Violet "RM-Peacock": description and rules of cultivation

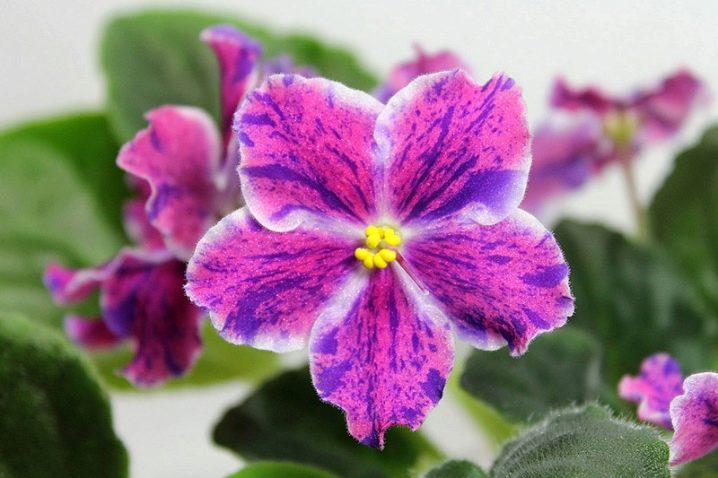
Violet "RM-Peacock" is a flower of amazing beauty, characterized by expressive bloom, combining tenderness, sensuality and elegance. The flower stands out noticeably against the background of other indoor plants. Let's talk in more detail about the features of growing this variety.
Description
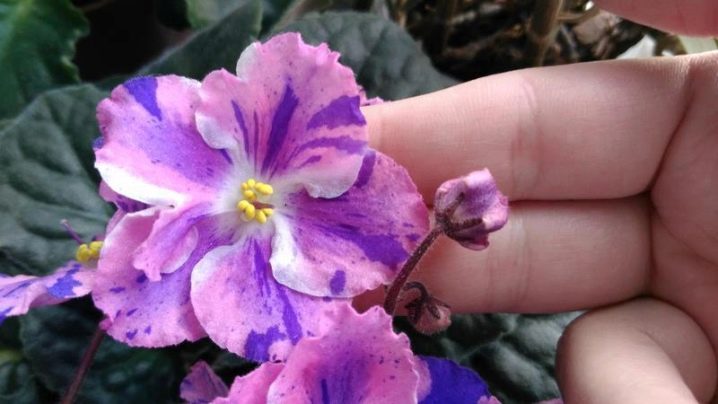
The shrub of this room violet is decorated with large buds. In the center, the flower is painted white. Most of each petal is covered with bright colors: blue, pink, purple. In combination, several shades create an expressive pattern. The texture is semi-double. Experts note that the saturation of the shades depends on the temperature conditions in which the violet grows.

The color of the leaves is standard, green. With proper development, a uniform and small rosette is formed. The foliage is oblong and rounded. The first flowers appear after 9 months. With proper care, a lush bloom is observed. Due to the original color, this variety stands out noticeably against the background of others.
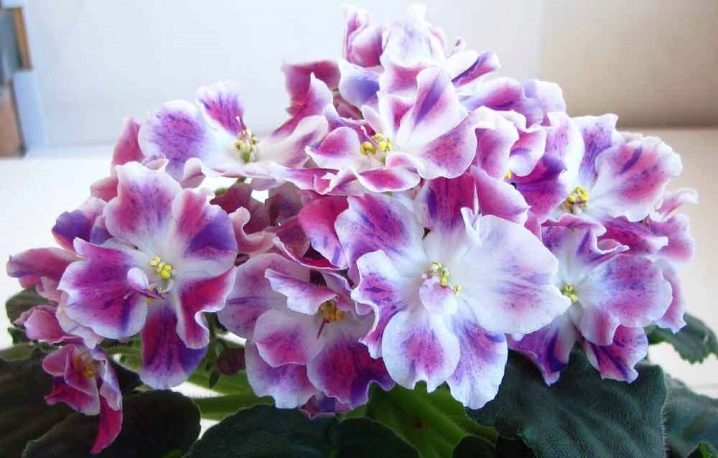
Officially, this variety and other indoor violets belong to the genus of herbaceous plants called "Saintpaulia". All of its representatives have a beautiful and expressive color.
Also, plants of this species combine growing and care conditions.

General rules of care
Plants belonging to the above genus need a sufficient amount of sunshine. A full daylight hours should be about 12-13 hours, however, the plant must be protected from direct rays. Evening and morning light can touch the plant, it will not cause any harm.

Compliance with this condition is very important for a beautiful and expressive color.
When the indicator drops to below 15 degrees Celsius, the plant stops growing. In the hot season, the flower feels great in conditions of 24 degrees Celsius above zero. With the onset of a cold snap, this indicator can be omitted. Experts strongly recommend not to take the bushes out into the street with the onset of heat.
Indoor violets, like other indoor plants, do not tolerate drafts. Also, their condition is significantly affected by sudden changes in temperature. In a compact pot, the flower will feel great. This condition is necessary for the formation of a large number of buds. Small plastic containers are ideal. The size of the container should be 3 times smaller than the rosette of the plant.
Composition of the earth
The right substrate available in the store is great for plants from the Saintpaulia genus. It contains all the necessary elements for the nutrition and development of the shrub. In addition, the finished product does not need to be hardened or further processed. You can also prepare the mixture yourself, adhering to the following proportions: 0.5 part of sod land, 2 parts of leafy soil, 1 part of humus and 1 part of sand.




A few pinches of bone meal and a spoonful of superphosphate are added to the above components. All elements are thoroughly mixed. The ideal soil for violets should be airy and low in acidity.

When transplanting, be sure to line the bottom of the pot with drainage and make several holes.
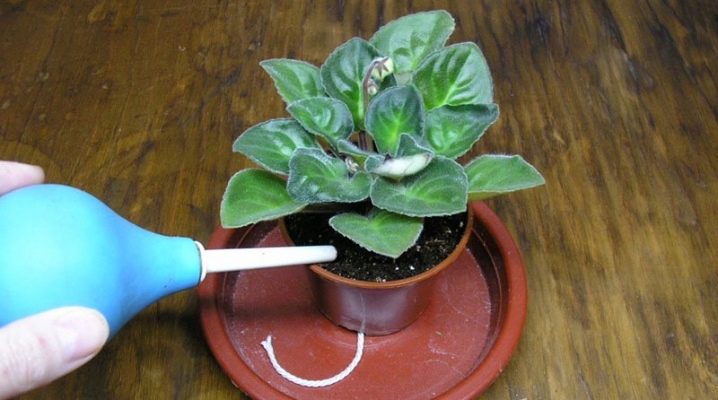
Watering
The first watering is carried out after transplanting the plant (in the event that you have purchased a rooted leaf or baby). The violet does not need constant moisture. It is enough to water the plant from time to time when the topsoil dries up.Typically, the soil is moistened about once every 10 days. Warm water is used, which was previously settled for several days.

Top dressing
Every plant needs additional nutrients, especially when it comes to flowering shrubs. For indoor violets, ready-made complex formulations are used. They are introduced during the growth of foliage, once every 10 days (along with watering). Shrubs do not fertilize during the flowering period.

Diseases
Powdery mildew is most often encountered by flower growers growing Saintpaulia. Symptoms are white bloom on the green mass of the plant. If you notice brown marks on the leaves, this may indicate late blight. Because of this ailment, the root system of the plant also begins to rot.


If a pale coating appears, be aware that you are dealing with gray mold. In this case, the affected areas are removed and the soil is changed. Sections are treated with a fungicide. Stagnant water leads to fusarium, as a result of which the leaves and stems of the shrub begin to rot.

Plant rust appears as small brown spots. Many diseases are treated by treating the flower plant with special preparations, according to the instructions.
It is also advisable to renew the earthen mixture and disinfect the container.
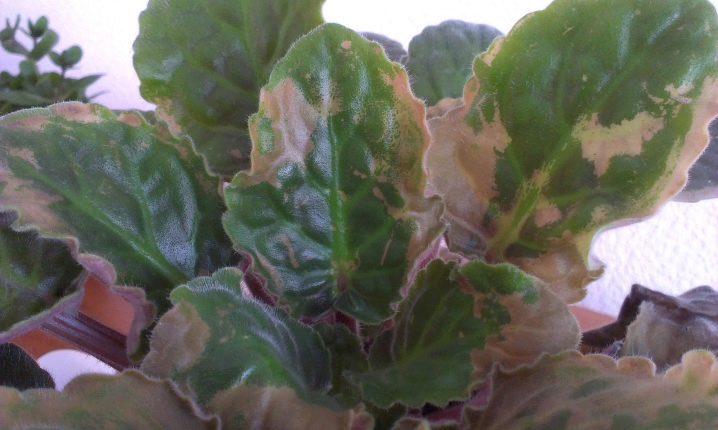

Pests
Ticks are considered the most dangerous and common pests that attack house plants. Their presence is indicated by a cobweb on the leaves. Shields can also be a problem. They leave a sticky and viscous substance on the plant's body.


Thrips harm both the green mass and the flowers of the shrub. In this case, the plant is cut and treated with a special preparation. The plant begins to rot from nematodes. Experts compare this pest with gray rot, but in this case there will be no plaque on the plant.... The shrub begins to quickly rot and wither when attacked by nematodes.
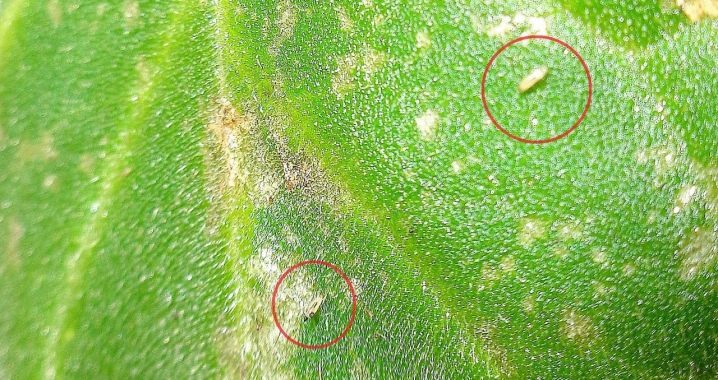
As a rule, the shrub is destroyed and the soil is no longer used.
Examine the violet regularly for symptoms of disease or pest attacks. If an ailment is found, use medicinal formulations. Regular inspection increases the chances of the plant rescuing. Before using drugs, be sure to read the instructions for use.

For information on how to treat a violet from a tick, see the video below.































The comment was sent successfully.