White rosehip and its cultivation
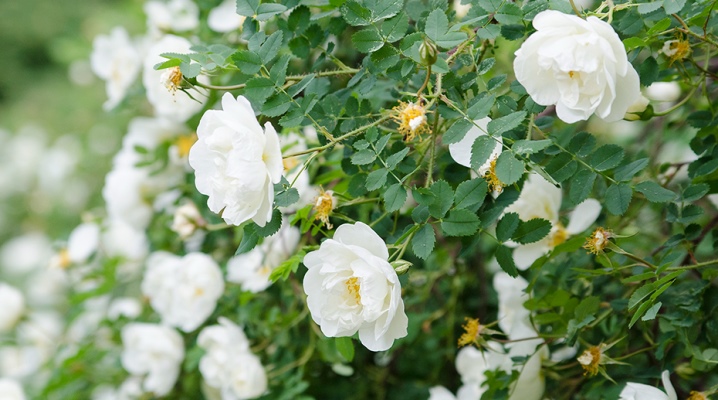

The song about the white rosehip is known, perhaps, to all residents of the post-Soviet space without exception. The song about this flower gained immense popularity after the release of the musical opera "Juno and Avos". It was after the premiere of the performance that this inconspicuous shrub became the personification of pure love with a sad outcome.
general description
Nowadays, white rosehip is one of the most popular gardening plants, it is widely used in landscape design. The scientific name of the culture is "multiflorous rosehip". In accordance with the accepted scientific classification, it belongs to the department of angiosperms, the Pink family. Taiwan is considered the historical homeland of this rosehip; its age is estimated at about 40 million years. Scientists claim that it was this fragrant bush that became the progenitor of all varieties of roses that exist on the planet.
Nowadays, white rose hips are found in nature mainly in Taiwan, Japan, as well as in China and Korea. However, it is actively cultivated in European countries. Gardeners appreciate it for being undemanding to external factors. It can grow on any drained substrate - dry and wet, acidic and neutral.



Despite the fact that the plant prefers sunlight, it is quite shade-tolerant. White rose hips are resistant to cold and winds, easily tolerate heat and prolonged drought. And the berries remaining on the branches retain their taste properties even with the onset of frosts down to -9 degrees.
The multi-flowered dog rose belongs to the group of upright shrubby plants. It is distinguished by graceful, wide-open, arched branches, dotted with snow-white flowers. The height of the plant is 2-3 m, under favorable conditions the bush can reach 5 m in length and 3 m in width.


The bark is brown or reddish-green, the shoots, depending on the variety, can be with or without thorns. Leaves are alternating, unpaired pinnate, 5-8 cm long and 2-4 cm wide. The number on each branch is 7-9 pieces. The lower surface of the leaf blade is matte, the upper surface is shiny, deep green in color. The leaves are slightly pubescent and do not fall from the branches for a long time.
The flowers are small, but cover the bush profusely, giving it a peculiar resemblance to exuberant flowering cascades. Flowering begins in mid-June and lasts 3-4 weeks. The fruits are small, the size of a pea, the shade is red. They remain on the branches for a long time, even with the arrival of winter.

Popular varieties
There are many wild and domesticated varieties of white rose hips. In horticulture, this shrub is represented by beautiful hybrids. Usually these varieties have double buds and resemble roses in appearance. The most popular are the following varieties.
- "White Pavement" - Rosehip of this variety grows up to 1.2 m, it is distinguished by leaves of a rich dark green hue. Flowering continues throughout the summer. The flowers look like semi-double buds with multiple golden stamens in the center. In autumn, bright red-orange fruits are formed, which support the decorative effect of the shrub until the arrival of frost.
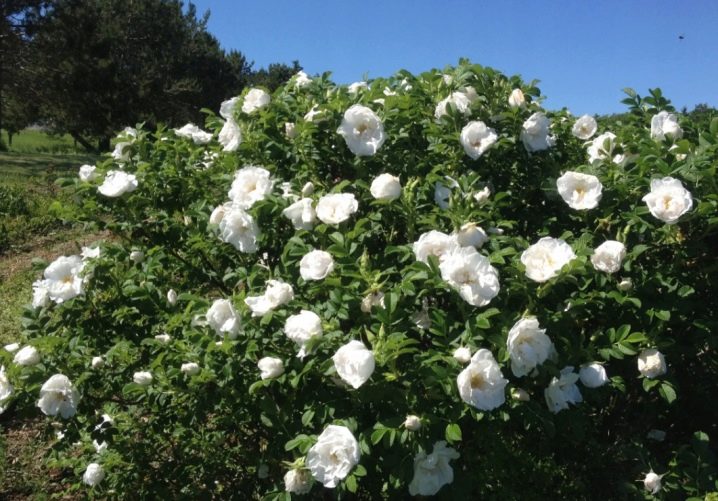

- "Waterloo" - this variety reaches 1.5 m. Abundant flowering, while the buds are large enough - up to 2.5-3 cm, gather in beautiful panicles.This variety of rose hips prefers illuminated areas, it is distinguished by its resistance to cold weather. It can easily withstand temperatures as low as -20-25 degrees.
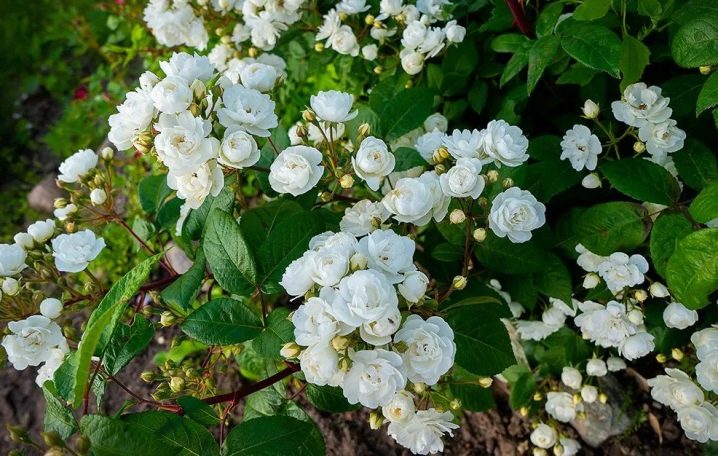

- "Suaveolens" - one of the most beautiful subspecies of white rose hips, it looks like a rose. It can grow up to 1.3 m and spread up to 1.5-2 m wide. Branches with thorns, leaves are dark green with a bluish tint. Flowering continues throughout the summer, openwork flowers, up to 5 cm in diameter, exude a pleasant fruity aroma. The culture easily withstands frosts down to -35 degrees, therefore it is often planted in Siberian regions.
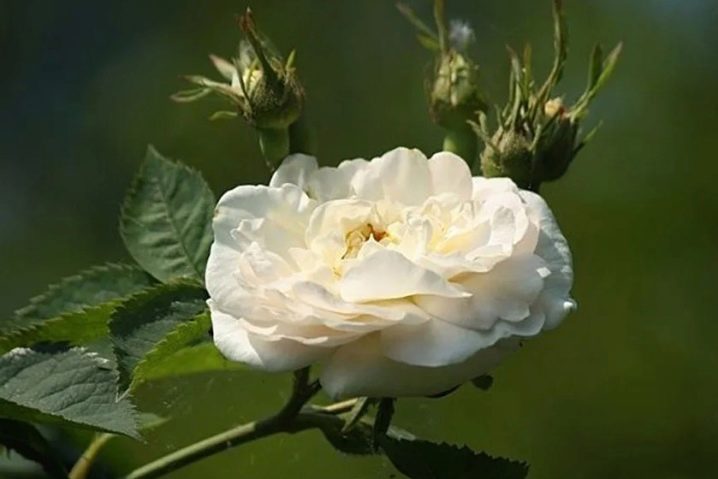

- "Madame Plantier" - a vigorous bush with spreading branches, the number of thorns is minimal. Flowers bloom at the very beginning of summer. At this moment, the terry buds are painted in light pink shades, but over time they become snow-white. Collected in beautiful brushes of 7-20 pieces.
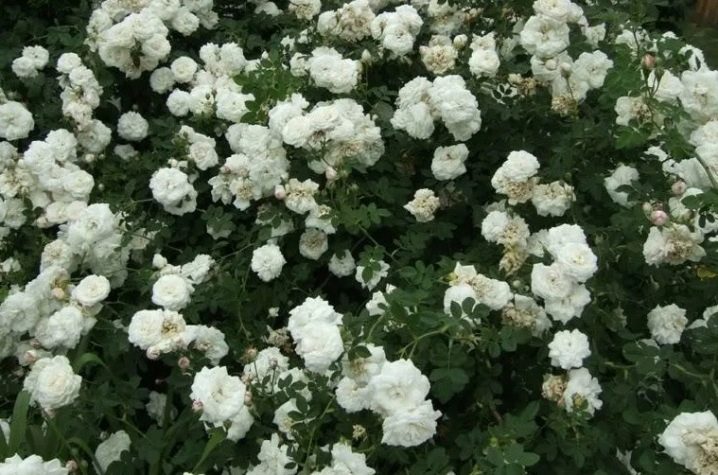

- Louise Bagnet - This elegant variety of multi-flowered rose hips has a very effective color scheme. Until the moment of blooming, the bud is colored red, but as it opens, the upper petals change their shade to pure white. At the same time, the lower ones remain dark cherry or have a pinkish tint.


- "Lac Mezhu" - a powerful, vigorous shrub, blooms in early June. Gives quite large buds, combined in inflorescences of 5 pieces. In autumn, flowers are replaced by red fruits - they do not carry significant nutritional and medicinal value, but they look very interesting.


- Alba Madeiland - this unpretentious variety gives compact double buds, combined in panicles of 7-10 pieces. Flowering continues from the very beginning of summer until the arrival of autumn. The height of the bush is not more than 7 cm, but in width it can stretch up to 2 m. The variety does not require special care and pruning after flowering. It emits a soft, but very pleasant aroma.

Landing
Experienced gardeners argue that decorative rosehip seedlings planted in autumn take root most successfully. The optimal period for planting is considered to be the second half of October - early November. The sequence of actions is standard here.
- First, you need to form planting pits about 20-25 cm deep. If the earth is acidic, lime, chalk or dolomite flour should be added to it first.
- Compost or rotted manure is added to each hole.
- Immediately before planting, the seedlings are cut so that the thickest branch does not exceed 8-12 cm in length, the roots are shortened to 12-15 cm.
- Before planting, the rhizome of the dog rose is moistened with a clay talker - this will prevent the roots from drying out.
- After that, the seedling is placed in such a way as to deepen the rhizome below the surface of the earth by 5-7 cm.
- Then the roots are straightened, sprinkled with a prepared substrate, after which they irrigate and mulch the ground with peat or sawdust.


Care
The vitality and undemandingness of the white-flowering rosehip allows it to easily adapt in the garden and grow quickly. Caring for him includes standard agrotechnical measures.
The plant is resistant to high temperatures. However, if the protracted sultry weather lasts, then three times a season the shrubs need watering. At the same time, 4-5 buckets of liquid are poured onto each bush.
If fertilizers were applied to the planting hole, then in the first year no additional feeding will be needed for the dog rose. In the second year of life, nitrogen-containing compounds give the greatest result.
The first time the plants are fed in March, immediately after the snow melts, the next procedure is performed in July at the stage of active growth and development of shoots, the final feeding is performed in early autumn.
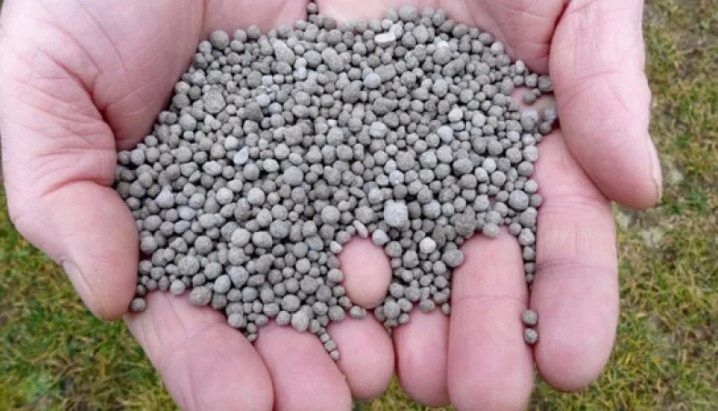

All subsequent years, the bush is fertilized every 3 years, bringing 3-5 kg of humus or compost under each bush. After applying organic fertilizers, the soil in the trunk circle must be loosened, watered abundantly and sprinkled with a layer of mulch.
As the area is overgrown with weeds, weeding is performed. To improve the structure of the soil and provide the root system with oxygen, after each watering, as well as in dry weather, the ground around the rose hips must be loosened to a depth of 12-15 cm.

Reproduction
Rosehip can be propagated in several ways. The vegetative ones are recognized as the simplest and most practical. Although it is also possible to grow an ornamental crop from seeds.
Cuttings
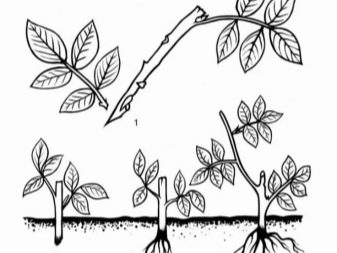
The most effective and yet simple method involves the use of green cuttings. The decomposition algorithm is as follows.
- In spring, shoots up to 12 cm long are cut from an adult rosehip bush, it is advisable to take flexible annual branches.
- On each cutting, remove all the lower leaves and leave 2-3 internodes.
- Then an oblique cut is formed and placed in a solution of "Epin" or "Kornevin" for 20-30 hours.
- The cuttings are moved into peat containers filled with nutrient medium and covered with a plastic bottle to create a greenhouse effect.
During the entire period of root formation, the shoots must be periodically ventilated and moistened the ground. When future plants begin to grow actively, they can be transplanted into open ground.

Seeds
The seed method of growing requires significant effort from the summer resident. The breeding scheme is as follows.
- In late August - early September, ripe berries are harvested. The fruit is carefully cut, the seeds are removed and washed under running water to get rid of the pulp.
- The resulting seedlings are planted on a temporary bed, deepening by 2.5-3 cm with a step between individual seedlings of 2 cm.
- The plot is watered, moistened and covered with mulch. In the course of drying the substrate, irrigation is carried out.
- As soon as two true leaves appear on the seedlings, the seedlings are transplanted to a permanent site.
Seed propagation has a significant disadvantage. In the case of hybrid varieties, the daughter plants very often lose their parental characteristics when using this technique.


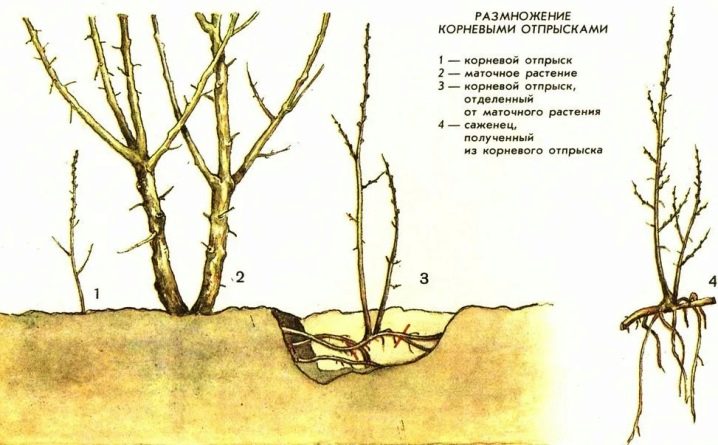
Root offspring
There are two techniques that can be used with this breeding method. In the first case, an offspring with a height of 30-40 cm is selected and carefully separated with a shovel or pruning shears from the mother bush. This work can be done both in spring and autumn. According to the second technology, the adventitious bushes are not separated from the mother, but simply spud and watered periodically.
By dividing the bush
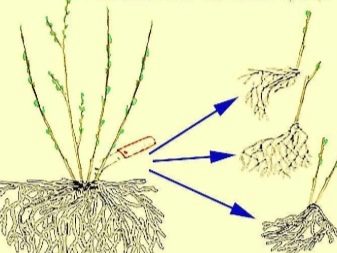
For the propagation of plants over 5 years old, division is often used. The procedure is pretty straightforward.
- The white rose hips are carefully dug up. It is advisable to moisten the ground around the plant in advance so as not to injure it when removing the bush.
- The rhizome is carefully divided into 2 or more parts with the help of any pointed instrument, the cuts must be neat.
- Immediately after this, the plots are transplanted into prepared pits and intensively watered until rooting.
When making plots, you need to keep in mind that each should have one growth point and at least 2-3 full-fledged shoots.

Diseases and pests
The main diseases of the multiflorous rosehip are the following.
- Powdery mildew - manifests itself in the form of a whitish bloom on the leaves of the plant, after which the bush stops in development and dries up quickly. For the treatment of this disease, a solution of colloidal sulfur is used. And it is possible to increase the resistance of the crop to the disease by applying potash fertilizers.
- Rust - it can be identified by brown-brown spots on the back of the leaves. All affected plant fragments must be cut off and burned, and the ground under the bush must be dug up with a copper-containing preparation.
- Black spot - with this pathology, black spots appear on the leaves and petioles of the bush, soon the foliage dries up and dies. To get rid of the misfortune, you should cut off all affected shoots and destroy them.The soil near the plant is dug up and treated with any fungicide.


Among the pests that attack white rose hips, the following species cause the greatest damage.
- Spider mite - microscopic insect no more than 1 mm long. It is impossible to consider it, its appearance is indicated by an ultra-thin silvery-white cobweb on the leaf plates. These parasites feed on the vital sap of the bush, after their attacks, the plants begin to wither. To get rid of the pest, it is necessary to work with acaricidal agents.
- Rose aphid - these are small insects of brown or green shades. They live in colonies, suck moisture and nutrients from the plant, and also infect it with viruses. Such formulations as "Karbofos", "Actellik", and also "Rogor" work against this pest.
- Slobbering penny - This is a yellow-olive insect 5-6 mm in size. Usually parasitizes on the back of the leaf plates. To combat such a pest, they are treated with insecticides.


Application in landscape design
Decorative rose hips are widely used in garden landscaping. Depending on the purpose of plant placement, the rules for planting seedlings differ. So, if a hedge is formed, the distance between individual holes should be 40-50 cm.
If the bush plant is single, then there should be much more free space around it.



































































The comment was sent successfully.