How is cuckoo flax different from sphagnum?
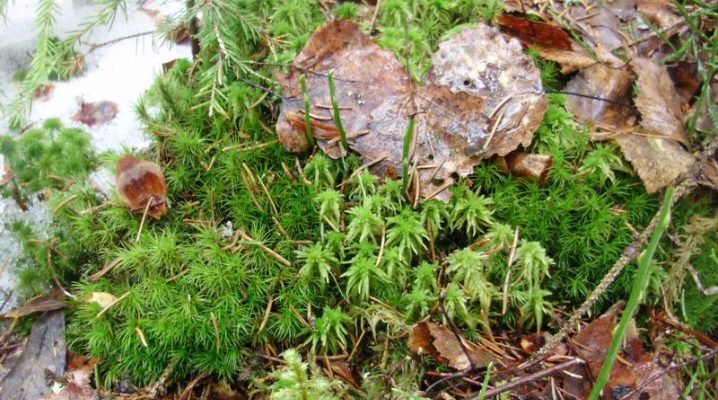

If you find cuckoo flax and sphagnum in nature, then at first glance they are no different. Both the one and the other form a star-shaped shaggy rugs. However, these are plants from different classes. Let's see how else cuckoo flax differs from sphagnum.

Comparison of structure
From the point of view of botanists, plants have more differences than similarities. Both plants are included in one department - Mossy. But their class, order, family and genus are completely different. Kukushkin flax is included in the Polyrichous class, sphagnum is in the Sphagnum class.
Kukushkin flax also belongs to leafy mosses. This is a class of mosses that, unlike other similar representatives, have stems and leaves. The class is extensive, 95% of all mosses are included in it.
Kukushkin flax is the most famous. He is the leader in length. In favorable conditions, cuckoo flax can reach half a meter in height.


External signs by which cuckoo flax differs from sphagnum.
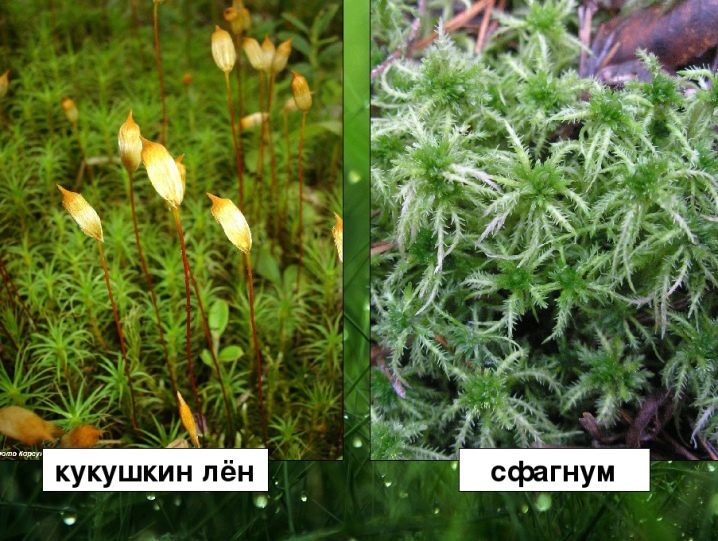
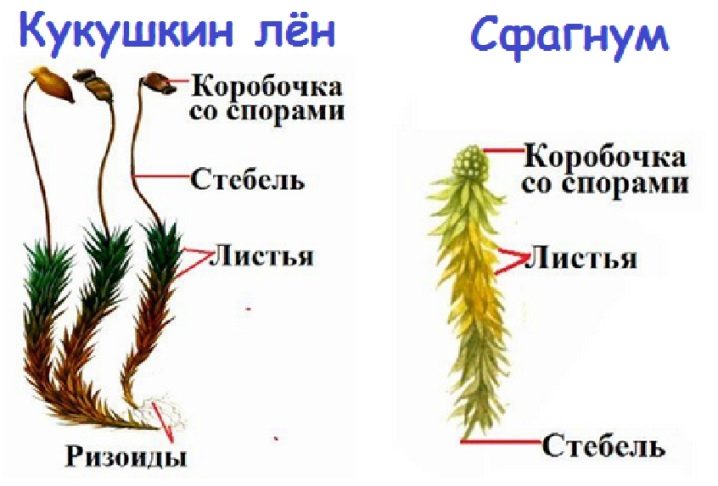
- Kukushkin flax does not branch, it is a single stem with small, elongated leaves, located often. The sphagnum has a completely different structure: on the stem there are additional branches in bunches, covered with small leaves-scales. Therefore, sphagnum looks more shaggy and lush.
- If you look closely, sphagnum has two types of leaves: the leaves on the main stem and on the lateral ones are different. In flax, all the leaves are the same.
- Flax has dark trunks, reddish-brown to the very top. In mass plantings, it seems brighter. In sphagnum, the trunks turn brown only at the bottom, where the plant is already dying, and there is no difference in color with the leaves. Sphagnum often becomes faded from above, depending on the type of its glades, it can appear yellowish, light green, whitish or pinkish, but never red.
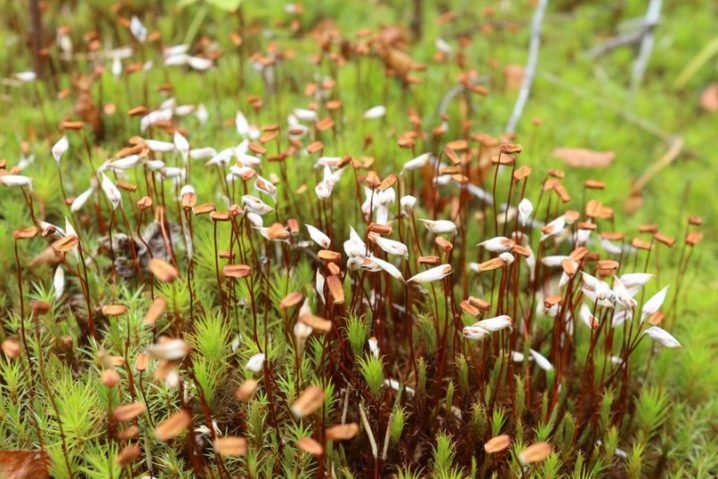
- The sporangium boxes in flax are elongated, resemble flattened tubes; in sphagnum, the sporangia are round.
- Flax has special hairs (rhizoids), they cling to the soil. They are located below, on the stalk, under the leaves, which have already turned brown. In sphagnum, rhizoids are absent, it absorbs moisture from the whole body.
- Plants absorb water differently, but visually, this difference is not striking. In sphagnum, dead cells are intended for the absorption of moisture by leaves and stems. They are hollow. The plant looks like a sponge under the microscope. Flax has a separate water supply system to absorb moisture, albeit a primitive one - special cells are involved in absorbing moisture.

Similarities.
- Both plants are quite large for mosses - usually up to 15-20 cm, although flax is potentially taller, but in nature it does not always realize its potential.
- In both plants, the leaves consist of one layer of cells.
- Both moss reproduce by spores, albeit in different ways.
- Both species actively reproduce vegetatively. New plants can emerge from a piece of stem.
- Both plants have no real roots.
It is rather difficult to distinguish both plants from a distance outside the sporulation period. They form bright green, shaggy-looking curtains.
To distinguish one plant from another, you need to pull out one sprout and take a closer look. Cuckoo flax will have white hairs at the end - these are rhizoids. And the stem will have a reddish brown tint.


Habitat
Both plants are forest plants, they like cool, shady places with an abundance of diffused light. Plants may seem to prefer shade, but they are not. With a lack of light, the plants wither and begin to stretch.In the forest, they receive a lot of side light, rays that the foliage of trees scatters.
In nature, the cuckoo flax is found in the north and in the middle lane, chooses damp meadows or marshes prone to waterlogging. It grows rapidly, forms dense turf cushions.
Sphagnum also lives in the temperate zones of the Northern Hemisphere. 42 species of sphagnum grow in Russia. He also loves wet places. Forms loose turf, the lower part gradually dies off, turning into peat.
The habitats of both plants in nature can overlap. For example, cuckoo flax is found in the Saratov region in several regions, including Novoburassky. In the Novoburassk region, there is the Mokhovoe bog, where a rare flat-leaved sphagnum, included in the Red Book of the region, was discovered.


Reproduction similarities and differences
Kukushkin flax is a bisexual plant. There are male and female specimens. Male ones are very effective: reddish star-shaped rosettes are formed at the ends of the stems. The ends of the stems of female plants are crowned with dark brown capsules with long legs. The structure of the boxes is quite complex - they look like barrels with lids. It is from them that spores spill out.
In sphagnum, all plants during the breeding season are covered with round brown capsules. They also have a small lid, but the shape of the "container" is perfectly round.
It is easier to distinguish between both plants during fruiting. Cuckoo flax clumps will be brownish from tall sporangial legs. Sphagnum looks almost as bright green as at any other time.
Other differences
The name of sphagnum is white moss. The names of cuckoo flax are long moss, red moss, boring rye (in the Arkhangelsk region). Both types of moss are widely used in human economic activities, although there are differences.
- Sphagnum has the unique ability to absorb moisture (20-25 times its weight), contains an antiseptic - phenol, which kills bacteria. Sphagnum is almost not subject to decay and is able to protect nearby objects from putrefactive processes. Kukushkin flax contains bactericidal substances: the glycoside linamarin, which decomposes with the release of hydrocyanic acid. It also absorbs moisture, but does it less intensively - it is able to absorb water 7 times its weight.
- Both plants are used in construction - they protect wood from rotting, mold, repel pests. Both moss keep warm indoors, while allowing air to pass through. In Russia, both plants were actively used - they were used to lay logs in the construction of houses. Kukushkin flax has a solid length, it was laid across the logs, so that the ends hang down, a new log was installed on top. It was hardly used for caulking. But sphagnum is more versatile - it can be used to drill seams of any size.
- Sphagnum is actively used in floriculture., especially for the cultivation of tropical plants, the roots of which need a lot of air and moisture. Kukushkin flax is used less often for these purposes, hydrocyanic acid is poisonous. However, the plant is used in folk medicine. It cures coughs, colds, pneumonia.
- In the formation of peat, the first role belongs to sphagnum, but cuckoo flax also contributes to waterlogging of the soil. However, its role is more auxiliary. Kukushkin flax often settles in damp, but not yet swampy areas. Its lower parts gradually die off, the conditions become more suitable for sphagnum mosses. Kukushkin flax is more often involved in the formation of lowland peat - this type of peat is formed mainly from leafy mosses. Transitional peat is the remains of sphagnum, green marshy grasses, shrubs, and, more rarely, trees. High moor peat is usually sphagnum, cotton grass, heather and some trees. All types of peat are useful, but in different ways.Horse is less nutritious, has high acidity, absorbs moisture well, and is an excellent source of heat. It is often used as a structural component of soils - it is he who will provide the ideal looseness of the soil for other plants.
Low-lying peat is more nutritious and can itself act as a fertile soil for growing cultivated plants.















The comment was sent successfully.