All about powdery mildew on currants
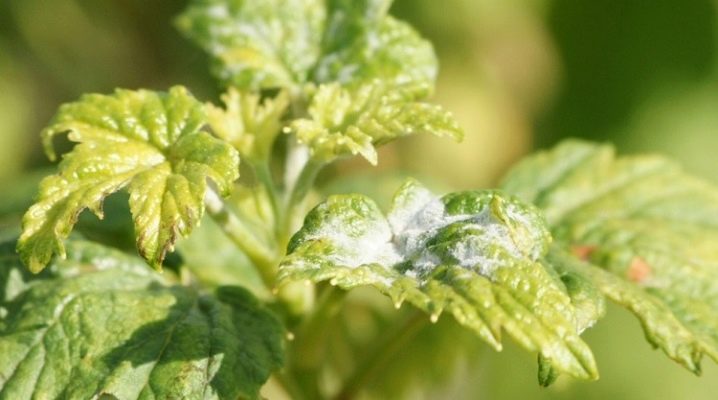

Along with anthracnose and mosaic, powdery mildew is one of the most common currant diseases. The disease is dangerous, capable of destroying 80% of blackcurrant plantings in 1 year. Even experienced gardeners should know everything about powdery mildew on currants in order to protect plants and crops.


general description
Powdery mildew can appear on any type of currant: black, red, golden, white. Although it is especially dangerous for the black one. The disease looks like flour, ash, or frost. Whitish spots appear first on the leaves and shoots, then on the petioles and fruits. At the beginning of the disease, the plaque is very light, as it develops, it becomes more and more "greasy": it turns into a dense gray-brownish crust. Leaves with such spots dry, curl into a tube and fall off, the berries turn gray and rot.
The causes of powdery mildew are parasitic fungi from the genus of true powdery mildew fungi. This is a whole family, in which there are 700 species of fungi, and all of them infect the outer parts of flowering plants. The characteristic white bloom on the affected leaves, petioles or flowers is the mycelium, the body of the fungus. With the help of special devices, the mushroom is fixed on the tissue of the plant - this is its only food. Ripe fungus spores are transparent dew-like droplets. The incubation period is 3-10 days. Mushrooms love warmth, develop most rapidly at temperatures of + 18 ... 25 ° C, prefer high humidity. Spores are carried mainly by the wind, wake up in April-May, but will manifest themselves as soon as it gets warm.
Signs that a plant is sick can be quickly spotted by regularly examining the bottom of the bushes, ovaries and young leaves. The first whitish spots with transparent droplets will be noticeable where it is damp, dark, or the shoots are young and cannot resist disease well enough.


How can the bushes be processed?
Already affected bushes should be sprayed with antifungal drugs (fungicides). All affected parts of the plant should be removed and burned. Drugs can be of two types: chemical and biological. Chemicals are toxins, and biofungicides can remove like like. They contain cultures of bacteria or parasites that are safe for the plant, but infect the pathogen of powdery mildew. The most famous representative of this category of drugs - "Fitosporin", it contains a culture of Bacillus subtilis, or hay bacillus, soil bacteria, completely safe for humans.
Chemicals have a very different composition. The drug "Hom" is copper oxychloride, it combines well with other fungicides and has a wide range of antibacterial and antifungal effects, fights late blight, anthracnose and other ailments. And "Topaz" (active ingredient - penconazole) was developed specifically to combat powdery mildew, but on different crops. What drug to fight - choose according to circumstances and opportunities.
Biofungicides are safer, they can be used during the ripening of berries, but they have a short duration of action, they are quickly washed off during rains. Treatments have to be carried out more often than by chemical means. Sometimes only combined treatments will help get rid of powdery mildew.


Chemicals
The choice of drugs on the modern market is extensive, it is not easy to choose the best remedy.
- "Topaz". It is a systemic fungicide.Systemic drugs even act on those parts of the pest with which they do not come into contact (as opposed to contact ones). And he is also highly selective, that is, extremely selective. Acts pointwise, on a specific pathogen. Designed for the treatment of a wide variety of garden crops affected by powdery mildew. Works even in conditions favorable for the development of powdery mildew (heat). The number of treatments per season is 2-3 times.
- "Tiovit Jet" - contact fungicide and acaricide (acts against ticks). The active substance is sulfur. The number of currant treatments is from 1 to 3.
- Topsin-M. The active substance is the contact-systemic pesticide thiophanate-methyl. The action is universal. Effective against powdery mildew and dozens of other popular bacterial and fungal diseases, it also has acaricidal and insecticidal effects. No more than 2 treatments in 1 season.
- Greenbelt "Forecast" - contact fungicide against powdery mildew, rust, scab. The active ingredient is the pesticide propiconazole. During the season, currants need to be processed 2-3 times with an interval of at least 2 weeks.
- "Speed" - contact systemic fungicide based on difenoconazole. It works against dozens of diseases, works during rain and wind, stimulates immunity and plant growth, seeds are often treated with the drug. 2 hours after spraying, it penetrates into plant tissues and blocks the growth of pathogens. The number of treatments per season is no more than 4. Good for controlling powdery mildew before the stage of sporulation.
- Fundazol. Contact systemic fungicide. The active ingredient is benomyl, which acts on the reproductive system of fungi. And also suppresses the reproduction of mites. Quite toxic, belongs to hazard class 2 (most of those already mentioned - to 3). The number of treatments is 3 times.
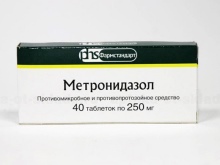
- "Metronidazole" or "Trichopol". The drug is intended for people, but it successfully suppresses the activity of bacteria in the garden. The tablets are dissolved in water (2 tablets per 1 liter), the affected plants are sprayed. According to reviews, the remedy is effective for treating the initial signs of the disease. No more than 4 treatments are carried out per season. Important: the method is not described in the scientific literature.
- Previkur. Systemic fungicide to combat root rot, downy mildew (downy mildew), late blight and a number of other diseases caused by oomycetes. Composition: carbamides and organophosphates. Allowed up to 5 treatments per season.


To increase the effectiveness of the preparations, you can use "Rapsolan" based on rapeseed oil. It is compatible with most fertilizers and pesticides, except for strongly acidic, strongly alkaline and based on copper, sulfur and boron. This eco-friendly solution improves the quality of spraying, especially if the plants are dusty, dirty, dense, and protects from insects - as a result, fewer treatments per season are required.
All fungicides are used strictly no more than a certain number of times per season, intermittently, not during fruiting. It is advisable not to get carried away with one remedy, the pathogens develop a habit. With regular use of one drug, the resistance of the fungus to it can increase 10 times.
And you should also carefully select a fungicide. "Fundazol" will not help against downy mildew, "Previkur" is intended to fight against oomycetes (they look like fungi, but do not belong to the kingdom of fungi).


Biological preparations
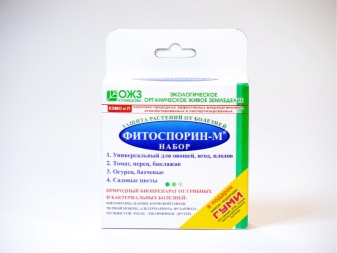
The most popular drug in this group is Fitosporin-M. Its composition is a culture of bacteria Bacillus subtilis + potassium humate and trace elements. It is not only a fungicide, but also an immunomodulator, stimulant, enhances the protective ability of plants. Can be used at any stage of crop development, from seed to fruiting. Combines with chemicals. There are many other preparations based on the bacteria Bacillus subtilis: "Fitodoc", "Baktofit", "Alirin-B" (tablets for dissolving in water).
If you want to avoid unnecessary spraying, "Glyokladin" will do. The active ingredient is Trichoderma harzianum fungi.Fertilizer tablets. They are added to the soil, heal the soil microflora, disinfect and protect against pathogenic bacteria.

Folk ways of fighting
Many common products and fertilizers have an antiseptic effect. Proponents of all-natural methods can use different means.
- Soda ash. Soda disinfects, perfectly cleans the affected areas from the fungus, it is safe for the plant. Recipe: 10 liters of water, 10 g of liquid soap, 50 g of soda. Spray before and after flowering, avoiding the active open flower period. You can take baking soda, it is softer, so it is permissible to use 50-70 g in the same recipe.
- Mustard. Dissolve 50-70 grams in a bucket of water, spray. Tobacco mustard dust is commercially available in the form of a ready-made mixture. It will take 6-8 treatments.
- Milk whey or kefir. Lactic acid bacteria resist powdery mildew pathogens. The dairy product is diluted in cool water in a ratio of 1 to 10.
- Tansy. The near-trunk circle is sprayed with a decoction of tansy (30 g of dry raw materials per 10 liters of water, boil for 2 hours). The procedure is carried out in the spring.
- Copper sulfate (copper sulfate) - a popular remedy for treating plants from pests to bud dissolution, a source of copper, dries up, burns if used incorrectly. It is part of the famous Bordeaux mixture (copper sulfate + lime). For preventive treatment for 10 liters of water, 50-100 g of the drug will be required, for medical treatment, 300 g are diluted in 10 liters of water.
- Iodine, potassium permanganate - antiseptics, effective in the early stages. Solution options: 10 liters of Bordeaux liquid + 3 g of potassium permanganate; 10 liters of water + 50 g of potassium nitrate + 3 g of potassium permanganate; 10 liters of water + 1 ml of iodine. Spraying is repeated every 3 days. Be sure to coordinate with the fertilization schedule to avoid overfeeding.
- Boric acid is a good antiseptic. It is also a source of boron, which is especially beneficial during flowering, ovary formation and fruit growth. 1-2 grams are diluted in 10 liters of hot water, cooled, sprayed. The tool is useful and can be used when it is no longer possible to use fungicides, but it does not fight directly with the fungus. And also it is unacceptable to overdo it with fertilizers. It is best used on plants that really lack boron (small, twisted leaves with chlorosis spots, slow growth of apical shoots, weak flowering and set formation).
- Ash is not only a valuable fertilizer, is also used as a means of protection against diseases and pests. In a small amount of boiling water, 300 g of ash are diluted, cooled, filtered and diluted with water to 20 liters. Spray 2-3 times with an interval of 10 days. If the disease has just appeared, the plant can save even a simple dusting of the affected areas.
A combination of drugs will allow you to completely defeat powdery mildew. Folk remedies can successfully treat small lesions, but you should focus on the condition of your plants.


Processing tips
The most important treatments are carried out in the spring, without waiting for the powdery mildew to manifest itself.
- Scalding with boiling water. Carried out before the snow melts. The tops of the branches are quickly dipped in boiling water. Requires skill.
- Spraying branches with copper sulfate (based on 1 liter of water 1 gram). Carry out until the kidneys swell.
- Spraying with colloidal sulfur during growth (3-4 grams per 1 liter of water).
Spring replacement of the topsoil with fresh humus is very useful. In the spring, treatment with any fungicide can be carried out. In summer, it is better to treat with Fitosporin, and use fungicides only as a last resort and no later than 4 weeks before harvesting. Currant - an early plant, already in July bears fruit. During fruiting, you can make a solution based on the usual means: 1 liter of water + 1 tbsp. l. baking soda + 20 drops of brilliant green + 10 drops of iodine + potassium permanganate on the tip of a knife, stir, dilute in 5 liters of water and spray.
All treatments are carried out in the evening, in dry, calm weather. Only dry foliage can be sprayed. Carefully monitor the compatibility of drugs in order to avoid phytotoxicity - detailed information on compatibility is always on the packaging of the drug. And also nuances in processing are possible. Some drugs ("Tiovit Jet") have a gas phase, that is, they act even in those places where the spray bottle did not reach, others require careful processing of both sides of the foliage, petioles and ovaries.


Prevention measures
It is better to provide protection to currant bushes until the visible manifestations of powdery mildew. The causative agent of the disease withstands very severe frosts and heat, hibernates in the soil, fallen leaves. Therefore, the first preventive measure is a thorough autumn cleaning. All fallen leaves are burned, the soil is mulched only with fresh sawdust. Particular attention should be paid to currant bushes if the summer is humid and warm.
The disease can be provoked by:
- weeds under plants;
- exceeding the norms of nitrogen fertilizers;
- placement of landings on the leeward side;
- open access to winds from neighboring, contaminated areas;
- foliar dressing, the fungus loves spraying.
If in a particular area the plants regularly suffer from powdery mildew, the problem may be a lack of calcium and silicon in the soil. Deficiency of these macronutrients makes the cell walls fragile, making it easier for fungi to penetrate. If the currant is often and very sick, it is better to refuse from the spring nitrogenous dressings, instead of them add a mineral complex with potassium and magnesium.


Resistant varieties
There are no varieties of currant completely resistant to powdery mildew. But selection in this direction is underway. There are cultures that are not as susceptible to disease as others. The Russian varieties "Temptation" and "Kipiana" were specially bred to obtain a high complex immunity: they do not "burn" from powdery mildew, rust, and the kidney mite does not bother them too much.
Among the Russian ones, Binar, Selechenskaya-2, Ilya Muromets are just as good. The already familiar Swiss "Titania" is beyond competition, although some gardeners find it not the most delicious. The Belarusian currant crops "Memory of Vavilov", "Ceres", "Katyusha", "Klussonovskaya", "Kupalinka" have excellent immunity. It is better to select zoned varieties bred in similar climatic conditions. In "strangers" all plant indicators change for the worse.
Comprehensive measures taken in advance - and a meeting with powdery mildew on currants may not even take place. Preventive treatments, general health of the site, inspection of new planting material and purchases from reliable nurseries will help.











The comment was sent successfully.