All about ivy bud

Having learned everything about ivy bud, its botanical description, it will be possible to correctly represent this plant. It is important to understand the use of dog mint in landscape design, with the family and formula of the flower of this weed, with the inflorescences of the plant. And you also need to find out the nuances of growing, find out what pathologies and pests threaten the culture.
general description
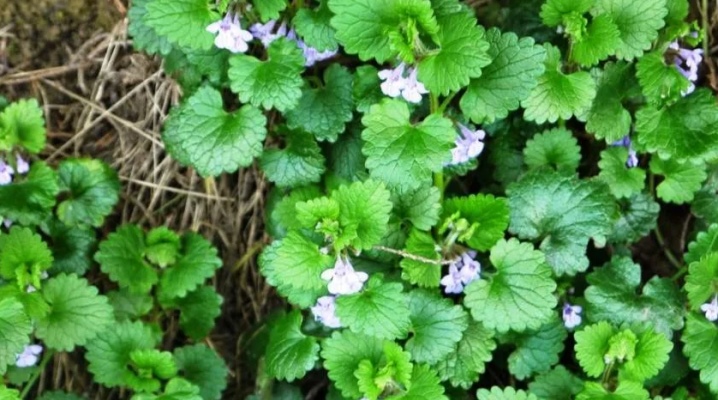
Ivy budra is one of a large number of perennial herbaceous ground cover plants. This species perfectly adapts to a wide variety of growing conditions. You can meet him in various regions of the Northern Hemisphere. In England, they often talk about earthen ivy, and in Russia the name dog mint is more common. It is believed that the cultivation of this species is available to any person who owns a dacha.
This representative of the genus Budra is a member of the family of lamines, and its relatives, according to the current botanical classification, are:
-
lavender;
-
sage;
-
rosemary;
-
Melissa;
-
mint;
-
oregano.

More distant "relatives" it can be considered:
-
Saintpaulia (violet);
-
pemphigus;
-
privet;
-
ash;
-
lilac;
-
paulownia;
-
Snapdragon;
-
plantain;
-
foxglove and vervain.
A typical flower formula is H (5) L (2 + 3) T4P (2). Ivy budra is distinguished by creeping shoots. During flowering, it looks tender; this period lasts from the beginning of the weather spring to the beginning of July. The name "dog mint" is given by association. By rubbing the flowers of purple color or the stem, you can feel an expressive aroma, really close to the mint aroma.


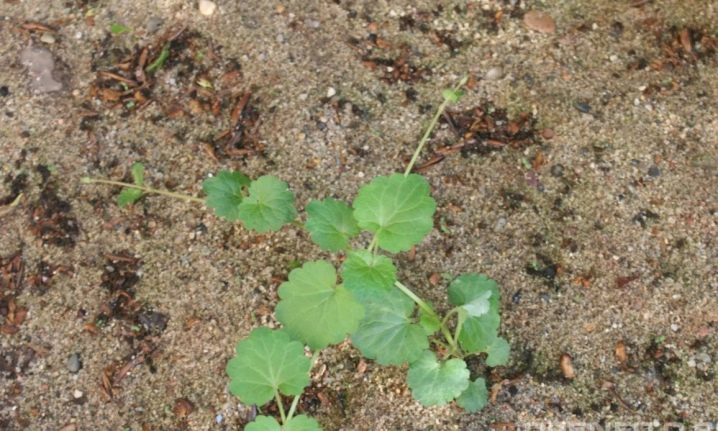
Speaking about the characteristics and structure of ivy budra, it is worth pointing out that its shoots reach 0.5 m in length, sometimes even more. Such shoots are able to autonomously gain a foothold in the ground in various places. Even under the snow, the plant retains an attractive green color for a long time. In the spring, when thawed patches appear, unusual purple spots are visible in them. Such decorative properties allow you to decorate the site with ivy-shaped budra year-round.
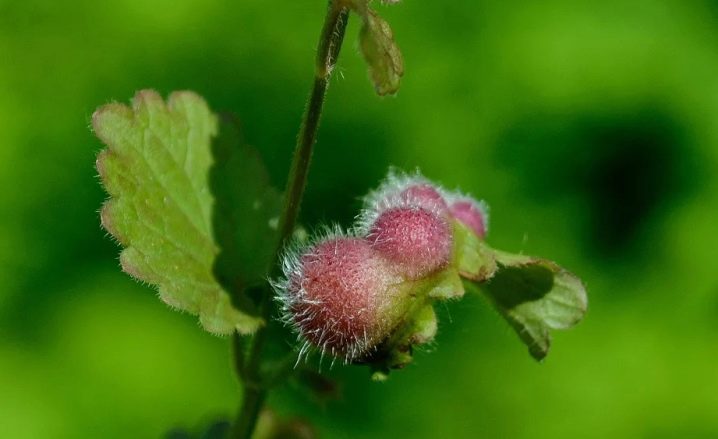
In many places, this species grows like a weed. It just spreads chaotically, beyond any human control. The habitat of Budra is not only vegetable gardens, but also paths in forests, meadows and recent clearings. Its aroma is not very pleasant, which also stimulates many people to get rid of such a "guest". The fruits are visually similar to the unusual shape of nuts - even their color is the same.

Height ranges from 5 to 15 cm, according to other descriptions, up to 60 cm. There is pubescence, but it is relatively small. The description of the inflorescence in the main sources on the topic is missing. The leaves are arranged in an opposite pattern. They have elongated petioles, similar in shape to a rounded kidney or heart, and the edge has a crenate structure.
The fruits are divided into 4 nuts. Their ripeness is reached from June to August. The root system is invariably creeping. The two-lipped flowers are vaguely bell-like. They are light blue or pale purple in color.


Popular varieties
For decorative characteristics, budra stands out favorably ivy variegata... It is appreciated for the graceful appearance of the foliage, covered with a white border. This type will grow very quickly. In most cases, the height reaches only 15-20 cm. Therefore, Variegata looks more like a typical ground cover creeping culture.In other cases, a typical ampelous variety is also suitable as a medicinal culture.


The nuances of growing
Conditions
It is quite possible to plant ivy budra in the soil of the most varied composition, in almost all areas. Houses and in the country usually make up a substrate, including sod and leafy soil. Additionally, sand and humus are used. Growing on the balcony is quite possible and even encouraged, because this species needs a lot of sunlight, at least 15 hours a day.
However, it must be checked that the light is scattered. Direct rays of the sun can cause burns. On the street at the time of landing, it should not be colder than +10 degrees. Uniform heating of the soil is also extremely important. Pots and other containers are recommended to be oriented south, southwest or southeast. In the summer, the plant is taken out into the fresh air, necessarily shading it at the same time.
You can sow seeds in early spring and autumn. Before sowing, the soil is loosened and weeded. It needs to be additionally moistened. The seeds are laid out in random order, then sprinkled with a small amount of soil, which is compacted. Then, until the formation of shoots, ridges or containers should be watered once every 3 days.
Planting can be carried out with cuttings. For this purpose, several shoots are separated up to 10-15 cm. There should be no flowers on the separated fragments. Such planting material is placed in moist sand. Sometimes a mixture of sand and peat or even plain clean water is used instead. As soon as the roots appear, this is a sign that you can start transplanting to the final place.


Watering
Ivy budra is not too picky to care for. It only needs moderate irrigation. A long drought affects this plant badly, and watering in the summer should be done no more than 2 times a week. Regularity is more important than intensity. However, during hot periods, water will have to be plentiful. For the winter, of course, it is better to forget about this procedure.

Top dressing
As soon as Budra wakes up (this is March or April), it will enter the stage of intensive growth. Then they begin to feed her. The time of intense activity ends in different years in late August or early September.
Complex formulations based on minerals are preferred. They are laid monthly, observing the dosage recommended by the manufacturer.


Pruning
This manipulation is extremely important for creating graceful, neat shrubs. It is best to do it in March or April, before the active growth phase begins. With a sharply sharpened pruner, diseased and dried shoots are cut out. The instrument is disinfected as often as possible. It is preferable to combine sanitary and formative pruning with cuttings.
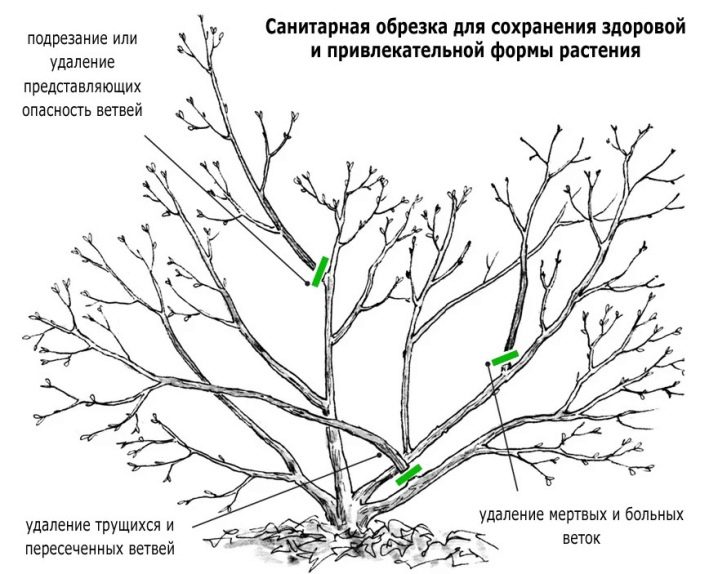
Transfer
You should move such a culture to new places less often. It is necessary to carefully understand whether there is such a need or not. The optimal time for transplanting is April or May. It is more correct to navigate at the moment when it becomes steadily warm.
Important: before transplanting, you will have to get rid of all the shoots.

Reproduction
If seed reproduction is chosen, you must wait for autumn or spring. Sowing takes place directly into the open ground. Cutting and layering is practiced in the summer. Stem cuttings are preferred over other options. They are taken only from an adult plant.
Such biomaterial is placed in water or planted in sand. It will be necessary to ensure that the sand is constantly well moistened. Roots will emerge in 3-4 days. Then the sprouted stalk is planted in street soil or in a room container of your choice. If done correctly, additional fertilization will not be needed soon, and regular watering will be the main concern.


Diseases and pests
Ivy budra can withstand a variety of aggressive factors. A potted culture suffers more often than one planted in open land. Among the pathologies, the most dangerous are powdery mildew and root rot. They are eliminated by treatment with synthetic drugs. Fighting rot often requires removing deformed areas and replanting the plant. Of insects, aphids, whiteflies and spider mites are dangerous; specialized means help to fight them.


Use in landscape design
This culture is often planted in pots. In this case, the leaves will hang in bunches. The ivy leaf is also adorned with lawns, flower beds and curbs. It is also planted in dachas, since the soil will not dry out, and foreign plants will be suppressed. A good companion is the seaside asteriscus.


How to get rid of the lawn?
Budra is not just a weedy creeping grass. It is also toxic, which causes additional inconvenience. Weeding a plot or lawn may not be enough. To combat ivy grass, you can use a herbicide - the best are Roundup and Tornado. Both formulations are used taking into account safety requirements.
The herbicide is applied once a season. The early growth is destroyed in the spring. Serious thickets must be cultivated in the fall. A good control measure is the use of borax. This reagent is non-toxic and can be purchased from pharmacies or hardware stores all over the place.
Typically 0.4 kg of sodium tetraborate is diluted in 200 ml of water. This saturated solution is diluted in 10 liters of water. A similar portion of homemade pesticide is enough for 300 m2. With a small amount of harmful grass, each copy is processed separately, applying the composition with a brush. It is better to repeat the treatment after 10-14 days. In the fall, you will have to dig deep into the ground, and remove all the remnants of the budra, which allows you to get rid of the weed with a guarantee.















The comment was sent successfully.