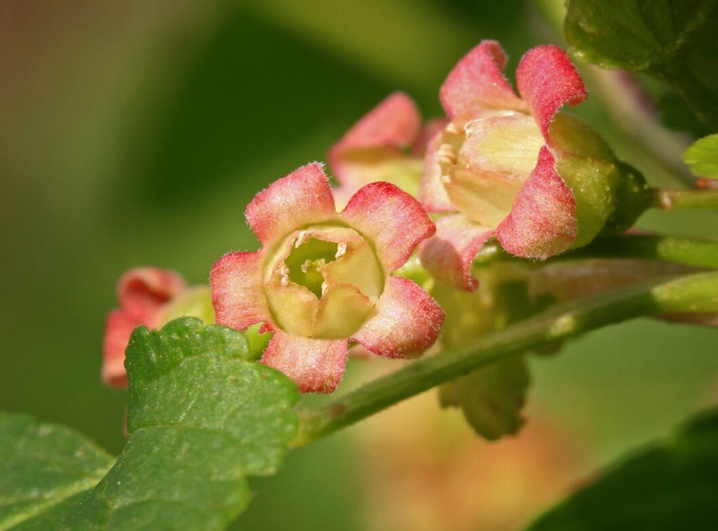
Blackcurrant inflorescences look like drooping brushes. Their length reaches 8 cm, although in most cases it is limited to 3-5 cm. From 5 to 10 flowers are distinguished in each inflorescence. Both naked and downy pedicels are characteristic. The flowers themselves, with a length of 7-9 mm, reach a section of 4-6 mm; the petals are oval.

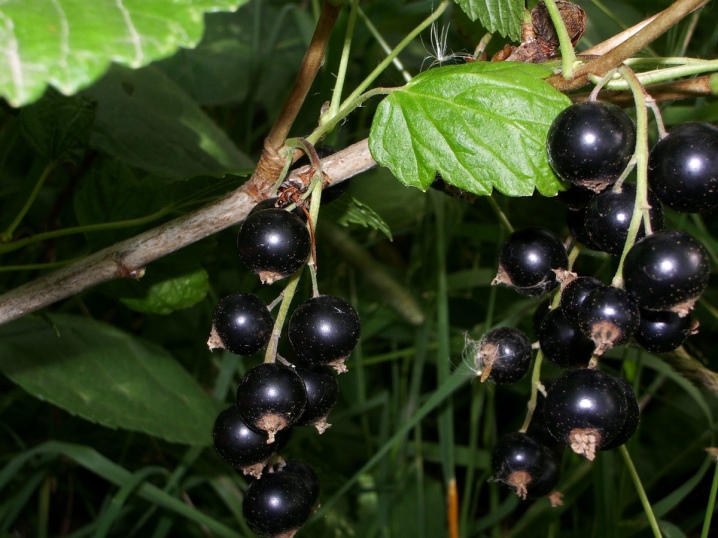
The fruits of black currant are fragrant glossy berries. Their average diameter does not exceed 1 cm. The berry may contain from 3 to 37 seeds, which are extremely light. There are approximately 3300 fruits per 1 kg.

Black currant blooms in May and in the first third of summer; harvesting usually occurs in July.
Buds on the lower branches, taking in heat from the ground, begin to grow almost as soon as the snow melts. On average, black currant yields up to 300 kg of berries per hectare. Under the most ideal conditions, this figure can reach 1850 kg. The taste of the fruits obtained is very varied. It covers the whole gamut from sweet to sour sensation, and the specific impression depends on the variety, on the growing conditions, on the shelf life of the crop.
Ripe berries will quickly crumble. Foliage falls very late. In many cases, the bushes are green until the onset of cold weather. This species is characterized by the next leaf arrangement. Its root system is of the surface type.
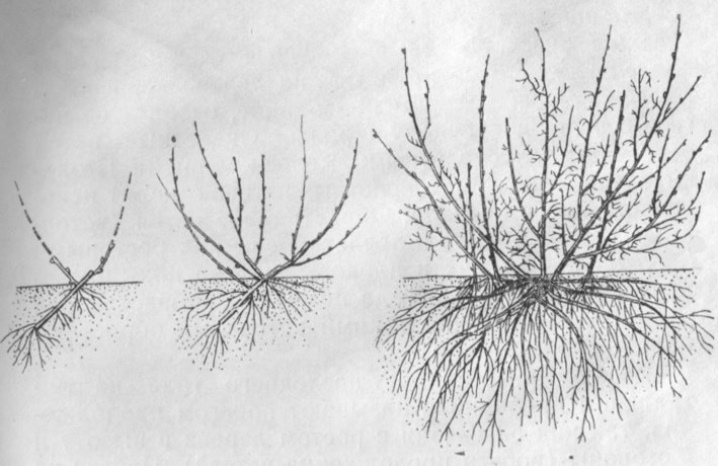
Fibrous currant roots go to a depth of 50 cm. Because of this, active regular watering is required. In the wild, black currants have populated almost all of Eurasia. It is found from the shores of the Atlantic Ocean, up to the basins of the Yenisei and Baikal. And also its area covers the territory of Kazakhstan, Mongolia and the PRC; introduced shoots are found in North America.
Mostly currant bushes are found:
-
on the banks of rivers and lakes;
-
in moist deciduous, coniferous or mixed forest;
-
along the swamps;
-
in a wet floodplain meadow (both single plants and small groups can be seen everywhere in these places).


Varieties
The variety of cultivated subtypes of black currant is so great that all interested farmers can choose them. The difference may relate to taste and aroma properties, the ability to adapt to environmental conditions. It is worth considering the ripening time. Black currant "Pearl" is popular. It is suitable for all climatic zones.
This variety is characterized by a solid size. Their weight ranges from 4.4 to 8.4 g. The plant belongs to the mid-season group. The greenish pulp is more like jelly in shape. It is sugary and has a mild sour note that gives the crop a spice.

The Mavladi currant is most effectively grown in the Moscow region. it self-pollinated a variety that is not particularly whimsical. He endures disease with great strength. The plant produces large (up to 5.2 g) fruits. They always note a pleasant taste.

The Morena variety is adapted to the conditions of the Urals and Siberia. This plant produces tall (up to 2 m) bushes. They ripen pretty quickly. Berries "Morena" weigh from 2.7 to 3.3 g. Dessert taste is harmonious.

Speaking about the classification according to the growing areas, we should also mention the Favorit variety. It is cultivated in the Black Earth and Non-Black Earth regions. Such a plant is less susceptible to drought and cold. The bushes grow up to 1.45-1.55 m. The yield exceeds 3 kg.

Among the ultra-early currants, the variety "Golubichka" is distinguished. This plant develops compactly and tolerates cold weather. The low probability of disease and pest damage also testifies in its favor. It got its name "Golubichka" for its characteristic bloom on sour-sweet fruits. The harvest is tender, the berry usually weighs 1.6-1.9 g.

Ultra-ripe flowering is typical for "Minx". This black currant was bred in the Tambov region. It forms compact bushes and tolerates cold weather. The berries are covered with a thin skin. The average fruit weight is 1.5 g.

Mid-season black currant varieties are also popular. Among them, there are many types containing a lot of ascorbic acid and vitamin E. The sprawling "Summer Resident" can be considered a good example of this kind. It is a short plant, not very well protected from powdery mildew. Its oblong berries weigh from 2.1 to 2.4 g, are distinguished by an excellent smell and special tenderness of the sweet and sour pulp.

Moscow breeders answer “Dachnitsa” with “Sorcerer”. This is also a compact currant variety. In addition to resistance to cold weather, it is little susceptible to the effects of kidney mites and pathological fungi. The taste is ambiguous, varies widely. On average, the berries weigh 1.2-1.6 g and have a pronounced aroma.

Mid-late varieties are valued for their ability to produce fresh berries for a long time. Often such currants hang on the bushes for a long time. Spoilage is not typical for it, instead it turns out rather a natural analogue of raisins.
The mid-late group includes such a Moscow variety as "Barmaley". Its spreading bushes are low.
Winter "Barmaleem" is well tolerated. The likelihood of damage from pests and diseases is also low. The brushes contain a large number of berries and stretch quite far. The taste is formed by a sweet-sour combination. The result of the tasting examination is 4.5 points. The berries are moderately large.

Mid-late currant "Rusalka" was created by the Ural developers... Its bushes are quite tall. The likelihood of being affected by powdery mildew is low. Damage to the kidneys by the mite is almost impossible. The taste is multifaceted, but mainly refers to the dessert group.

It is important to pay attention to the regional specifics. The experience of growing black currants has long made it possible to determine the optimal varieties for each area. So, for the north-west (Leningrad region, Karelia), the well-known Veloy, which has been known since the 1980s, can be considered a good choice. It firmly resists droughts and anthracnose, cold weather and powdery mildew. Even fungal rust and viral terry are not scary to him, and the harvest ripens amicably; however, overripe fruits in damp weather often burst.

"Nezhdanchik", on the contrary, is a product of the latest selection. It was entered into the State Register only in 2019. It is a medium-late maturing plant with thick, spreading stems. Cold resistance of "Nezhdanchik" is decent, but disease and insect damage is quite probable. The miniature size of the berries is offset by their sweetness.

In the Moscow region and other areas of the middle lane, any winter-hardy black currant can be successfully grown. The Litvinovskaya variety has proven itself very well. This is an early maturing plant that is immune to fungal and parasitic infections. The fruits are not just sweet, they also have a refreshing effect. Their mass ranges from 1.9 to 3.3 g.

Self-fertile "Sevchanka" can compete with this variety. Such early ripening currants are resistant to dry periods. Her flowers are almost not beaten by frost. It is also important to emphasize the resistance to rust, anthracnose and powdery mildew. Sevchanka's brushes are long, and the berries weigh from 2 to 3.5 g; even in an overripe condition, they do not fall off.

In the Urals and in the Volga-Vyatka region, characterized by a moderate continental climate, "Dar Smolyaninova" is considered a good option - it is appreciated for its ultra-early maturity... The plant also resists frost well, which is not surprising given this choice of the target area. "Gift of Smolyaninova" does not suffer from a kidney mite, but fungal infections affect it very strongly. The pulp is very sweet.

The strength of the shell guarantees long-term preservation and mechanical reliability of the fruit.
Black currant "Lazy" is highly valued for its resistance to pathogenic fungi and cold weather. This is a late-ripening variety. It forms tall, thickened stems. Spreading is typical for them, but not too pronounced. The varied taste of the fruit is rated from 4.6 to 5 points.

Landing features
Choice of time and place
For some reason, the opinion is widespread that such a shrub as black currant grows everywhere and always, even under minimally favorable circumstances. However, this is nothing more than a delusion. More precisely, the seedling can take root everywhere, but you should not count on effective fruiting. The optimal planting time is from late September to mid-October.
It is very important that the seedlings are able to live for 3 or 4 weeks in normal conditions before the frost sets in.
Until spring comes, the soil around the roots will become denser. Therefore, they will receive food and winter calmly. Planting in the spring is much more troublesome. This solution is only suitable for places where the snow cover is not too thick and there is a high risk of freezing the roots. At the time of planting, the layer of melted soil should be about 20 cm.
With high acidity, the soil will have to be limed. In general, currant bushes develop better on productive black soil. But you can use, along with it, sandy loam and medium loam. It is unacceptable to choose places where water stagnates. Perfectly leveled plots are best, and crop can also be placed on top of the slopes.

Soil and pit preparation
Too acidic soil is desirable to lime. At the same time, it is impossible to get too carried away with the introduction of lime, since it can be harmful. Sandy loam is improved with organic additives. Organic matter must also be added to the loam, but then mineral components are also needed.
You don't have to dig the earth... Then local domestication is carried out. It involves digging wide planting holes. They are saturated with fertile soil mixed with humus. 0.2 kg of crushed limestone is placed in each hole.

Selection of seedlings
You definitely need to give preference to zoned varieties.... They are ideally adapted to the conditions of the specific area. The choice of first-class planting material is no less important. They can be both one-year and two-year-old seedlings.
There should be no foliage on them, but the strength of the plant is definitely needed.
Be sure to check if there are any pathologies. It is worth looking at the condition of the roots. In healthy seedlings, they are thoroughly developed and shaped like a fibrous type. And also there should be 3 or 4 skeletal roots, the length of which reaches 15-20 cm.

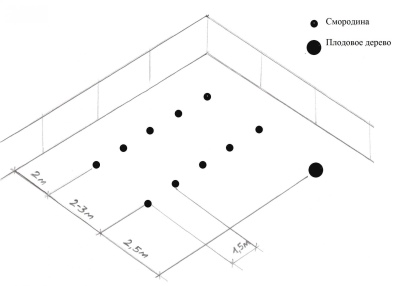
Landing scheme
A gap of 2 m is left between the pits.Their cross-section should be about 60 cm.The depth is about 50 cm. It is necessary to choose a well-lit area. The pits are prepared about 12-16 days before the procedure, so that the soil settles and the chlorine that got along with the manure evaporates.
The bottom of each pit is sprinkled with humus. A slide formed from it is filled with a 1/3 hole. After adding a glass of wood ash there, all this is mixed. Mineral fertilizers are covered with fertile soil in advance so that the roots are not burnt. The roots themselves are straightened neatly. Saplings are introduced not along a strict vertical, but at an angle of 45 degrees.
It is also important:
-
place the root collar 6 cm below the edge of the notch;
-
add earth, filling in the gaps between the roots;
-
compact the soil;
-
water the currant seedling using 5 liters of water;
-
fill the hole to the end;
-
form a hole;
-
water the plant abundantly;
-
cut it above the 5th bud with a pruner.

Care
Watering
This is one of the most important conditions, without which the currant does not give a decent harvest. Without generous active watering, at least some kind of berry picking is out of the question. Irrigation should be especially intense when the bush is in bloom and when the berries are ripe. Grooves about 20 cm deep are made near the plants; each instance is watered using 20-30 liters of water. To weaken the evaporation of water, you will need to use mulch, which also protects from too much heating of the roots.

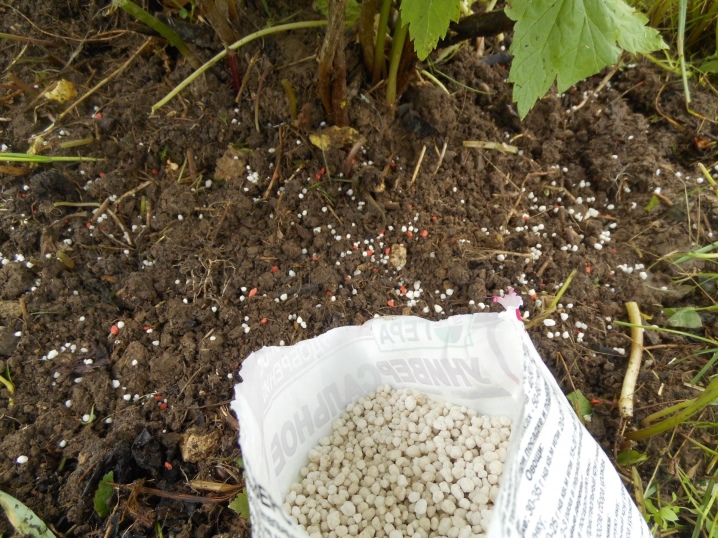
Top dressing
Nitrogen is required during the spring and summer months. For the first time, nitrogen fertilizers are applied when the buds are just beginning to bloom. The best option is to add urea. After the end of flowering, another nitrogenous fertilizer is used, already of a complex composition. Along with branded products, it is recommended to use organic infusions, such as bird droppings or cow dung.
When berries are poured violently, potassium and phosphorus must be added. Nitrogen additions are minimal. At this point, it is best to use urea. When the last harvest is taken, it is time to apply organic matter. In the summer, a combination of small amounts of copper sulfate, permanganate and boric acid is introduced along the leaf; all this is bred in a bucket of water.

Pruning
Branches on large-fruited blackcurrant bushes age quickly. The bush has to rejuvenate already in the 4th year. Too old shoots can be easily distinguished by their black color and almost complete lack of yield. Normally, only brown branches should remain.
The less intensive the growth, the more radical it is necessary to cut the shoots.
On young bushes, 2-3 even, strongest shoots of the first year are left. Everything that is weak and thickens the bush is sent to compost pits. In case of damage with a glass or a kidney mite, the currants are cut to the ground level. This will allow the bush to renew itself by releasing new healthy shoots. True, you will have to wait for the next growing season.

Reproduction
Cuttings
Using green cuttings is easiest. However, it must be understood that this method is ineffective and threatens with the transmission of pathogens from the original bush.... In addition, reducing the crown of the currant can reduce the yield. However, at the same time, the planting material will take root before the beginning of winter. With the right approach, the loss of cuttings will be minimized.

Layers
Horizontal layering is used from a plant that is 3, 4 or 5 years old. Under it, in the early spring, they loosen and fertilize the soil. Then, furrows are dug along the perimeter in the direction from the bush.Branches 1-2 years old are placed there. The tops should be pinched off so that all the buds on the shoots germinate more actively and form a solid one-year growth.
After the buds swell, the shoots are sprinkled with earth. Only the tops should remain on the surface. After a while, vertical layers will appear. You can fill them with moist, loose earth when a height of 10-15 cm is reached.

After 2-3 weeks, hilling is repeated, fertilized and loosened all summer, and in the fall they are cut off with a pruner and divided into parts.
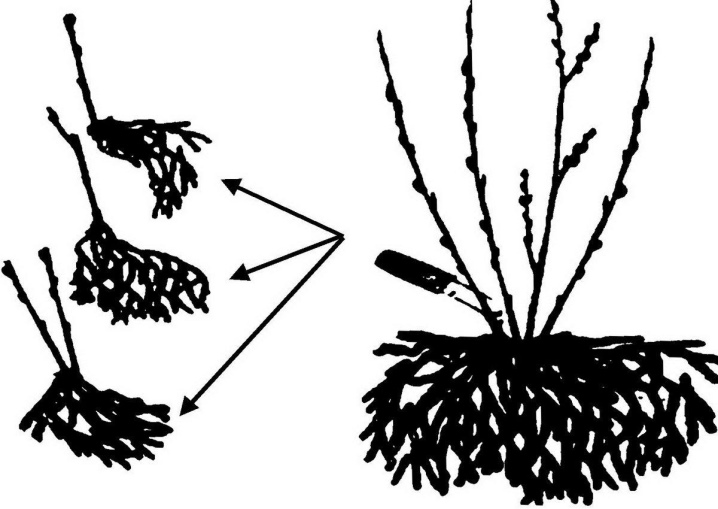
By dividing the bush
This procedure is carried out in spring or autumn.... It is usually combined with transplanting the plant to a new location. The bushes must be dug along with the root system, carefully freeing it from the soil. Each bush can be cut into 3 or 4 pieces using an ax and a garden saw. Harvest after transplanting parts to a new place can only be expected in a year, when the roots are restored; layering and cuttings allow you to count on faster fruiting.
Diseases and pests
Fungal pathologies mainly develop during heavy rains and low temperatures. Virals are found in almost any weather and are harder to cure. Among the fungal hazards, a particular risk is associated with:
-
anthracnose;
-
rust;
-
powdery mildew;
-
septoria.




Of the viruses, the pathogens of terry and striped mosaic pose the greatest threat. The first ailment threatens with complete sterility of the bushes, the second destroys them altogether. Both infections are incurable. Sick bushes are uprooted and burned.
Prevention of lesions:
-
selection of healthy planting material;
-
systematic inspection of the bushes;
-
proactive processing;
-
regular insect control;
-
collection and burning of fallen leaves;
-
timely, but not excessive, complementary feeding with minerals.



More than 70 species of insects can parasitize on black currants. Gall midges, spider mites, shoot aphids and scale insects are especially dangerous. Bordeaux mixture helps with gall midges. The preparation Fitoverm is capable of eliminating the spider mite; processing is especially relevant on hot dry days... From the shoot aphid use "Karbofos" and "Actellic", and from the shields - "Nitrafen".
















The comment was sent successfully.