How can a plum be propagated?

A plum tree can grow from a seed. You can propagate this culture with the help of grafting, but there are several more ways, which we will discuss in detail in the publication. So, you will learn how to propagate a plum by cuttings, using cuttings, how to get a new tree from root growth. Consider all aspects of each breeding method.
Propagation by cuttings
The garden plum can be propagated by both mature and green cuttings. The method is not false, but many beginners fail in this, and all because they do not strictly follow the following rules:
- you need to take into account the temperature and humidity indicators;
- rid the soil of harmful creatures and pathogenic bacteria;
- it is important to choose the right variety for such a propagation method as cuttings.
It should be borne in mind that not all varieties are suitable for such reproduction, and even if you choose a suitable variety, only 25-70% of the cuttings will take root.


In the greenhouse, it is desirable to maintain a high level of humidity, and in order to cleanse the ground and minimize the death of seedlings from diseases, it is necessary to disinfect the soil with copper sulfate. Consider the stages of cuttings.
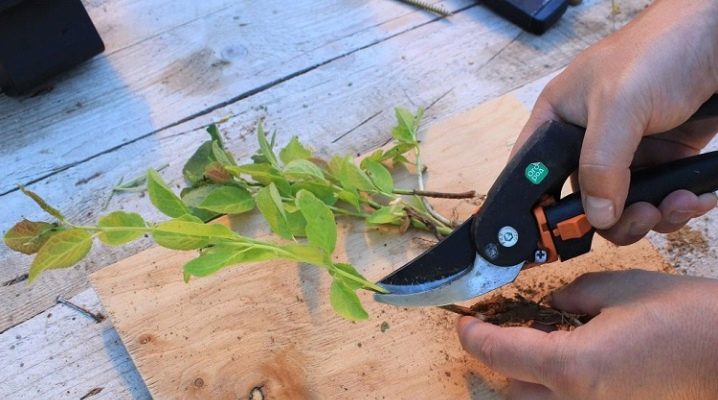
- Blank. As cuttings, good branches are selected without damage or signs of disease. They are engaged in harvesting in the fall after the completion of the sap flow processes. You can store the workpieces either in the basement or in the refrigerator compartment on the lower shelf. In the latter case, they must be wrapped in foil paper or stored in a waterproof paper bag. As a last resort, tie the cuttings in a bundle and bury, mulch and leave until spring.
- Rooting. It will not be entirely correct to talk about certain dates - they depend on the varietal characteristics of the tree and the specifics of the growing area. Experienced gardeners determine by external factors: when young shoots give redness at the base, the time comes for cuttings. Cuttings are taken in the early morning hours (at this time they are most saturated with moisture), preferably in cloudy weather. Each of them should have at least three leaves, the bottom is cut off at an angle of 45 degrees, the top is cut so that the cut is perpendicular to the trunk. The cuttings are kept in a growth stimulator for about 15-18 hours. In the meantime, a place is being prepared for their disembarkation.
- Landing. Drainage is done in the pit, then a composition of compost, humus and wood ash is added. A layer of river sand is poured (about 3-4 cm) - in this layer the process of rooting of cuttings will take place. They are planted vertically - so that only the stem is deepened, the foliage should not touch the ground. Water thoroughly.
The landing is covered with a box made of glass or polycarbonate, you can stretch the film over the arcs. Such an impromptu greenhouse needs to be aired daily to get rid of accumulated condensation. Roots and new leaves will begin to appear in 2 weeks, in some cases in a month, it depends on varietal characteristics. Before wintering, the greenhouse is carefully insulated - you can use special materials, for example, spunbod, or you can use a layer of mulch. Prepared cuttings are planted with the onset of spring days.



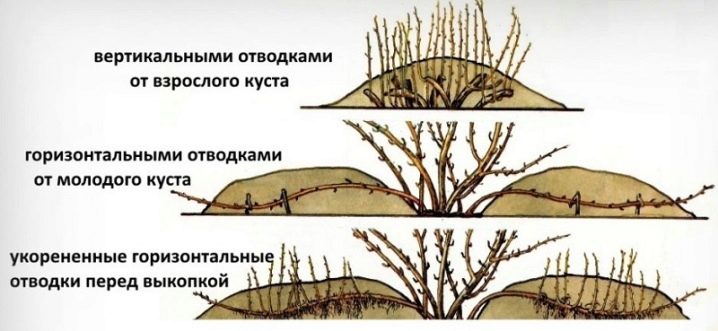
How to propagate by layering?
This method of spreading plums does not require as much attention as grafting. The main thing here is to get down to business in a timely manner. It is necessary to root air or ground layers in the spring before flowering (about 7-8 days). This method is especially good for breeding large-fruited varieties. The rooting technology of air layers is as follows.
- Choose good branches (preferably last year's development).
- At the beginning of the shoot, 2 cuts are made parallel to each other at a distance of 1-1.5 cm, all the bark is removed in this area. All actions are carried out carefully so as not to damage the core.
- Several more grooves are made a little higher from the annular cut, and chips, matches or toothpicks are placed under the notches so that the branch "does not heal".
- A stimulant is applied to the sections to accelerate root formation and everything is enveloped with wet moss.
- Then they wrap it with plastic black wrap, and so that it holds, it is fixed with electrical tape.
- You just have to moss the moss sometimes in the summer. To do this, make small holes in the film and water the sphagnum with an ordinary syringe.
Before the onset of cold weather (about a month), the young shoot is separated from the mother base and given the opportunity to germinate further in a separate hole. And in order to protect the seedling from frost, it must be well insulated. Ground layers are bent to the ground and deepened immediately into the ground to a depth of 4-5 cm, after making cuts and treating these places with a means to stimulate growth. So that the branch is well pressed to the ground, it is fixed with an arc made of wire or with a special garden hairpin.
The top remains on the surface, but it should not be spread over the ground. If this happens, it must be lifted and fixed with a peg. The rooting site is watered and covered with mulch or film material.
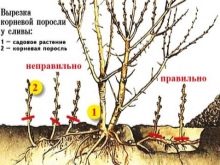
Using the undergrowth
Many varieties of plum give growth, and gardeners use this to multiply the culture. It should be noted: this method is only suitable for own-rooted plums. Other varieties may not bear fruit or produce poor yields. You can dig up and replant shoots both in spring and autumn. In the first case, before the formation of kidneys, in the second - about 4 weeks before frost. In regions where the summer is very short, it is better to plant the shoots from spring, so that young seedlings can take root and gain strength before the cold weather. A two-year-old shoot growing from the mother tree at a distance of two to three meters is suitable for reproduction. A young plant is cut off with a rhizome of at least 15 cm.
To prevent infection - both in the uterus tree and in the young shoots - the root system is treated with garden lime. A mixture of compost, sand of river and turf soil is added to the pit, observing the proportions of 2: 1: 2. Where the area is with heavy clay soil, a drainage layer is made before that, and then the nutrient mixture is spread. Do not deepen the root collar of the seedling, otherwise the tree will get sick, it will lag behind in development. The root collar should be on the surface - this is a fundamental point. The seedling is fixed with a peg. Quite an easy way, but only for own-rooted varieties of plums.









The comment was sent successfully.