What does perennial penstemon look like and how to grow it?
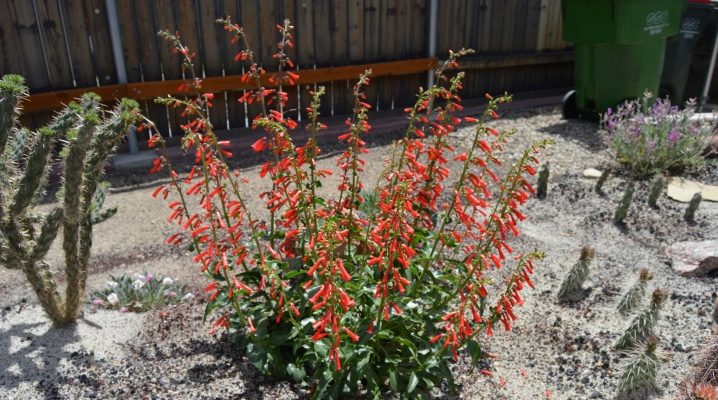

Penstemon is a perennial plant that is found in two types: bushy and creeping. The bright green leaves of the plant contrast with the white, pink, red or purple flowers, which gives the shrub a decorative look. Penstemon is perfect for decorating garden plots, its bright flowers and pleasant unobtrusive aroma are loved by many gardeners and landscape designers.


general description
Perennial Penstemon is a shrub and semi-shrub plant native to Central and North America. The appearance of plants is quite different depending on the type and variety of the crop. The penstemon bush can grow up to 120-150 cm in height. One bush can have up to 4 erect shoots on which flowers form. The leaves on the stems are bright green, in some varieties purple.
The first flowers appear in late May - early June, depending on climatic conditions, flowering lasts all summer until September or early October. The flower has the shape of a bell (resembles Snapdragon), the colors range from white and light pink to maroon and purple. The core of the flowers is lighter (almost white) compared to the whole flower. Flowers unfold sequentially from bottom to top on upright arrows. Hybrid varieties have a more intricate color, can be two- or three-color, or with contrasting blotches.


Popular species and varieties
There are about 270 species of plants from the genus penstemone in the world. They all differ in the color range of flowers and leaves, as well as the height of the shrub, the number of shoots and green mass. The flowering period and the life span of the plant depend on the variety.
The most popular plant species are whitish penstemon, alpine, bearded, red-leaved, foxglove and many others.
The foxglove species tolerates frost well, differs in pale pink flowers, sometimes completely white. The bushes are quite tall, reaching 1 meter. Suitable for planting in central Russia.


"Harvega" - one of the most popular varieties, has flowers of different colors on one bush. The inflorescences are large. In this case, the core is always white. The height reaches 50-60 cm, and the shrub blooms almost until the first autumn frosts.
"Hasker Red" - another frost-resistant variety. Differs in red leaves (almost bronze), shoots reach 90 cm in height. Flowers, on the other hand, are very delicate, with a pink tint.
Flowering begins relatively late, in late June - early July.


Penstemon the bearded - a hybrid species with large flowers. Arrows reach a height of 90 cm. Differs in early abundant flowering. Flowers on the same bush can be of different shades.
Penstemon pine-haired - undersized evergreen representative of this species. Its bright red, orange flowers can completely cover the shrub. The leaves are needle-shaped, and the shoots are rather thin and flexible. Duration of abundant flowering is about 2 months.


Landing
The plant is rather unpretentious, but prefers lighted areas. With enough sunlight, flowers and leaves become richer in color. While a plant planted in the shade (without access to sunlight), although it can develop, the color of flowers and leaves will be a few shades paler.It is better to choose a place without drafts, but with constant access to fresh air.
When planting a plant on a site, it is important to choose the right soil. The soil should be light and loose. It is recommended to use organic fertilizers (humus) for feeding. Fertilize in the spring, before the penstemon bloom.


Penstemon is easy to germinate from seed. The culture is characterized by rapid growth and will begin to bloom in the first summer, after planting the seeds. Seed material is recommended to be sown for seedlings in early March. The seeds are slightly deepened into moist soil; there is no need to sprinkle the seeds with earth. The temperature for rapid germination is needed not lower than + 25 ° С. It is recommended to cover the boxes with foil, periodically opening them for ventilation. The first shoots should appear in the second week after sowing.
After the formation of 3-4 full-fledged leaves, the sprouts are transplanted. An excellent option for a temporary transplant will be peat pots, which are subsequently placed directly into the open ground. Leave about 30 cm between the bushes.
A perennial culture does not like frequent transplants and can get sick, which will negatively affect further growth and flowering.



Growing care
Penstemon is an unpretentious culture, but still requires some attention. With proper care, the plant will delight the gardener with abundant flowering of bright bell-shaped flowers. The plant requires regular watering and loosening of the soil. It is necessary to monitor the condition of the soil around the crop, remove weeds and periodically mulch the soil using chopped sawdust or compost. To improve drainage during planting, it is recommended to put fine gravel in the holes.
In the open field, in one place, penstemon can grow well and bloom up to 4 years (some varieties up to 7 years). After that, the bushes grow old and lose their decorative appearance. Periodically, it is better to remove old plants and plant new ones in their place. This can be done using pre-prepared seedlings or cuttings.


Watering
The crop requires regular watering, provided that the soil is well drained. Avoid stagnant moisture under the bush. Otherwise, the plant may die. Between waterings, the ground should dry out a little from above (about 3-5 cm in depth), but not dry out too much. The bushes can be sprayed periodically.

Top dressing
Over-feeding the plant can begin to form new shoots abundantly, but without flowering. The bush will only grow green mass. To avoid such a negative effect, it is recommended to feed in the spring before the active growth of the plant begins.
If the soil is not saturated enough, then feeding can be repeated 1-2 more times over the summer. To do this, use natural organic fertilizers or fertilizers with a high phosphorus content. Phosphate fertilizers are recommended to extend the flowering period. In the summer, you can mulch the soil 1-2 times using compost, peat or crushed sawdust.


Pruning
Gardeners recommend removing faded buds and cutting off the shoots after flowering ends. This is done for the earliest possible start of repeated profuse flowering. The plant will not waste energy and nutrients to maintain shoots without formed ovaries. It is recommended to thin out large adult bushes, removing the oldest shoots, this will give a more decorative appearance to the plant.

Preparing for winter
In the fall, the bushes are completely cut off and covered with spruce paws. For the winter, it is better to cover the place around the rhizome warmer in order to avoid freezing of the soil and minimize damage to the root system.
In dry soil, penstemone can withstand frosts down to -10 ° C.

Reproduction
The fastest and most commonly used method of breeding penstemon is to divide a large bush into 3-4 parts. This procedure is carried out in the spring before the period of active growth. The rhizome of a large plant is divided into several equal parts, or a small part is separated and planted in a prepared place. After transplanting, the first few days, it is necessary to ensure good watering, the soil must remain moist.
Bushes that are 3 years of age or older are suitable for dividing. Younger shrubs will die when separated. Division also helps to rejuvenate the old plant, this should be done after 4-5 years of the life of the shrub. Otherwise, it ceases to bloom, the height stretches and loses its attractive appearance.


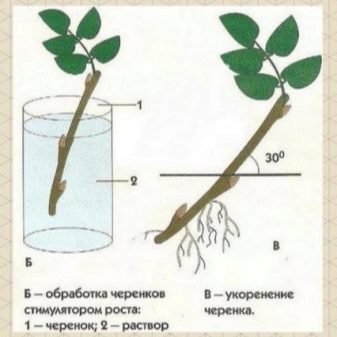
Another common breeding method is the cuttings method. In spring, when pruning, cut off the required number of young healthy shoots. They are buried 2-3 cm into a mixture of compost and peat (or moss), removing the lower leaves. Some gardeners recommend treating the cut sites with special agents that accelerate the formation of the root system ("Kornevin"). In moist soil, cuttings quickly begin to take root. When the root system is fully formed (it takes about a month), the cuttings are ready for planting in open ground.
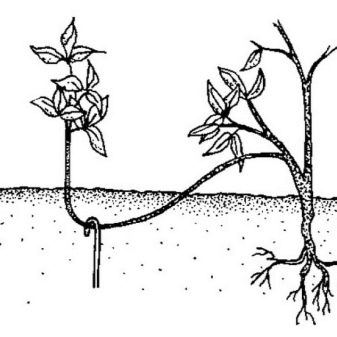
For creeping varieties, the breeding method is used by branches. Part of the young shoot is deepened a little and sprinkled with soil. This place requires constant watering, complete drying of the soil is not allowed. After about a week, the first roots will appear, then the young plant is separated from the mother bush by cutting off the shoot. After some time, when the young plant gets stronger, it can be transplanted to another place.
Diseases and pests
Most pests do not bother penstemone. The root system can begin to rot with excessive watering and stagnation of moisture in the soil. A pathogenic fungus (gray rot, for example) may appear on the roots, and the plant will die. Therefore, regular loosening of the soil around the bush is recommended. An already diseased plant can be well shed with a fungicide solution and thoroughly loosened the soil.
Sometimes gardeners are faced with the problem of drying out the top of the bush. In this case, it is better to cut off the shoot completely, otherwise you can lose the entire plant.
Penstemon has good growth and will quickly sprout new healthy shoots.


Use in landscape design
Due to its varied color scheme and different shoot heights, penstemon will fit into almost any landscape composition. Shorter varieties are often used for landscaping balconies and loggias. Small bushes feel good not only in open ground, but also in large pots and flowerpots. Tall shrubs are used to decorate alpine slides and large suburban areas.
Penstemon feels good in the neighborhood with other plants. It goes well with echinacea, carnations and catnip, chamomile and ornamental sedge. Some species (for example, whitish penstemon) prefer rocky soil, which is suitable for decorating rock gardens and artificial waterfalls, rockeries.
Landscaping designers often use penstemone to decorate the borders and edging of flower beds. With regular pruning, the shrub keeps its shape well and pleases with long, abundant flowering.


















The comment was sent successfully.