Description of Kirkazon and its cultivation
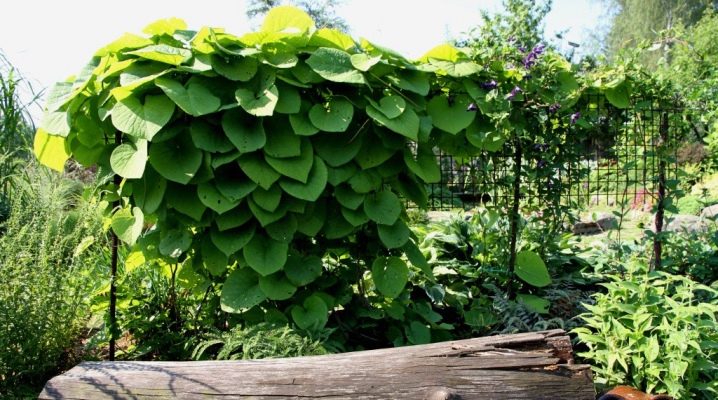

Kirkazon (aristolochia) is a liana-like plant from the Kirkazonov family. Due to the original shape of large leaves and flowers, the plant has an attractive decorative appearance, it is called the royal vine. Flowers give off an unpleasant aroma of spoiled rotting meat to attract a large number of insects, without which the culture is incapable of natural reproduction. Most often, the plant is found in latitudes with tropical and subtropical climates. Only 7 species of Kirkazon are grown on the territory of Russia.


General description of the plant
Plants of this species have been known since ancient times. Their medicinal and poisonous properties are described by Hippocrates and Theophrastus. Shoots of liana-like culture reach half a meter in length. The total height can be up to 15 meters. On the shoots, large, cupped leaves of a matte green color are formed. Flowers are often in the form of jugs, have a specific smell. The size and color of the inflorescences depend on the species and variety. Colors range from pastel white to bright yellow and almost red.
The shape of the flower allows you to catch insects for full pollination. The first time flowering occurs in the 5-7 year of the plant's life. Liana begins to bloom at the end of May, the period of abundant flowering lasts about a month. Fruits of an unusual shape (pear-shaped or elongated oval) are rarely formed, but the plant reproduces well by dividing the rhizome or by layering.


The culture is quite frost-resistant, tolerates temporary drought well, and is resistant to diseases and pathogenic microorganisms. With a well-developed aboveground part, the fibrous root system is located in the upper layers of the soil.
Outwardly, the plant without flowers or fruits is very similar to an ordinary grass with powerful stems and bright green leaves. The stems are slightly branched and differ in color depending on age. The color ranges from light green to dark gray.
Large leaves are formed alternately on the liana, overlapping each other in the form of tiles, forming a continuous canvas.

Kirkazon is known for its medicinal properties for humans. Aristolochia essential oils are used in the treatment of colds (flu, acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections), they stimulate the respiratory system and improve the heart rate. Phenolic acids are used to fight microorganisms in wounds and abscesses. When using these substances, the dosage is very important, exceeding the norm is fraught with the opposite effect.
Overdose can cause mucosal burns or poisoning. Even direct contact with leaves or shoots of some plant species causes 1 and 2 degree burns to the skin. When growing Kirkazon, do not forget that the plant is poisonous.


Popular types
There are approximately 380 species of kirkazon in the world. Most of them belong to ornamental or medicinal plants. Only a few species are widespread on the territory of Russia. The most popular of them are large-leaved (tubular), Manchu, clematis, graceful and felt. They grow in the European part of the country and in the territory of Primorye. More often Kirkazon grows along the banks of rivers and bays, in humid and shady places.
- Kirkazon large-leaved differs in liana color, the color of young shoots is dark green, eventually acquires a light brown color with small cracks.The size of the giant leaves reaches 30 cm in diameter, and the color range varies in different shades of green on the same bush. By autumn, the leaves do not change color. Single flowers begin to form in early summer, are yellowish-green in color. Poorly tolerates severe frosts and requires shelter for the winter.

- Manchurian variety resembles large-leaved in appearance. It grows on the territory of Primorye, Korea and China. Differs in the color of inflorescences that have a brown tint. And the leaves with the first frost begin to turn yellow and fall off. The Manchurian Kirkazon is more frost-resistant and requires only pruning before the beginning of winter.
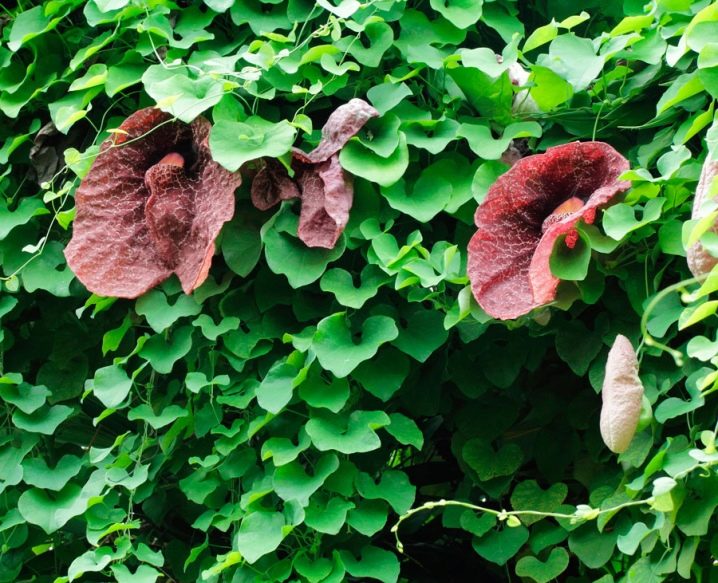

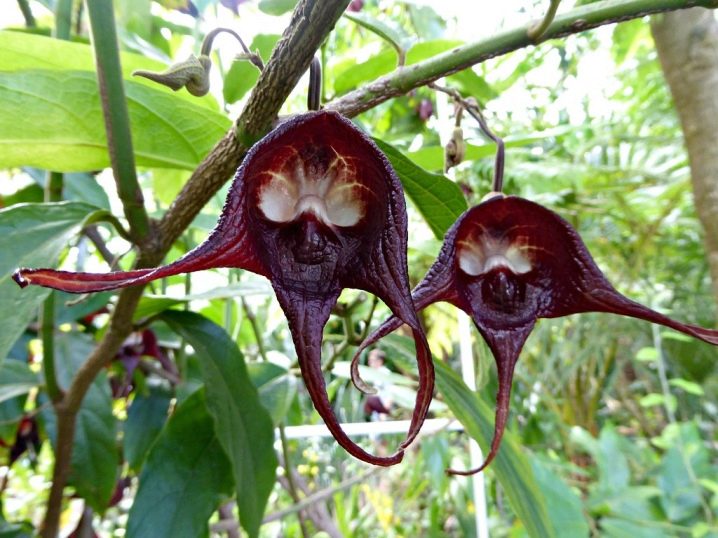
- Kirkazon of Salvador it has an extravagant flower shape. Its flower is shaped like a skull with gaping eye sockets. The plant looks very impressive. Another name for this species is “devil's flower”.

- Kirkazon graceful (elegant) - evergreen representative of the species. The heat-loving liana feels best in partial shade with loose, moist soil, without drafts. The flowers, dark purple with a brown tint, resemble the trumpet of a gramophone. The flowering period lasts from late June to early September.
The variety propagates by cuttings or branches, the seeds rarely have time to ripen and have poor germination.
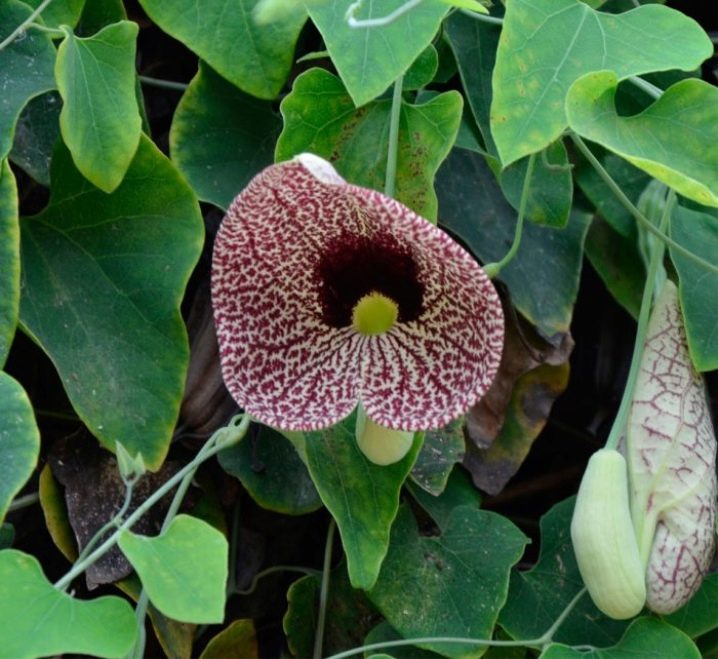

- Aristolochia giant it has huge leaves of a regular heart-shaped shape and even more gigantic flowers about 30 cm long. During flowering, the plant emits a specific cadaverous smell to attract flies and beetles that pollinate it. This makes it difficult to grow in a backyard near benches and windows.
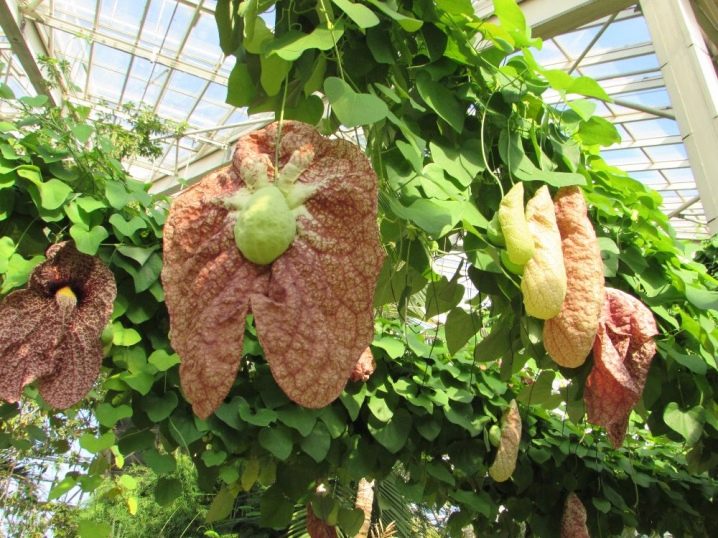

- Aristolochia twisted has medicinal properties. For decoctions, the roots and fruits of the liana are used. They are most commonly used in Chinese traditional medicine. Lianas are lighter in color, can reach 1 meter in length. Twisted kirkazon begins to bloom in July, and by the end of August, fruits are formed. During flowering, it gives off an unpleasant smell of spoiled meat.
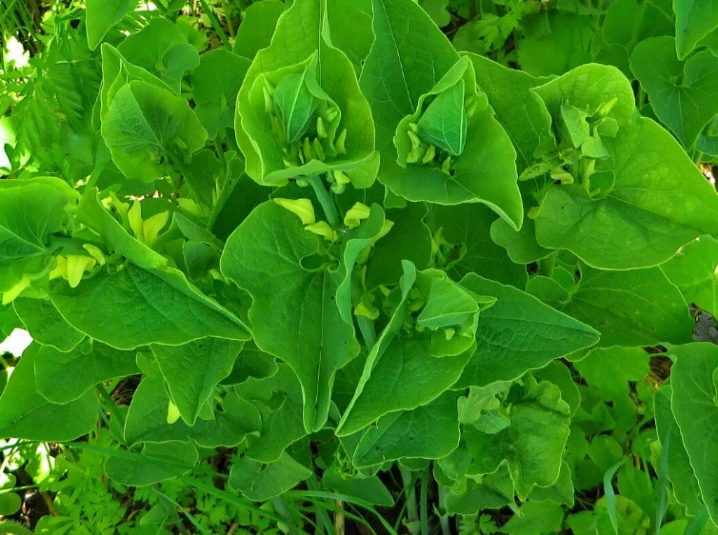

- The leaves and shoots of the serpentine kirkazon are toxic. They can cause burns to the skin and mucous membranes in the body. But at the same time, its juice is an effective antidote for snake bites.
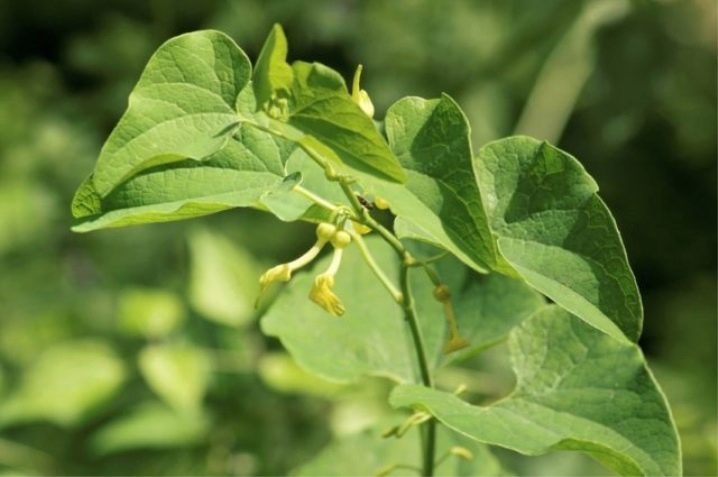

- Aristolochia Shteip grows on the territory of Russia in the Krasnodar Territory. It is distinguished by large single flowers of bright yellow color with a purple border. This species is listed in the Red Book.
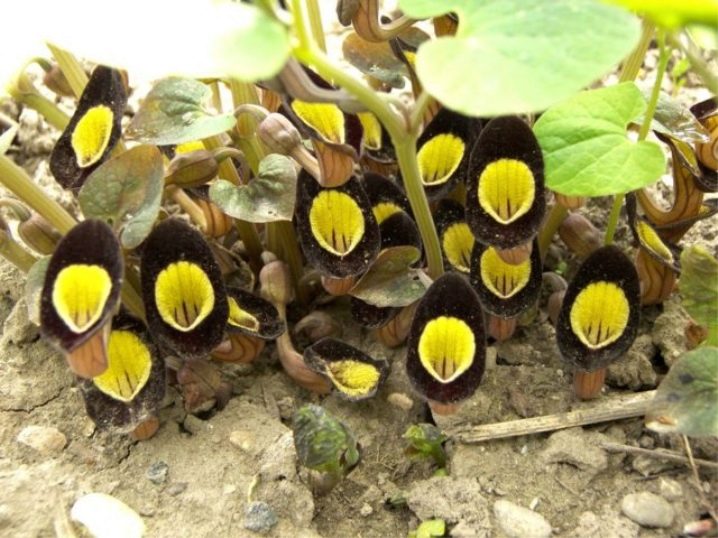

Landing
It is better to plant Kirkazon in a shady or semi-shady place of the site, without direct exposure to sunlight and wind. The plant prefers neutral or alkaline soil. Liana does not like waterlogging and stagnant water, so the soil is selected well-drained.
Cuttings are best planted in autumn or early spring, after the end of the night frost. To do this, you need to dig a trench about half a meter deep. It is recommended to fill up fine gravel or broken brick at the bottom of the trench - this will improve soil drainage. The drainage layer is covered with sand or earth (5-10 cm thick). After that, you can add organic fertilizers (compost or humus) or a mixture of mineral additives. Before planting the shoots, their roots must be cut by 1/5 of the length of the rhizome. Plants are planted at a distance of 1 meter from each other.
Liana requires a mandatory support, which wraps around counterclockwise.



In the first year, the vine does not grow in height, strengthening the shoots and expanding in breadth. In the second and subsequent years, the vine begins active growth upward, using a support (there can be specially prepared supports of various shapes or trees growing nearby).
When growing plants from seeds, they are planted in late autumn, before the first frosts in open ground. The place is chosen in partial shade, with good soil drainage. Young shoots do not tolerate drying out of the soil and require regular watering. When sowing in spring, it is recommended to freeze the seeds at a temperature of -5-10 ° C. After the appearance of 4-5 full-fledged leaves, the seedlings can be dived.Seedlings should be transplanted to a permanent place for 2-3 years of life.



Care
Different varieties of plants can grow in almost any conditions; every gardener is able to choose a variety for his site in certain climatic zones. The plant needs fertile soil with good drainage and air permeability. With a constant draft, the leaves lose their color and vitality, drooping on the vines.
In constant shade, the plant grows well, but does not produce flowers. He needs a place with partial shade and a short period of sunlight in the morning and evening. In a long sun, the plant withers. It is better to grow a decorative liana in places protected from drafts and strong gusts of wind, which can damage young shoots and large leaves.


Not all varieties of aristolochia are characterized by winter hardiness and are able to survive frost. Frost-resistant species tolerate frosts down to -15 ° C, provided that the root system is covered with fallen leaves and snow. Without pruning and covering, the vine can withstand temperatures not lower than + 5 ° C. The older the plant, the better it tolerates cold. After 3-4 years of life, the vine can be cut off in moderate frosts.
Cultivation of vines is a rather troublesome task. With regular watering, fertile soil and sufficient sunlight, shoots can grow up to 10-15 cm per day.

Watering
The plant does not tolerate long-term drought, but it should not be flooded either. Watering is carried out 2-3 times a week during dry periods and once every 7-10 days during rainy periods. Between waterings, the soil should be loosened and periodically mulched. Some plant varieties are recommended to be sprayed regularly, especially in dry air. To prevent the leaves from losing their bright color, in hot dry weather, the plant should be sprayed in the morning and evening.


Weeding
The plant requires regular weeding and loosening of the soil. The soil around the rhizome must be kept clean and free of weeds. The soil should be loosened shallowly, the root system of the plants is close to the surface.


Top dressing
In the summer, with insufficiently fertile soil, fertilizing can be carried out 2-3 times. It is better to use mineral or organic liquid fertilizers. After feeding, watering with clean water is required. Do not use coniferous waste (sawdust or chopped bark) to feed the plant.

Pruning
Regular pruning is required to give the plant a more decorative look. This will allow you to control the rapid and active growth of shoots. When pruning, diseased and old, underdeveloped or crooked shoots are removed. Pruning is carried out several times a year.


Shelter in winter
In regions with cold winters, the plants must be removed from the support and young unripe shoots are pruned. Mature vines are carefully laid on the ground and covered with spruce branches or other foliage; artificial breathing materials can be used. In southern regions with mild winters, the plants are covered directly with snow. Some varieties do not tolerate frost, they need to be dug up and left in a warm, lighted place.


Reproduction
The plant reproduces poorly naturally (independently) without sufficient pollination by insects (in particular, flies). Most often, the culture is propagated by dividing the rhizome, by grafting or by branching.
If the cuttings are prepared in the fall (early October), then you can use the young shoots of this year. For spring cuttings, it is better to choose more mature semi-lignified shoots. Cuttings are cut about 20 cm long and rooted in nutrient soil with the addition of peat, leaving 1-2 buds on the surface. The cuttings must be watered abundantly, you can cover them with foil or separate containers.
Typically, roots begin to form 3 weeks after planting.

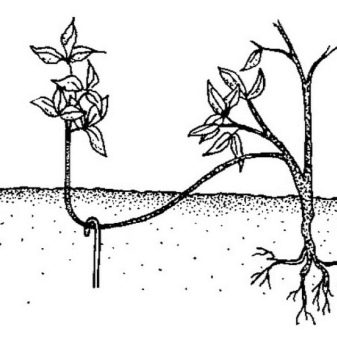
When propagating by branches, young shoots are buried shallowly into the ground. The tip of the vine must be left outside.For reliability, the shoot can be secured with a wooden slingshot. It is advisable to make several shallow cuts on the bark of the bends and treat them with a root formation stimulator "Kornevin". Root formation is slow, the process can be separated from the mother bush and transplanted to a new place only after 1-2 years.

Diseases and pests
Kirkazon is practically not susceptible to diseases and pests. Lianas do not require special treatment with chemicals, being a poisonous plant.
In the vicinity of affected plants, aphids and spider mites can move to the vine. The spider mite feeds on the sap of the liana; when it appears, the plant must be treated with insecticides.


If there is not enough space for the root system of the plant, planting of individual bushes is too frequent, then rot or powdery mildew may develop on the roots, the liana may completely die. In such a situation, radical thinning and removal of part of the shoots is required. Also, the vine must be sprayed with fungicides.
Prolonged drying of the soil can cause the death of Kirkazon. The leaves of the vine begin to wither, then fall off, and the plant dies. But with timely regular watering, the bush can be saved. Withered leaves and tips of shoots should be cut off; with active growth, Kirkazon will quickly recover.


Use in landscape design
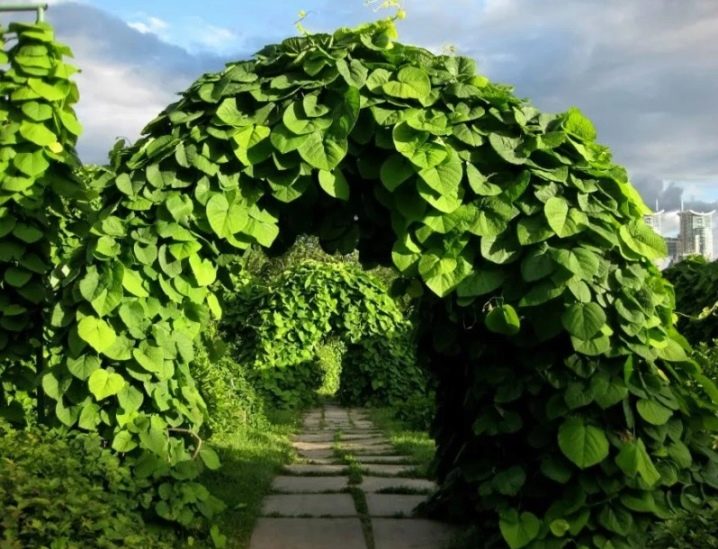
A liana-like plant with large leaves is widely used in landscape design. It is used to decorate gazebos, arches and fences. Kirkazon is suitable for landscaping suburban areas, city yards or alleys. In one place, a liana can grow up to 30 years old, it is often used to decorate dried trees or garden buildings. Kirkazon stands out among other species of vines with unusual flowers and an abundance of foliage on the shoots.
Due to the active growth and abundance of greenery, Aristolochia is often used to create green walls, fences or vertical landscaping of building facades. Arches and tunnels decorated with liana look spectacular.















The comment was sent successfully.