Overview of diseases and pests of plums

Plum is one of the most hardy fruit crops. Nevertheless, even she is not immune from pathologies and attacks of insect pests. Let us dwell in more detail on the description of the problems that can threaten plum plants and tell you how to protect yourself from them.

Treatment of fungal diseases
The danger of fungal infections is that they are very quickly transmitted from one plant to another.
The ideal environment for the development of this pathogen is excess moisture and thickened foliage, and the peak of the spread of fungi occurs during warm and humid periods. Pathogens hide in young plant tissues and form mycelium there.
If measures are not taken in a timely manner, the tree will wither very quickly. Powerful fungicides are used to treat such infections.

Coccomycosis
This fungus mainly affects foliage, roots and fruits also suffer from it. Plants with a weakened immune system are most susceptible to disease. The first sign of the disease is reddish-red or purple-purple spots on the leaf plates. Quite quickly, they increase in size and merge, while on the back side, the edge acquires a light pink tint. Soon the foliage begins to turn brown and fall off, the growth of fruits stops.
To combat this fungus, it is necessary to cut off all affected fragments, as well as to process healthy tissues with Bordeaux liquid or copper oxychloride. An obligatory stage in the fight against coccomycosis is to get rid of all fallen leaves, since the causative agent of the fungus very often arranges a wintering place in it. That is why, in order to prevent it, the soil near the trunk in the autumn time needs to be thoroughly dug up.

Rust
Rust makes itself felt in early June and immediately infects tree leaves. The fungus weakens the plum tree and becomes susceptible to frost. If in winter the temperature is kept below -15 degrees for a long time, then the plum tree may not survive the frost.
It is very simple to detect the fungus - brownish spots appear on the leaf plates. If untreated, they soon transform into pillows, which are the main carriers of spores. Leaves from such trees crumble, and it is in them that the fungus will winter.
Today there are no plum varieties that are 100% rust resistant. But each tree can be more or less susceptible to disease. The culture can be treated using Bordeaux liquid or copper sulfate with the obligatory removal of damaged fragments and their burning.
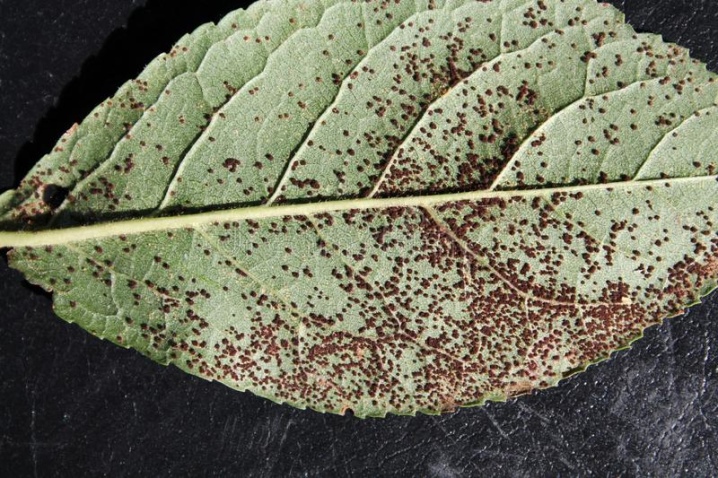

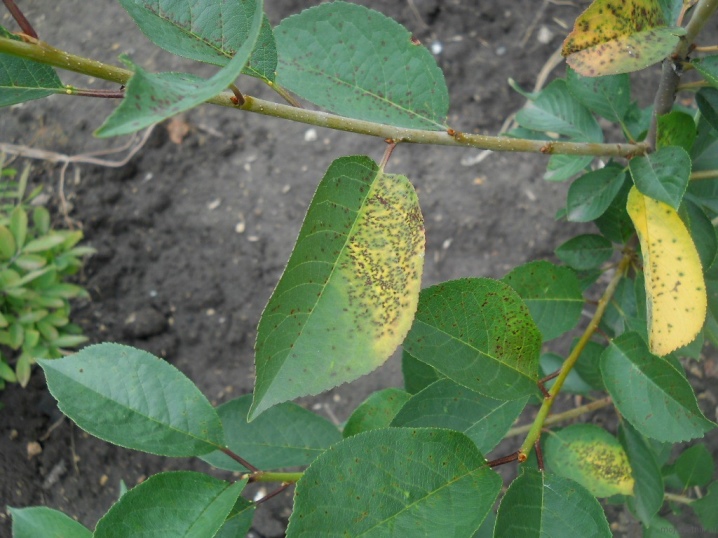
Brown spot
This disease can destroy up to half of the crop in a short time.
The conditions favorable for the development of this fungus are reduced immunity of the fruit crop, prolonged rains and other unfavorable weather conditions. Spores are spread by wind, birds and insects.
The first signs of brown spotting appear in the spring, when reddish-brown spots with purple edging appear on the leaves. Gradually, the spots begin to increase in size and soon cover the entire leaf plate, as a result, the leaves become curly and fall off. The fruits are suspended in development, not having time to ripen.
If you start fighting the fungus in time, you can save most of the crop.The maximum efficiency is provided by prophylactic spraying of the tree with a solution of copper sulfate before the beginning of the growing season. The working solution is prepared in the proportion of 100 g of the drug per 10 l of water.
At the end of flowering, it is necessary to spray the crown and trunk with Bordeaux liquid. If the infection is massive, then re-processing is carried out 2-3 weeks before harvesting. In autumn, it is important to pay attention to digging and burning plant residues.

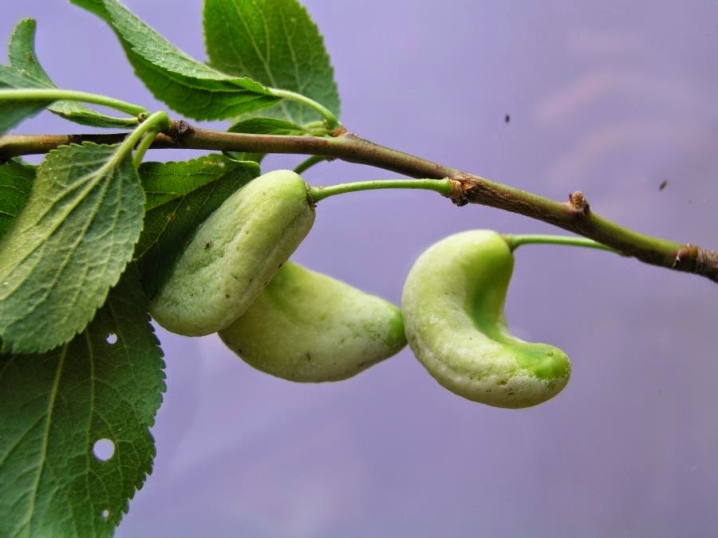
Plum pockets
The causative agent of the infection is a marsupial fungus. The defeat leads to the fact that the appearance of the fruit changes - they become sac-like, covered with a sticky bloom. Spores overwinter in cracks in the bark. The first signs can be seen already in the spring, especially the activity of the fungus is favored by the prolonged cold spring months with high humidity. In such weather, the fungus penetrates the flower and affects the ovaries.
The pathogen grows and develops in the fruit. Such plums do not have pits, so they fall off very quickly. It is very difficult to save plants, therefore, special attention should be paid to preventive measures - autumn pruning, burning all damaged branches, cutting down rotten fruits. This should be done before the fungus spreads over the surface. Diseased plants are sprayed with copper sulfate. The treatment is repeated three times - until the buds swell, before the beginning of flowering, and also immediately after its completion. If you do not carry out medical measures, then the infection will destroy up to 2/3 of the crop.

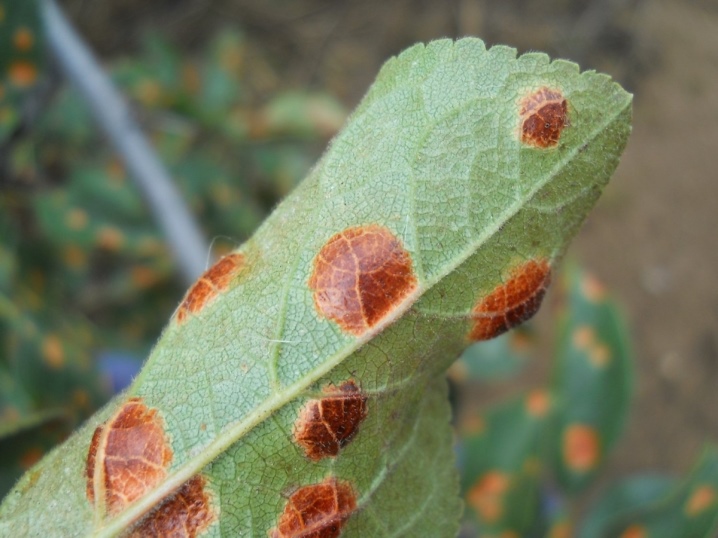
Clasterosporium disease
This disease affects the aerial parts of the fruit tree, spores overwinter in the buds, shoots, as well as in cracks and wounds. Spreaders are insects, the infection can be carried by the wind and through garden tools. The first sign of pathology is brown spots with a red edging, they have an oval shape, the diameter is 4-5 mm. Over time, holes appear on the damaged fragments. In addition, spots can be seen on the shoots, the bark cracks, the buds turn black, the leaves dry out, and the flowers begin to fall off, subsequently spots appear on the fruits, gum flows from them.
To save plants, you need to carry out constant processing. To do this, the tree must be sprayed at least 3 times with Bordeaux liquid from the crown to the ground line: at the stage of budding, during budding and immediately after the growing season. The treatment is repeated every two to three weeks so that the most recent one falls on the period after the foliage has fallen off.
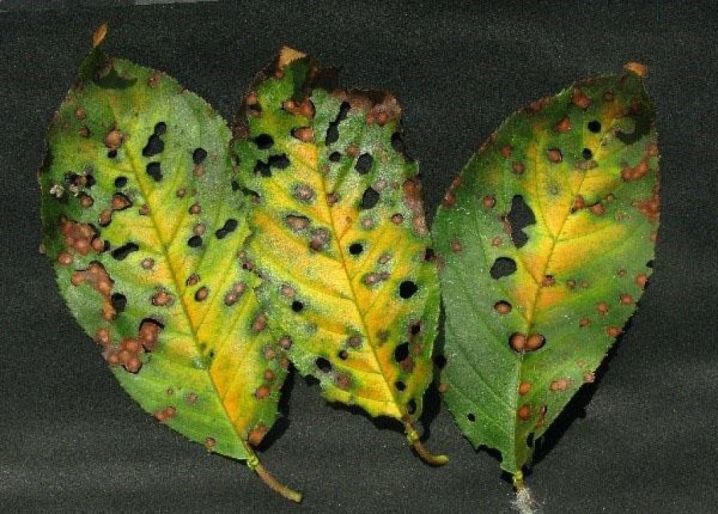

Stone fruit moniliosis
This disease causes monilial burn of fruits, gardeners call it gray rot. The causative agents of the fungus overwinter on unharvested fruits and in shoots. If the tree is sick, it will be very difficult to cure it. Frequent temperature changes and high humidity contribute to the activity of the fungus.
You can recognize the pest by the drying of flowers and leaves. At the next stages of the lesion, the branches begin to crack, and fluid flows out of them. In general, the tree looks like a burnt one. Thickening forms on the bark, the shoots become lethargic, and the fruits begin to rot right on the branches.
Diseased plants are treated with Bordeaux liquid or iron vitriol. If the fruits begin to rot, they should be removed and sprayed again. All infected branches, leaves and fruits must be collected and burned. In addition, the trunk should be whitewashed, and all wounds on the bark should be covered with garden varnish.
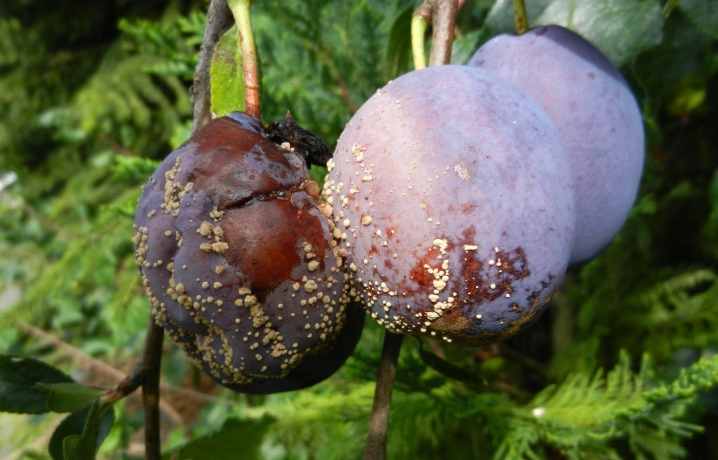

Witch's broom
All parts of the plant, without exception, suffer from damage by this fungus, so it can be difficult to determine the source. To do this, you need to carefully look at the tree - in the place where spores appear, the shoots become thin and branched, resembling dead ones. The leaves on the affected branches become smaller and crumble, at the end of summer you can notice a grayish bloom on them. To cure the plum, it is necessary to remove and burn all damaged shoots, and spray the tree with Bordeaux liquid.
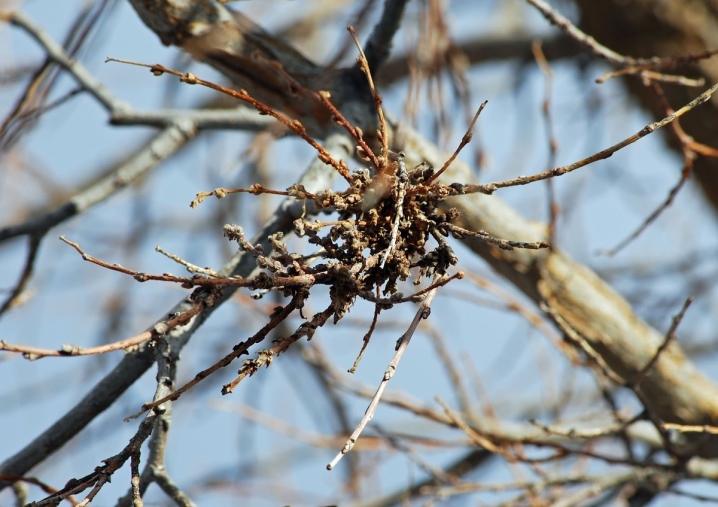

Milky shine
Another fungus that can kill the plum tree. It is passed from one tree to another. The most vulnerable are plants that are frozen and cracked in winter.
The presence of the parasite can be established by the leaves - they change their shade to silver, soon dry out and break.
There is no cure for this disease, neither folk methods nor the most powerful chemicals will save. Such a plant must be cut down and burned. In order to prevent sad consequences, it is necessary to buy seedlings only from trusted sellers, insulate trees for the winter, and carry out preventive spraying.
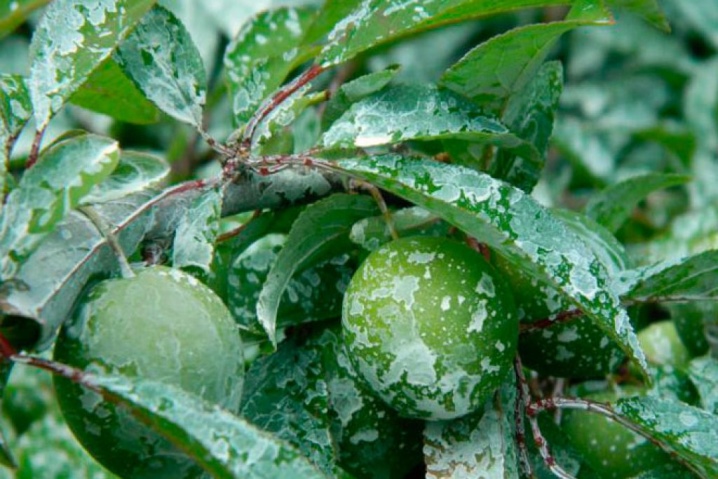

Fruit rot
In its manifestations, this plant resembles gray rot, but only affects the fruits. The disease is promoted by high humidity, most often plums begin to hurt in wet weather with prolonged rains. As a result, gray spots appear on the cream, they grow rapidly and capture the entire fruit. The plant can be saved by treatment with Bordeaux liquid and the removal of all infected fragments.
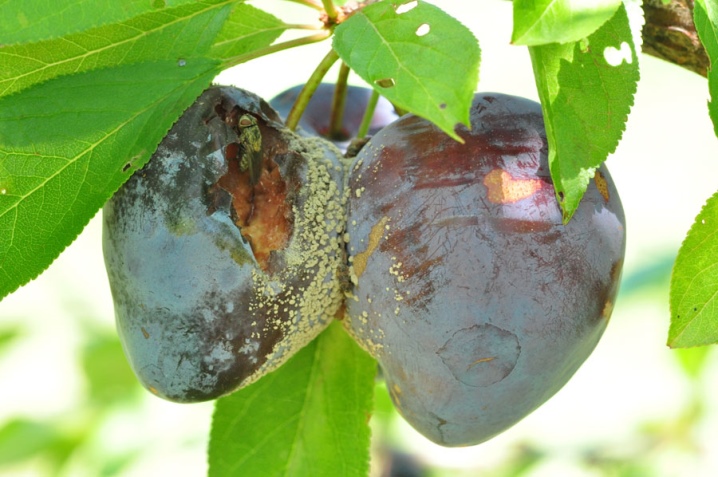

Sooty fungus
The people call sooty fungus niello. Its danger lies in its numerous pathogens that live on foliage in colonies, and this makes full photosynthesis impossible. The plant weakens and withers. The first signs of the disease are expressed in the appearance of black plaque, which can be erased with your fingers. To delay the development of infection, it is necessary to spray the plum with a copper-soap solution. To do this, take 5 g of copper sulfate on a bucket of water and add 140 g of a soapy substance, it is best to take laundry soap.
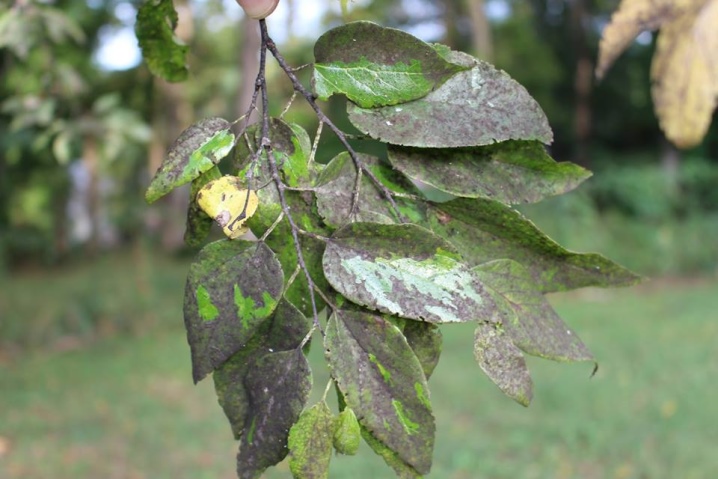

Infectious and non-infectious diseases
Infectious and viral pathologies pose a great danger to plums. Their difficulty lies in the fact that they are almost not amenable to treatment.
Smallpox
Gardeners often call this attack a shark. Such a disease leads to the appearance of stripes and spots on the foliage. Carriers are aphids, infection can occur through garden tools. You can determine the problem by the fruit - deep spots appear on them, which affect the flesh of the fruit to the bone.
Over time, the spots become as if depressed, plums fall or dry out on the branches. There is no cure for smallpox. Control measures should be cardinal - this is the uprooting of the plant and burning.

Scab
Another dangerous disease is scab, it is provoked by bacteria and pathogenic microorganisms. It affects the entire plant, which leads to a significant decrease in yield. The first sign of the disease is olive-colored spots with a light velvety bloom. Depending on age, type of wood and weather conditions, the number of stains may increase.
The spread of the disease is facilitated by thickened plantings, excessive soil moisture and varietal susceptibility to diseases. The plant cannot be cured, so special attention must be paid to prevention. It includes cleaning and burning all affected plant fragments, carrying out sanitary pruning and treating the stem with whitewash.
In addition, proper feeding and spraying with Bordeaux liquid increase immunity.
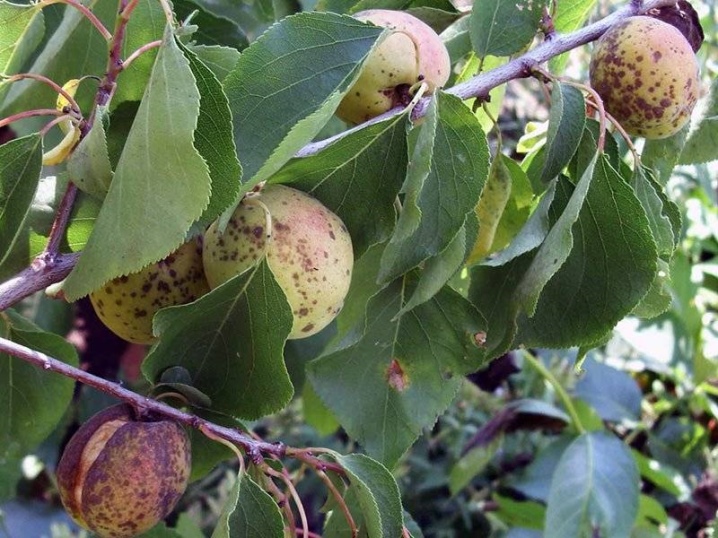

Plum crops are often prone to non-communicable diseases. They are the result of non-compliance with the rules of agricultural technology. If fruit trees are not properly cared for, problems may arise over time that cannot be corrected with existing chemicals.
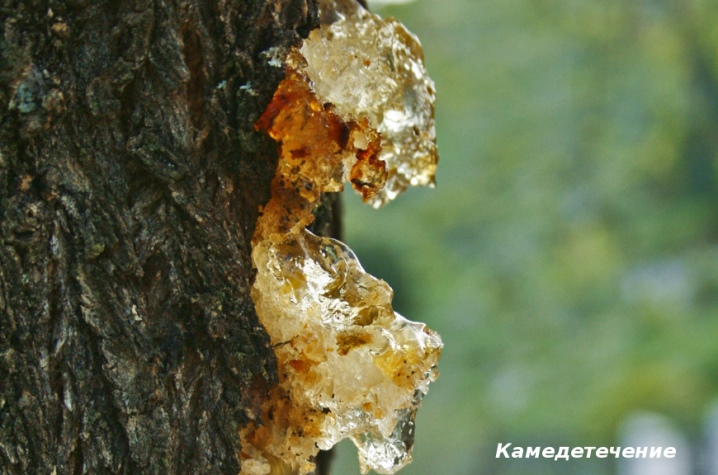
Gum therapy
This disease predominantly affects stone fruit cultures. Despite the fact that it has a non-infectious nature, it is nevertheless extremely dangerous for the tree. If the problem is not solved promptly, the tree will quickly die.
Gum disease often occurs in trees that are frozen in winter or have had a fungal disease. You can determine the disease by droplets of translucent resin - there is a feeling that the tree is shiny.
Culture can be helped. To do this, it is necessary to clean the area from which the liquid flows out with a sharp garden knife, and treat the wound with a solution of copper sulfate. After 2 hours, rub the affected area with sorrel leaves. The procedure is repeated 3 times, and covered with garden var.

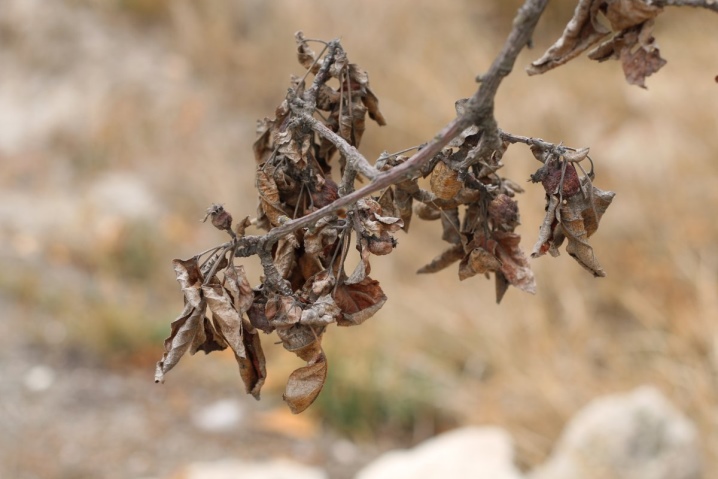
Shrinking
Gum flow, plant freezing, a high level of groundwater occurrence, excessive acidity of the earth often lead to drying out of the plant. To save him, you need to neutralize unfavorable factors, as well as observe the basic rules of agricultural technology. However, if the plant is severely affected, all that remains is to get rid of it.

Pest control
Plum trees are often affected by pests and other parasites - beetles, ants, and worms. Let's dwell on the most dangerous enemies of this culture.
Plum moth
Outwardly, such a parasite looks like a gray-brown moth. The moth lays its larvae in green immature fruits, which feed on juicy pulp. As a result, the fruits are suspended in development, darken, begins to rot and fall off.
Spraying with "Karbofos" will help to save the plant from the moth. In this case, it is necessary to process not only the tree itself, but also to shed the soil. In this way, you can destroy not only the pests themselves, but also destroy their nests. The damaged areas are treated with a pale solution of potassium permanganate, and covered with garden varnish.
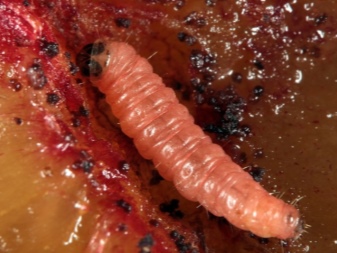

Aphid
Aphids feed on vital plant juices, so they are very dangerous for fruit crops. This insect lives in huge colonies and has a high reproduction rate. The defeat leads to the fact that the tree weakens, the shoots of the plum begin to curl, growth stops, the foliage dries up and rapidly falls off. It is possible to save the plant if, at the initial stages of the lesion, spraying with a solution of Bordeaux liquid or other specialized preparations against aphids is performed.
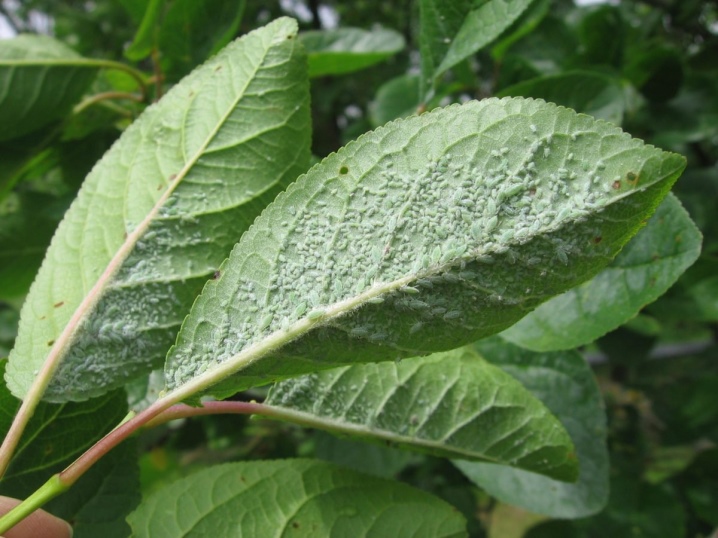

Hawthorn
The daytime butterfly is quite impressive in size, painted in black and white. The caterpillar is furry, black with an orange stripe. The parasite feeds on juicy plum fragments, and the only part of the tree they don't eat is the bark. As a result of the attack, the tree quickly loses strength and dies.
To fight the parasite, you need to use the maximum range of resources. First, you need to physically throw the caterpillars off the trees, spray with a solution of copper sulfate and urea at the rate of 500 g of carbamide and 100 g of sulfate per bucket of water.


Prevention measures
Diseases and attacks of parasites cause great damage to the plant, lead to its wilting, reduce productivity, and can even cause death. Therefore, it is best to prevent the appearance of pests. For this, special attention should be paid to prevention - it includes the simultaneous use of agricultural techniques and chemicals.
- At the beginning of spring, sanitary pruning should be carried out, to get rid of all diseased shoots, to cover up cracks in the bark formed from frost. At the same time, it is necessary to dig up the soil in the near-trunk circle, spill the earth with a solution of "Nitrafen".
- At the flowering stage, it is impossible to use any chemical preparations, at this moment only folk remedies will help.
- At the end of the growing season, to protect the tree, they are sprayed with a solution based on copper sulfate or copper oxychloride.
- All infected plant fragments should be disposed of in a timely manner. In the fall, after fruiting, it is necessary to collect fallen leaves and weeds, dig up the ground in the near-stem circle and whitewash the trunk. A couple of weeks before the arrival of frost, the whitewash is repeated.



Resistant varieties
And in conclusion, we offer an overview of plum varieties that are resistant to adverse external factors.
-
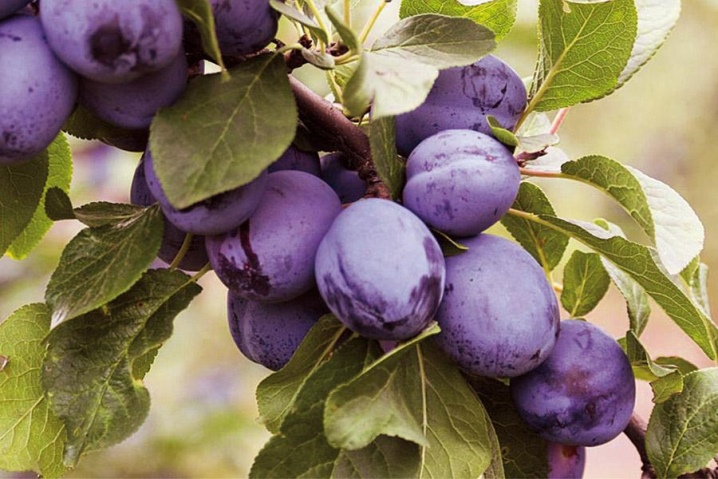
"Bogatyrskaya" - the name of this variety fully corresponds to its essence, it gives great fruits, up to 35-40 g.The pulp is sour-sweet, very juicy, the tasting score corresponds to 4.5 out of 5 points. From one tree, you can get a harvest of up to 80 kg. Plants are highly winter-hardy, practically not affected by diseases and insect pests.

-
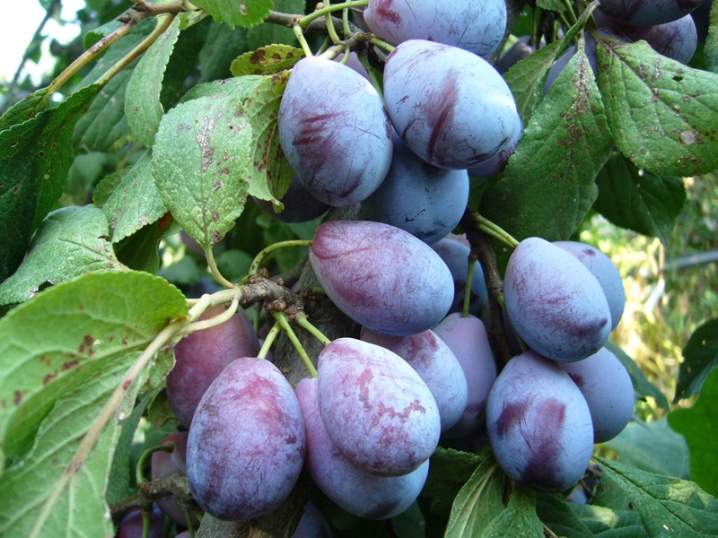
"Hungarian Korneevskaya" - another large-fruited variety, the mass of berries is 30-35 g. The taste is sweetish, up to 30 kg of fruits can be harvested from one plant. The variety is winter-hardy, only with prolonged frosts below -25 degrees, flower buds can die. Resistant to insects and fungal infections.

-
Volgogradskaya - a variety with large berries up to 35 g. From each tree you can get up to 60 kg without pollinators, and if you plant another variety nearby, the yield can reach 100-150 kg. The pulp is juicy, the tasting mark is 4.5 points. Differs in resistance to severe frosts, does not suffer in the absence of moisture, is practically not affected by pests and infections.

-
"Zarechnaya early" - plum with heavy fruits up to 45-50 g. One of the largest plants, up to 50 kg can be harvested from one tree. Easily tolerates subzero temperatures, the variety is resistant to attacks by pests and pathogenic fungi.

- "Peaceful" - plums with large fruits weighing up to 30 g. This is the most delicious variety, its tasting score corresponds to 4.8 points. From one tree, you can collect from 20 to 40 kg. The species is resistant to drought, although with regular watering, the fruits are more juicy and sweeter. Quite frost-resistant, practically not susceptible to infections and attacks of parasites.






The comment was sent successfully.