How to propagate plums by shoots and will they bear fruit?
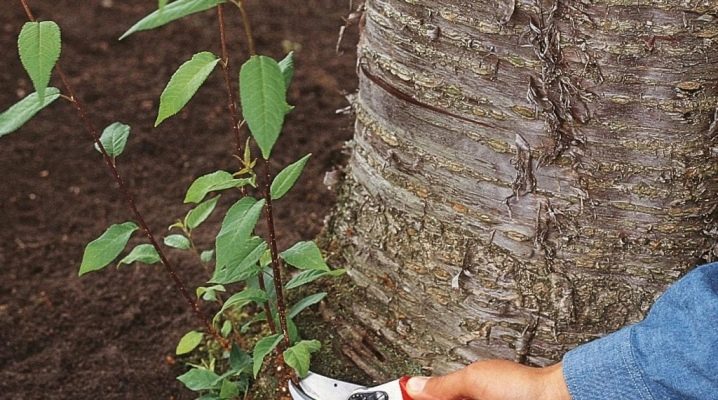

Plums are propagated by seeds, grafting, green cuttings. The option of planting root shoots seems very tempting and convenient. How to propagate a plum by a shoot, whether it will bear fruit - the answers to these questions are especially relevant for those who want to grow a rare variety or renew an old tree.
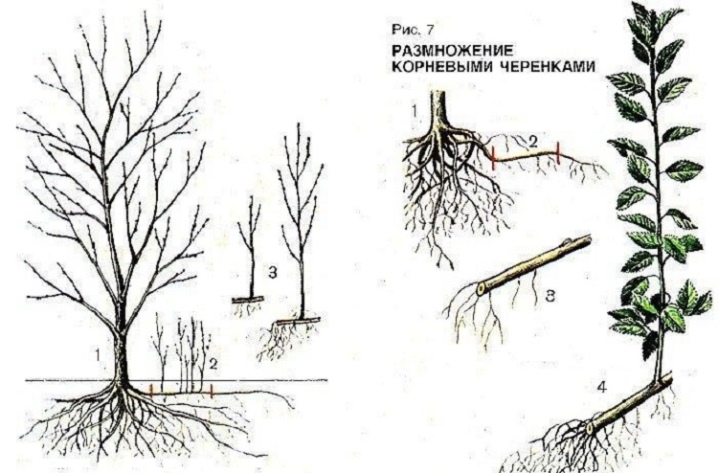
What is overgrowth?
Shoots are called shoots that form in the lower near-stem part of the plant. In plums, they can even appear quite far from the mother plant. Separating root shoots is the easiest breeding method.
The grower can get ready-made seedlings with a root system: hardy and old enough to quickly begin to bear fruit.

Plum (Prunus domestica) is a tree or shrub with a height of 1.5 to 15 meters. The birthplace of the ancestor of modern varieties is Asia Minor and the Eastern Caucasus. Over the years of breeding, cultivars have acquired increased winter hardiness. But the latter still remains relatively low, especially for tasty large-fruited varieties. Therefore, varietal plums are often grafted onto a wild plum stock.
If the variety is not grown on its own roots, the growth will be new wild plum plants.
Gardeners do not welcome the active formation of shoots in the garden, as it depletes the main plant., does not allow him to direct all his forces to the harvest. When it comes to reproduction, they try to minimize the reasons for the formation of overgrowth.

The reasons for the appearance of overgrowth should be listed.
- Fit too high. Plums are not afraid of burying the root collar. When planting grafted trees, the grafting site can be deepened by 5 cm. With bare roots, the plum will give a lot of root growth. This feature can be used by planting uterine bushes a little higher. And if the plants are needed only for harvesting, then the mother bushes should be planted lower.
- Mechanical damage to the roots or trunk. Any cut stimulates tissue growth. Most likely, new branches will start appearing in this place. If they are undesirable, the damaged areas should be well covered with garden varnish.
- Incorrect cropping. Sometimes trees need to be heavily pruned, but it is always important to maintain a balance between the upper and underground parts. If there are many roots left, but few branches, the plant compensates for this by an increased formation of shoots.
- Unsuccessful grafting or death of the stock. In some cases, the scion does not take root. In this case, the grafting site thickens, and the leaves turn yellow. New plants actively begin to grow from the roots. The same will happen if the upper varietal parts are affected by frost, disease or malnutrition.
- Overfeeding the trunk circle. This mistake is often made by novice gardeners. Fertilizers are often applied under other trees, scattering them over the soil, and then digging them up. You cannot do this with a plum. Any damaged root will sprout. The soil can only be gently loosened. But it is better to apply fertilizers in liquid form.


In addition, the grooming technique can affect the appearance of overgrowth.
Lack of watering, too dry summer, poor shelter for the winter - anything that leads to the death or poor health of the branches of the main tree will provoke the formation of overgrowth.
The plant is trying to restore its volume.
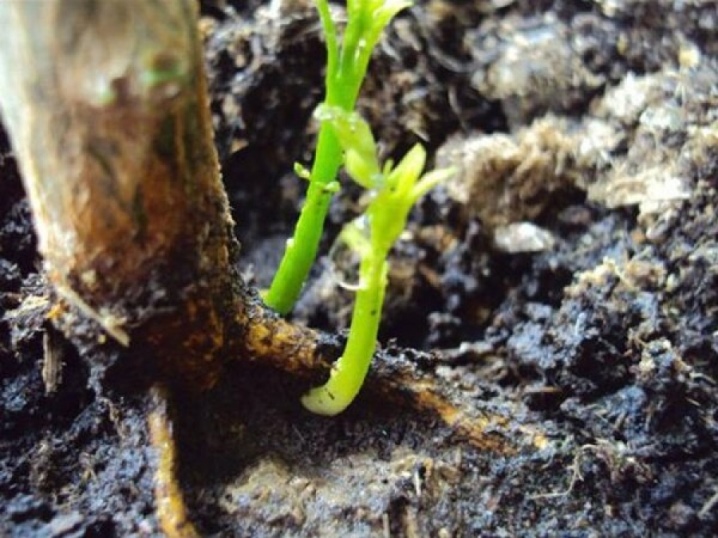

Can a tree be grown and will it bear fruit?
Viable and strong plants grow from the root of the plum. They grow well, as they are adapted to the conditions of the site on which the mother plants are planted. But gradually the gardener notices that there are no flowers or fruits.
This means that the offspring were taken from a wild plum tree. Before reproduction, you should understand what specific genetic material is taken for further cultivation. High-quality plums are rarely propagated by shoots due to the fact that their native root system does not tolerate Russian conditions. Almost all varietal specimens are grafted plants. The roots are wild plum, the ground part is varietal. To get a varietal plant from a grafted specimen, you need to take green cuttings for propagation, and not shoots.

Plants grown from wild growth are technically very convenient. They grow quickly, are strong, healthy, winter-hardy. To get good fruits from such plants, they need to be grafted with varietal plums.
The wild plum (thorn) will bear fruit in 2-3 years. The quality of the thorn fruit depends on its variety. As a rule, these are few, small and do not taste good fruits. Some types of thorns (for example, cherry thorns) are grown for aromatic and tart fruits, perfect for compotes mixed with some kind of berry. But then you need to know for sure that the propagated tree belongs to this particular species.
Saplings obtained from the sprouts of own-rooted varietal plum bear fruit depending on the variety. Some will bear fruit in the second year, others only by 8-9, when the tree grows tall enough.
If there is no information whether the plum is grafted or rooted, you need to inspect the trunk at a height of up to 50 cm. A scar will be visible on the grafted plant.
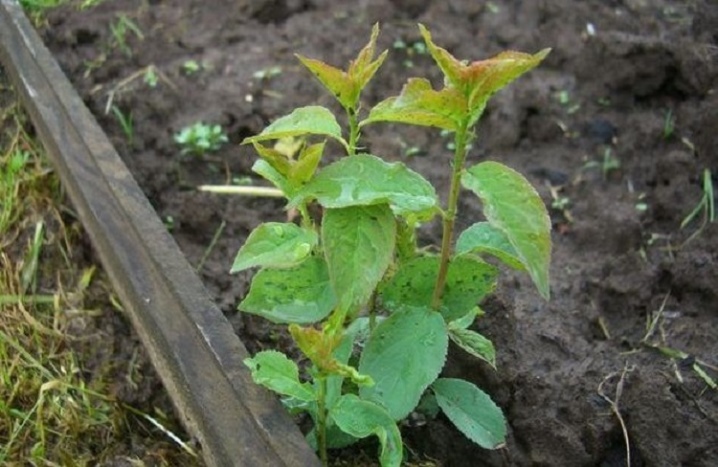

Selection of appendages
The best shoots are those that grow farthest from the tree. They are the most independent. If there are none, you can take it under the bush. But it will be more difficult for them to adapt to a new place, since they do not have an abundant number of their own small roots.
Take shoots no more than half a meter in height. The optimal age is 1 year. Two-year-old shoots usually have a weak root system, feeding on the mother tree for too long.
You should take the shoot of the plum that is the best: the healthiest, hardy, fertile, moderately rooted.
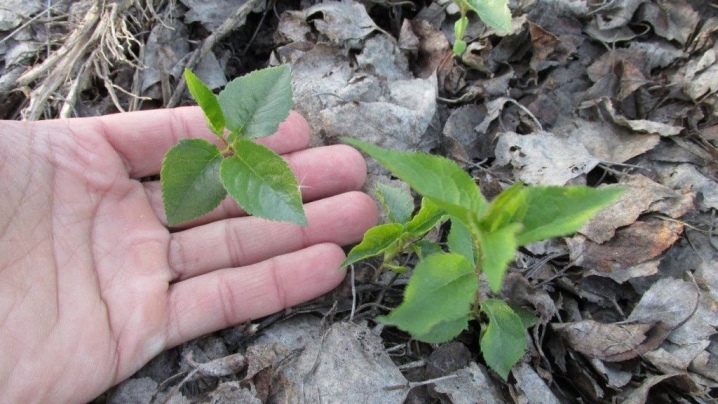

Breeding technology
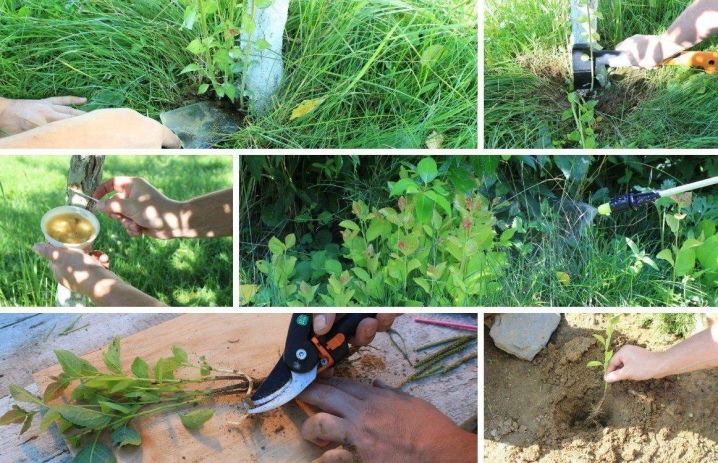
Plum can be propagated by shoots at the end of April or on the threshold of autumn. Shoots should be taken only in spring in regions where the autumn is too early cold: the Leningrad region, Siberia, the Far East. In other regions, you can pick up planting material in late August, September, early October. The exact time is determined depending on the onset of stable cold weather. The offshoot must be allocated at least two months for adaptation, then it will have time to prepare well for winter.
Spring planting is performed only before the start of sap flow.
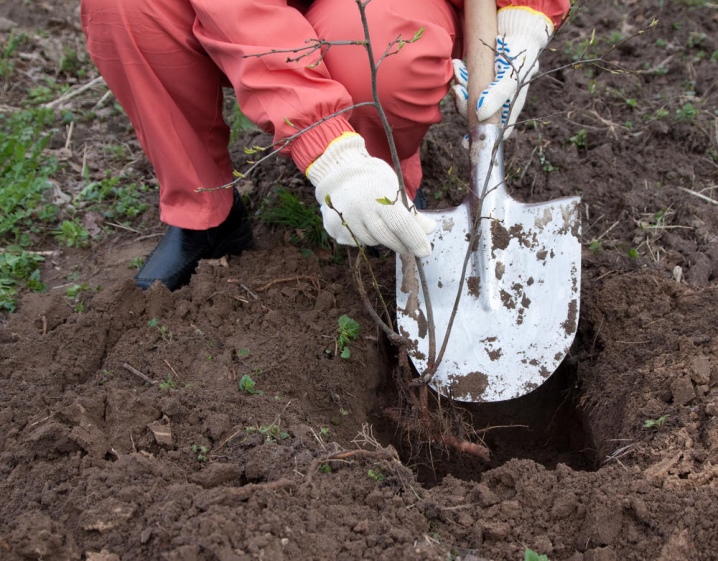

To propagate the plum, the root connecting the shoot to the mother bush is cut. The seedling is gently pry off with a pitchfork or a shovel to transfer it to the transplant site. They are transplanted with a lump of earth, but you can shake it off if the transplant to a new place does not drag on. The place of the felling for the mother bush is a wound, therefore it is advisable to treat it with garden varnish in order to prevent infection with infections or fungal spores.

Landing
Seedlings should be planted in prearranged locations. Dig holes up to 50 cm deep. The diameter is about the same. The soil dug out of the hole is sorted out, removing all the roots of weeds and stones. Then the soil is mixed with compost, ash, superphosphate and potassium salt (1 bucket, ½ kg, 300 g, 70 g, respectively). A quarter of the resulting mixture is poured into the hole itself with a mound. If the soil on the site is too dense, a pit is made a little deeper with the organization of a drainage layer (pebbles or gravel, then sand).
A seedling is placed on the mound, the roots are straightened, a peg is driven in, if a garter is needed, covered with soil, slightly shaking the plant to fill the voids between the roots. The soil is well crushed. It is poured abundantly with water, sprinkled on top with a layer of earth.


The distance between plum saplings is not less than 3-4 m. Varieties that bloom at the same time are compiled for pollination.
When choosing a site, the illumination, the level of groundwater are taken into account. Plums love abundant moisture, but do not tolerate stagnant water. The groundwater level should be no closer than 1.5 m. The site should be light, partial shade is not suitable.
Successful planting can be seen by the appearance of new stems and shoots.
There is another way of reproduction. In the spring, the seedling is isolated by chopping off from the mother plant. But they do not dig it out, but only provide him with intensive care. In the fall, a mature seedling with a well-grown own root system is transplanted to a permanent place.
Excavated plants can be stored for up to 10 days in a bucket of moistened soil. Shoots with a small number of roots are buried a little deeper.

Care
Growing plum shoots after transplanting is no different from caring for ordinary young plums. The rules of care can be determined by several points.
- You need to carefully monitor the hydration. In the first year, abundant watering will be required at least 1 time a week. In very dry weather, water should be watered 2-3 times a week. If it is not possible to vigilantly monitor the site, after watering, the plums are loosened, and the trunks are mulched.
- If watering is carried out using a sprinkler, it should work for at least 2 hours.
- There is no point in fertilizing young plants: only next spring is watered or sprayed with a solution of urea (700 g per 10 l of water) until the buds dissolve. No fertilizers are needed during the year.
- Weeds are removed several times per season. It is preferable to pull them out by hand.
- It rarely happens that young plants begin to give new root shoots. It must be cut close to the ground, and the cuts must be carefully processed with pitch.
- In the fall, the area is carefully removed from the fallen foliage. It attracts pests and rodents. The trunks can be treated with a strong mint solution to scare away rodents.
- For the winter, plants must be covered. To simultaneously protect the planting from mice, spruce branches and juniper branches are used.


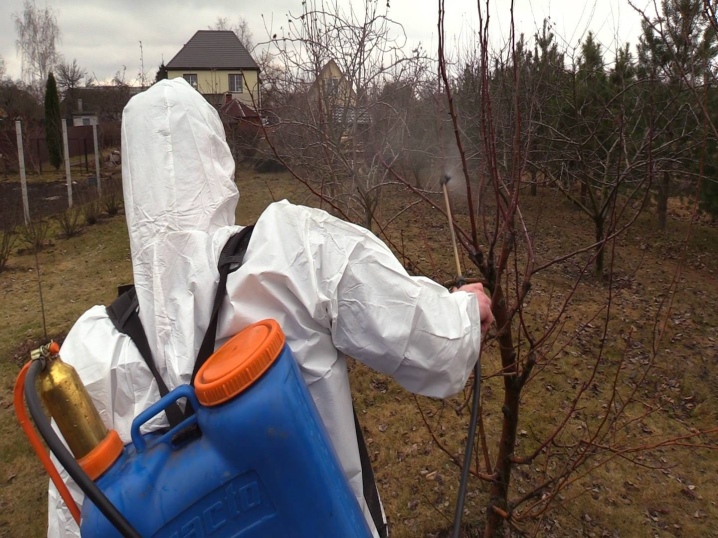
Several times a season it will be necessary to spray the plant from pests. For the first time, the urea solution performs the function of protection. In the spring, it is most convenient to carry out the treatment with urea, since it is also a fertilizer. If the buds have already blossomed, they are sprayed with Fitoverm. It is useful to spray newly planted seedlings with a solution of "Epin" or "Zircon" (biostimulants).
Autumn spraying against pests is carried out in October.

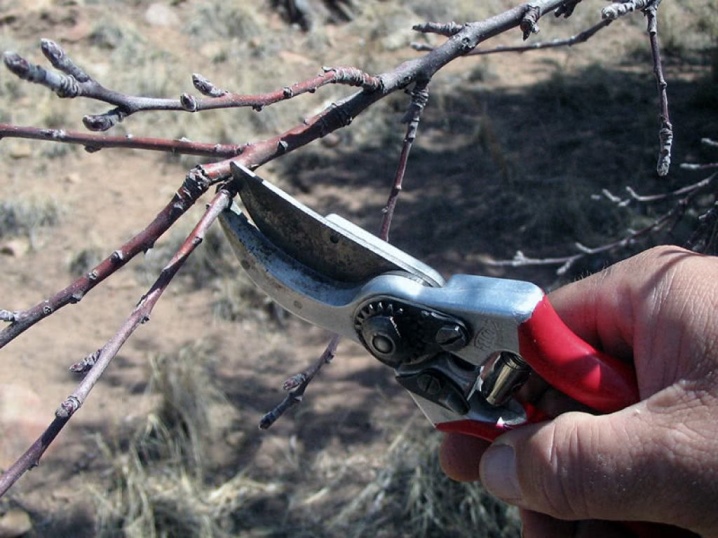
In the first year of planting, you do not need to cut the plants from the overgrowth. But if it is clear that the root system is underdeveloped, the branches can be shortened. The first formative pruning can be carried out one year after planting (if the plant is formed in the form of a trunk).
It is necessary to tune in to 5 years of crown formation. They start with the formation of the lower tier at a distance of 45-50 cm from the ground, leaving 5-7 skeletal branches. They should extend from the barrel at a 45 ° angle. All branches below are removed. Skeletal ones are shortened by 1/3, the rest are cut into a ring, without leaving hemp.

If new growth appears around the plant, it must be removed correctly. Digging or cutting right at the trunk will have a negative effect, as more new plants will appear in the damaged areas. Unnecessary plum shoots should be stubbornly shortened to such an extent that only hemp without leaves remains. Gradually, unnecessary shoots will stop growing.
Competent cultivation of plum sprouts is very beneficial. Dozens of new seedlings of good quality and high survival rate can be obtained from one mother plant (in contrast to seedlings obtained from cuttings).The method is very good for self-rooted plants. It is better to remove the shoots of grafted plants or consider the resulting seedlings as a rootstock for varietal plums.








The comment was sent successfully.